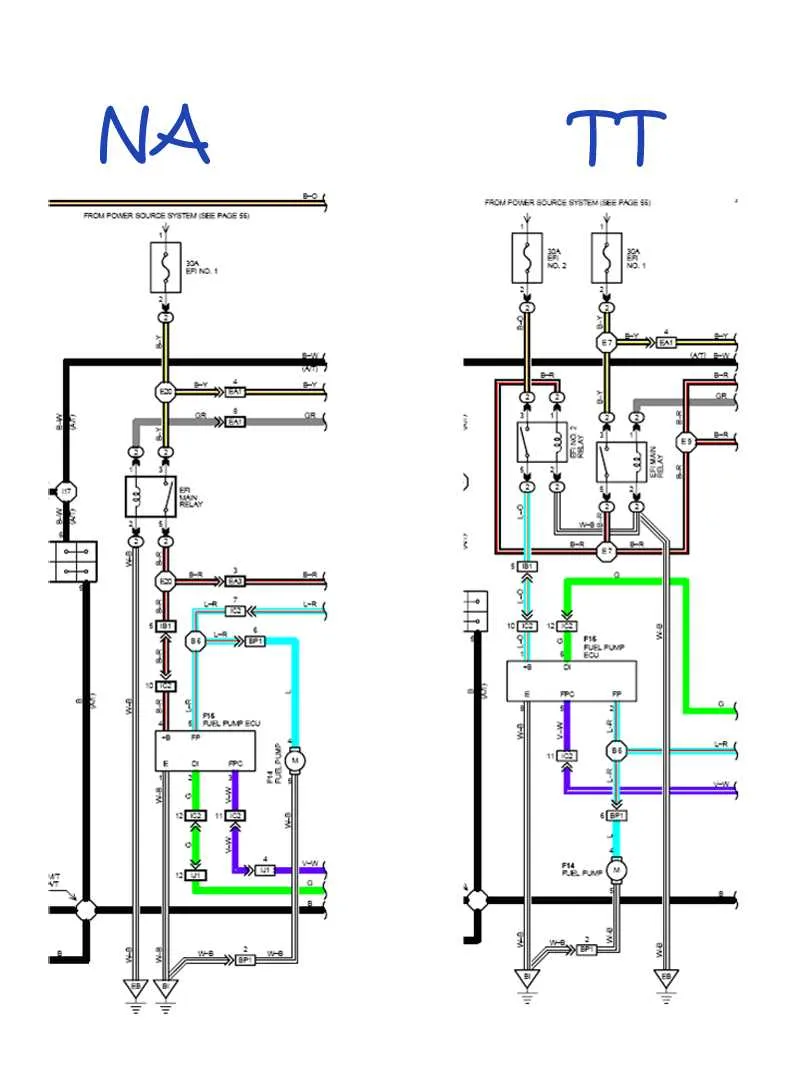
When dealing with electrical connections in your vehicle, accurate identification of wire signals is crucial for any repair or upgrade. Each wire typically corresponds to a specific function, and understanding the role of each conductor can prevent costly mistakes. For instance, red wires commonly indicate power, while black wires usually represent ground connections. Ensure you always verify the correct pairing with your vehicle’s documentation before proceeding.
For reliable results, use an automotive wiring chart or reference guide that matches your vehicle’s make and model. These resources will help you match the correct wire colors and ensure they are routed properly. For instance, blue wires often connect to accessories like lights or horn systems, while green wires may be used for sensors.
Another vital point is the consistency of color coding across different systems within the vehicle. Manufacturers tend to use a similar color scheme, but it’s always advisable to confirm through specific vehicle guides to avoid confusion. For high-risk repairs, use a multimeter to double-check voltage levels before making any permanent connections.
Never attempt to modify or repair electrical systems without proper knowledge and tools. If in doubt, consult a professional to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Understanding Electrical Circuit Color Identification for Toyota Vehicles
For effective troubleshooting and repairs, it’s crucial to recognize the standard hues associated with each wire function in Toyota’s electrical systems. Below are the main guidelines:
Red: Indicates power supply or battery connection. Often used for primary power circuits like ignition and control systems.
Black: Commonly found in ground connections. It completes the circuit by connecting various components to the vehicle’s chassis.
Green: Represents various sensors and actuators in the vehicle’s engine management or HVAC system.
Blue: Typically associated with the lighting system, including headlights and interior lights.
Yellow: Denotes circuits for safety features, such as airbags or seatbelts. Special attention should be given when working with these, as they often carry higher voltage and may be more sensitive.
White: Used for communication lines, such as data transfer between control units or sensors.
Brown: Generally used for circuits related to auxiliary functions or additional accessories like power windows or mirrors.
Gray: Usually connected to interior lighting, such as dashboard lights or ambient cabin illumination.
Each color has a specific role within the electrical layout, so using a detailed reference chart can save time and reduce the likelihood of errors. Always double-check wire functions before cutting or splicing any connections to avoid disrupting critical vehicle systems.
Understanding the Basic Toyota Wiring Color Code System
To correctly identify connections, it’s important to know the basic color pattern used for electrical systems in various Toyota models. Each hue represents a specific function or component.
- Red – Usually denotes power, commonly used for positive connections.
- Black – Typically used for ground or negative connections, ensuring a safe return path for current.
- Yellow – Often signals accessory connections, such as those linked to lights or additional features.
- Blue – Usually indicates communication or control circuits, like for sensors or data transmission.
- Green – Commonly found in systems related to safety, including airbags and related components.
- White – This color is often associated with signaling systems, including indicators and turn lights.
In addition to the primary hues, you’ll find secondary shades such as yellow/green or blue/black, which are used to provide more specific functionality within sub-circuits or multi-component setups.
- Orange – Indicates a circuit tied to heating or cooling systems.
- Brown – Frequently used in circuits related to the interior, like dashboard lights or control panels.
When troubleshooting, it’s essential to match the physical connections to their respective colors. Be sure to cross-reference these colors with vehicle-specific documentation to avoid errors.
Commonly Used Wiring Colors for Key Components
When working on automotive electrical systems, knowing the typical wire colors for key components helps to avoid confusion and errors. Below are some standard wire colors for crucial functions:
| Function | Wire Color |
|---|---|
| Battery Positive | Red |
| Ground | Black |
| Ignition | Yellow |
| Starter Motor | Green |
| Alternator | White |
| Headlights | Blue |
| Turn Signals | Light Green |
| Brake Lights | Pink |
| Fuel Pump | Brown |
| Air Conditioning | Gray |
Refer to these colors when troubleshooting or performing modifications to ensure correct connections and prevent damage to critical systems.
How to Decode and Troubleshoot Electrical Schemes
Start by identifying the wire types and their corresponding connections in the diagram. Pay attention to the thickness of the lines–these indicate different wire gauges, which can affect current capacity and resistance.
Next, match each line to its respective component. Use the component symbols provided in the chart, ensuring that each part is correctly linked. Verify the power sources and grounding points, as these are critical for troubleshooting power issues. If you encounter discrepancies, check the circuit’s continuity with a multimeter to ensure proper function.
Common issue: If a wire shows signs of wear or physical damage, it might indicate an internal break or short. Inspect each path carefully, especially at connectors or junctions. A visual inspection paired with voltage testing can help isolate where the flow is interrupted.
Cross-reference the component labels with your vehicle’s electrical manual to ensure accuracy in your diagnosis. For troubleshooting, always start from the power source and work towards the output. Use a process of elimination when faced with unclear paths, and check for any missing or incorrect connections in the system.
Remember, correct grounding is essential for proper function. Verify that all grounds are securely attached and free from corrosion. Inconsistent or improper grounding is a frequent cause of electrical malfunctions.
Tip: For high-voltage systems, wear insulated gloves and take necessary precautions to avoid electrical shocks. Always disconnect the power before working on any circuit.
If problems persist, consult a detailed repair manual specific to your vehicle’s model. It will contain precise routing and connection details that can guide you to pinpoint complex issues.