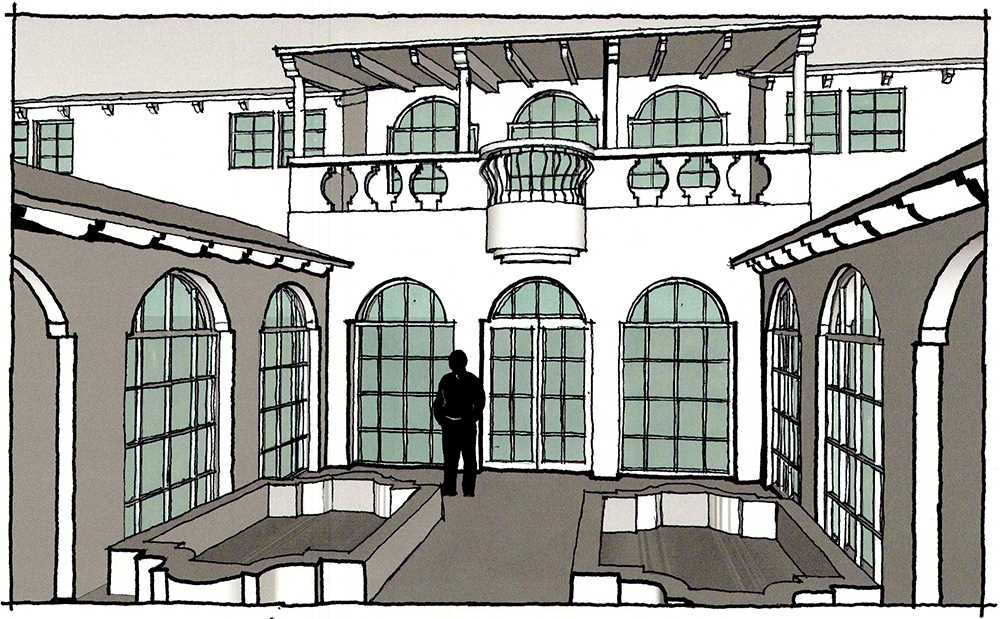

In the field of architecture, schematic design is an essential phase in the design process that sets the foundation for the entire project. It involves establishing the overall concept and layout of a building or space, as well as determining the key features and elements that will shape its design. Schematic design is often the first opportunity for architects to translate client requirements and vision into tangible architectural ideas and solutions.
During the schematic design phase, architects use a combination of sketches, diagrams, and 3D models to visualize their ideas and communicate them to clients and other stakeholders. These representations help to convey the general form, scale, and spatial organization of the project. Architects may also explore different design options and evaluate their pros and cons, taking into consideration factors such as functionality, aesthetics, sustainability, and cost.
One of the primary goals of schematic design is to establish a clear design concept that aligns with the client’s goals, budget, and timeline. This phase requires close collaboration between architects and clients to identify and address any conflicts or discrepancies early on. Through discussions and iterations, architects refine their initial ideas and create a design that captures the essence of the project while meeting all the functional and aesthetic requirements. The final schematic design serves as the basis for further development and detailing in the subsequent phases of the architectural design process.
Understanding Schematic Design in Architecture
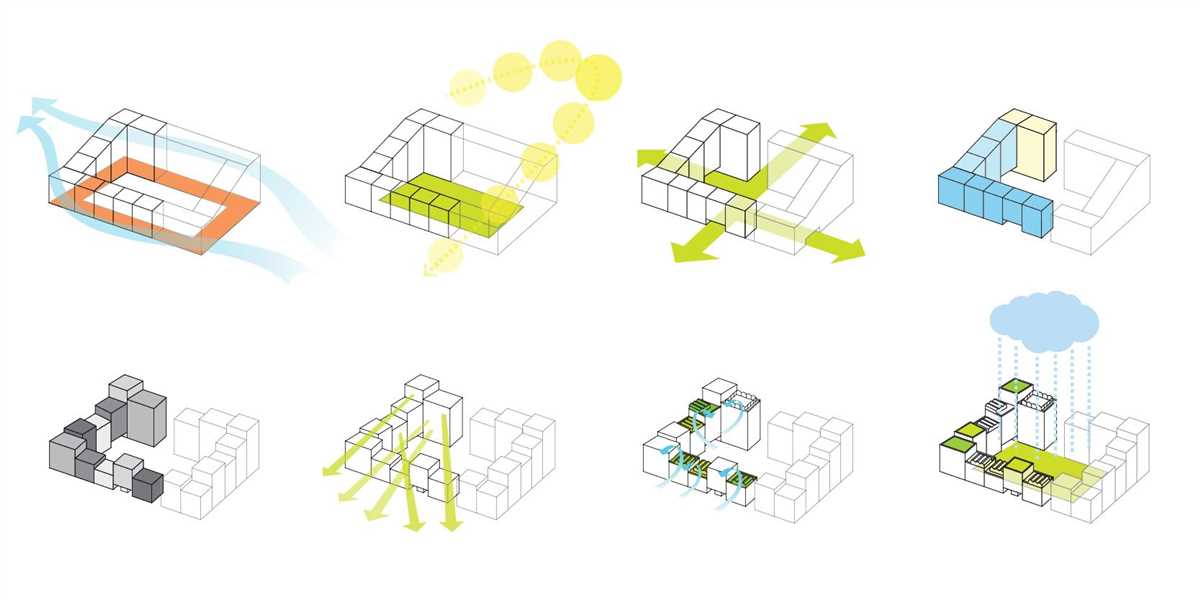
Schematic design is an essential phase in the architectural design process. It is the initial stage where architects conceptualize and develop the overall design of a building or structure. During this phase, architects work closely with clients to understand their needs, requirements, and design preferences. They also consider factors such as site conditions, budgetary constraints, and local building codes to create an initial design proposal.
The main goal of schematic design is to create a visual representation of the proposed building or structure. Architects use various tools and techniques, including sketches, diagrams, and 3D modeling software, to illustrate their ideas and communicate the design concept to clients and stakeholders. This helps ensure that everyone involved in the project has a clear understanding of the proposed design and can provide feedback or make modifications if needed.
During the schematic design phase, architects focus on key design elements such as the building’s spatial layout, circulation patterns, and overall massing. They consider factors such as natural lighting, ventilation, and accessibility to create a design that is functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable. Architects also take into account the surrounding environment and context to ensure that the design integrates well with the existing urban fabric and enhances the overall visual appeal of the area.
In addition to creating the initial design proposal, the schematic design phase also involves a preliminary cost estimation. Architects collaborate with cost estimators to determine the approximate construction costs based on the proposed design. This helps clients make informed decisions about the feasibility of the project and allows them to adjust the design or allocate the budget accordingly.
To summarize, schematic design in architecture is an important phase where architects develop the initial design proposal, create visual representations of the proposed building or structure, consider key design elements, and collaborate with cost estimators to determine the project’s feasibility. It lays the foundation for the subsequent phases of the architectural design process, such as design development and construction documentation.
The Importance of Schematic Design
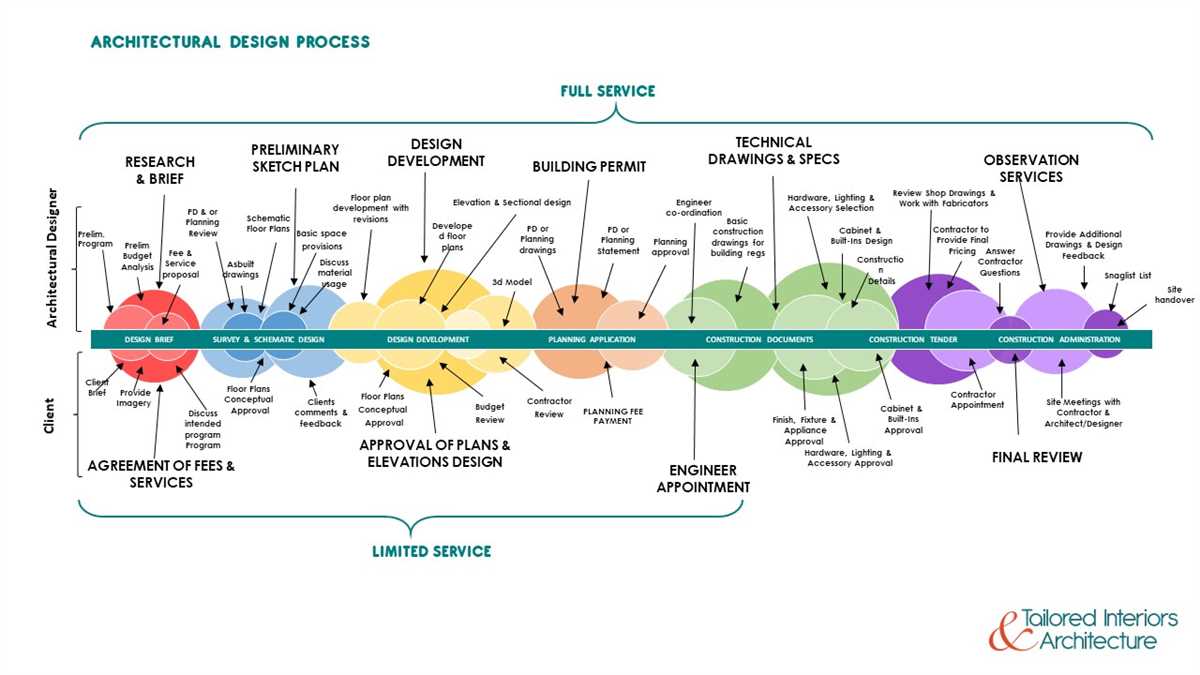
Schematic design is a crucial stage in the architectural process. It is the initial phase where ideas, concepts, and rough sketches are transformed into tangible designs. This stage acts as a foundation for the entire project, setting the direction and guiding the decision-making process. Schematic design is where architects experiment, explore different possibilities, and find the most effective solutions to meet the client’s needs and requirements.
A well-executed schematic design is essential because it helps architects and clients visualize the overall concept of the project. It allows them to see how the building will look, how the spaces will be arranged, and how different design elements will interact with each other. This visual representation is critical in making informed decisions regarding the project’s design, functionality, and aesthetics.
During schematic design, architects also consider important factors such as site analysis, building codes, regulations, and sustainability. By addressing these factors early on, architects can make educated design decisions that will benefit the project in the long run. They can identify potential challenges and constraints and find creative ways to overcome them, ensuring that the final design meets all the necessary criteria.
The schematic design phase also allows for effective collaboration between architects, clients, and other stakeholders. It provides an opportunity for clear communication and mutual understanding of the project goals and visions. Through discussions and iterations, architects can refine their designs, incorporate feedback, and ensure that the final design aligns with the client’s expectations.
In summary, schematic design is an integral part of the architectural process. It sets the stage for the project, helps visualize the design concept, considers important factors and constraints, and facilitates effective collaboration. Investing time and effort in the schematic design phase ensures a strong foundation for the project and increases the chances of its success.
Key Elements of Schematic Design
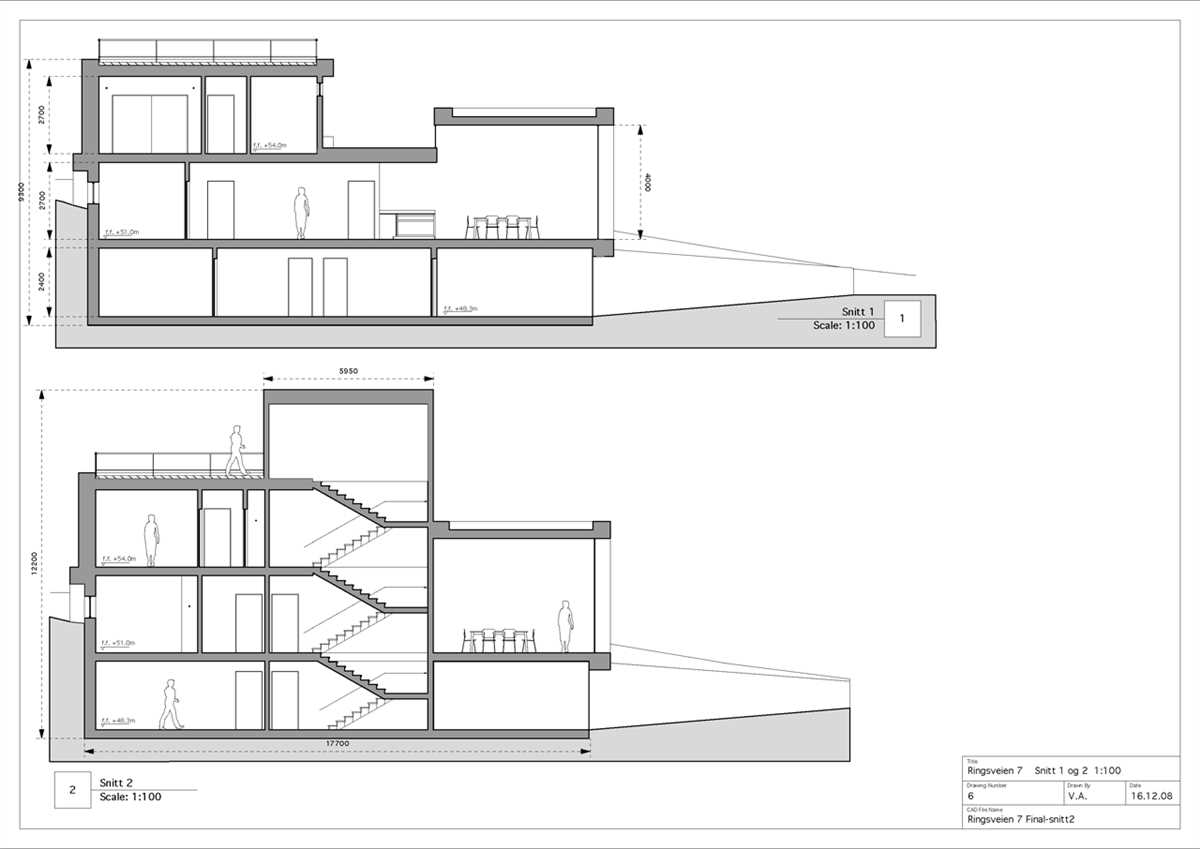
Schematic design is a crucial phase in the architectural design process where the overall concept and preliminary design ideas are developed and refined. This phase lays the foundation for the entire project and sets the direction for the subsequent stages of design. There are several key elements that are essential to consider during the schematic design phase.
1. Site Analysis and Planning
One of the key elements of schematic design is conducting a thorough analysis of the site and its surrounding context. This includes studying factors such as topography, climate, existing structures, and potential constraints. By understanding these site conditions, architects can develop a design that responds to its surroundings and maximizes advantages while minimizing negative impacts.
2. Conceptual Design
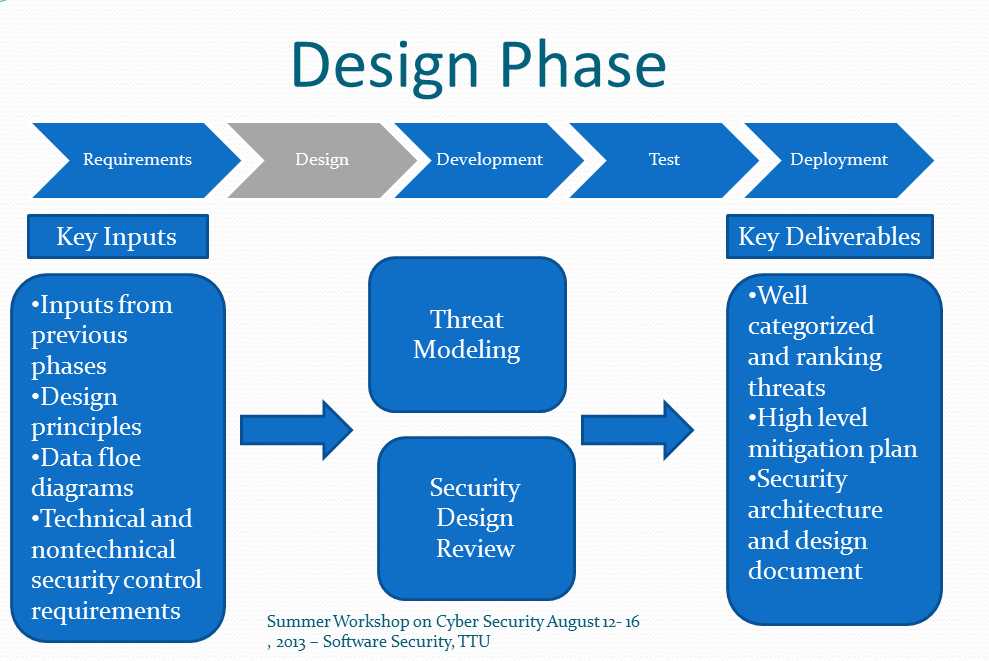
The conceptual design is the central idea that informs the overall design of the project. It forms the basis for all the design decisions that follow. During schematic design, architects explore different conceptual design options, experimenting with forms, materials, and spatial arrangements. The goal is to create an innovative and cohesive design concept that captures the essence of the project.
3. Space Planning
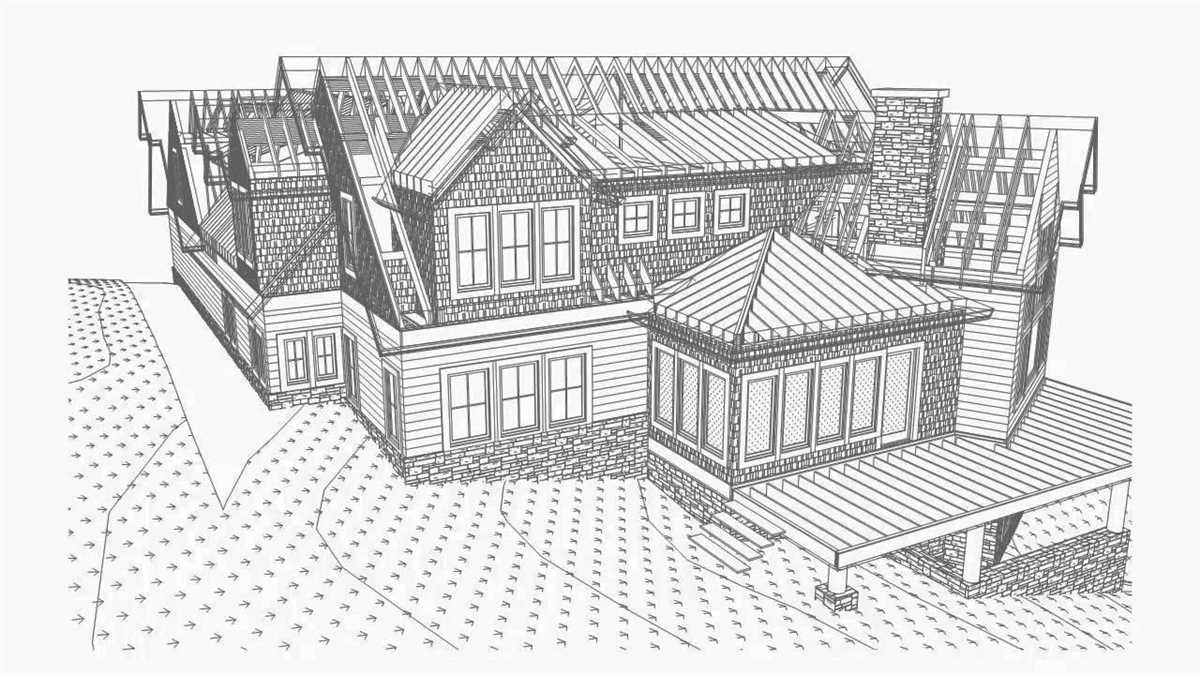
Space planning is a critical aspect of schematic design, as it involves organizing and allocating different areas within the building. Architects must consider the functionality, flow, and spatial relationships between various spaces. During this phase, architects also consider flexibility and adaptability to accommodate future needs and changes.
4. Preliminary Structural Design
During schematic design, architects work closely with structural engineers to develop a preliminary structural design. This involves determining the general layout, materials, and dimensions of the building’s structural elements, such as columns, beams, and foundations. The goal is to create a safe and stable structure that supports the architectural vision.
5. Cost Estimation and Budgeting
Another crucial element of schematic design is cost estimation and budgeting. Architects work with clients and consultants to develop a cost estimate based on the design concept and specifications. This helps ensure that the design aligns with the client’s budget and allows for adjustments if necessary.
6. Sustainability Strategies
Sustainability is an increasingly important consideration in architectural design. During the schematic design phase, architects explore strategies to incorporate sustainable elements, such as energy-efficient systems, green materials, and passive design techniques. This not only reduces environmental impact but also contributes to the long-term economic and social viability of the project.
Overall, the key elements of schematic design are site analysis and planning, conceptual design, space planning, preliminary structural design, cost estimation and budgeting, and sustainability strategies. By carefully considering these elements, architects can create a strong foundation for the subsequent stages of design and ensure the successful realization of the project.
The Role of Schematics in the Architectural Process
Schematic design is a vital phase in the architectural process, representing the initial step in transforming a conceptual idea into a tangible design. During this stage, architects utilize schematics to explore and develop their ideas, refine the overall concept, and begin to establish the framework for the final design.
Schematics offer a visual representation of the proposed building or structure, presenting an overall layout, size, and scale of the project. This allows architects to visualize and communicate their ideas to clients, consultants, and other stakeholders. By mapping out the basic relationships and arrangement of spaces, the schematic design provides a crucial foundation upon which the rest of the design process can be built.
The development of schematics involves a combination of creative thinking and technical knowledge. Architects must analyze the site, assess its constraints, and consider various factors such as building codes, zoning regulations, and environmental impact. This information is then translated into a schematic plan, which outlines the general arrangement of spaces, circulation patterns, and key design elements.
As the first step towards realizing a design vision, the schematic design phase establishes the overall direction and concept of the project. It allows architects to explore different design options, experiment with materials and construction techniques, and evaluate the potential impact on the surrounding environment. This iterative process of refining and revising the schematics helps to ensure that the final design aligns with the client’s goals, meets functional requirements, and complies with all relevant regulations.
In summary, schematics play a crucial role in the architectural process by providing a visual representation of the design concept, establishing the framework for the final design, and guiding the subsequent phases of development. Through schematics, architects are able to communicate their ideas, explore design options, and ensure that the project meets all necessary requirements. By investing time and effort into the schematic design phase, architects lay the foundation for a successful and cohesive architectural project.
Benefits of Schematic Design
Schematic design is an essential phase in the architectural process that plays a crucial role in the success of a project. This phase allows architects to visualize and explore design concepts, ultimately leading to the creation of a solid foundation for the final project. The benefits of schematic design are numerous and can greatly contribute to the overall success and efficiency of a project.
1. Exploration of Design Concepts: During the schematic design phase, architects have the opportunity to experiment with various design concepts. This exploration allows them to assess different ideas, test their feasibility, and select the most suitable design approach for the project. By exploring different possibilities, architects can create unique and innovative designs that meet the project’s goals and requirements.
2. Visualization of the Project: Schematic design allows architects to develop 2D and 3D representations of the project. This visualization helps clients, stakeholders, and the architectural team to better understand the proposed design. It enables them to evaluate the spatial relationships, proportions, and overall aesthetic of the project before moving forward with detailed design and construction.
3. Cost Estimation and Value Engineering: Schematic design provides architects and project owners with a rough estimate of the construction cost. This estimation allows them to evaluate the feasibility of the project within the budgetary constraints. Additionally, schematic design enables value engineering, where architects can review and adjust the design to optimize the cost without compromising the design quality.
4. Effective Communication and Collaboration: Schematic design serves as a communication tool between the architect, client, and other project stakeholders. The visual representations and design narratives facilitate effective communication and collaboration, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and working towards a shared vision. This phase also allows for timely feedback and adjustments, reducing the potential for errors and rework during later stages.
5. Decision-making and Approval Process: Schematic design plays a significant role in the decision-making and approval process. The architectural team can present alternative design options and explain the pros and cons of each approach, helping clients and stakeholders make informed decisions. Schematic design also allows for early input and feedback, which ensures that the design aligns with the project’s goals and expectations.
Overall, the benefits of schematic design are instrumental in setting the stage for a successful and well-executed architectural project.
Common Challenges in Schematic Design
Schematic design is a critical phase in the architectural process, and it comes with its own set of challenges. Architects and designers need to navigate these challenges to create a successful and functional design. Here are some common challenges faced during schematic design:
1. Limitations of the Site: The site on which the building will be constructed can pose various limitations and constraints. Factors such as topography, climate, and neighboring buildings can influence the design and layout of the structure. Architects need to carefully consider these limitations and find creative solutions to incorporate them into the design.
2. Budget Constraints: Budget is a significant challenge in any architectural project. Architects need to balance the client’s vision and requirements with the available budget. They must find cost-effective design solutions without compromising the integrity and functionality of the building.
3. Regulatory Requirements: Compliance with building codes and regulations is crucial in schematic design. Architects need to thoroughly understand and adhere to the relevant regulations, which can vary from region to region. Failure to meet these requirements can result in delays, fines, or even legal consequences.
4. Design Complexity: Each architectural project comes with its unique design requirements and challenges. Architects need to find innovative design solutions that meet the client’s objectives while considering practicality and functionality. Balancing aesthetics, spatial efficiency, and technical aspects can be a complex and demanding task.
5. Client Expectations: Understanding and managing client expectations are crucial during schematic design. Architects must communicate effectively with clients to gather their requirements, preferences, and goals. They need to ensure that the design aligns with the client’s vision and aspirations, while also providing professional guidance and expertise.
Overall, schematic design requires architects to navigate various challenges and make critical decisions that shape the entire project. By overcoming these challenges, architects can create successful designs that meet both the functional and aesthetic needs of the client.