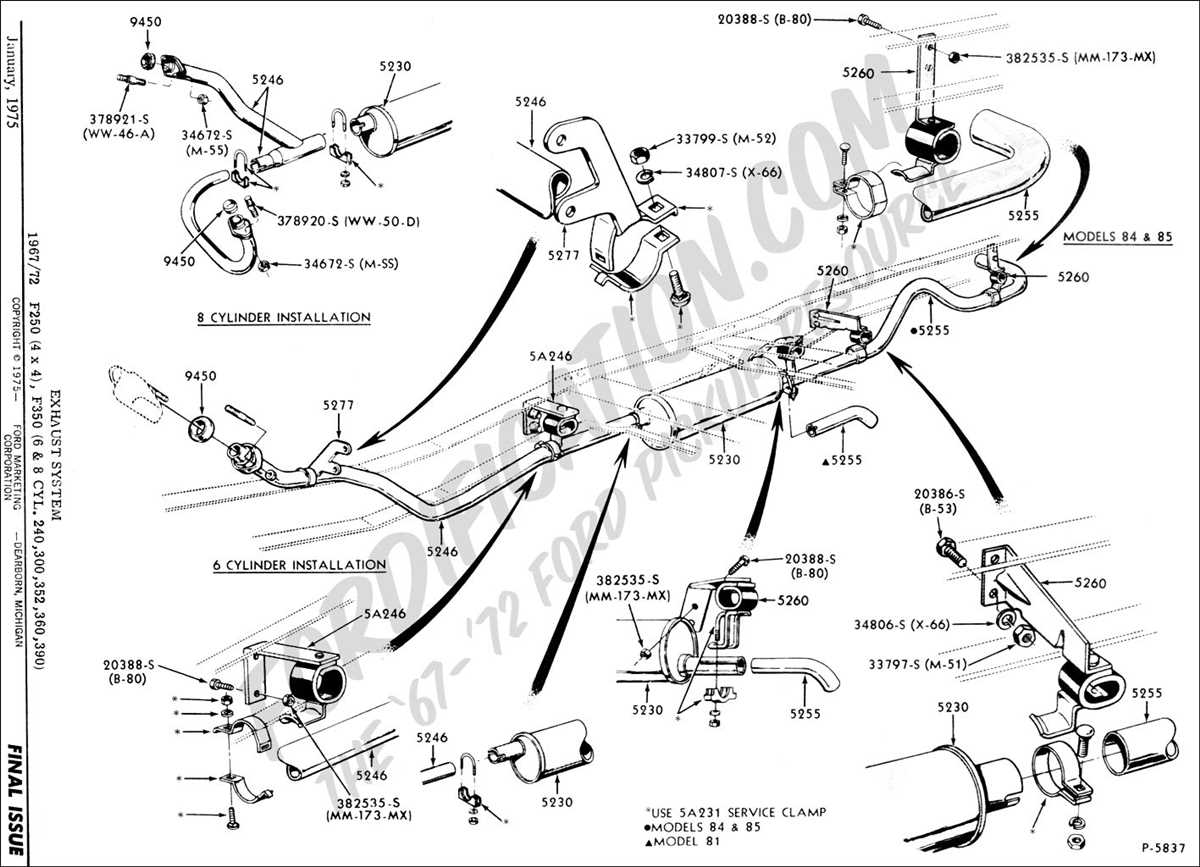
The exhaust system is an important component of any vehicle, including the Ford F150. It plays a crucial role in removing harmful gases produced during the combustion process and maintaining the overall performance of the engine. Understanding the layout and components of the exhaust system can help in diagnosing and repairing any issues that may arise.
The exhaust system of a 1997 Ford F150 consists of several main components. These include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each component has a specific function in the overall operation of the system.
The exhaust manifold is the first component that the exhaust gases pass through. Its primary purpose is to collect the gases from the engine cylinders and direct them towards the catalytic converter. The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. From the catalytic converter, the gases flow into the muffler, which is designed to reduce noise and provide additional airflow. Finally, the gases exit the system through the tailpipe.
Having a clear understanding of the layout and function of the exhaust system can be beneficial when it comes to maintenance and repairs. By identifying and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure that your 1997 Ford F150’s exhaust system performs optimally, prolonging the life of the vehicle and reducing environmental impact.
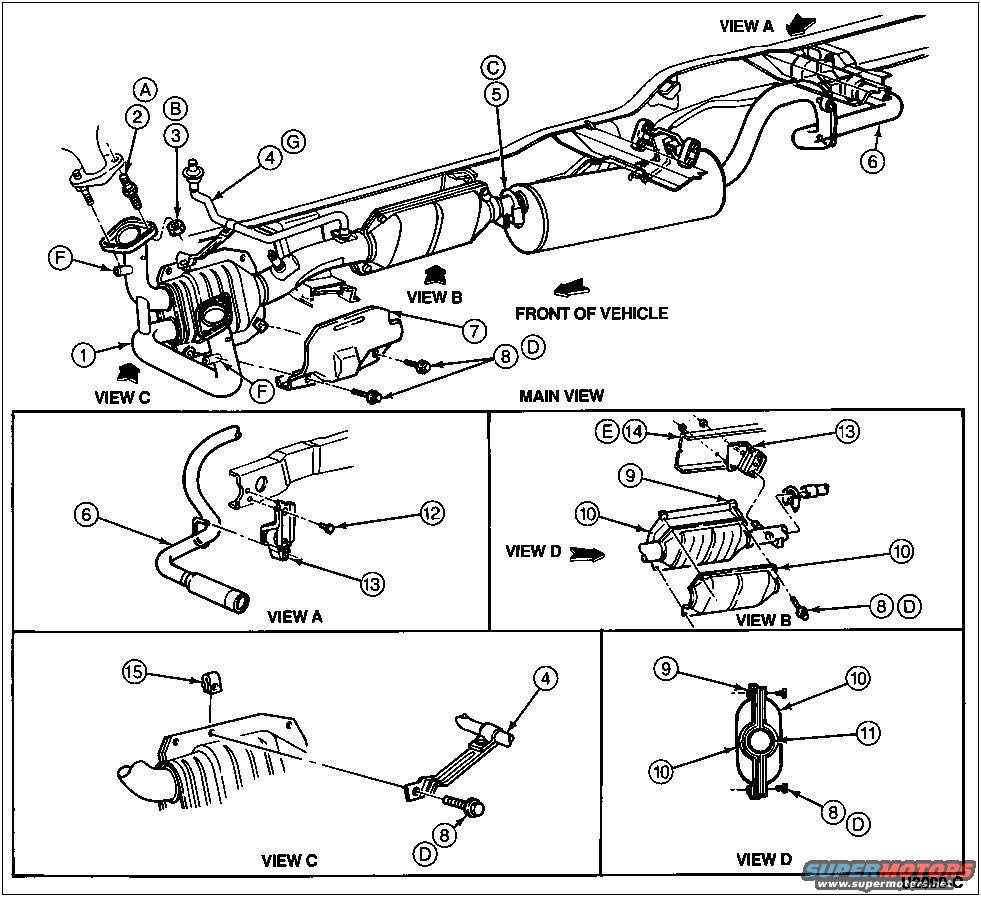
1997 Ford F150 Exhaust System Diagram
The 1997 Ford F150 is equipped with a complex exhaust system that is responsible for directing exhaust gases away from the engine and reducing noise emissions. Understanding the components and layout of the exhaust system is crucial for troubleshooting and performing maintenance or repairs.
Main Components: The exhaust system of the 1997 Ford F150 includes several key components. These include the exhaust manifolds, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. The exhaust manifolds collect exhaust gases from each cylinder of the engine and direct them into the rest of the exhaust system. The catalytic converter helps reduce harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. The muffler is responsible for reducing exhaust noise, while the tailpipe releases the exhaust gases into the atmosphere.
Layout: The exhaust system of the 1997 Ford F150 follows a specific layout. The exhaust manifolds are attached to the engine block on each side, collecting exhaust gases from the cylinders. The exhaust gases flow from the manifolds into the catalytic converter, where they undergo chemical reactions to reduce emissions. From the catalytic converter, the gases continue into the muffler, where noise is reduced. Finally, the gases exit through the tailpipe at the rear of the vehicle.
Importance of Maintenance: Proper maintenance of the exhaust system is essential for the overall performance and longevity of the 1997 Ford F150. Regular inspection of the system for leaks, cracks, or rust is important to prevent exhaust gases from entering the cabin and to ensure optimal engine performance. It is also important to address any check engine lights related to the exhaust system, as they could indicate a problem that needs attention.
Conclusion: Understanding the layout and components of the 1997 Ford F150 exhaust system is crucial for maintenance and repairs. With proper maintenance and timely repairs, the exhaust system can continue to function efficiently, reducing emissions and maintaining a smooth and quiet driving experience.
Overview of the Ford F150 Exhaust System
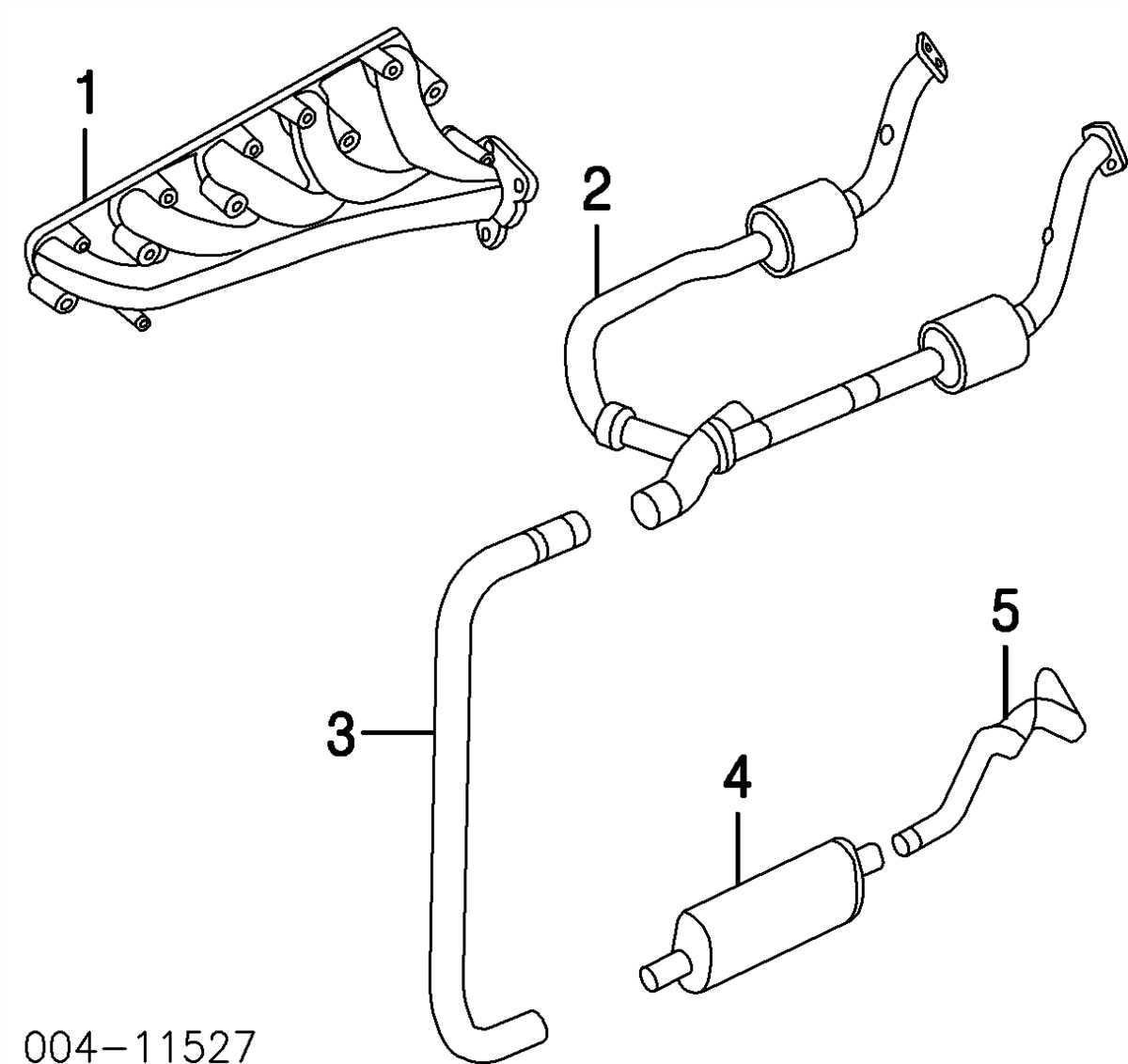
The exhaust system is an essential component of the Ford F150, responsible for removing combustion gases from the engine and reducing noise. A properly functioning exhaust system is crucial for the vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall emissions control.
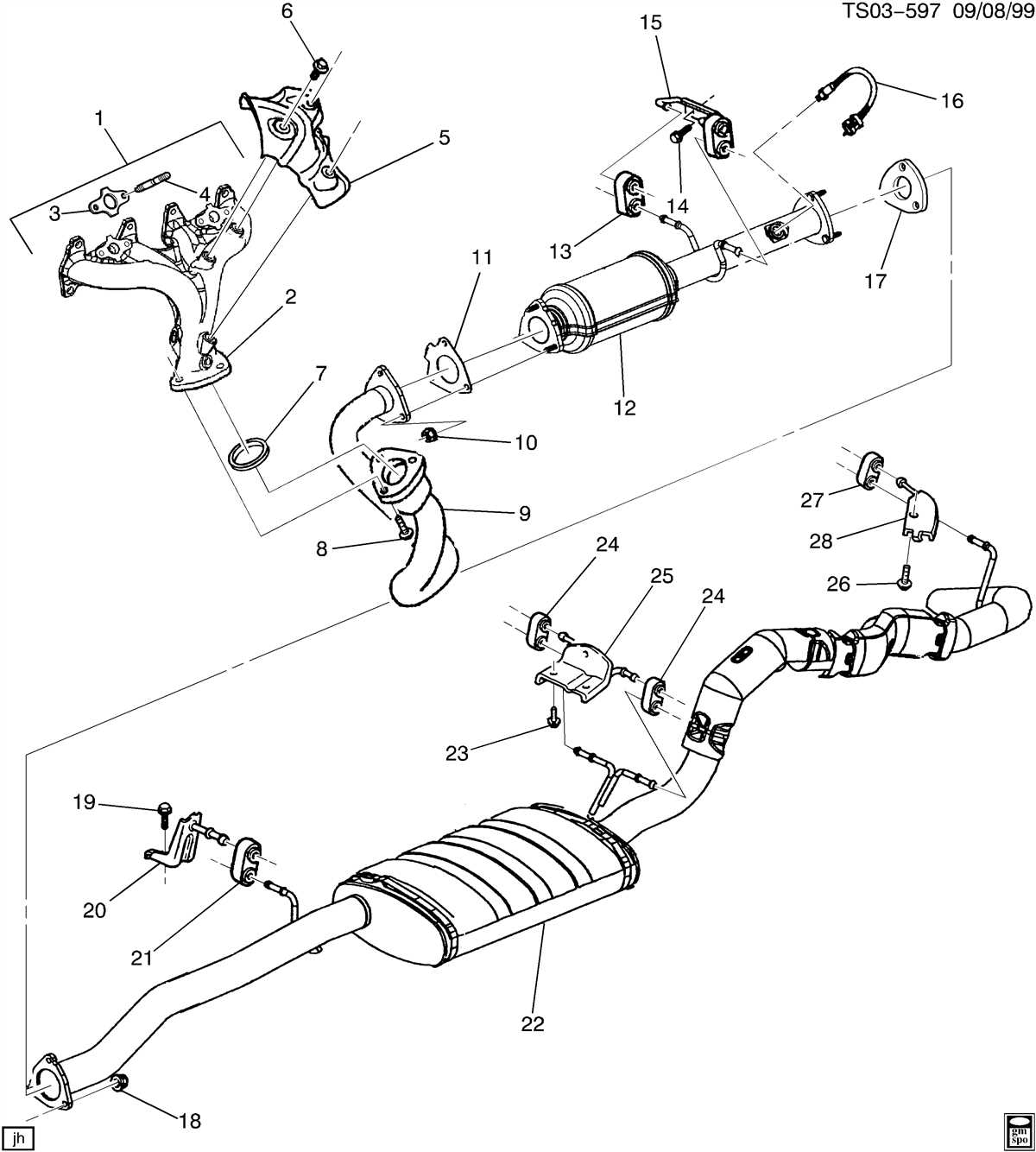
The exhaust system of a 1997 Ford F150 consists of several key components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each component plays a specific role in the overall function of the system.
- Exhaust Manifold: The exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from each cylinder and channels them into a single pipe.
- Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances through a catalyst.
- Muffler: The muffler helps reduce noise produced by the engine as the exhaust gases pass through. It contains baffles and chambers that help dampen and redirect the sound waves.
- Tailpipe: The tailpipe serves as the exit point for the exhaust gases to be released into the atmosphere.
It is important to regularly inspect and maintain the exhaust system of a Ford F150 to ensure optimal performance. Common issues that may arise include rust and corrosion, leaks, and damage to any of the components. Any signs of a malfunctioning exhaust system, such as loud noises, decreased fuel efficiency, or the smell of exhaust fumes, should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage and maintain the vehicle’s safety.
Components of the Exhaust System
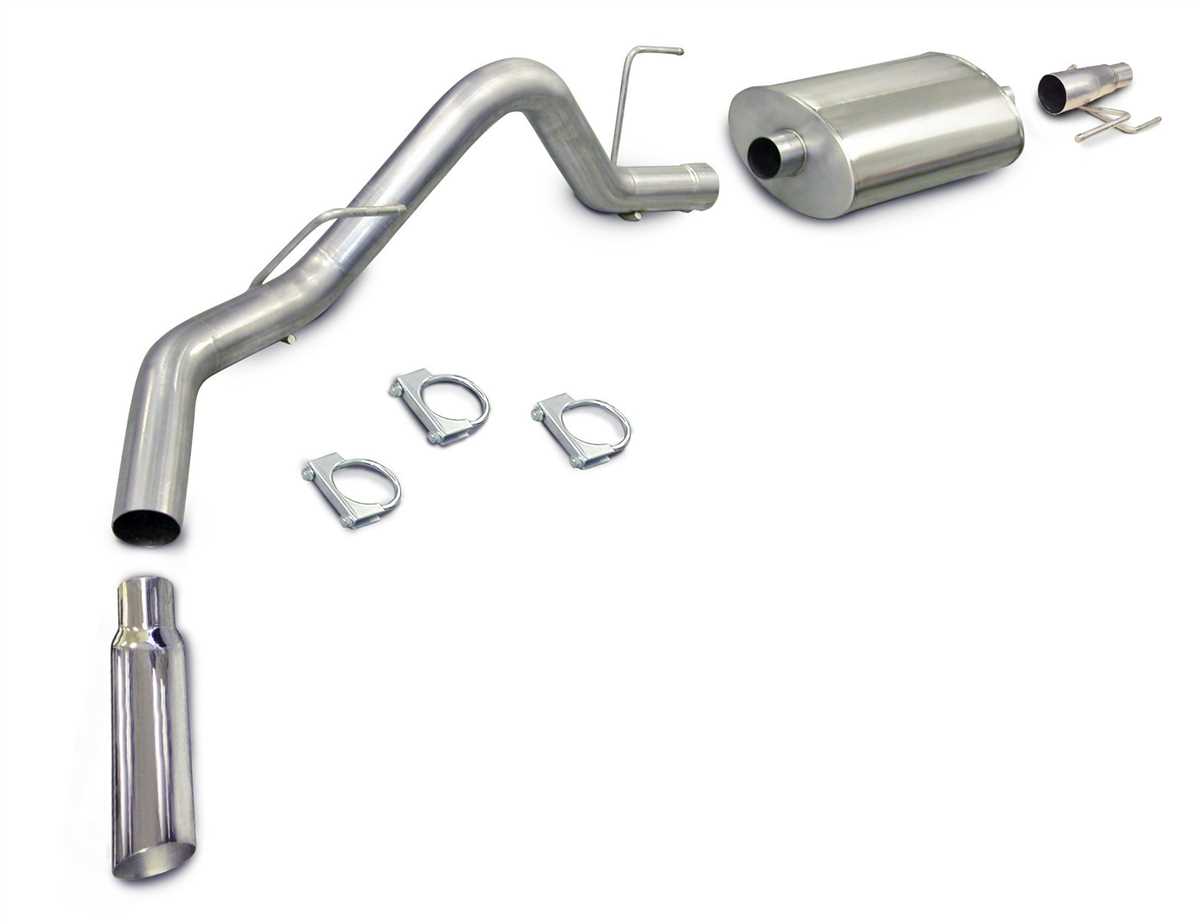

The exhaust system is an integral part of a vehicle’s engine performance and emissions control. It is responsible for directing and removing exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing backpressure, and minimizing noise levels. The 1997 Ford F150 exhaust system is comprised of several key components.
Exhaust Manifold: The exhaust manifold is located at the engine’s cylinder head and collects exhaust gases from each cylinder. It channels the gases into a single outlet, which connects to the rest of the exhaust system. The manifold is typically made of cast iron or stainless steel to withstand high temperatures.
Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is an essential component of the exhaust system that helps reduce harmful emissions. It contains a catalyst material, such as platinum or palladium, that promotes chemical reactions to convert harmful gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
Muffler: The muffler is responsible for reducing noise produced by the engine’s exhaust. It contains sound-absorbing materials and chambers designed to dissipate and cancel out sound waves. The muffler also helps regulate backpressure, optimizing engine performance.
Exhaust Pipes: The exhaust pipes transport the gases from the exhaust manifold to the rear of the vehicle. They are typically made of aluminized steel or stainless steel for durability. The pipes connect various components of the exhaust system, such as the catalytic converter and muffler, using clamps and flanges.
Exhaust System Hangers and Heat Shields: The exhaust system hangers support the weight of the exhaust system and keep it securely attached to the vehicle’s frame. Heat shields are used to protect sensitive components, such as fuel lines, from excessive heat generated by the exhaust system.
Exhaust Tips: Exhaust tips are often the only visible part of the exhaust system and provide a decorative touch. They come in various sizes and shapes and are usually made of stainless steel or chrome-plated steel. Exhaust tips can enhance the vehicle’s appearance and may affect the sound produced by the exhaust system.
In conclusion, the 1997 Ford F150 exhaust system consists of multiple components working together to enhance engine performance, reduce emissions, and minimize noise levels. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the system, ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently and complies with environmental regulations.
Exhaust Manifold Design and Function
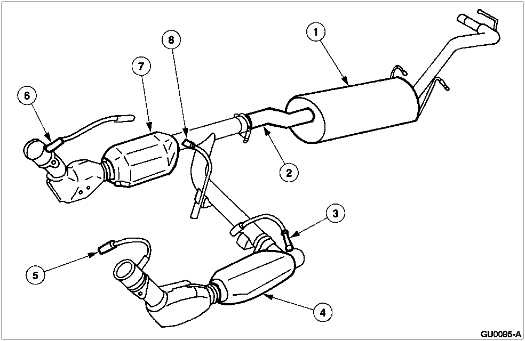
The exhaust manifold is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. Its primary function is to collect the exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders and direct them into the exhaust system. The design of the exhaust manifold plays a crucial role in optimizing engine performance.
Collector design: The exhaust manifold usually consists of individual runners that collect the exhaust gases from each cylinder and merge into a common collector. The collector design is critical for achieving an efficient flow of exhaust gases. By carefully designing the length and diameter of the runners and the size and shape of the collector, the exhaust manifold can help improve exhaust gas scavenging, reducing backpressure, and enhancing engine power.
Material selection: The choice of materials for the exhaust manifold is crucial due to the high temperatures and harsh conditions it operates in. Common materials used for manufacturing exhaust manifolds include cast iron, stainless steel, and more recently, lightweight alloys like ductile iron or even ceramic coatings. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on factors such as cost, durability, heat resistance, and weight.
Heat management: The exhaust manifold is exposed to extremely high temperatures that can cause thermal fatigue and reduce its lifespan. To minimize this, exhaust manifolds are often designed with heat management features like heat shields, insulation, or cooling fins. These features help dissipate heat and protect surrounding components from excessive heat exposure, increasing the overall durability of the manifold.
Integration with other components: The exhaust manifold is also designed to integrate with other components of the exhaust system, such as the catalytic converter or turbochargers. Proper integration ensures optimal exhaust gas flow, efficient emission control, and maximum power output. The design of the exhaust manifold should take into consideration the specific requirements and characteristics of these components.
In conclusion, the design of the exhaust manifold is critical for optimizing engine performance and ensuring efficient exhaust gas flow. Factors like collector design, material selection, heat management, and integration with other components play a significant role in achieving these objectives.
Catalytic Converter Operation and Maintenance
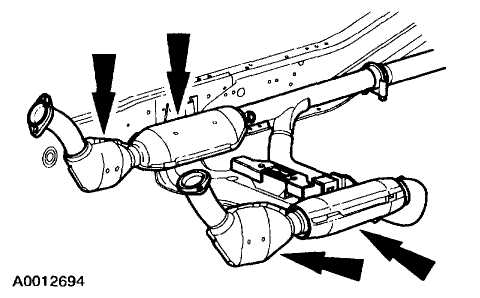
The catalytic converter is a critical component in the exhaust system of a vehicle. Its primary function is to reduce harmful emissions produced by the engine, converting them into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The catalytic converter works by using a combination of metals, including platinum, palladium, and rhodium, as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions that break down harmful gases. It operates at high temperatures, typically between 400 and 600 degrees Celsius, to optimize these reactions.
Maintenance of the catalytic converter is essential to ensure its proper functioning and longevity. One crucial aspect is making sure that the engine is running efficiently, as a poorly running engine can lead to an increased production of harmful emissions that can damage the converter over time.
Regular inspections to check for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or leaks, are also recommended. These can be indications of excessive heat or impact, which can impair the converter’s performance. If any damage is found, it is important to address it promptly to prevent further issues.
In addition to inspections, it is necessary to maintain the proper fuel and engine oil quality, as contaminated or poor-quality fluids can lead to increased emissions and potential damage to the converter. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for fuel and oil specifications is crucial.
Furthermore, it is essential to avoid using any aftermarket modifications, such as performance chips or exhaust systems, that can alter the engine’s emissions control system. These modifications can significantly impact the converter’s efficiency and may even result in legal consequences in some regions.
Overall, ensuring the proper operation and maintenance of the catalytic converter is vital for both the vehicle’s performance and the environment. Regular inspections, proper engine maintenance, and using high-quality fluids can help extend the lifespan of the converter and reduce harmful emissions.
Muffler Types and Sound Control
A muffler is an essential component of an exhaust system that is designed to reduce noise produced by the engine. It consists of chambers and baffles that help to dampen and control the sound waves generated by the exhaust gases.
There are several different types of mufflers available for vehicles, each with its own unique characteristics and sound control capabilities. One common type is the chambered muffler, which uses a series of chambers and perforated tubes to create a specific sound. This type of muffler is known for its deep and aggressive tone, making it popular among performance enthusiasts.
Another type of muffler is the straight-through muffler, also known as a glasspack muffler. This design features a straight pipe with sound-absorbing material wrapped around it. The straight-through design allows for unrestricted exhaust flow, resulting in improved performance. However, this type of muffler tends to produce a louder and less muffled sound compared to other types.
The third type is the turbo-style muffler, which is commonly found on turbocharged vehicles. This design incorporates a series of perforated tubes and chambers, which help to reduce exhaust noise while maintaining optimal flow dynamics for turbocharged engines. Turbo-style mufflers are known for their combination of performance and sound control.
When choosing a muffler, it’s important to consider your desired sound level and performance goals. Some mufflers are designed to be more aggressive and provide a louder, more noticeable exhaust note, while others are engineered for a quieter, more subdued sound. Additionally, some mufflers may offer performance gains, while others may prioritize sound control.
In conclusion, mufflers play a crucial role in controlling the sound produced by a vehicle’s exhaust system. Understanding the different types of mufflers available can help you choose the one that best suits your desired sound and performance needs.
Exhaust System Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of your 1997 Ford F150. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting can ensure that your exhaust system operates effectively and remains in good condition. Here are some tips to help keep your exhaust system running smoothly:
Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Routinely inspect the exhaust system for any signs of damage or leaks. Look for rust, loose connections, and cracks in the pipes or muffler.
- Cleanliness: Keep your exhaust system clean to prevent the buildup of dirt and debris. Use a gentle cleanser and a soft cloth to wipe away any grime.
- Replace Worn Parts: If you notice any damaged or worn-out components, such as a faulty catalytic converter or a damaged muffler, replace them promptly to prevent further damage to the exhaust system.
- Tighten Connections: Over time, the connections between the different parts of the exhaust system may become loose. Regularly check and tighten these connections to ensure a secure fit.
Troubleshooting
- Unusual Noises: If you hear strange noises coming from the exhaust system, such as rattling or hissing sounds, it could indicate a problem. These noises could be caused by loose or damaged parts or an exhaust leak.
- Excessive Smoke: If your exhaust system is producing excessive smoke, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning component, such as a failing catalytic converter or an engine oil leak.
- Reduced Performance: If you notice a decrease in your vehicle’s performance, such as a loss of power or reduced fuel efficiency, it could be attributed to a faulty exhaust system. The reduced airflow caused by a damaged muffler or a clogged catalytic converter can impact the overall performance of your vehicle.
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting of your exhaust system will help ensure that your 1997 Ford F150 operates efficiently and safely. By following these tips, you can keep your exhaust system in good condition and address any potential issues before they become major problems.