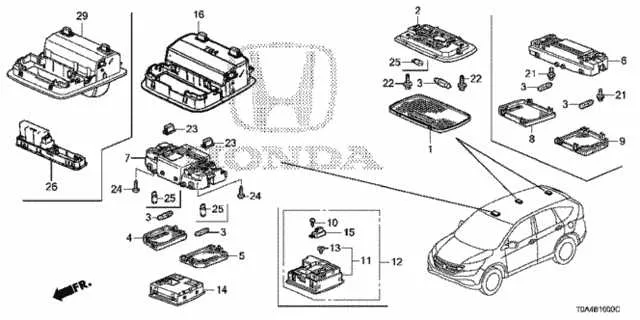
Understanding the layout of electrical components in your car can save you time and money on repairs. If you experience issues with any of the car’s systems, a detailed guide on the placement and function of these parts is crucial. Identifying which specific part controls each system will allow for quicker diagnostics and more accurate troubleshooting.
First, locate the main control panel, typically found under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. This central unit manages most of the car’s electrical functions, from lighting to power supply to other systems. Once located, it’s important to refer to a clear mapping of connections, as it will help determine whether a malfunction is due to a blown circuit or an internal wiring issue.
The diagram for these elements will show the individual connections for different systems, such as the headlights, air conditioning, and power windows. It’s essential to check for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage around each connection. A common cause of electrical failures is a loose or corroded terminal, so regularly inspecting these areas can prevent unexpected issues.
Make sure to check the labeling of each terminal; this helps you quickly spot any miscommunication in the system. For any electrical troubleshooting, always remember to disconnect the battery before working on any components to avoid the risk of short circuits or electrical shocks.
Electrical Component Layout for 2014 Vehicle Model
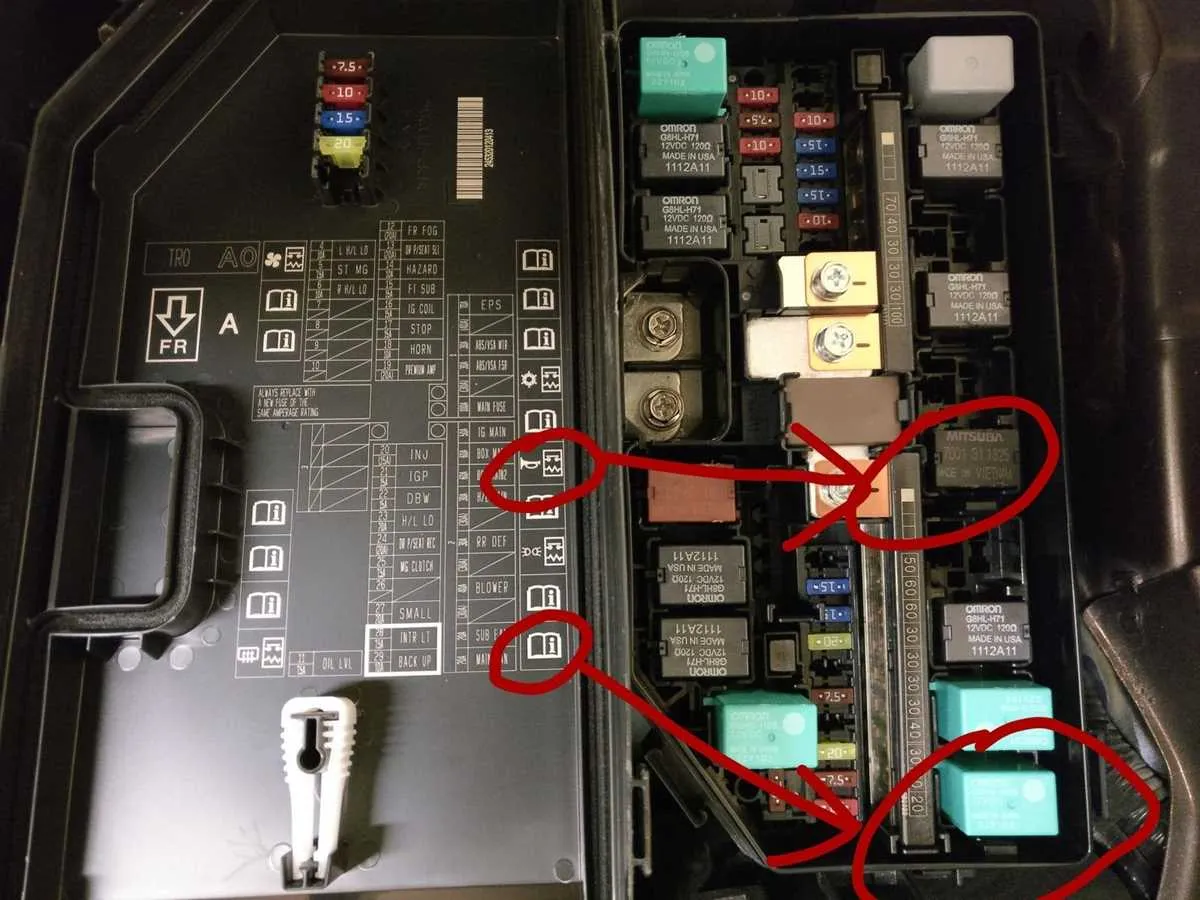
For efficient troubleshooting, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the layout of electrical components in your vehicle. The main power distribution unit is located near the driver’s side dashboard, specifically under the panel adjacent to the footwell. This unit houses various relays and fuses for critical systems, including lighting, air conditioning, and safety features.
To locate the main power distribution center, gently remove the cover by pulling it towards you. Inside, you’ll find a set of numbered slots, each corresponding to a specific electrical component. For instance, Slot 1 typically handles the main ignition relay, while Slots 2 through 5 may be assigned to auxiliary components like power windows and radio. Make sure to check the individual fuse ratings to avoid overloads.
The secondary unit, typically located in the engine compartment near the battery, is responsible for the vehicle’s larger systems such as the alternator and cooling fan. This section is protected by larger fuses that can manage higher amperage. If you encounter issues with the engine or major accessories, inspecting this area is essential.
Key Tips: Always use the correct amperage replacement for any blown fuses, as using a higher-rated fuse can cause overheating or electrical failure. If you’re uncertain about any fuse’s role, refer to the included vehicle manual or consult with a professional mechanic for assistance.
Note: It’s recommended to regularly check both the interior and engine compartments for any signs of wear or corrosion on fuse connections. Keeping these areas clean and functional is key to preventing future electrical failures.
Locating the Electrical Panels in Your Vehicle
The primary electrical panel inside the cabin is located beneath the dashboard, to the left of the steering wheel. To access it, simply remove the cover panel by pulling it away gently with your fingers or a plastic trim tool. This panel houses key circuits, including those for lights, climate control, and the infotainment system.
Another critical panel is located in the engine compartment, on the driver’s side near the windshield. To open it, unlatch the cover by releasing the clips and lifting the lid. This area contains fuses responsible for engine components, sensors, and other vital mechanical systems.
Both locations are easily accessible for quick troubleshooting, but ensure you use proper safety precautions when handling electrical components to avoid accidental shorts or damage.
Understanding the Electrical Component Layout
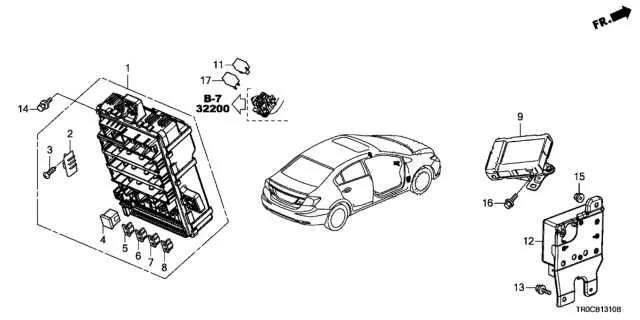
To efficiently manage the electrical system, focus on identifying key relays and circuit breakers associated with different car components. The primary distribution panel is divided into sections, each serving specific functions such as lighting, air conditioning, and safety systems.
Check the marked slots for components like the ignition, battery management, and entertainment system. These often use high-amperage connections, so ensure they are protected by larger relays. The smaller fuses are typically responsible for lower-power systems, like interior lights and sensors. In case of a malfunction, inspect the relevant sections for burnt-out elements or blown protection units.
The layout usually includes both under-hood and cabin sections. The under-hood panel handles higher-voltage circuits, while the interior panel focuses on more delicate electronics. Each circuit should be clearly numbered, making it easier to identify which component corresponds to a particular fuse or relay.
Ensure that all connections are secure, and consider keeping a replacement kit for frequently used units like the air conditioning system and starter motor, as they tend to wear out over time. Regularly inspect for corrosion, particularly around the battery terminals and ground connections, to avoid short circuits.
Replacing Electrical Components: Step-by-Step Guide
If any electrical system stops working, it might be due to a blown component inside the vehicle. Follow these precise steps to identify and replace it.
- Locate the correct unit. The main unit is usually under the dashboard or near the engine compartment. You can find its location in the vehicle’s manual.
- Turn off the engine and remove the key. Disconnect the battery to avoid any electrical mishaps.
- Identify the problematic component. Use a test light or multimeter to check which one is faulty.
- Once identified, carefully remove the defective part. Use a plastic tool or small pliers to avoid damage to surrounding areas.
- Insert the new part by aligning it properly into its slot. Ensure that the new part matches the rating of the original one (voltage, amperage).
- Before closing the panel, check that the new part is securely in place. Turn on the engine and test the affected system to ensure it works correctly.
Repeat the process for any other units that need replacing. Always keep a replacement kit with various types for emergencies.