In a reverse triangular merger, a subsidiary of the acquiring company executes the purchase of the target company. When this occurs, the stock of the target. In a reverse triangular merger, a subsidiary (“Sub”) of the acquiring corporation (” Acquiring”) merges into the target (a)(2)(E) Reorganization Diagram.
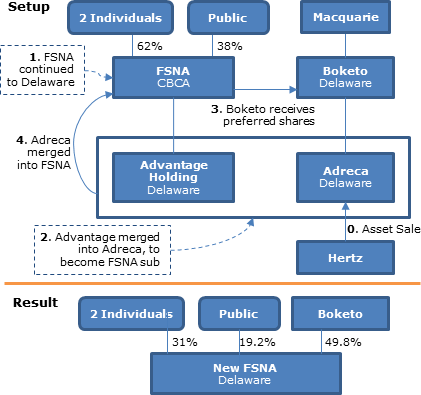
Reverse and Forward Triangular Mergers. Alternative Approaches to Structure M&A Transactions,.
Implications for Anti-Assignment Clauses. Taxable Acquisitions – Reverse Subsidiary Merger. • Treated as a stock purchase for .
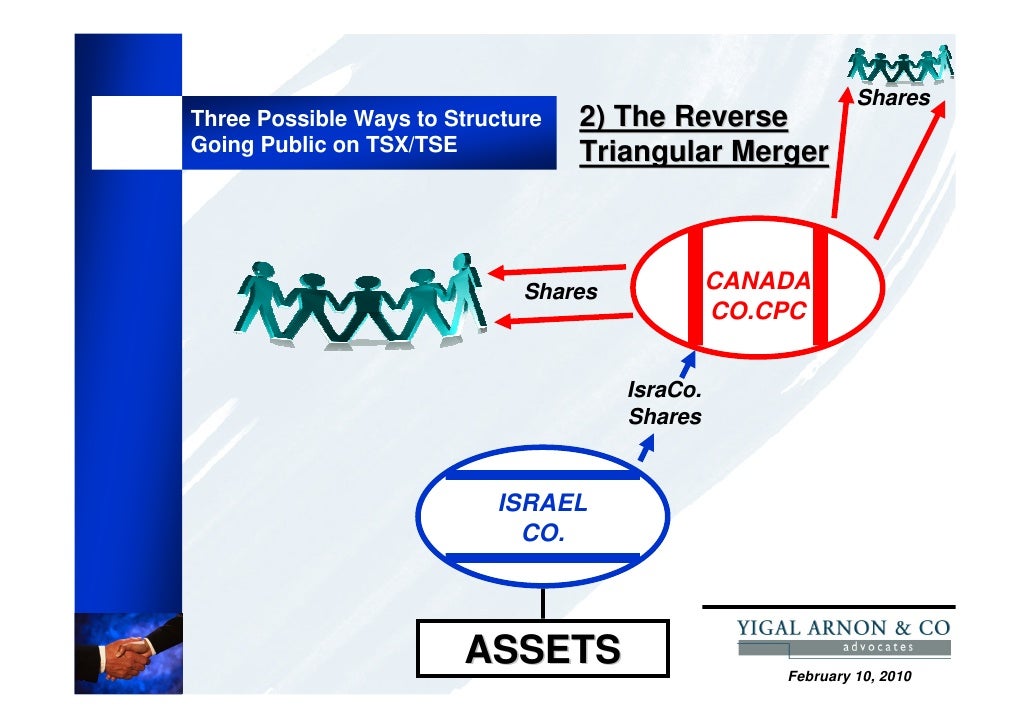
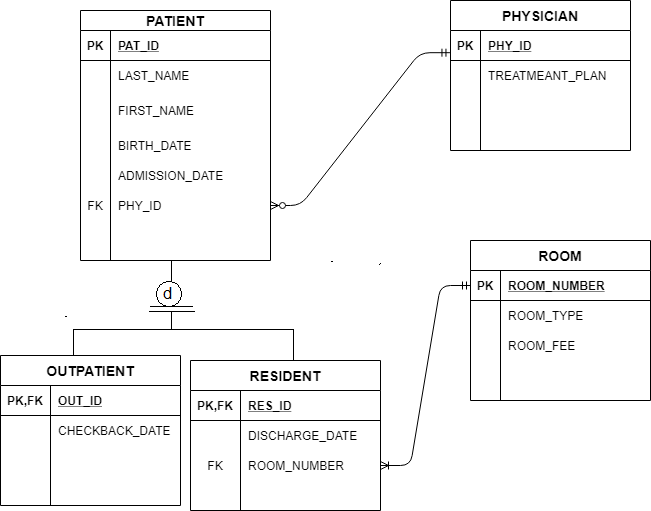
Type “A” Reorganization – Reverse Triangular. Merger.
1. Merger Co. A reverse triangular merger occurs when an acquirer creates a subsidiary, the subsidiary purchases a target and the subsidiary is absorbed by.The Reverse Triangular Merger A reverse triangular merger is the same as a triangular merger, except that the subsidiary created by the acquirer merges into the selling entity and then liquidates, leaving the selling entity as the surviving entity, and a subsidiary of the acquirer.

Aug 11, · In a basic reverse triangular inversion, as illustrated in the corresponding diagram, U.S. shareholders transfer all of their stock to a US subsidiary corporation and receive foreign parent stock in return. U.S.
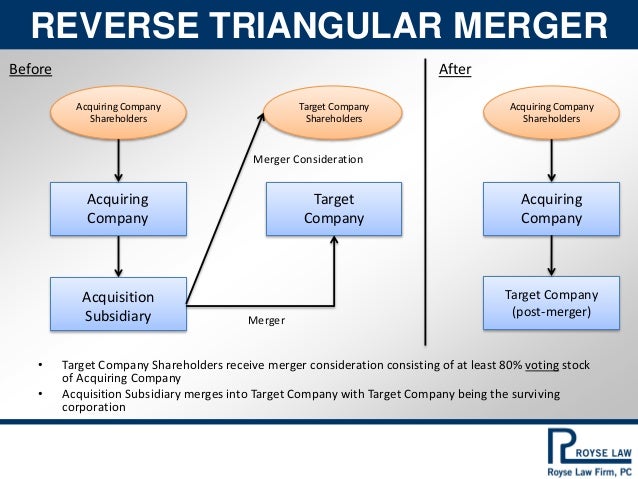
parent corporation merges into foreign subsidiary with foreign subsidiary not surviving the merger. Reverse Triangular Merger. A form of merger in which: The buyer forms a subsidiary and that merger subsidiary merges with and into the target company. The target company assumes all of the merger subsidiary’s assets, rights, and liabilities by operation of law.
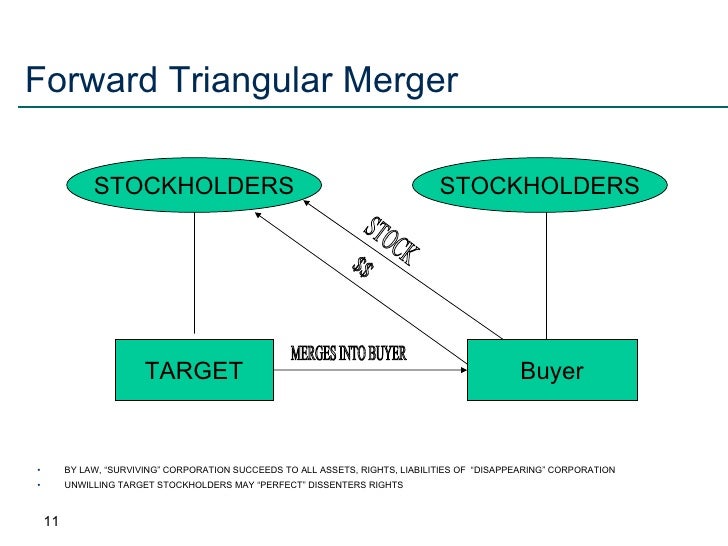
Reverse and Forward Triangular Mergers: Corporate Law Requirements. Overview of Structure of Triangular Mergers. Acquisition Subsidiary Target Company Shareholders Target Company.
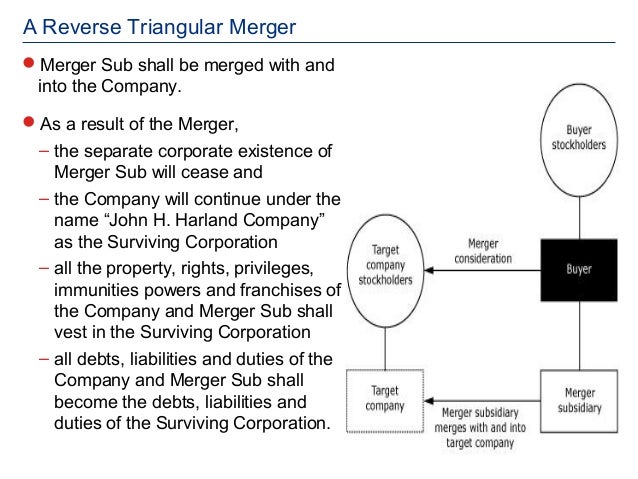
Merger Consideration. Merger. Reverse Triangular Merger Target Company Shareholders receive Merger Consideration and Target Company shares are cancelled.

Object moved to here.Reverse Triangular Mergers: (a)(2)(E) ReorganizationsForward Triangular Mergers: (a)(2)(D) Reorganizations