If you’re experiencing issues with engine performance, focusing on the proper routing of the intake and air pressure components is essential. A well-maintained air circulation setup ensures optimal engine efficiency, reducing the risk of power loss or misfires. Below is a guide that explains the component connections and their optimal arrangement in the 5.4L V8 engine setup.
The key to ensuring smooth engine operation lies in correctly identifying and tracing the system paths that control airflow. Incorrectly placed connectors or damaged seals can lead to inconsistent air delivery, affecting engine performance. Specifically, the key components include the primary intake connectors and the system regulating pressure under varying engine loads.
Key Connections to Check: Pay attention to the connections between the manifold and the pressure regulators. These are prone to wear, and even small leaks can cause a noticeable decrease in engine power. The routing from the intake manifold to the throttle body should be free of obstruction and tightly secured to avoid air loss.
Maintenance Tip: Regular inspection of the pressure regulators and air delivery system components is necessary. Over time, these parts can degrade or become misaligned. Replacing them or adjusting the connections to meet manufacturer specifications ensures that air pressure remains consistent under all driving conditions.
Lastly, any inspection or repair should begin with identifying the correct component layout as per the factory specifications. Be sure to refer to the engine schematics to locate critical points for disconnection and reassembly.
Vacuum Routing for Ford 5.4L Engine

For proper engine function, ensure all connections are tight and in the correct positions. The system relies on precise routing to maintain optimal performance and efficiency. Verify each component, including sensors and actuators, for leaks or damage. A faulty connection can lead to poor engine response, stalling, or decreased fuel efficiency. Pay attention to the following critical points:
First, confirm the correct attachment of the intake manifold to the engine block, ensuring that the seal is intact. Any air leaks here can cause unstable engine behavior. Next, inspect the connectors to the manifold, particularly the ones linked to the throttle body. These must be securely fixed to prevent idle issues and hesitation.
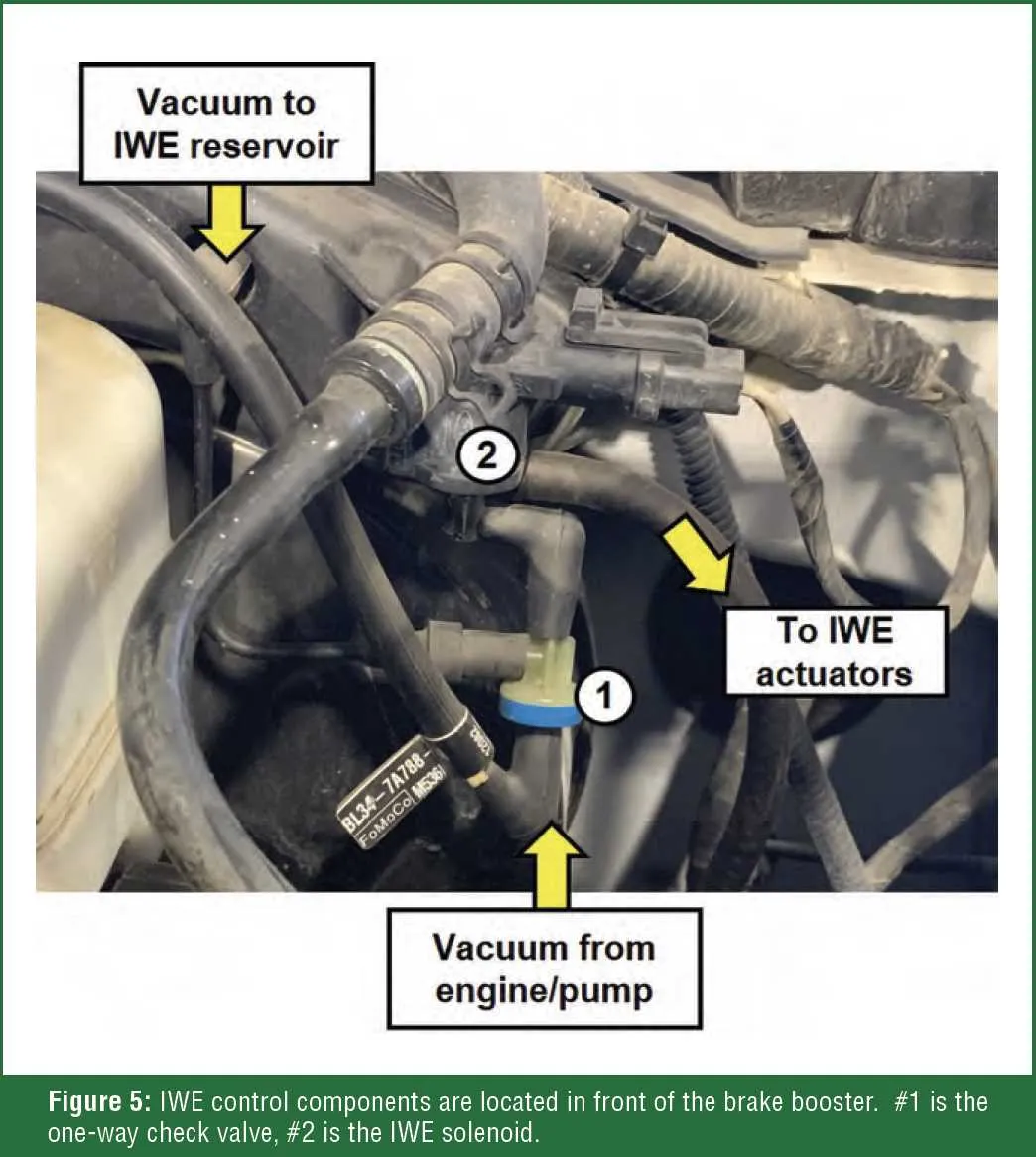
For the secondary components, check the connections to the vacuum-powered brake booster and the emission control system. These parts play a key role in maintaining system pressure. Make sure the hoses running from these systems to their respective actuators are undamaged and not obstructed by debris.
Additionally, review the routing of the lines to the fuel pressure regulator and EGR system. Incorrect placement or wear in these hoses can result in engine misfire or rough idling. Lastly, if you’re dealing with engine codes related to performance or airflow, these systems often require re-routing or replacement of the components involved.
How to Identify the Correct Airflow Tube Routing in a 5.4L Engine
Start by locating the intake manifold and the components that connect to it. The primary air passages will lead to sensors, throttle body, and other critical elements. Ensure that each flexible conduit is routed in a way that allows for smooth airflow without kinks or twists.
Next, identify the connections that go from the engine to the vacuum reservoirs. These tubes should be free of cracks and ensure a secure fit to their corresponding ports. Often, these will be marked with color codes or part numbers, making it easier to match them correctly to the appropriate ports on the engine block and intake system.
Inspect the connections near the fuel pressure regulator and the intake manifold. These tubes must be positioned with minimal slack, securing them to their designated attachment points. It’s essential that they aren’t exposed to extreme heat or moving parts that could cause wear over time.
Double-check the routing for the auxiliary systems, like air conditioning and power steering, which may have smaller tubes running parallel to the main air passages. These should also follow a path that avoids direct contact with high-heat components.
Finally, verify that the connectors are tight and intact. A loose or improperly routed tube can result in inconsistent engine performance or erratic readings from the engine management system.
Common Issues with Air Leaks and How to Fix Them on Ford 5.4 Engines
To prevent performance issues, start by inspecting the intake and related components for any air leakage. A common problem arises from cracks or loose fittings in rubber tubes, leading to unregulated air entering the engine.
- Leaking Hoses: Check all rubber connectors and tubes for visible wear, cracks, or splits. Even small leaks can disrupt engine performance. Replace any damaged hoses with OEM-quality parts to ensure proper seal.
- Loose Connections: Loose clamps or fittings can also cause air to leak. Tighten all connections around the intake manifold, throttle body, and other air routing points. Make sure seals are intact and securely fastened.
- Cracked Intake Manifold: Inspect the intake manifold for cracks or warping, especially near the gasket area. Over time, heat can weaken the material. If damaged, replace the manifold or use an appropriate sealant to restore a proper seal.
- Faulty Sensors: Faulty MAF (Mass Air Flow) or MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensors can also lead to incorrect air-fuel mixture. Test these sensors with a multimeter and replace them if readings are outside of specification.
- Faulty Gaskets: Worn-out gaskets between the intake manifold and engine block can cause air leakage. Inspect and replace any gaskets that show signs of wear, as even minor leaks can cause rough idling and poor acceleration.
- PCV Valve Issues: A malfunctioning Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve can result in excess air being drawn into the intake system. Test the PCV valve and replace it if it doesn’t close or open as it should.
After repairs, clear any trouble codes with a diagnostic tool and perform a road test to ensure all issues are resolved. Ensure proper idle speed and smooth acceleration as indicators of a successful fix.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Hoses in a 5.4L V8 Engine
Begin by locating the damaged or worn-out tubes. These are typically found around the intake manifold and connected to various sensors and components. Ensure the engine is off and cool before starting the replacement process.
1. Disconnect the battery to prevent any electrical issues while working with the engine. This is a safety precaution that should never be skipped.
2. Remove the engine covers if necessary. Some covers might obstruct access to the tubes. Use the appropriate tools to detach them carefully.
3. Identify the damaged components. Look for cracks, discoloration, or brittleness in the tubes. Damaged parts may cause air leaks, affecting engine performance and fuel efficiency.
4. Loosen the clamps that secure the damaged tubes. Use a wrench or screwdriver to carefully loosen them without damaging the clamp or surrounding areas. If clamps are rusted or difficult to remove, consider replacing them.
5. Disconnect the tubes from the components they are attached to, such as the intake manifold or vacuum sensors. Be gentle to avoid damaging the connections. If the tubes are stuck, use a little lubricant to ease their removal.
6. Prepare the replacement tubes. Ensure the new tubes are the correct size and length. Check the fittings to make sure they match the original parts exactly.
7. Install the new components. Carefully connect the new tubes to their respective points. Secure them with the original clamps or new ones if necessary. Tighten the clamps firmly, but avoid over-tightening, which can cause damage to the tubes.
8. Recheck connections for leaks or misalignments. Gently tug on the tubes to make sure they are firmly in place and won’t come loose during operation.
9. Reattach engine covers if removed earlier. Ensure everything is back in place before starting the engine.
10. Test the engine. Start the vehicle and let it idle. Listen for unusual sounds or idle fluctuations. If everything runs smoothly, the replacement is complete.
After completing these steps, your engine should function more efficiently, with all components properly connected and sealed. Always use high-quality replacement parts for the best results.