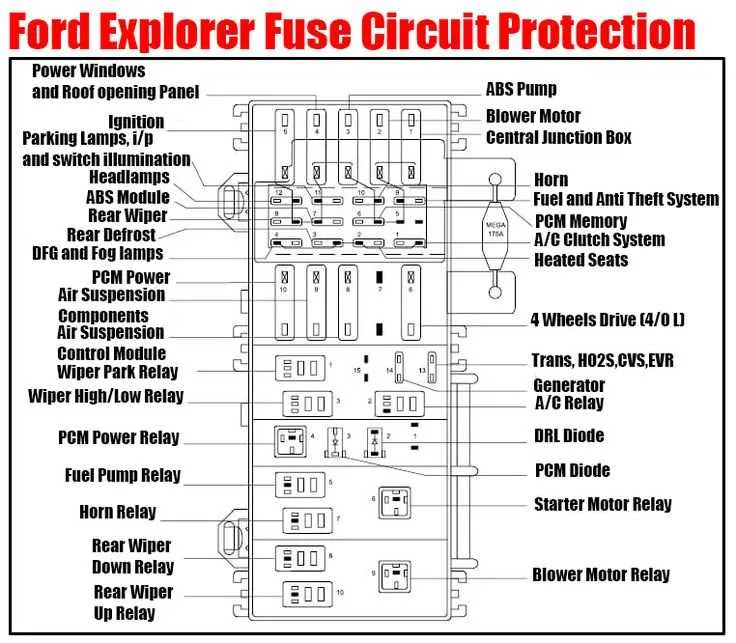
For quick troubleshooting and maintenance of your vehicle’s electrical components, it’s essential to know where the critical circuits are located. The system diagram can be your first reference when looking for specific fuses or relays. Make sure you have the owner’s manual at hand for exact positioning and function of each element.
Locate the Main Power Distribution Area. This unit, typically found under the dashboard or near the driver’s side, holds the essential power relays that control key systems like lighting, ignition, and climate control. If you’re dealing with electrical malfunctions, check these areas first.
Refer to the Labeling System for each individual fuse or relay. The correct labeling will tell you the amperage rating and the circuit it powers, helping you identify which one to replace or repair when there’s a failure in a particular system.
Electrical System Layout for 2006 Model

If you’re experiencing electrical issues in your vehicle, it’s crucial to know the placement of key components. The primary unit for managing circuits is located inside the cabin and engine compartment. Refer to the detailed chart to identify the exact positioning of each relay and connection, ensuring proper diagnostics and replacements when necessary.
The main section, found near the driver’s side dashboard, handles critical functions such as lighting, radio, and climate control. A secondary cluster near the engine manages the powertrain and auxiliary systems, including airbags and ignition. Make sure to follow the specifications for fuse ratings to avoid damage to any connected systems.
Key Recommendations:
- Check the connections regularly to avoid circuit damage.
- Ensure correct amperage when replacing any component to prevent short-circuits.
- Use labeled diagrams as a reference for quick troubleshooting.
It is advisable to replace any blown components immediately to prevent electrical malfunctions that could lead to more severe issues down the line. Consult the layout chart for a clear visual guide on where each element is located.
Understanding the Main Electrical Panel Locations and Layout
The primary electrical panel in your vehicle is crucial for controlling various electrical components. It is usually located in two main spots: under the dashboard and within the engine compartment. The interior panel is typically found on the driver’s side, either beneath the steering wheel or near the kick panel. The second panel is commonly placed near the battery under the hood, often beside the engine block for easy access. These areas are where you’ll find the individual relays and components connected to critical systems like the lights, ignition, and air conditioning.
Interior Electrical Unit – This is typically located beneath the dashboard or to the left side of the driver’s footwell. It houses the circuits for cabin electronics such as radio, power windows, and interior lights. To access, remove the panel cover, and you’ll find the layout clearly marked for each relay and fuse. A detailed map inside the cover will help identify the right component quickly when troubleshooting.
Engine Bay Electrical Unit – Positioned close to the engine, this panel is designed for circuits linked to the engine, alternator, and other high-power components. The cover is often labeled with specific identifiers for each circuit. To access this unit, you’ll likely need to remove a few securing clips or bolts that hold the panel cover in place. Once open, each fuse and relay will be labeled, simplifying any maintenance tasks.
Both locations play an essential role in the proper functioning of the vehicle’s electrical system. Regular inspection of these panels ensures that all components are in working order and any issues are addressed promptly.
How to Identify and Replace Faulty Fuses in Your Vehicle
Start by turning off the ignition and ensuring the vehicle’s electrical system is not powered. Locate the main electrical panel, which is typically under the dashboard or near the engine. Inside, you will find individual components protected by small metal strips.
To identify a blown element, visually inspect the thin metal wire inside the component. If it is broken or burnt, it needs to be replaced. For a more precise check, use a multimeter to measure continuity across the component. No reading indicates the part is faulty.
When replacing a damaged item, always select a new one with the same current rating and specifications. Using a part with a higher or lower rating could lead to electrical malfunctions or potential damage to your vehicle’s wiring system.
| Component | Common Cause of Failure | Replacement Type |
|---|---|---|
| Headlights | Excessive current draw | Standard 15A replacement |
| Radio | Sudden voltage surge | Standard 10A replacement |
| Power Windows | Short circuit | Standard 20A replacement |
After replacing the component, ensure it is securely seated. If you continue to experience issues, inspect the wiring for potential short circuits or damaged connections. Once everything is restored, test the electrical components before closing the panel.
Common Electrical Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Fuse Panel Problems
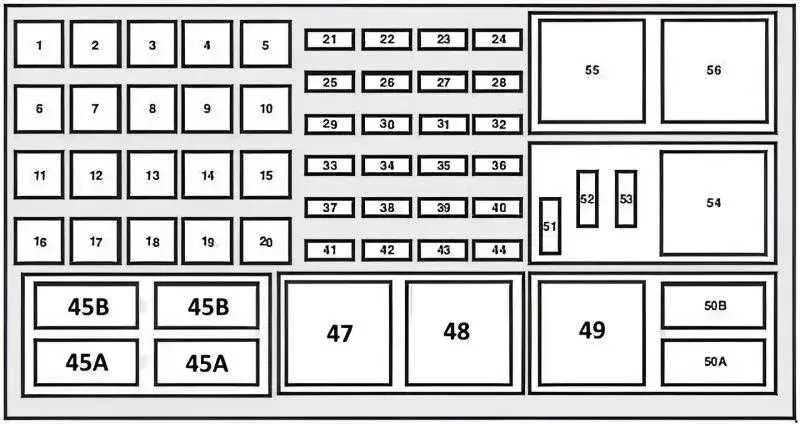
When dealing with electrical malfunctions in your vehicle, the primary step is to locate the source of the issue. Below are some of the most common problems and the troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Blown Circuit Protection Devices: One of the most frequent causes of electrical failure. If you experience a sudden loss of power to specific components, inspect the protective units for damage or wear. Replacing a damaged unit often resolves the issue.
- Corroded Contacts: Over time, moisture and dirt can cause corrosion on the contacts. This may prevent proper power flow to certain systems. Clean the terminals with a non-abrasive cleaner or use a corrosion-resistant spray to restore function.
- Loose or Faulty Connections: A common culprit for intermittent electrical problems. Check all connectors for tightness, especially the ones attached to the power distribution system. Loose connections can result in malfunctioning components.
- Short Circuits: If you notice unexpected electrical issues, a short circuit might be the cause. Inspect the wires and connectors for signs of wear or exposed wires. Replace damaged wires to prevent further damage.
- Power Surges: Power surges often occur when there is a sudden spike in electrical load. This can damage internal components. Using a surge protector or replacing faulty electrical components may resolve the issue.
- Overloaded System: Too many devices running off a single circuit can overload the system. Ensure that the electrical load is evenly distributed across circuits and avoid running too many devices from a single power source.
For quick diagnostics, use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at various points in the circuit. Replace any worn or damaged components, and remember that regular maintenance is key to avoiding future issues.