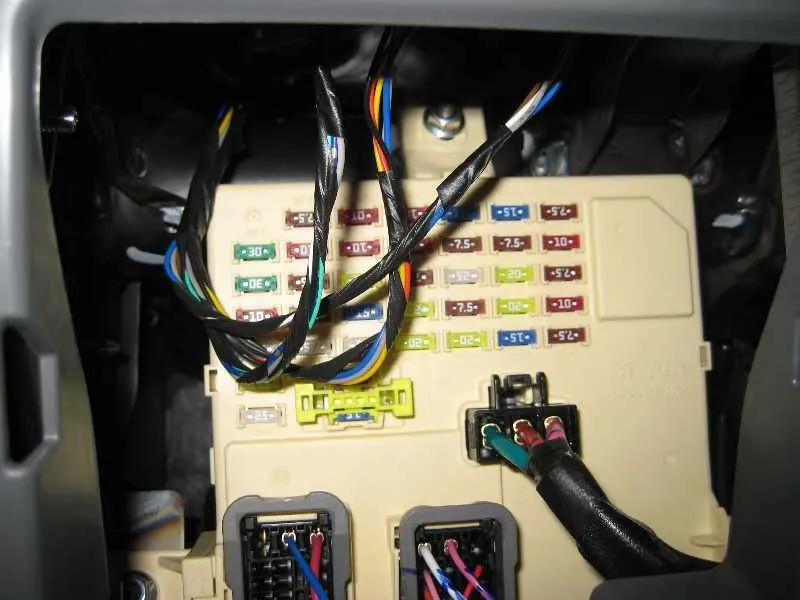

If you’re experiencing electrical issues, knowing the layout of the power distribution system is crucial. For quick troubleshooting, identify the main and auxiliary relays that manage the key functions in your car. This guide provides an in-depth look at the central components and their respective locations within your vehicle’s electrical setup.
Begin by inspecting the primary panel, often located in the driver’s side, under the dashboard, or in the engine compartment. It houses the critical circuits that control the ignition, lights, and air conditioning. Additionally, the secondary unit, typically near the battery or fuse compartment, manages components such as the horn, wipers, and fuel system.
For accurate diagnostics, refer to the layout that highlights the exact spots for each component. Pay particular attention to the specific identifiers marked next to each slot to avoid unnecessary confusion. This detailed schematic will help you pinpoint faulty connections, blown connectors, or malfunctioning switches.
Make sure to verify the amperage ratings on each unit to ensure no overloading occurs, which could lead to further damage or even safety risks. For optimal performance, it’s recommended to follow the manufacturer’s prescribed values when replacing or reassigning components.
By understanding the arrangement and function of these circuits, you can perform more precise repairs or upgrades, ensuring your vehicle operates at peak efficiency. If in doubt, consult a professional mechanic for further advice and assistance.
Electrical Components Layout for the 2013 Sedan
To ensure proper functioning of all electrical systems, it is crucial to locate the main electrical panels in the cabin and engine compartment. Below is a quick guide to the layout of key components:
- Interior Panel (Cabin): Located beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. This controls systems such as lights, airbags, and entertainment.
- Engine Compartment Panel: Positioned near the battery. It handles critical components like the alternator, air conditioning, and power steering systems.
Always ensure the correct amperage and fuse type are used when replacing a blown component. Below are some key positions for common elements:
- Headlights: Located in position #7 of the interior panel.
- Wipers: Found at position #5 on the same interior panel.
- Battery: In the engine compartment, check position #3 for the main power supply.
Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for any updates on component placement or to ensure you are replacing with the correct part. In the event of electrical failure, first check the panels before addressing any deeper system issues.
How to Locate and Identify Electrical Panels in the 2013 Model
To access the main electrical panels in this vehicle, first check the interior compartment located beneath the dashboard. You’ll find a panel on the driver’s side, near the left footwell. Open the cover by gently pulling it toward you, revealing a cluster of connectors and fuses. The second compartment is located in the engine bay, near the vehicle’s battery. This unit is often shielded by a black plastic cover which can be removed by unclipping or unbolting it.
For easy identification, the components inside these compartments are typically labeled. A guide on the rear of each cover provides a list of connections and their associated functions, making troubleshooting easier. Ensure to replace any faulty parts with identical specifications to maintain optimal vehicle performance.
Interior Panel: Located just below the steering wheel on the driver’s side. It controls interior systems, including lighting and climate controls.
Engine Compartment Panel: This larger unit manages power to high-demand systems like the alternator, ignition, and air conditioning compressor. It is typically located on the passenger side of the engine compartment, near the windshield.
Both panels are critical for ensuring that all vehicle systems operate correctly. If there’s an issue with any electrical system, these panels should be the first places to inspect.
Understanding the Functions of Fuses in the 2013 Hyundai Sonata
It is crucial to regularly check the electrical circuit protection components to ensure proper vehicle performance. Fuses act as the safety net for electrical systems, preventing overloading and damage to delicate components. If a fuse blows, it usually indicates an overload or a short circuit. Each fuse corresponds to a specific electrical component or system within the vehicle, such as lights, audio systems, or power windows.
Identifying and replacing a blown fuse requires a basic understanding of the assigned amperage and its purpose within the system. For example, a higher amperage fuse protects high-power systems, like the air conditioning unit, while lower amperage fuses safeguard more sensitive components such as the radio or dashboard lights.
When diagnosing issues, start by inspecting the fuses related to the malfunctioning component. If a component like the windshield wipers suddenly stops working, check the corresponding fuse first before moving on to other possible causes. Using a multimeter to test continuity can help identify a faulty fuse quickly.
It is recommended to replace fuses with the correct amperage to prevent electrical issues. Over-amping a fuse can cause damage to the wiring or other connected systems. Always refer to the owner’s manual to confirm the exact specifications for each fuse, as using the wrong type can create safety hazards.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues with the Fuse System
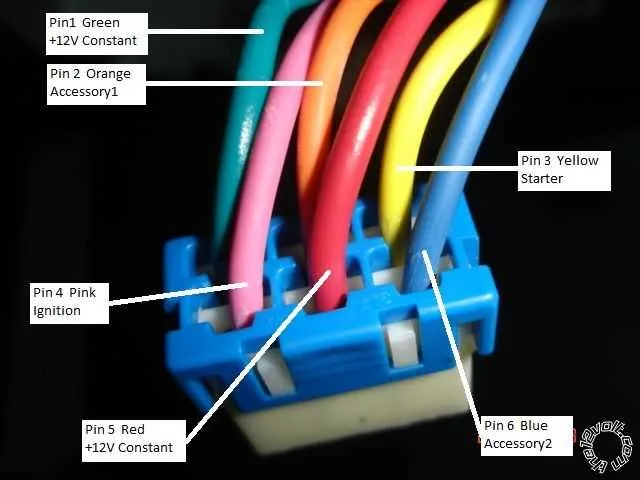
Check for blown fuses immediately when facing power loss in specific electrical systems. A quick visual inspection can reveal damaged connections, but testing with a multimeter provides a more accurate diagnosis. Replace any faulty units with correct amperage specifications to prevent further damage.
Inspect relays for malfunctioning components. Faulty relays can often be the cause of failure in electrical circuits. Test by swapping with a known working relay to see if the problem persists. If the issue is resolved, replace the faulty relay.
Examine wiring for shorts or loose connections. Inspect the wiring near the electrical center for any visible signs of wear, fraying, or corrosion. Tighten or reattach any loose wires and ensure they are not touching any metal parts, which could cause short circuits.
Check the battery voltage to ensure proper power supply to the system. Insufficient voltage can lead to erratic behavior in electrical circuits. If the battery voltage is low, recharge or replace the battery as needed.
Verify ground connections. Poor ground connections can create irregularities in the electrical system, leading to malfunctioning components. Clean and secure ground terminals to ensure a stable connection for all components.
Inspect the fuse block for corrosion. Over time, exposure to moisture can cause corrosion in the fuse block, affecting the reliability of electrical connections. Clean any corroded areas with an appropriate cleaning solution and ensure all terminals are intact and free of rust.
Consider professional diagnostics if basic troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the issue. Persistent electrical problems may require specialized equipment to identify deeper faults within the electrical system. A professional can pinpoint issues such as faulty control modules or wiring harness failures.