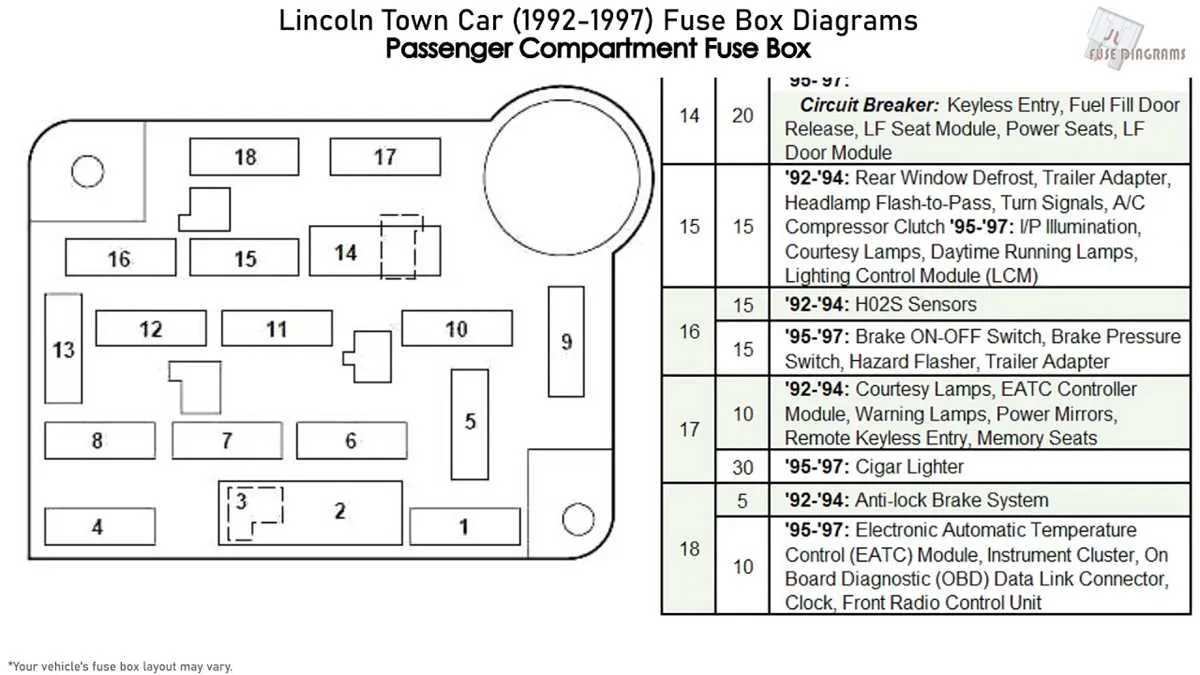
For anyone working on the electrical system of their vehicle, it’s crucial to identify the locations and functions of various protective components. The fuse board layout is a key reference for troubleshooting and ensuring proper functioning of the car’s electrical systems.
Locate the primary fuse panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side. This is where most of the circuits for lights, radio, and other essential functions are protected. For more specialized systems like the climate control or power windows, check the secondary fuse boxes often found under the hood or in the trunk area.
Each of the protective devices in the system has a specific amperage rating that corresponds to the electrical load it supports. Make sure to replace any blown component with one of the same rating to avoid damage to the electrical system or fire hazards.
Be cautious while working with these components. Always disconnect the battery before attempting any repairs, and double-check your fuse box layout to ensure you’re addressing the correct part of the system. A thorough understanding of the electrical layout will help prevent unnecessary complications during your maintenance process.
Electrical System Overview
For proper operation of the vehicle’s electrical components, ensure all relays and circuit breakers are correctly positioned and functioning. Check the main power distribution box located near the driver’s side, which houses critical components like the power windows, lighting systems, and ignition relay. If a system fails to operate, inspect the relevant fuses to ensure they are not blown or disconnected.
Pay attention to the specific location of each relay. The interior box is located beneath the dashboard, accessible near the driver’s knee area. The rear section contains fuses for auxiliary functions like the HVAC system, audio system, and seat controls. A blown relay often causes power loss to critical features such as the engine control module or starter motor. Consult your manual for the exact positions and amperage ratings for each component.
In case of failure, replace blown fuses with the recommended amperage. Incorrect fuse ratings may cause further damage to the wiring or devices. Always use a fuse puller for safety, and verify the new fuse is correctly seated. Ensure that any signs of corrosion or damage around the fuse terminals are addressed promptly.
Identifying Main Panel Locations
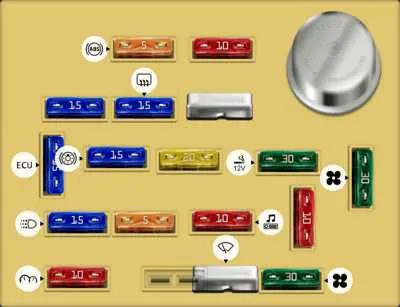
The primary electrical control panels in this model are located in two main areas: inside the cabin and under the hood. To access the first, you’ll need to open the driver’s side door and locate the panel beneath the dashboard, to the left of the steering wheel. It is typically protected by a plastic cover that can be removed with ease.
The second panel, placed under the hood, is found near the battery. It is often located in the vicinity of the engine bay’s right side, adjacent to the vehicle’s firewall. This is the primary panel responsible for high-current circuits, including those controlling key components like the alternator and air conditioning.
Both panels are secured with latches or clips, so ensure you are using the appropriate method to access them without damaging the covers. Always check for any signs of wear or corrosion on the connections when performing maintenance or troubleshooting electrical issues.
Common Electrical System Problems and Solutions
If certain electrical components aren’t working, the first step is to check the circuit protection elements. A blown unit often causes malfunction in lighting, radio, or power windows. Use a multimeter to check continuity across each element–if there’s no continuity, the circuit is likely open. Replace the faulty unit with one of the correct amperage rating to avoid damage to other components.
Loose or corroded connections can also cause electrical failures. Inspect all terminals and connectors for any sign of wear, oxidation, or looseness. Clean and tighten them as necessary. Corrosion around connectors often results in intermittent power issues or complete failure of the affected circuits.
If multiple systems are affected simultaneously, such as the dashboard and exterior lights, check for issues with the main control module. Resetting the module or performing a system reboot might resolve the issue. However, if the problem persists, further inspection of the wiring for any shorts or damaged sections is required.
Be cautious with the use of replacements–incorrect amperage ratings or poor-quality units can lead to overloading or improper function of the affected system. Always match the original specifications and ensure that components are of sufficient quality to handle electrical demands.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Fuses in Your Vehicle
Follow these detailed steps to replace electrical components in your vehicle efficiently:
- Locate the power control center under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Open the panel carefully, ensuring not to damage the clips or fasteners.
- Use a fuse puller tool to remove the blown unit from its slot. Ensure the tool grips securely to avoid damaging the component.
- Inspect the removed unit for signs of a broken filament. A darkened or burnt spot usually indicates damage.
- Select a replacement part with identical specifications, including voltage and amperage ratings. Do not substitute with a different size or type, as this can damage the system.
- Insert the new unit into the same slot, ensuring it fits snugly without forcing it into place.
- Once replaced, close the panel and verify the electrical system’s functionality by testing the affected circuit.
Remember to keep a set of spare components in your vehicle to handle future issues quickly. Always double-check connections and confirm the new parts are secure to prevent recurring problems.