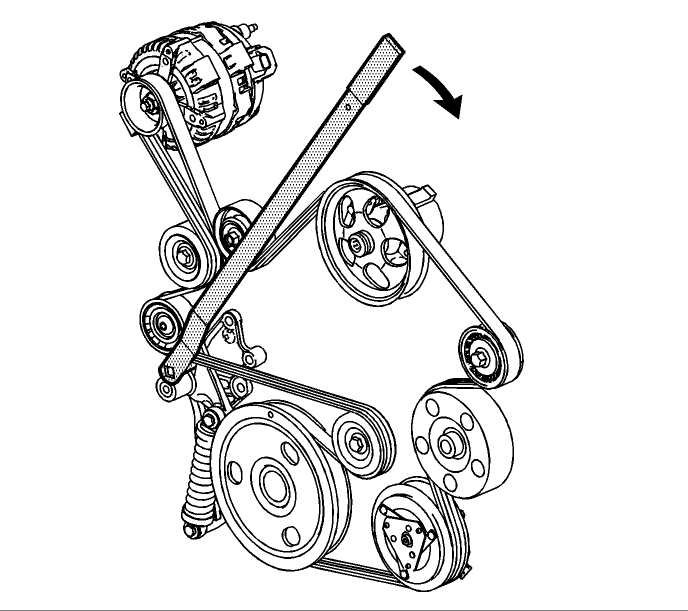
The 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 Belt Diagram is an essential tool for anyone working on their Pontiac Grand Prix’s engine. This diagram visually illustrates the routing of the engine’s belts, including the serpentine belt and the accessory drive belt. With this diagram, you can easily identify and understand the correct placement of each belt, ensuring that your engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
For those unfamiliar with the Pontiac Grand Prix’s engine layout, the serpentine belt is responsible for powering various components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The accessory drive belt, on the other hand, powers additional components, such as the water pump and the air conditioner compressor. Understanding the routing of these belts is crucial, as improper placement can lead to inefficiency and potential damage to the engine.
The 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 Belt Diagram is especially beneficial for DIY enthusiasts who prefer to work on their own vehicles. By having a clear visual representation of the belt routing, you can save time and avoid frustration when replacing or adjusting the belts. Additionally, this diagram can serve as a helpful reference for professional mechanics who may encounter Pontiac Grand Prix models regularly.
Overall, the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 Belt Diagram is an invaluable resource for anyone working on this particular model of car. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, this diagram provides an easy-to-understand visual guide for proper belt placement, ensuring that your engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Overview of the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 Belt Diagram
The 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 is a popular car model known for its powerful performance and sleek design. One important aspect of maintaining this vehicle is to understand the belt diagram, as it plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of various components.
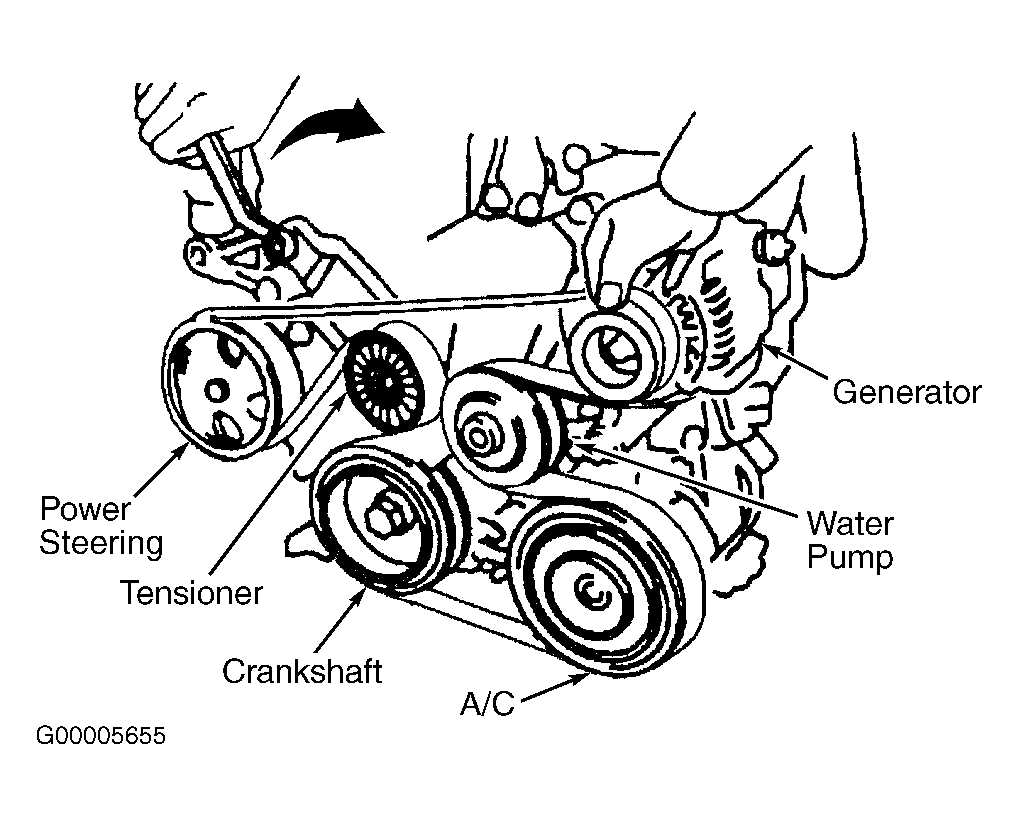
The belt diagram for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 showcases the routing of the accessory drive belt, which is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the various accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Having a clear understanding of the belt diagram helps in identifying the correct routing and tension for optimal performance.
Components and Routing
The belt diagram for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 consists of various components, including the crankshaft pulley, power steering pulley, tensioner pulley, idler pulley, and various accessories pulleys. The belt wraps around these pulleys in a specific pattern to ensure efficient power distribution.
The correct routing of the belt is crucial to avoid any slippage or improper functioning of the accessories. It is essential to follow the specified diagram, which is typically found in the owner’s manual or a diagram sticker located in the engine compartment.
Belt Tensioning
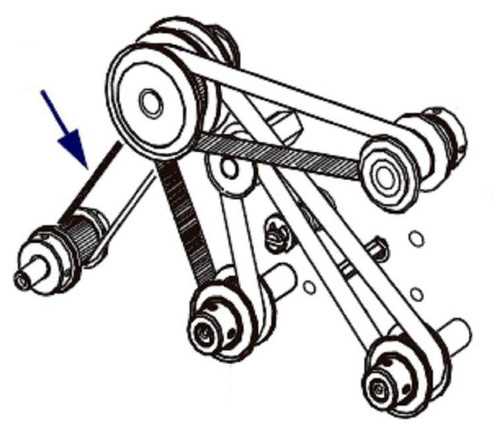
In addition to understanding the routing, proper belt tensioning is also critical. The tensioner pulley ensures that the belt is tensioned correctly, preventing any slack or excessive tightness. Tensioning the belt properly not only ensures optimal performance but also extends the lifespan of the belt and related components.
If the belt is too loose, it may slip, leading to a loss of power in the accessories or even belt failure. On the other hand, if the belt is too tight, it can put excess strain on the pulleys and accessories, leading to premature wear and possible damage.
Maintenance and Replacement

Regular inspection and maintenance of the belt are necessary to ensure its proper functioning. Over time, belts can become worn, cracked, or damaged, and they should be replaced promptly to prevent any issues or failures.
When replacing the belt, it is essential to consult the belt diagram and follow the correct routing and tensioning procedures. This helps in ensuring that the new belt is installed correctly and will provide reliable performance.
In conclusion, understanding the belt diagram for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 is essential for proper maintenance and performance of the vehicle. Following the correct routing and tensioning procedures helps in avoiding issues and prolonging the lifespan of the belt and related components.
Understanding the Belt Diagram System
The belt diagram system in a 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 plays a crucial role in the operation of various components in the vehicle. It is important to understand how this system works in order to properly maintain and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
The belt diagram:
The belt diagram illustrates the routing of the serpentine belt, which is responsible for driving multiple components such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. It shows the path the belt takes around each pulley and helps ensure proper alignment and tension. The diagram is usually located on a decal under the hood of the vehicle, providing a visual reference for belt replacement.
Belt tensioner:
The belt tensioner is a vital component of the belt diagram system. Its purpose is to maintain the proper tension on the serpentine belt, ensuring proper operation of the driven components. It is designed to automatically adjust the tension as the belt wears and stretches over time. If the belt tensioner becomes faulty or fails, it can result in a loose or improperly tensioned belt, leading to reduced performance or complete failure of the affected components.
Maintenance and troubleshooting:
Regular maintenance and inspection of the belt diagram system is essential to ensure its proper operation and prevent unexpected failures. This includes checking the belt tension, alignment, and condition on a regular basis. Signs of a worn or damaged belt may include squeaking or squealing noises, visible cracks or fraying on the belt, or excessive wear on the pulleys.
If any issues are identified, such as a loose or misaligned belt, it is important to refer to the belt diagram and follow the correct routing to rectify the problem. Additionally, if the belt tensioner is suspected to be faulty, it should be inspected and replaced if necessary to ensure proper tension is maintained.
Understanding and following the belt diagram system in a 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 is crucial for maintaining the proper operation of its various components. By regularly inspecting and maintaining the belt tension, alignment, and condition, drivers can help prevent unexpected failures and ensure the longevity of their vehicle.
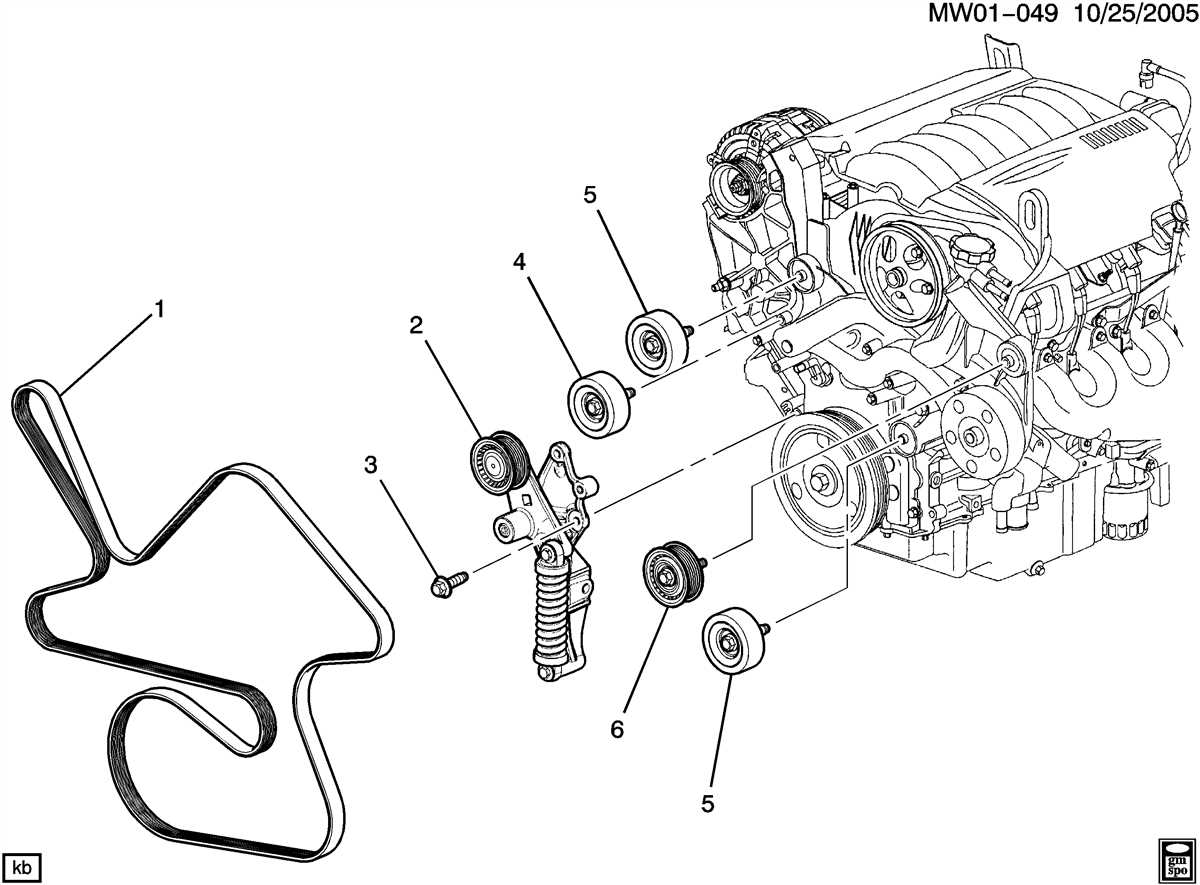
Components of the Belt Diagram
The belt diagram for a 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 engine represents the routing and arrangement of the various belts that are responsible for driving multiple components of the engine and other systems. It is important to understand the components of the belt diagram in order to properly maintain and replace the belts when necessary.
1. Crankshaft Pulley: The crankshaft pulley is connected directly to the engine’s crankshaft. It is responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the other components of the engine. The crankshaft pulley is typically the largest pulley in the belt diagram.
2. Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley is designed to maintain proper tension on the belts as they rotate. It is usually spring-loaded and applies tension to the belts to prevent slippage and ensure efficient power transfer. The tensioner pulley is often located near the center of the belt diagram.
3. Idler Pulleys: Idler pulleys are additional pulleys that help guide the belts and maintain tension. They are typically used in situations where the belts need to change direction or wrap around multiple components. Idler pulleys can be found at various points throughout the belt diagram.
4. Alternator: The alternator is responsible for generating electrical power and recharging the battery while the engine is running. It is connected to the belt system and is driven by the engine’s rotation. The alternator is usually located near the top of the engine, and its pulley can be seen in the belt diagram.
5. Power Steering Pump: The power steering pump assists in turning the wheels by providing hydraulic pressure to the power steering system. It is connected to the belt system and driven by the engine. The power steering pump can be found on the front of the engine, and its pulley is represented in the belt diagram.
6. Air Conditioning Compressor: The air conditioning compressor is responsible for cooling and dehumidifying the air inside the vehicle. It is connected to the belt system and driven by the engine’s rotation. The air conditioning compressor is typically located near the bottom of the engine, and its pulley can be seen in the belt diagram.
In summary, the belt diagram for a 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 engine includes components such as the crankshaft pulley, tensioner pulley, idler pulleys, alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Understanding the function and location of these components is crucial for properly maintaining and replacing the belts in the engine system.
Belt Routing for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8
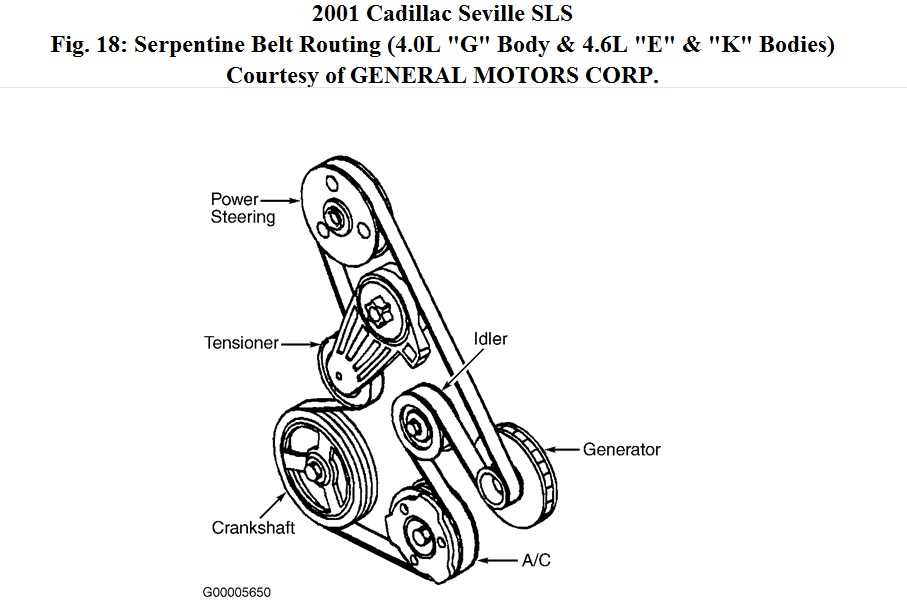
When it comes to keeping your 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 running smoothly, knowing the correct belt routing is essential. The belt routing diagram shows you the path that the serpentine belt takes as it drives various components in your engine. By following this diagram, you can properly install a new belt or troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing.
The 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 has a single serpentine belt that drives several important components, including the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. To ensure proper belt tension and functionality, it is important to follow the recommended belt routing as specified by the manufacturer.
Here is the belt routing diagram for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8:
| Belt Routing Diagram: |
|---|
 |
When installing a new belt, it is important to note the correct path that the belt should follow. Start by locating the different components that the belt needs to connect to, such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. Then, carefully thread the belt around these components according to the belt routing diagram.
Once the belt is installed, double-check that it is properly seated on each pulley and that there is sufficient tension. A properly tensioned belt should have about 1/2 inch of deflection when pressed firmly on its longest span.
By following the correct belt routing for your 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8, you can ensure that your engine’s components are functioning properly and avoid any belt-related issues. If you have any doubts or questions, consult the vehicle’s manual or seek assistance from a professional mechanic.
Common Belt Problems and Solutions
Belts are an essential component of a vehicle’s engine system, responsible for driving various components such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. However, belts can experience problems over time, leading to performance issues and even potential damage to the engine. Here are some common belt problems and their solutions:
1. Squeaking or squealing noise: If you hear a high-pitched noise coming from the engine, it could indicate a loose or worn-out belt. A loose belt can be tightened by adjusting the tensioner, while a worn-out belt should be replaced.
2. Cracks or fraying: Over time, belts can develop cracks or fraying due to wear and tear. It is important to regularly inspect the belts for any signs of damage and replace them if necessary. Cracked or fraying belts are more likely to break, leading to vehicle breakdown.
3. Belt slippage: A slipping belt can result in poor performance of the driven components, such as the alternator not charging the battery effectively. This can be caused by a lack of tension or contamination by oil or coolant. Adjusting the tension or cleaning the belt and pulleys can resolve the issue.
4. Improper alignment: Belts should be properly aligned with the pulleys to ensure efficient power transfer. Misalignment can cause excessive wear on the belt and pulleys, leading to premature failure. Adjusting the belt alignment or replacing any misaligned pulleys can solve this problem.
5. Belt coming off: In some cases, a belt may come off due to a damaged tensioner or pulley, improper installation, or excessive belt wear. When a belt comes off, the driven components will stop working. It is important to identify the cause and address it promptly to prevent further damage.
6. Regular maintenance: To prevent belt problems, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. This includes regular belt inspection, checking for proper tension, and replacing belts when they show signs of wear or damage.
By addressing these common belt problems and ensuring proper maintenance, vehicle owners can prolong the life of their belts and maintain optimal engine performance. Regular inspections and proactive measures can save time and money by preventing costly repairs and breakdowns.
Maintenance Tips for the 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 Belt Diagram
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring that your 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8 runs smoothly and efficiently. One of the key components of your vehicle’s engine system is the belt diagram, which helps to route the serpentine belt correctly. Here are some maintenance tips to keep in mind when it comes to the belt diagram:
1. Regular Inspection
It is important to regularly inspect the belt diagram for any signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. A damaged belt can lead to engine overheating, a loss of power steering, and other issues. If you notice any signs of damage, it is recommended to replace the belt as soon as possible.
2. Belt Tension
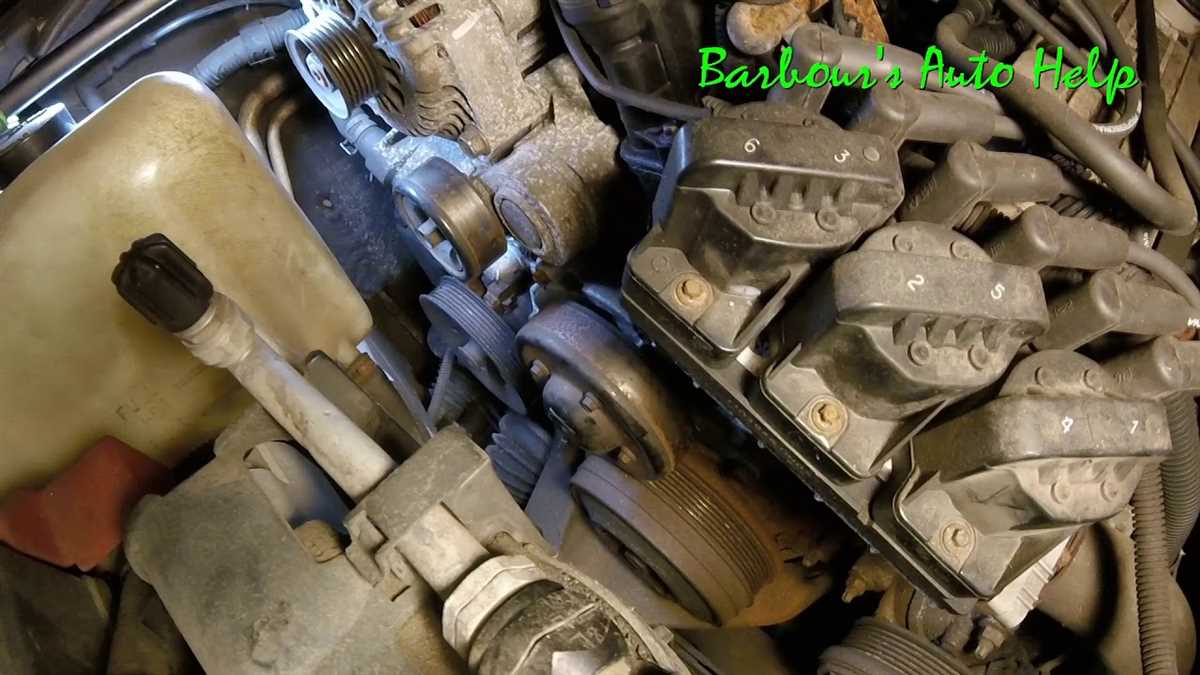

Check the tension of the belt regularly to ensure it is properly tightened. A loose belt can cause slippage and reduced efficiency, while an overtightened belt can put strain on the system and lead to premature wear. Refer to the belt diagram for the proper tension specifications.
3. Belt Alignment
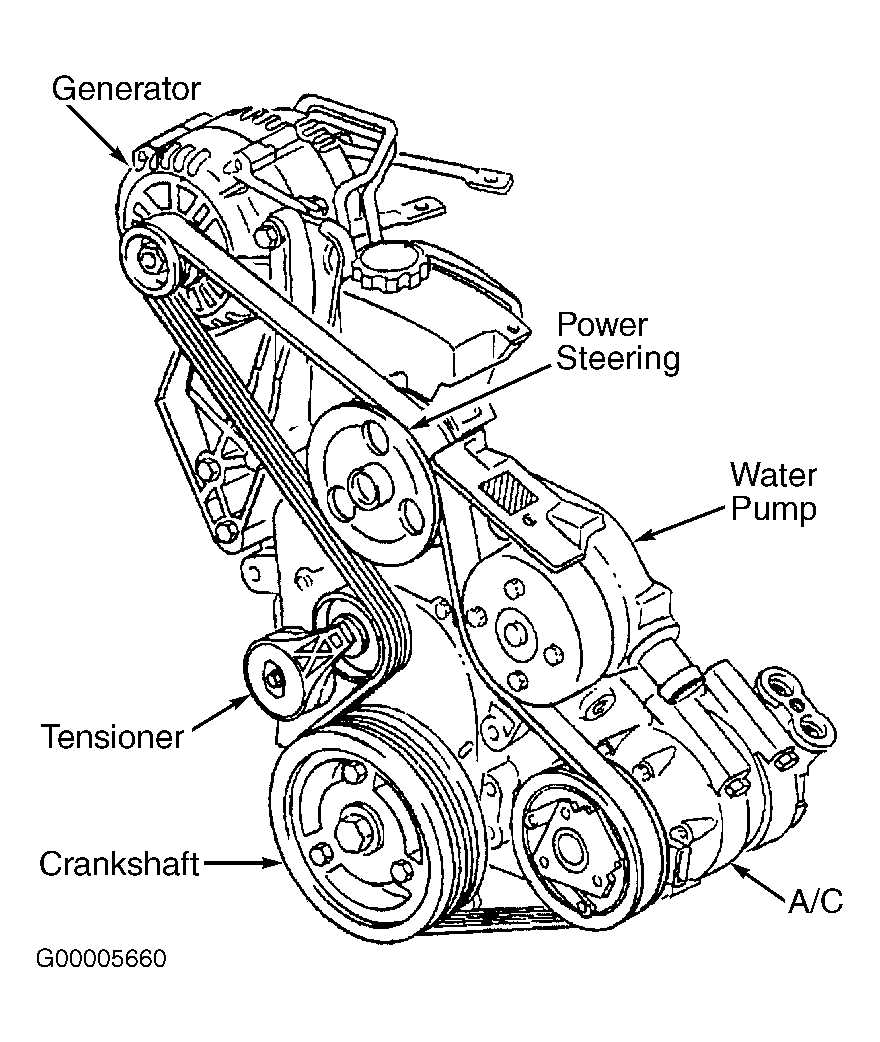
Make sure the belt is properly aligned on all the pulleys according to the diagram. Misalignment can cause excessive wear, noise, and even damage to the belt and other engine components. If you notice any misalignment, adjust it accordingly or consult a professional mechanic.
4. Belt Replacement
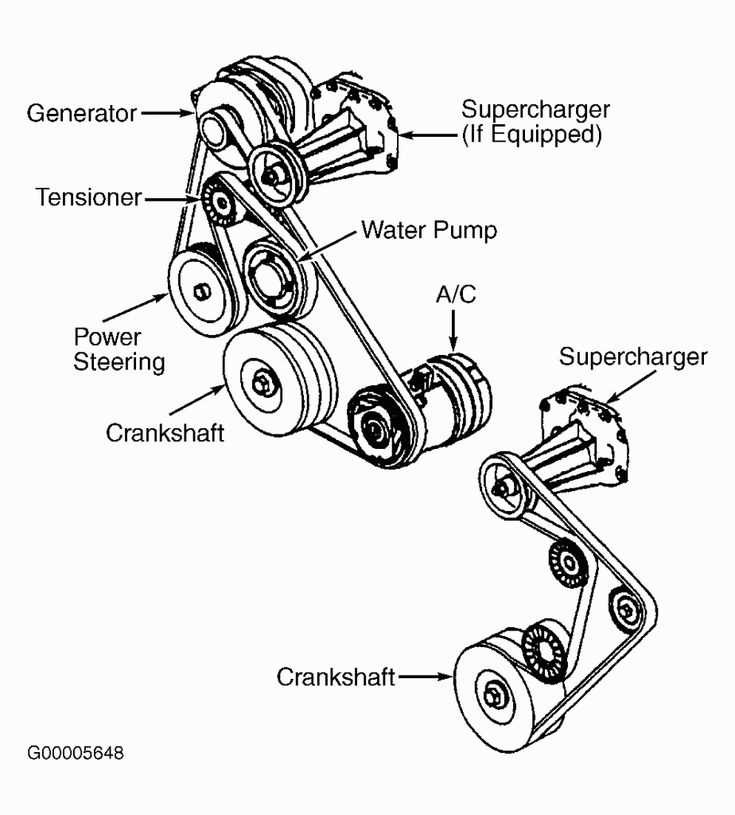
It is recommended to replace the belt at regular intervals, usually every 60,000 to 100,000 miles or as stated in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. Even if the belt appears to be in good condition, it can still deteriorate over time due to heat, friction, and age.
By following these maintenance tips and regularly inspecting and replacing the belt according to the diagram, you can help ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your 2007 Pontiac Grand Prix 3.8.