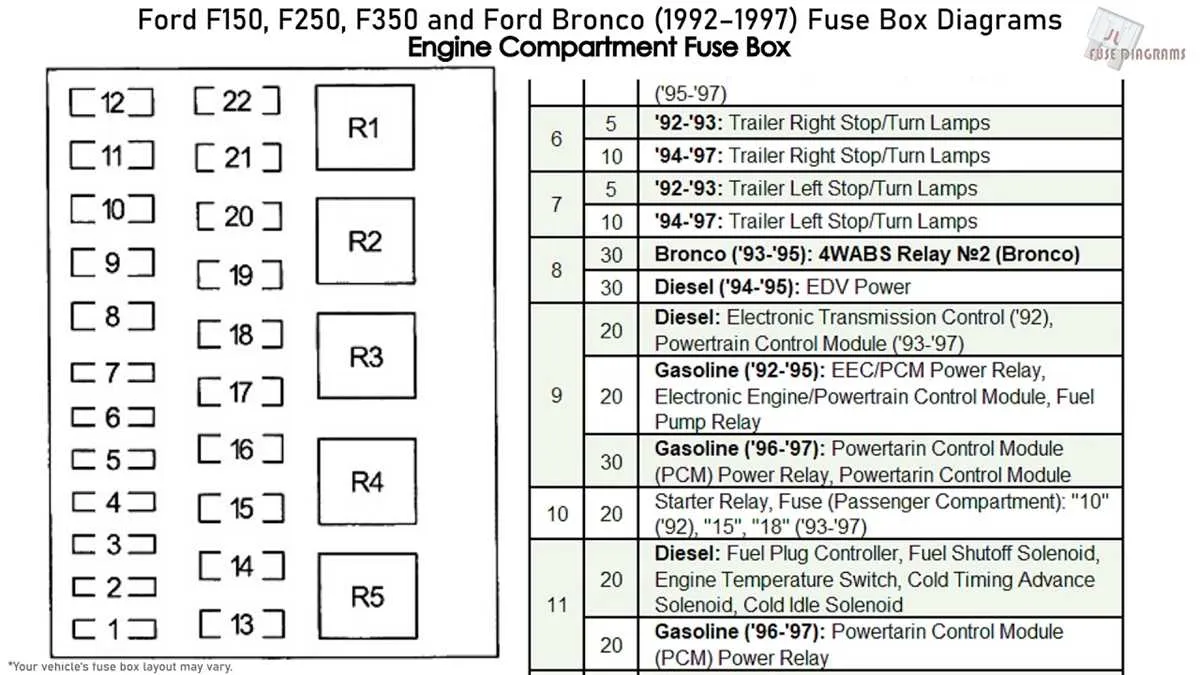
If you’re experiencing electrical issues, the first step is identifying the correct location of the electrical components. This specific model’s wiring structure is straightforward, but understanding the layout is essential to avoid further complications when replacing or testing individual components. The key to efficient diagnostics is the fuse and relay setup, as it controls many essential functions.
Start by inspecting the primary fuse block, typically located under the dashboard or near the driver’s side. The placement of each fuse varies, but a thorough understanding of the layout will help you pinpoint the exact area of malfunction. Make sure to check the connection points for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Refer to the guide for locating specific fuses associated with the ignition, lights, and other critical systems. For an accurate replacement, cross-check the specifications of the fuse with the vehicle’s electrical requirements. This will prevent potential overloading or short-circuits that can damage the system.
Electrical System Layout
Locate the main junction box under the dashboard near the driver’s side for access to critical components. Ensure the battery is disconnected before servicing any circuits. The layout includes specific fuses for ignition, lighting, and accessory systems. Always verify fuse ratings against the vehicle’s service manual to prevent damage. The secondary compartment, usually located under the hood, controls systems such as the cooling fan and alternator. For troubleshooting, start by checking the relays associated with high-power systems. A blown fuse typically causes circuit malfunctions, and replacing it with the correct amperage will restore function without causing further issues.
For convenience, label the fuse slots within the cover to ensure quick identification of potential issues. Replace any faulty components with those of equal specifications to maintain the integrity of the vehicle’s electrical system. Always use proper tools and take necessary precautions to avoid short circuits.
How to Identify the Locations of Electrical Circuits in a 1997 Pickup Truck
Check the owner’s manual to find the exact positions of each electrical component. The manual will list the individual circuits and their functions, helping you pinpoint the locations in the vehicle’s electrical system.
The driver’s side lower dashboard area is where you’ll typically find a major cluster of relays and circuits. Look beneath the dashboard near the footrest for easy access to most of the circuits.
The engine compartment also houses a secondary set of relays, often mounted near the battery or along the fender. It’s essential to know which side to check, as these relays usually control engine and auxiliary systems.
If the vehicle has a secondary electrical unit for specific systems like airbags or lights, it might be located in the rear cabin area. Check behind trim panels or near the back seats for such units.
Use a multimeter to test each component. After identifying the location, test the current to ensure that the right circuits are working properly. This helps to avoid misdiagnosing any issue.
Label each circuit clearly for future reference to prevent confusion during repairs or maintenance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Fuses in the 1997 Ford F150
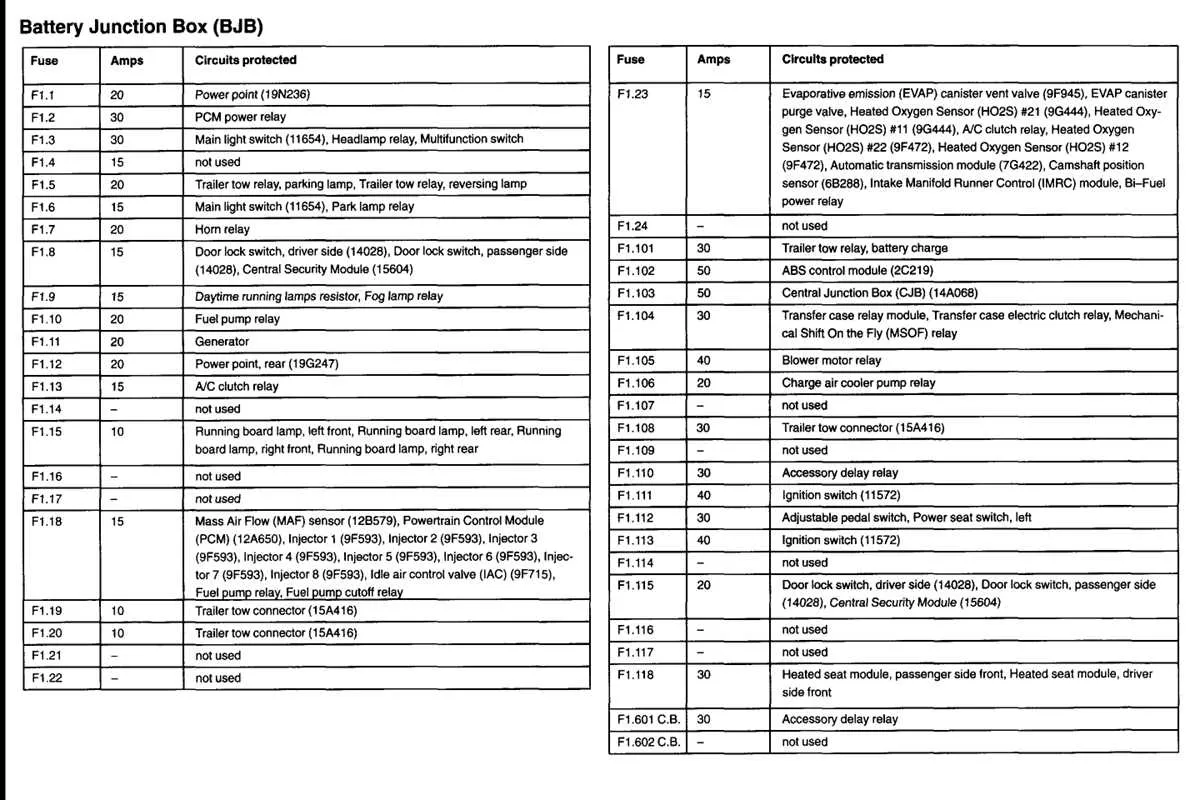
Start by identifying the location of the electrical components. The first step is to locate the fuse box under the dashboard or near the engine compartment. Once you’ve found it, ensure the vehicle is turned off and the key is removed to avoid any electrical shorts.
Next, open the cover of the compartment and locate the damaged or blown part. A blown unit typically appears darkened or has a broken wire inside. Refer to the corresponding chart, which usually provides a map of the slots and their respective components, to confirm the exact position.
Use a pair of fuse pullers or needle-nose pliers to safely remove the faulty part. Avoid using your hands, as this could cause accidental injury or damage to surrounding components.
Once removed, compare the amperage rating of the replacement component with the one you are removing. Make sure that the new piece matches the specified value, as using one with incorrect ratings could lead to electrical issues or fires.
Insert the new part carefully into the empty slot. Press it in firmly until it clicks into place. Double-check to ensure the new component is securely installed.
After installation, close the fuse box cover and start the vehicle. Test the affected system to ensure everything is functioning properly. If the system still doesn’t work, check for any other issues, such as wiring or connectors, and replace any additional damaged parts.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical System Issues

Start by inspecting the main power distribution block located inside the cabin or under the hood. If a particular component stops functioning, first check the related terminal connections for any signs of corrosion or loose wires.
If a malfunctioning accessory isn’t working, confirm whether the problem is due to a blown circuit by testing the associated relay or component through a multimeter. If you discover a non-responsive connection, replace the faulty relay and verify the new one is seated properly.
- Check for corrosion on the terminal contacts. Clean them with electrical contact cleaner.
- Verify all connectors are tight and making proper contact.
- If any fuses have blown, replace them with the correct amperage rating specified in the vehicle’s service manual.
For complex electrical issues, it may be necessary to test the power distribution system with a test light to ensure signals are being properly sent to key electrical components. A faulty distribution block may require replacement if it fails to send voltage where needed.
- Test continuity using a multimeter at the affected terminals.
- Inspect any inline fusible links for damage.
- If continuity fails at a specific point, troubleshoot by replacing connectors or resetting the associated control module.
For consistent issues, it might be worth inspecting the grounding points across the vehicle. Faulty grounds are a common cause of electrical failures. Use a ground tester to confirm connections at each critical point in the electrical system.