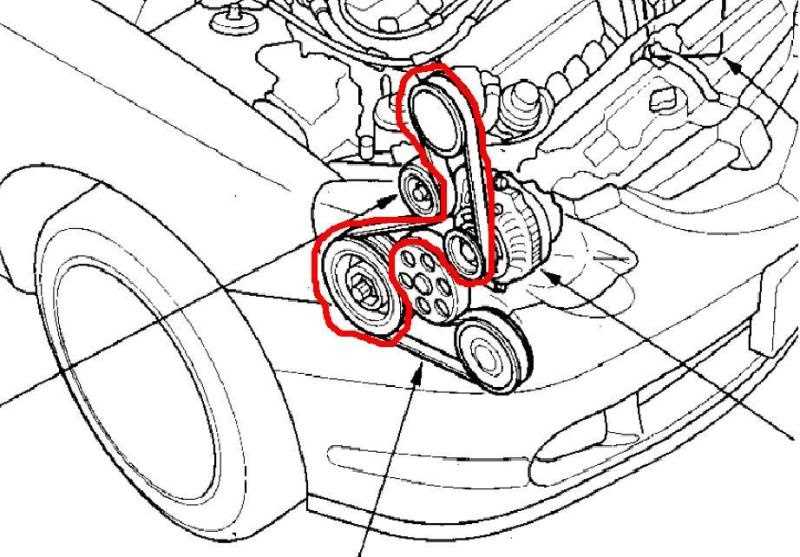
If you own a 2008 Honda Pilot and are looking for a diagram of the belt system, you’ve come to the right place. The belt diagram is essential for understanding how the various components in the engine are connected and how they work together to power your vehicle.
The 2008 Honda Pilot is equipped with a 3.5-liter V6 engine, and it has a serpentine belt that drives multiple accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The belt diagram shows the order in which the belt wraps around each pulley and how it is properly tensioned.
Having a belt diagram on hand can be helpful when performing maintenance or repairs on your vehicle. It can guide you in properly routing the belt and ensuring that it is tensioned correctly to prevent slipping or damage to the accessories it drives. This diagram can also be useful if you need to replace the belt and want to ensure that you install the new one correctly.
Overall, having a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 belt diagram can make it easier to understand the layout and operation of the belt system in your vehicle. It can be a valuable resource for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics, helping to ensure that the belt is installed and tensioned correctly for optimal performance and durability.
2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 Belt Diagram
When it comes to the 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5, having a belt diagram can be extremely helpful for maintenance and repairs. The belt diagram shows the routing of the serpentine belt, which powers various engine components such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. By understanding the belt diagram, you can easily identify the correct belt size and ensure proper installation.
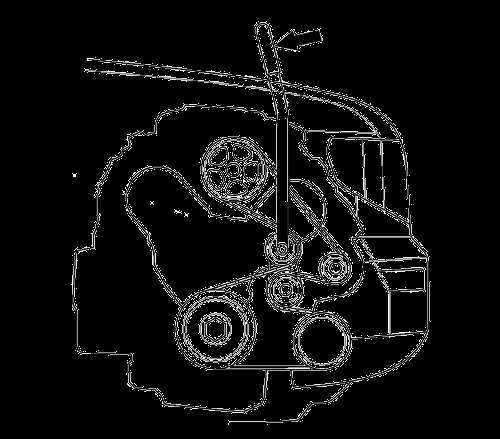
The belt diagram for the 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 is as follows:
- The serpentine belt starts at the crankshaft pulley and wraps around the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor pulleys.
- From the air conditioning compressor pulley, the belt turns towards the tensioner pulley.
- After going around the tensioner pulley, the belt loops back to the crankshaft pulley.
It’s important to note that the belt diagram may vary depending on the specific configuration of your vehicle. Therefore, it’s always recommended to consult the owner’s manual or a reliable source for the accurate belt diagram for your 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5. Additionally, make sure to inspect the belt regularly for signs of wear or damage, and replace it if necessary to avoid any potential issues or breakdowns.
Importance of the Belt Diagram
When it comes to the proper functioning of a vehicle, the belt diagram plays a crucial role. The belt diagram is a visual representation of the routing and configuration of the belts in a vehicle’s engine. It shows the placement of each belt and how they connect various components such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Having a clear and accurate belt diagram is essential for proper belt installation and maintenance.
The belt diagram provides valuable information for mechanics and car owners alike. It helps to ensure that the right belts are being used and properly installed, preventing any potential damage or malfunction. By following the belt diagram, mechanics can easily identify the correct routing of the belts, ensuring that they are properly aligned and tensioned. This is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the belts and the components they connect.
The belt diagram also serves as a reference for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes. If a belt breaks or starts making unusual noises, consulting the belt diagram can help identify the cause of the issue. It allows mechanics and car owners to pinpoint any potential misalignment, excessive wear, or other problems that may be affecting the belts or the components they power. With the help of the belt diagram, it becomes easier to diagnose and resolve any belt-related issues.
Overall, the belt diagram is an invaluable resource for ensuring the proper functioning of a vehicle’s engine. It provides essential information for belt installation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and overall system performance. Whether you are a mechanic or a car owner, having access to a clear and accurate belt diagram is essential for keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding the Belt Routing
The belt routing in a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 refers to the configuration and path that the engine belts take in order to operate various components of the vehicle. It is crucial to understand the belt routing in order to properly maintain and repair the belts in the engine.
The belt routing in a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 consists of several components:
- Drive Belt: The drive belt, also known as the serpentine belt, is responsible for powering multiple engine accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, and water pump. It follows a specific path around various pulleys to ensure efficient power transfer.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley is a component that helps to maintain tension on the drive belt. It automatically adjusts the tension of the belt to ensure proper function and prevent slippage.
- Idler Pulleys: The idler pulleys are additional pulleys that help guide and support the drive belt. They assist in maintaining the correct alignment and tension of the belt as it moves through the engine.
It is important to consult the belt routing diagram for the 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 to ensure proper installation and alignment of the belts:
| Component | Path |
|---|---|
| Drive Belt | Starts at the crankshaft pulley, wraps around the various engine accessories, and ends at the tensioner pulley. |
| Tensioner Pulley | Located near the drive belt, it maintains tension by applying pressure to the belt. |
| Idler Pulleys | Positioned strategically along the belt path to guide and support the drive belt. |
Proper understanding of the belt routing is essential for maintenance and repair tasks, such as:
- Replacing a worn or damaged drive belt
- Adjusting the tensioner pulley for optimal performance
- Inspecting the idler pulleys for wear or misalignment
In conclusion, the belt routing in a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 is a critical aspect of the engine’s operation. Understanding the path and components involved is necessary for maintaining and repairing the belts, ensuring proper power transfer and overall vehicle performance.
Components Connected by the Belt
The belt in a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 is an integral part of the engine’s operation, connecting several components to ensure their proper function. These components work together to power various systems in the vehicle and contribute to its overall performance.
1. Alternator:
The alternator is responsible for generating electrical power to charge the battery and operate the electrical systems in the vehicle. It is connected to the engine by the belt, which drives the alternator pulley and allows it to rotate.
2. Power Steering Pump:
The power steering pump helps in easing the effort required to steer the vehicle by providing hydraulic assistance. It is also connected to the belt, which enables it to turn and pump the power steering fluid, helping to make steering smoother and more manageable.
3. Air Conditioning Compressor:
The air conditioning compressor is responsible for compressing and circulating the refrigerant in the AC system, enabling the cooling of the cabin. The belt drives the compressor, allowing it to function and provide the desired cooling effect.
4. Water Pump:
The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine, helping to regulate its temperature. It is connected to the belt, which drives the pump pulley and enables it to pump the coolant and maintain optimum engine temperature.
5. Crankshaft Pulley:
The crankshaft pulley is an essential component of the engine, as it is directly connected to the crankshaft and helps convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion. The belt drives the crankshaft pulley, allowing it to rotate and power other components connected to it.
6. Tensioner Pulley:
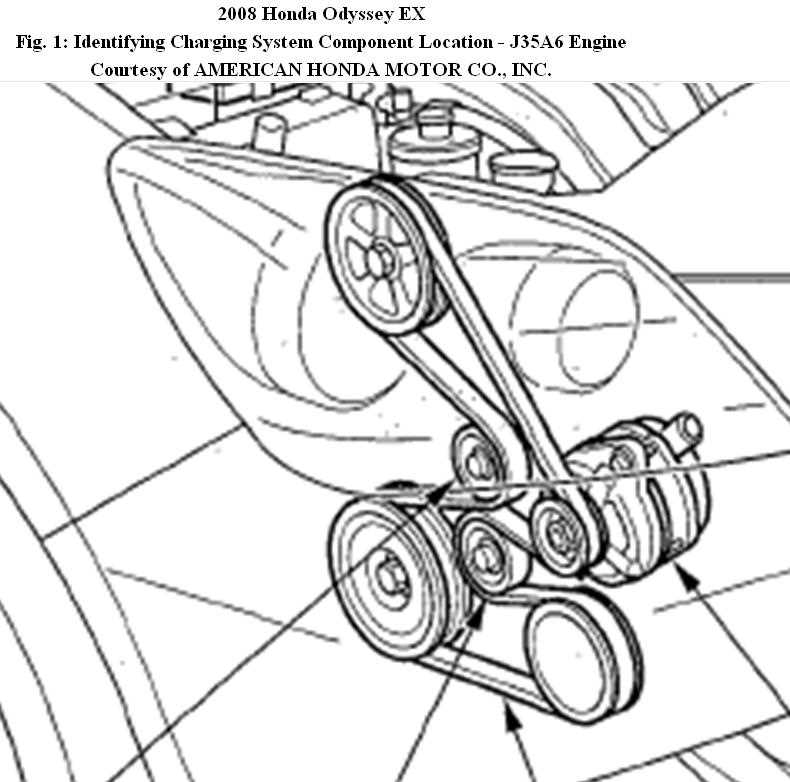
The tensioner pulley is responsible for maintaining proper tension on the belt, ensuring that it stays in place and drives the various components without slipping. It helps to prevent belt slippage and ensures efficient power transfer to the connected components.
In conclusion, the belt in a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 connects several vital components of the engine, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, water pump, crankshaft pulley, and tensioner pulley. These components work together to power electrical systems, facilitate steering, provide cooling, maintain engine temperature, and convert piston motion into rotary motion. The belt plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of these components and maximizing the overall performance of the vehicle.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replace the Belt
Replacing the belt on a 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5 requires a few simple steps. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you replace the belt.
Step 1: Prepare the Vehicle
Before starting the replacement process, you need to ensure that the vehicle is properly prepared. This includes turning off the engine and lifting the hood. It is also a good idea to disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent any accidental electrical discharge.
Step 2: Locate and Review the Belt Routing Diagram
Next, locate the belt routing diagram. This diagram can typically be found on a sticker in the engine compartment or in the vehicle’s owner’s manual. Review the diagram to understand the correct path and placement of the belt.
Step 3: Loosen the Belt Tensioner
The next step involves loosening the belt tensioner. Use a socket wrench to rotate the tensioner pulley in the direction specified on the belt routing diagram. This will release the tension on the belt, making it easier to remove.
Step 4: Remove the Old Belt
With the tension released, carefully remove the old belt from the pulleys. Take note of the path and orientation of the belt as you remove it, as this will help you when installing the new belt.
Step 5: Install the New Belt
Take the new belt and follow the routing diagram to ensure the correct placement. Begin by positioning the new belt on the pulleys, making sure it is aligned properly. Use the tensioner pulley to create tension on the new belt. Rotate the tensioner pulley in the opposite direction as before, allowing the belt to be securely tightened.
Step 6: Double-Check the Belt Placement
Once the new belt is installed, double-check the placement to ensure it is correctly aligned on all the pulleys. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure proper alignment.
Step 7: Reconnect the Battery and Test
After confirming that the belt is properly installed, reconnect the negative terminal of the battery. Close the hood and start the engine to test the new belt. Listen for any unusual noises or vibrations, and visually inspect the belt to ensure it is running smoothly.
By following these simple steps and using the belt routing diagram as a guide, you can easily replace the belt on your 2008 Honda Pilot 3.5.
Troubleshooting Common Belt Problems
Belts are an essential component of a vehicle’s engine system, helping to drive various systems such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. However, like any other mechanical part, belts can develop problems over time. This article will discuss some common belt-related issues and how to troubleshoot them.
1. Belt Squealing

If you hear a loud squealing noise coming from the engine area, it is likely due to a loose or worn-out belt. One possible cause is belt tension. Over time, belts can become loose, causing them to slip and produce a high-pitched squealing sound. To troubleshoot this problem, check the belt tension and tighten or replace the belt if necessary. Another cause of belt squealing is a worn-out or damaged belt. Inspect the belt for signs of wear, such as cracks or fraying, and replace it if needed.
2. Belt Slippage

When a belt slips, it fails to provide adequate power to the driven components, which can result in poor performance or complete failure of those systems. Belt slippage can be caused by insufficient belt tension, a misaligned pulley, or a worn-out belt. To troubleshoot this issue, check the belt tension and adjust it if necessary. Additionally, inspect the pulleys to ensure they are properly aligned. If the belt shows signs of wear, replace it with a new one.
3. Belt Misalignment
Belt misalignment can occur when the pulleys are not properly aligned or when a component is loose or worn. This can cause the belt to rub against other engine parts, resulting in excessive wear and noise. To troubleshoot this problem, visually inspect the pulleys to ensure they are aligned correctly. Tighten any loose components and replace any worn-out parts. Additionally, make sure all mounting bolts are securely fastened.
4. Belt Breakage
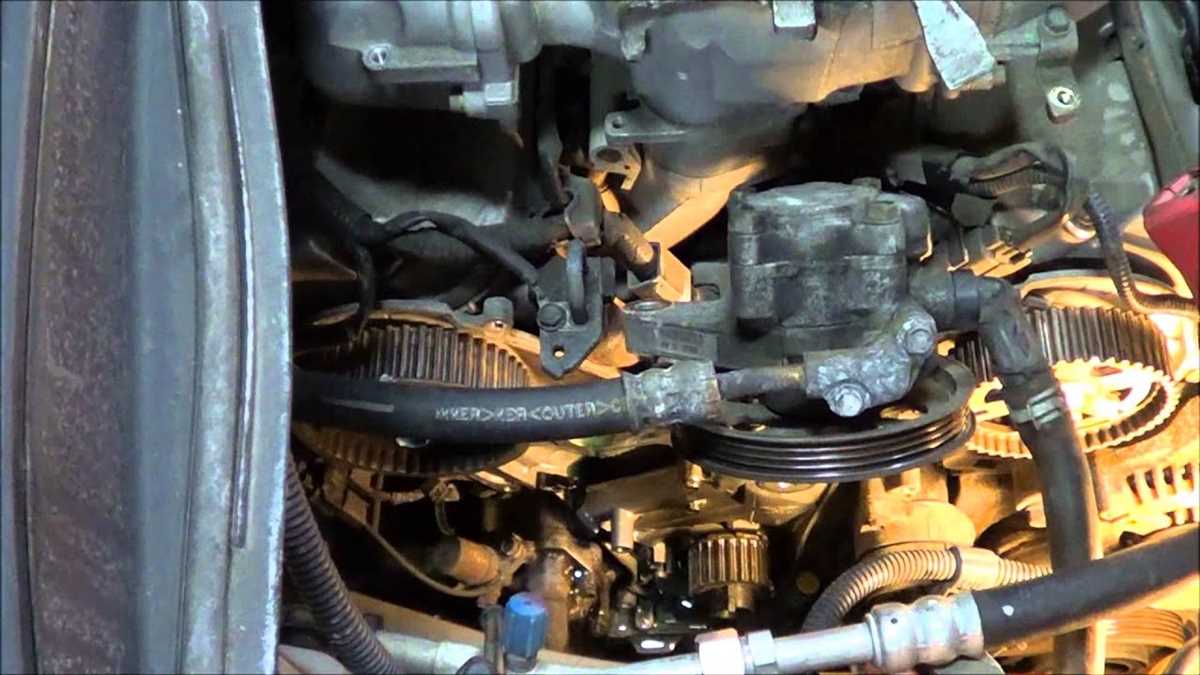

If a belt breaks, it can lead to the complete failure of the driven systems. Belt breakage can be caused by excessive wear, improper tension, or a misaligned pulley. To troubleshoot this issue, inspect the belt for signs of wear and replace it if necessary. Check the belt tension and adjust it accordingly. Make sure all pulleys are properly aligned and replace any damaged or misaligned pulleys.
In conclusion, troubleshooting common belt problems involves inspecting the belt tension, checking for signs of wear or damage, inspecting pulley alignment, and replacing any worn-out or damaged components. Regular maintenance and inspection of belts can help prevent these issues and ensure the proper functioning of the engine systems.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Belt Lifespan
Regular maintenance and care can significantly extend the lifespan of your Honda Pilot’s belts. Here are some tips to help you keep your belts in good condition:
- Inspect the belts regularly: Check the condition of the belts visually to identify any signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or stretching. Replace any damaged belts immediately to prevent further damage.
- Tighten the belts properly: If you notice any loose belts, make sure to tighten them properly to prevent slippage and unnecessary wear.
- Avoid excessive belt tension: Over-tightening the belts can cause premature wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended tension specifications for your specific Honda Pilot model.
- Keep the belts clean: Regularly clean the belts using a mild soap and water solution to remove dirt, grime, and debris that can cause abrasion and damage.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures: Extreme heat or cold can cause the belts to expand or contract, leading to potential damage. If possible, park your Honda Pilot in a covered parking area to protect the belts from extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Avoid belt contamination: Keep the belts away from oil, grease, or other chemicals that can deteriorate their material. If any fluid leaks onto the belts, clean it immediately.
- Replace the belts as recommended: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended belt replacement intervals. Over time, belts can become worn, stretched, or damaged, and replacing them at the specified intervals can prevent sudden belt failure.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help ensure the longevity and reliability of your Honda Pilot’s belts, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Q&A:
How often should I perform maintenance on my belt?
It is recommended to perform maintenance on your belt at least once a year or every 10,000 miles, whichever comes first.
What type of maintenance should I perform on my belt?
Some of the maintenance tasks you should perform on your belt include cleaning it regularly, checking for signs of wear or damage, and tightening or adjusting the tension as needed.
Can I use any type of cleaner to clean my belt?
No, it is important to use a cleaner specifically designed for belts. Using the wrong cleaner might damage the belt or reduce its lifespan.
How can I tell if my belt needs to be replaced?
You should inspect your belt regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or excessive stretching. If you notice any of these signs, it is time to replace your belt.