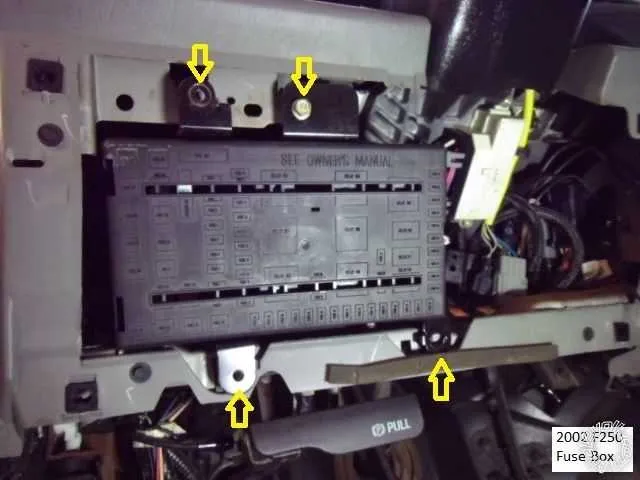
For any electrical troubleshooting or replacement tasks, refer to the precise positioning of components within your vehicle’s power network. Ensuring you identify the correct relays and connectors is essential when diagnosing issues with your vehicle’s electronics. This visual reference simplifies the process, helping you quickly locate the right areas without confusion.
First step: Always confirm that the correct power sources are disconnected before working with the wiring system to avoid any electrical hazards or component damage. Once the power is safely off, use the layout to pinpoint individual fuses and relays that control key systems such as lighting, engine management, and auxiliary functions.
Tip: Pay special attention to the system’s distribution points–typically located in the interior and engine compartments. Knowing which area houses critical electrical components allows for faster troubleshooting and efficient maintenance, reducing downtime and preventing unnecessary part replacements.
For a streamlined repair or part replacement, consult the provided map. The clarity of this schematic ensures you don’t waste time guessing the right connections, thus ensuring long-term reliability for your electrical systems.
Electrical Component Layout
For reliable operation, ensure all relays and electrical connections are properly aligned. Check the placement of fuses controlling critical systems such as headlights, wipers, and air conditioning. For a smooth process, start by locating the primary relay section, which is typically near the driver’s side dashboard or under the hood, depending on the system.
For the cabin, you will find a series of small rectangular connectors. The main units handle functions like interior lighting, power windows, and central locking. Be cautious with the powertrain-related connections, as these may need specialized attention to avoid accidental damage.
Make sure the electrical components near the battery area are free from corrosion or debris. Inspect for proper seating of the protective covers to avoid potential shorts or overheating. Consider using a multimeter to ensure all terminals provide correct voltage levels.
Before replacing any electrical parts, consult a detailed system manual to verify the amperage and compatibility of replacements to prevent malfunction. Always disconnect the vehicle’s battery when servicing the system to avoid accidental sparks or injury.
Identifying Key Fuses and Relays in the 2003 F250 Fuse Box
Start by locating the main panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side, and the auxiliary panel beneath the hood. These are the primary areas for troubleshooting electrical issues.
For the interior panel:
- Ignition Circuit – Typically found in position 4. It’s crucial for powering the engine’s ignition system.
- Fuel Pump – Located in position 20, this relay controls fuel delivery to the engine.
- ABS System – Check relay 15 for issues with the Anti-lock Braking System.
- Heated Seats – If you experience seat heating problems, check fuse 21.
- Windshield Wipers – Fuse 10 often controls the wiper motors and should be checked for proper operation.
For the under-hood panel:
- Starter Motor – The relay at position 12 ensures the starter motor engages when you turn the key.
- Alternator – Relay 8 is responsible for the charging system; inspect it if the battery isn’t charging properly.
- Transmission Control Module – Positioned at relay 7, it should be checked if there are transmission shifting issues.
- Cooling Fans – Relay 3 controls the cooling fan system, vital for engine temperature regulation.
If electrical systems aren’t working correctly, systematically check each component in these positions for continuity or visible damage. Replacing faulty units promptly prevents further electrical issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Blown Fuse in Your Vehicle

1. Locate the main electrical panel inside the cabin. It is typically situated under the dashboard on the driver’s side. For models with a secondary panel, check near the engine bay for additional access points.
2. Identify the malfunctioning circuit. Refer to the reference label on the cover of the panel to match the corresponding number or function of the component that isn’t working.
3. Using a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers, gently remove the faulty item. Make sure to avoid damaging the surrounding components.
4. Examine the piece for any visible signs of damage. A blown unit will typically show a broken wire inside or discoloration.
5. Select a replacement that matches the exact amperage rating of the original. It’s crucial to use the correct capacity to avoid electrical issues or potential damage to other circuits.
6. Insert the new part into the appropriate slot, ensuring it is securely in place. If needed, refer back to the reference guide for correct positioning.
7. Test the system by switching on the electrical function that was previously malfunctioning. If the issue persists, double-check the amperage and position of the new component.
Common Electrical Panel Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
If your vehicle is experiencing electrical malfunctions, the first thing to check is the main power distribution unit. A blown circuit or a damaged terminal often causes issues like malfunctioning lights, non-responsive accessories, or power loss to critical systems. Here’s a step-by-step approach to resolving these common problems:
1. No Power to Accessories: Start by inspecting the main connectors. Loose or corroded terminals can cause power loss. Tighten or clean the connectors as necessary. Use dielectric grease to prevent further corrosion.
2. Blown Circuits: Identify the damaged circuit by using a test light or multimeter. Once you locate the faulty circuit, replace the corresponding fuse. Ensure you use the correct amperage to avoid overloading the system.
3. Intermittent Power Issues: If electrical power is unreliable, check for worn out connections or burnt-out terminals. The connectors might not be making a solid contact, which can cause temporary outages. Cleaning the connectors or replacing the damaged ones will restore stability.
4. Faulty Relays: A defective relay can cause specific systems, like the air conditioning or ignition, to malfunction. Use a multimeter to test the relay’s continuity. If faulty, replace the relay and check if the problem persists.
5. Short Circuits: If you suspect a short circuit, carefully trace the wiring from the panel to the malfunctioning component. Look for exposed wires or areas where the insulation may have worn off. Repair any damaged wiring and ensure the insulation is intact.
6. Overheating: Excessive heat buildup is often a sign of an overload. Check for damaged circuits and ensure no wires are touching metal surfaces. If necessary, replace overheated components and ensure the system is properly grounded.