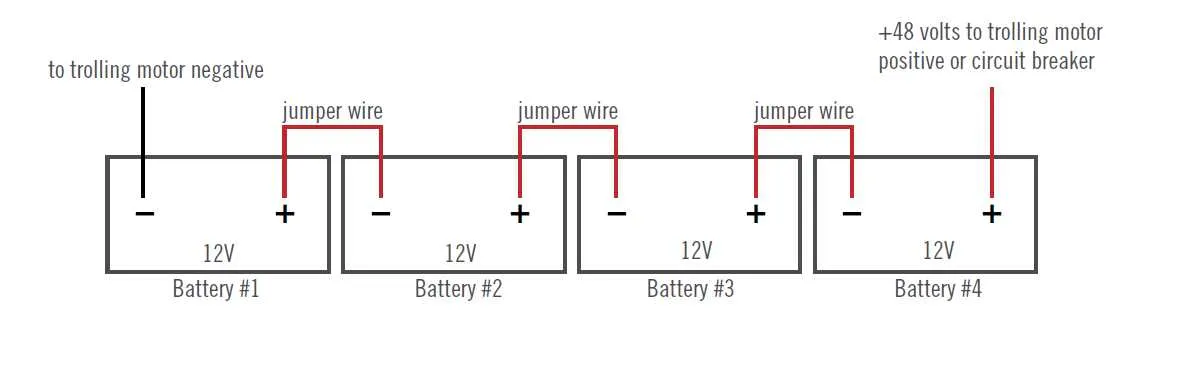
For an efficient and safe setup, ensure the correct battery connections are made to the system. Begin by choosing a suitable power source that matches the energy needs of your vessel. A pair of deep cycle batteries wired in series will provide the necessary output, delivering consistent performance over long hours of use. Each battery should be securely connected to the other, with the positive terminal of one linked to the negative of the other, allowing for an overall voltage of 24.
To charge the batteries efficiently, it’s important to select a charging unit designed for dual-battery configurations. Ensure the charger is rated for the 24V system, capable of handling the load without overcharging. Connect the charger to both batteries, observing correct polarity–positive to positive and negative to negative. This configuration guarantees balanced charging across both cells, prolonging their lifespan and ensuring reliable performance.
When running the system, double-check that all connections are tight and properly insulated. Use quality cables to minimize energy loss, and always use marine-grade components to prevent corrosion and ensure durability in harsh environments. Periodically inspect the setup to avoid any damage or wear that could compromise functionality.
24V Boat Propulsion System Setup
To ensure reliable performance, connect the 24V propulsion device directly to a dedicated 24V battery bank. Use appropriately rated cables for the current load, ensuring the connections are secure and corrosion-resistant. Consider using a 3-pin connector for seamless power distribution between the propulsion system and the battery pack.
For optimal power management, integrate a dual-channel charging unit. This allows independent charging for each of the two battery cells in your pack. Make sure the charge controller is configured to handle 24V, with an automatic switch-off feature once the batteries reach full charge to prevent overcharging.
The system should include a fuse block or circuit protection between the power source and the propulsion device, typically rated at 30-40A for safety. Ground the entire setup properly to avoid electrical interference and potential damage to sensitive components.
To enhance the longevity of the batteries, choose a high-quality charge regulator that minimizes the risk of deep discharge, which can shorten battery life. Always verify the charge rate and adjust the settings to match the battery manufacturer’s specifications.
Choosing the Right Wiring for a 24 Volt Trolling Motor System
Selecting the appropriate gauge for your electrical setup is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. For systems running on dual 12V batteries, it is essential to choose cables that can handle the current demands, typically around 30-60 amps, depending on the setup.
- Gauge Selection: Use 10 AWG or thicker for runs up to 10 feet. For longer distances, opt for 8 AWG or even 6 AWG to minimize voltage drop.
- Wire Insulation: Ensure the insulation is rated for marine environments, such as tinned copper wire with a high-quality protective coating to prevent corrosion.
- Connectors: Choose heavy-duty, marine-grade connectors that can withstand frequent exposure to water and humidity. Ring terminals are often more reliable for battery connections.
- Fuses: Install a fuse near the power source (battery) to protect the system from overcurrent. A 60-amp fuse is typically recommended for standard setups.
Remember that the quality of your components, including battery cables and connectors, plays a significant role in both performance and safety.
How to Integrate a Battery Charging System into Your Boat Setup
First, ensure the battery is of the correct type and capacity to handle continuous use while providing enough energy. Choose a unit with built-in overcharge protection to avoid damaging the battery. Install a dual-purpose switch for easy toggling between normal operation and charging mode.
Next, use marine-grade connectors to link the charging system to the battery. These connectors resist corrosion and provide a secure, watertight connection. Route the cables through the boat in a way that avoids sharp bends and ensures minimal exposure to saltwater or moisture.
Position the charging unit in a dry, ventilated area away from any heat sources. This will prevent overheating and ensure the device runs efficiently. Make sure to use proper insulation around the cables to reduce the risk of short circuits.
After installation, test the system by connecting it to a shore power supply. Check the voltage and current levels to ensure the battery charges correctly without exceeding safe limits. Always monitor the charging process, especially during the first few cycles, to confirm everything is functioning as expected.
Finally, consider adding an onboard monitoring system that tracks the battery’s charge status. This will allow for real-time checks and can help in optimizing charging times and preserving battery life over the long term.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Wires and Components for Optimal Performance
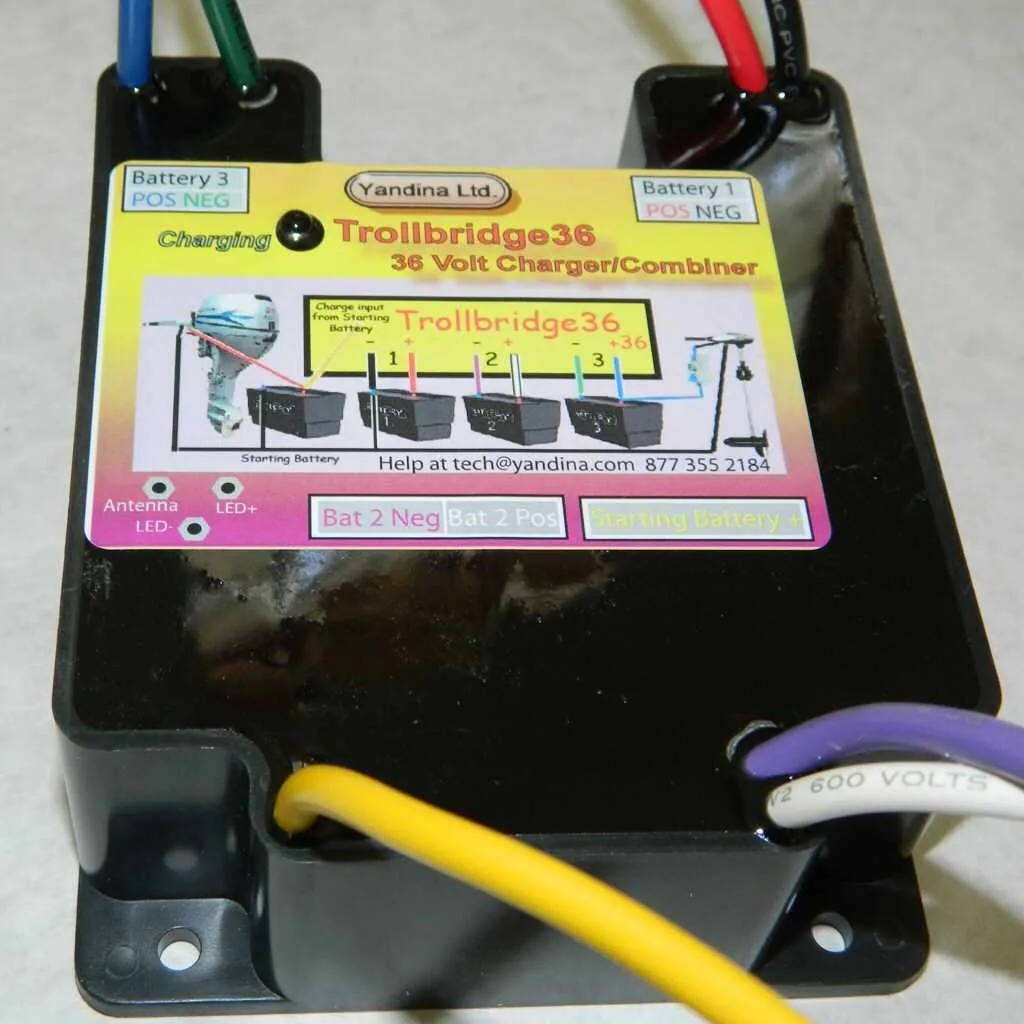

1. Begin by selecting the correct gauge wire: For a 24V system, use 10-12 AWG for the primary connections, ensuring minimal resistance and safe current flow. For smaller connections, 14-16 AWG is suitable.
2. Secure your battery connections: Use high-quality ring terminals to connect your battery leads. Ensure tight, corrosion-resistant connections to avoid voltage drops and improve efficiency.
3. Install the circuit breaker: Position the breaker close to the positive terminal of the power source. It will protect your system from overcurrent and potential damage. Make sure it’s rated for your setup’s current draw.
4. Connect the switch: Choose a reliable, waterproof toggle or rocker switch to control the system. Ensure it can handle the amperage without excessive heat buildup. Place the switch in a convenient, accessible location.
5. Use appropriate fuses: Add fuses at both the positive and negative sides of the circuit to prevent damage in case of a short circuit. Choose a fuse that matches the current rating of your setup.
6. Connect the leads to the device: Attach the leads securely to the component, ensuring a firm connection. Avoid any exposed wire to reduce the risk of short circuits.
7. Test for continuity: Before powering on, use a multimeter to check that all connections are complete and that there is no short circuit in the system. This will save time and prevent damage during operation.
8. Final inspection: Double-check the placement of all wires, making sure they are properly secured and routed away from moving parts or heat sources. Loose wires can cause wear or short circuits over time.
9. Power up the system: Once everything is connected, test the entire system to ensure it is functioning properly. Check the voltage output and verify that all components are receiving the correct amount of power.
10. Regular maintenance: Periodically inspect your setup for any loose connections, wear, or corrosion. Clean and tighten connections as needed to maintain optimal performance over time.