
For efficient troubleshooting and maintenance, it’s essential to know where to find each electrical component in your car. The key to proper diagnostics lies in understanding the connections and how each circuit functions within your vehicle’s electrical system. Whether you’re fixing a blown fuse, replacing a relay, or upgrading the wiring, accurate information on component locations saves time and effort.
Locate the Main Electrical Panel in the engine compartment or under the dashboard for quick access to the primary circuits. The positioning of these elements allows easy identification of critical components such as lights, wipers, and interior features. You’ll find the distribution points clearly marked for each specific function.
Check for Blown Connections regularly by referring to a clear layout map. Most models include a detailed chart that points out which fuses correspond to certain systems. Keeping this reference handy will help you troubleshoot quickly when an issue arises, ensuring a smooth repair process.
By following these guidelines, you ensure that your electrical system remains in top working order, reducing the risk of future malfunctions. Understanding the exact setup allows for effective repairs and prevents unnecessary replacement of parts.
Electrical System Layout for 2003 Vehicle
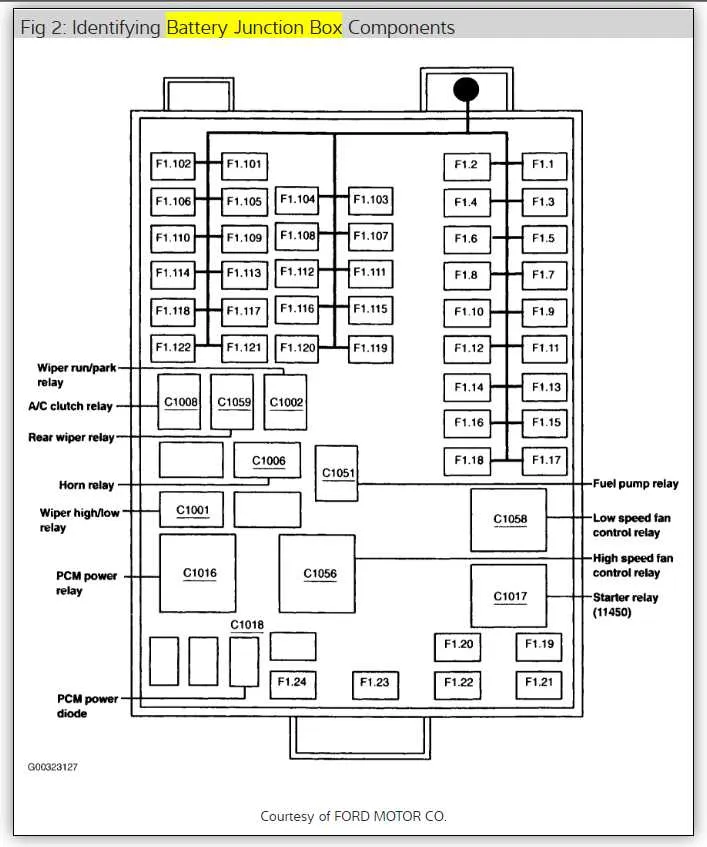
For troubleshooting or replacing any electrical components, it’s essential to know the exact position of each circuit and connection. Below is a detailed guide for the arrangement of fuses and relays in the vehicle’s central electrical panel.
- Power Distribution Unit: The main panel houses relays for critical systems like ignition, air conditioning, and power steering.
- Passenger Compartment Section: Includes circuits for accessories such as lights, radio, and HVAC controls.
- High-Powered Systems: Relays for engine cooling fans and fuel pumps are located in the primary section.
- Auxiliary Components: Separate fuses manage smaller systems like windows, wipers, and sensors.
If you encounter issues with specific functions, refer to the label that corresponds to the component you’re troubleshooting. A detailed map is often included in the manual or can be located on the cover of the panel itself.
- Always disconnect the battery before inspecting or replacing any components.
- Check the connection terminals for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Ensure the fuse amperage rating matches the specified value to avoid overloading.
For advanced repairs or wiring issues, seek professional assistance to avoid damage or further complications.
Understanding the Location of Electrical Component Panels in a 2003 Minivan
For optimal access, locate the main electrical panel inside the cabin, situated beneath the dashboard near the driver’s seat. It is often positioned on the left-hand side, near the footwell. Additionally, another key panel is found in the engine compartment, near the battery, usually along the driver’s side. Ensure to check both spots for all necessary circuits controlling interior and exterior electrical systems.
To easily identify the interior unit, inspect the lower dash area near the left knee of the driver. The engine compartment panel is typically secured with clips or screws for safe closure and access. Make sure to follow proper safety procedures when working around these components, especially when the engine is hot or the battery is active.
Identifying Common Fuse Issues and Their Solutions in 2003 Ford Windstar
Start by inspecting the electrical panel for any blown or damaged protective elements, as these typically cause loss of power to specific vehicle functions such as lighting, radio, or power windows.
Use a multimeter to test continuity across each protective device. A lack of continuity indicates a failure that requires replacement with an exact amperage rating to avoid circuit damage.
If a circuit repeatedly fails, check for underlying causes such as short circuits, corrosion on connectors, or faulty wiring harnesses. Address these faults before installing new components to prevent repeated issues.
For power distribution issues affecting multiple systems, verify the integrity of main power relays and ensure proper grounding connections, as poor grounds can mimic protective device failure symptoms.
When replacing components, always disconnect the battery to avoid electrical shorts, and consult the vehicle’s electrical reference manual to confirm correct slot placement and amperage specifications.
Routine inspection and cleaning of the panel terminals can prevent oxidation build-up that leads to intermittent electrical failures and erratic system behavior.
In cases of persistent malfunction despite component replacement, professional diagnostic tools may be required to trace complex wiring faults or module errors within the vehicle’s control network.
How to Replace Fuses in the 2003 Ford Windstar Fuse Box
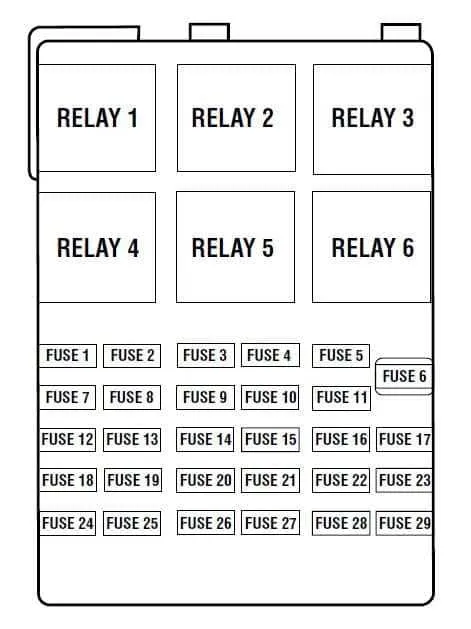
Begin by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery to avoid electrical hazards. Locate the power distribution panel beneath the dashboard or under the hood, depending on the system layout. Use the owner’s manual or service guide to identify the specific circuit protector requiring replacement.
Remove the faulty component carefully with a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to prevent damage to surrounding elements. Inspect the removed part for a broken filament or discoloration, confirming the malfunction. Replace it with an identical amperage rating to maintain proper electrical protection.
Ensure the replacement fits securely into its slot and avoid forcing the component into position, which may cause contact issues. After installation, reconnect the battery and test the affected electrical system for correct operation. If problems persist, verify the wiring and connectors for additional faults.