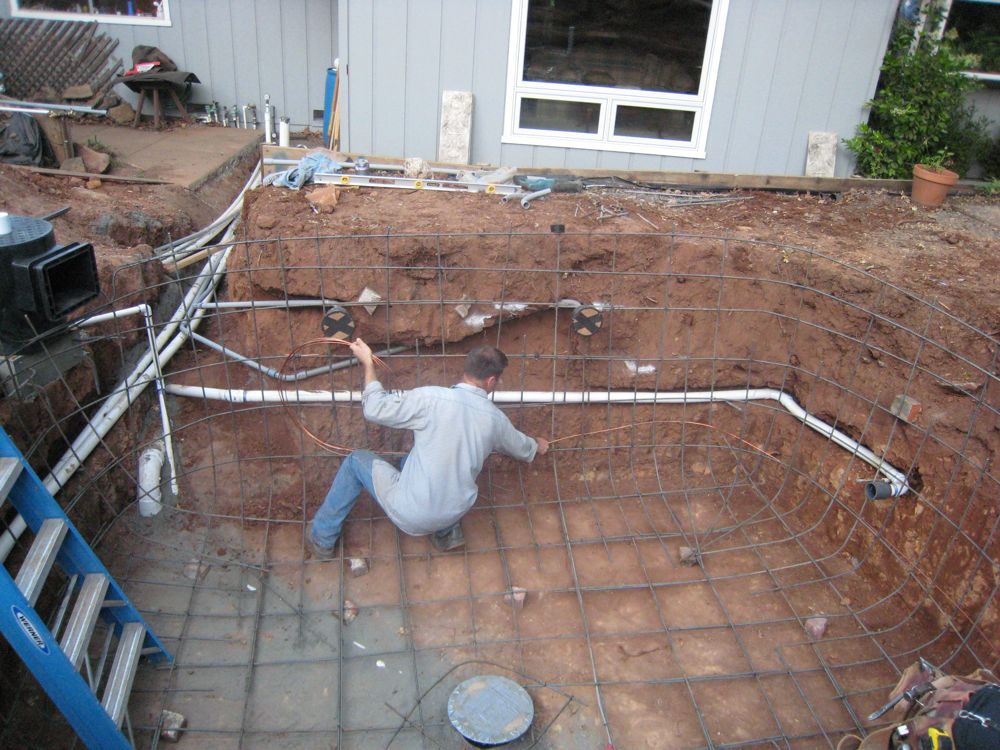

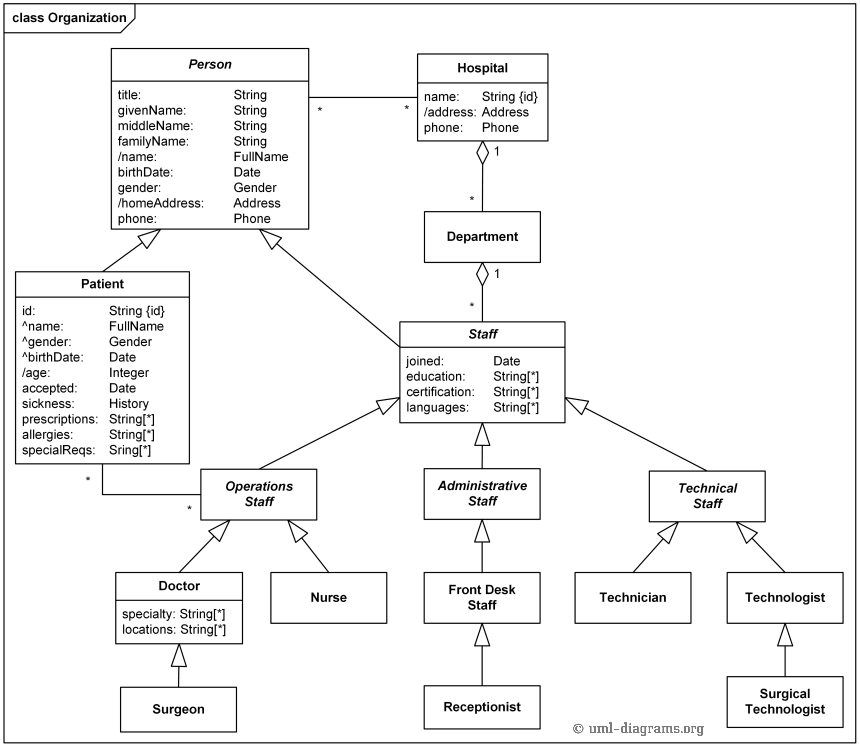
“Grounding” and “bonding” are important elements of a building’s electrical wiring . Note: This electrode is commonly referred to as the “Ufer ground”; and. The Ufer Ground is an electrical earth grounding method developed during World War II.
It uses a concrete-encased electrode to improve grounding in dry areas. Electrical Service Grounding.
Ufer Grounding. 2. Building Lightning Protection – A critical extension of grounding.
3. Building Interior Bonding and Grounding.
The requirements for a concrete-encased electrode, commonly called a “Ufer Ground” are included in (A)(3). This is an electrode developed by using.
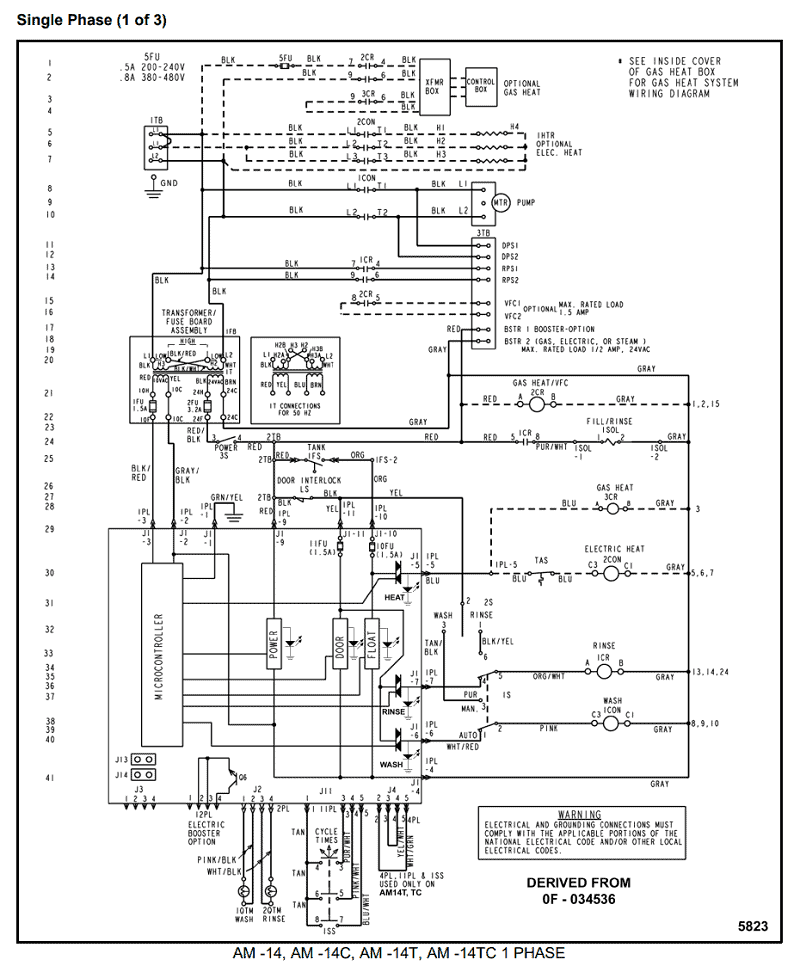
Download scientific diagram | Concrete-encased rod/Ufer ground. Fig.
6. Earthing ring. from publication: Electrical earthing in troubled environment | Cited BySERVICE ENTRANCE GROUNDING USM SERVICE ENTRANCE GROUNDING INDEX INDEX PURPOSE GENERAL INFORMATION BONDING GROUNDING ELECTRODE The minimum requirements for a UFER ground, as outlined in the NEC, Article , is a minimum of 20′ of bare copper wire, not smaller than #4, encased by at least 2″ of concrete and.
The City of Des Moines requires a UFER ground- ing system in all residential and commercial struc-tures. The UFER grounding system is in addition to all other electrodes within the building being bonded.

A “Ufer” ground is slang for what the National Electrical Code (NEC) addresses as a concrete-encased grounding electrode. The term “Ufer” does not appear in the Code, but many in the industry use it. Ufer is the name of the engineer who created it as a solution to .
Isolated Ground Reference One Isolated Ground Reference Two Isolated Ground System Diagram () [ Word ™ ] [ PDF ]. And How to Install Properly The Code defi nes “grounding” as the connecting to ground or to a conductive body that Note: This electrode is commonly referred to as the “Ufer ground”; and concrete-encased is referring to the electrode being part of the building’s footing or foundation.Ufer ground – WikipediaThe Ufer Ground
