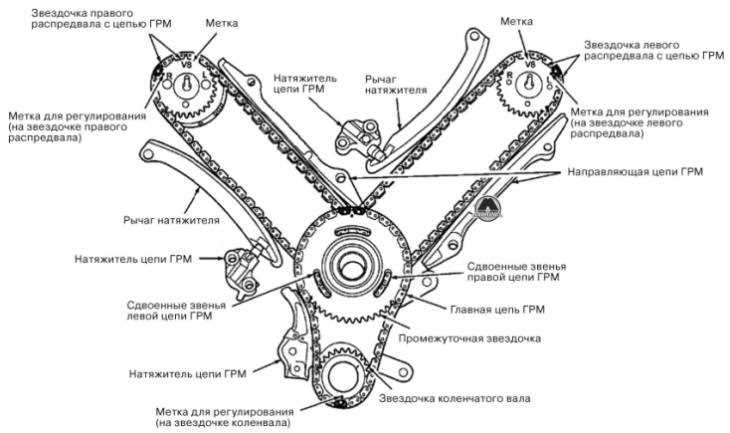
The 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine has become a popular choice among car enthusiasts due to its power and durability. Whether you’re a mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the engine’s components and their functions can help you maintain and troubleshoot your vehicle more effectively.
In this article, we will provide you with a detailed 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine diagram, breaking down each component and explaining its role in the overall functioning of the engine. From the intake manifold to the exhaust system, you’ll gain valuable insights into how these different parts work together to power your vehicle.
By familiarizing yourself with the engine diagram, you’ll be better equipped to identify potential issues, perform routine maintenance tasks, and even make more informed decisions when it comes to upgrades and modifications. So, whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a Durango owner looking to understand your vehicle better, this article is for you.
2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 Engine Diagram
The 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine diagram provides a visual representation of the various components and systems within the engine. This diagram can be helpful for understanding how the engine works and for identifying specific parts and their locations.
Engine Block: The engine block is the main component of the engine and houses the cylinders, pistons, and other internal parts. It is made of cast iron or aluminum and is the foundation of the engine.
Cylinder Heads: The cylinder heads are located on top of the engine block and contain the valves, fuel injectors, and spark plugs. They help to seal the combustion chambers and control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders.
Camshaft: The camshaft is responsible for opening and closing the valves in the cylinder heads. It is driven by the crankshaft and controls the timing and duration of the valve openings.
Pistons: The pistons are located inside the cylinders and move up and down to convert the heat and pressure from the combustion process into mechanical energy. They are connected to the crankshaft by connecting rods.
Fuel System: The fuel system delivers fuel to the engine for combustion. It includes components such as the fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel pressure regulator.
Ignition System: The ignition system provides the spark necessary for combustion. It includes components such as the spark plugs, ignition coil, and distributor or ignition module.
- Other components in the engine diagram may include the exhaust system, cooling system, lubrication system, and electrical system.
- It is important to refer to the specific engine diagram for the 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 model, as there may be variations in the configuration depending on the specific vehicle.
By referring to the engine diagram, owners and technicians can better understand the layout and function of the various components in the 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine. This can be helpful for troubleshooting engine issues, performing maintenance and repairs, or simply gaining a better understanding of how the engine works.
Engine Overview

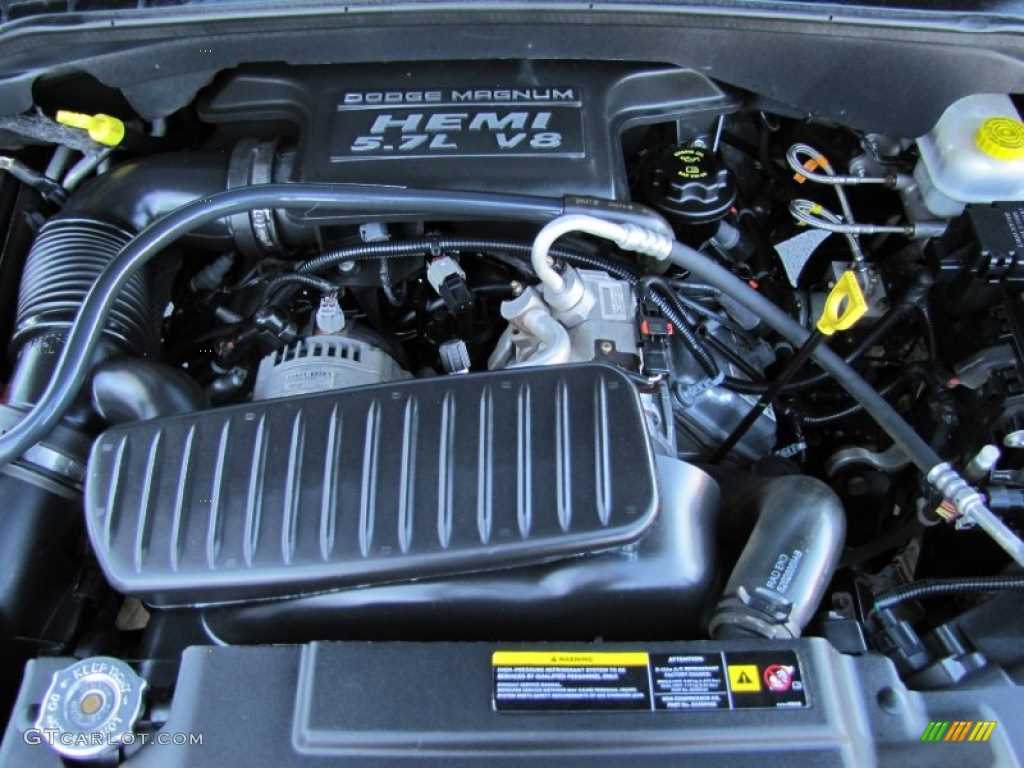
The 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine is a V8 engine that is commonly found in this model. It is a powerful and reliable engine that provides a good balance of performance and fuel efficiency.
The engine is a 4.7-liter engine, which means that the total displacement of all the cylinders in the engine is 4.7 liters. It features eight cylinders, which are arranged in a V shape. This V8 configuration allows for smooth and efficient power delivery.
The engine is equipped with an overhead camshaft, which controls the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. This helps to improve the engine’s overall performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, the engine has an electronic fuel injection system, which ensures precise fuel delivery and combustion efficiency.
The 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine also features an efficient cooling system to prevent overheating. It has a radiator, water pump, and cooling fan that work together to keep the engine’s temperature within a safe range.
In terms of power output, the 4.7 engine produces around 235 horsepower and 300 lb-ft of torque. This provides ample power for towing and hauling tasks. The engine is also equipped with a multi-point fuel injection system, which helps to optimize fuel delivery and improve overall performance.
Overall, the 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine is a reliable and powerful V8 engine that provides good performance and fuel efficiency. It is well-suited for both everyday driving and towing or hauling tasks.
Components of the 4.7 Engine
The 4.7 engine found in the 2000 Dodge Durango is a powerful and reliable engine that is made up of several key components. Understanding these components and how they work together can help with the maintenance and troubleshooting of the engine.
1. Cylinder Block: The cylinder block is the main supporting structure of the engine. It houses the cylinders and provides the foundation for the rest of the engine components. In the 4.7 engine, the cylinder block is made of cast iron for durability.
2. Pistons: Pistons are responsible for converting the pressure created by the combustion process into mechanical energy. In the 4.7 engine, there are eight pistons, one for each cylinder. They move up and down within the cylinders, transferring power to the crankshaft.
3. Crankshaft: The crankshaft is a rotating shaft that converts the up and down motion of the pistons into a rotational motion. It is connected to the pistons through connecting rods and transfers the power to the transmission and wheels.
4. Camshaft: The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. It is driven by the crankshaft and operates the valves through a series of lobes. The camshaft in the 4.7 engine is located at the top of the cylinder block.
5. Valvetrain: The valvetrain includes the valves, valve springs, and camshaft. It controls the intake of air and fuel into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. The 4.7 engine has two intake valves and two exhaust valves per cylinder.
6. Fuel System: The fuel system delivers fuel to the engine for combustion. It includes components such as the fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel rail. The 4.7 engine utilizes a multipoint fuel injection system for precise fuel delivery.
7. Ignition System: The ignition system is responsible for creating the spark that ignites the air/fuel mixture in the cylinders. It consists of components such as the ignition coil, spark plugs, and ignition control module. The 4.7 engine uses a distributorless ignition system for improved reliability.
8. Cooling System: The cooling system regulates the temperature of the engine to prevent overheating. It includes components such as the radiator, water pump, and thermostat. The 4.7 engine uses a liquid cooling system that circulates coolant through the engine to dissipate heat.
9. Lubrication System: The lubrication system ensures that all moving parts within the engine are properly lubricated. It includes components such as the oil pump, oil filter, and oil pan. The 4.7 engine uses a full-pressure lubrication system to maintain optimal lubrication.
Overall, the 4.7 engine in the 2000 Dodge Durango is a complex system made up of various components that work together to generate power and propel the vehicle. Understanding these components and how they function is essential for maintaining the engine’s performance and diagnosing any issues that may arise.
Fuel System
The fuel system of a 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine plays a crucial role in delivering fuel to the engine for combustion. It consists of several components that work together to ensure the proper functioning of the engine.
One of the main components of the fuel system is the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline or diesel fuel. The tank is located in the rear of the vehicle and is connected to the rest of the system through fuel lines. These fuel lines transport fuel from the tank to the engine.
Another important component is the fuel pump, which is responsible for pumping fuel from the tank to the engine. The fuel pump is usually located inside the fuel tank and is powered by electricity. It creates the necessary pressure to ensure a steady flow of fuel to the engine.
The fuel system also includes a fuel filter, which is designed to remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. The fuel filter helps to maintain the cleanliness of the fuel system and prevent damage to the engine caused by dirty fuel.
In addition to the fuel pump and filter, the fuel system also consists of fuel injectors. These injectors are responsible for delivering a precise amount of fuel into each cylinder of the engine. The fuel injectors are controlled by the engine control module (ECM) and ensure proper fuel atomization for efficient combustion.
Overall, the fuel system of a 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine is a complex system that plays a vital role in the performance and efficiency of the vehicle. Regular maintenance and proper care of the fuel system are important to ensure its optimal functioning and extend the lifespan of the engine.
Ignition System
The ignition system of a 2000 Dodge Durango with a 4.7 engine is responsible for providing the spark required to ignite the fuel mixture and start the engine. It consists of several components working together to generate and distribute the high voltage needed for spark production.
One of the key components in the ignition system is the ignition coil, which converts the low voltage electricity from the battery into a high voltage current that is sent to the spark plugs. This high voltage is necessary to create a strong spark that can ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber.
The ignition system also includes the spark plugs, which are connected to the ignition coil by spark plug wires. The spark plugs are responsible for actually creating the spark that ignites the fuel. They consist of a central electrode and a ground electrode, with a small gap between them. When the high voltage current from the ignition coil is sent to the spark plug, it jumps the gap between the electrodes, creating a spark.
To ensure proper timing and firing of the spark plugs, the ignition system also includes a distributor or ignition control module. This component helps control the distribution of the high voltage current to each spark plug at the correct time, based on signals from the engine’s crankshaft position sensor.
In addition to these main components, the ignition system may also include other components such as a rotor, cap, and ignition switch, depending on the specific design of the vehicle.
Overall, the ignition system plays a crucial role in the operation of the 2000 Dodge Durango’s 4.7 engine, providing the necessary spark to start the engine and ensure efficient combustion. Regular maintenance and inspection of the ignition system components is important to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues with engine starting and performance.
Cooling System

The cooling system in a 2000 Dodge Durango with a 4.7 engine is an essential component to ensure that the engine remains at the optimal operating temperature. It is responsible for preventing the engine from overheating and maintaining its efficiency.
The cooling system consists of several key components, including the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and various hoses. Coolant, also known as antifreeze, circulates through the engine and absorbs heat generated by the combustion process. It then flows through the radiator, where it is cooled by outside air before returning to the engine.
Radiator: The radiator is a heat exchanger located at the front of the vehicle. It is made up of a network of small tubes and fins that allow the coolant to release heat. The radiator fan, controlled by the engine’s cooling system, helps to pull air through the radiator and dissipate the heat.
Water Pump: The water pump is responsible for circulating the coolant throughout the engine and radiator. It is driven by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft and uses an impeller to create a flow of coolant. The pump ensures that the coolant is constantly circulated, preventing hot spots in the engine and promoting even cooling.
Thermostat: The thermostat is a valve located between the engine and the radiator. It regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature. When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed, allowing the coolant to circulate within the engine and warm it up quickly. Once the engine reaches the optimal temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator and cool the engine.
The cooling system in the 2000 Dodge Durango is designed to work efficiently and maintain the engine’s optimal operating temperature. Regular maintenance, such as checking coolant levels, inspecting hoses for leaks, and flushing and replacing coolant as needed, can help to ensure the longevity and proper function of the cooling system.
Cooling System Diagram

Below is a diagram of the cooling system in a 2000 Dodge Durango with a 4.7 engine:
| 1 | Engine |
|---|---|
| 2 | Water Pump |
| 3 | Thermostat |
| 4 | Radiator |
| 5 | Coolant |
| 6 | Radiator Fan |
| 7 | Hoses |
Please note that this diagram is for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect the exact configuration of the cooling system in every 2000 Dodge Durango with a 4.7 engine. It is always recommended to consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional mechanic for specific information and guidance on the cooling system.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system in a 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine is responsible for removing waste gases from the engine and reducing noise and emissions. It consists of several components that work together to direct exhaust gases out of the vehicle. Below is a summary of the main components:
- Exhaust Manifold: The exhaust manifold collects exhaust gases from each cylinder and funnels them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is an important component of the exhaust system that helps reduce harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: The muffler is responsible for reducing the noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the vehicle. It contains chambers and baffles that help to dampen the sound.
- Tailpipe: The tailpipe is the final section of the exhaust system that directs the gases away from the vehicle and releases them into the atmosphere.
The exhaust system in the 2000 Dodge Durango 4.7 engine plays a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s performance, reducing emissions, and ensuring a quiet ride. Regular maintenance and inspection of the exhaust system are important to identify any issues and keep the vehicle running smoothly.