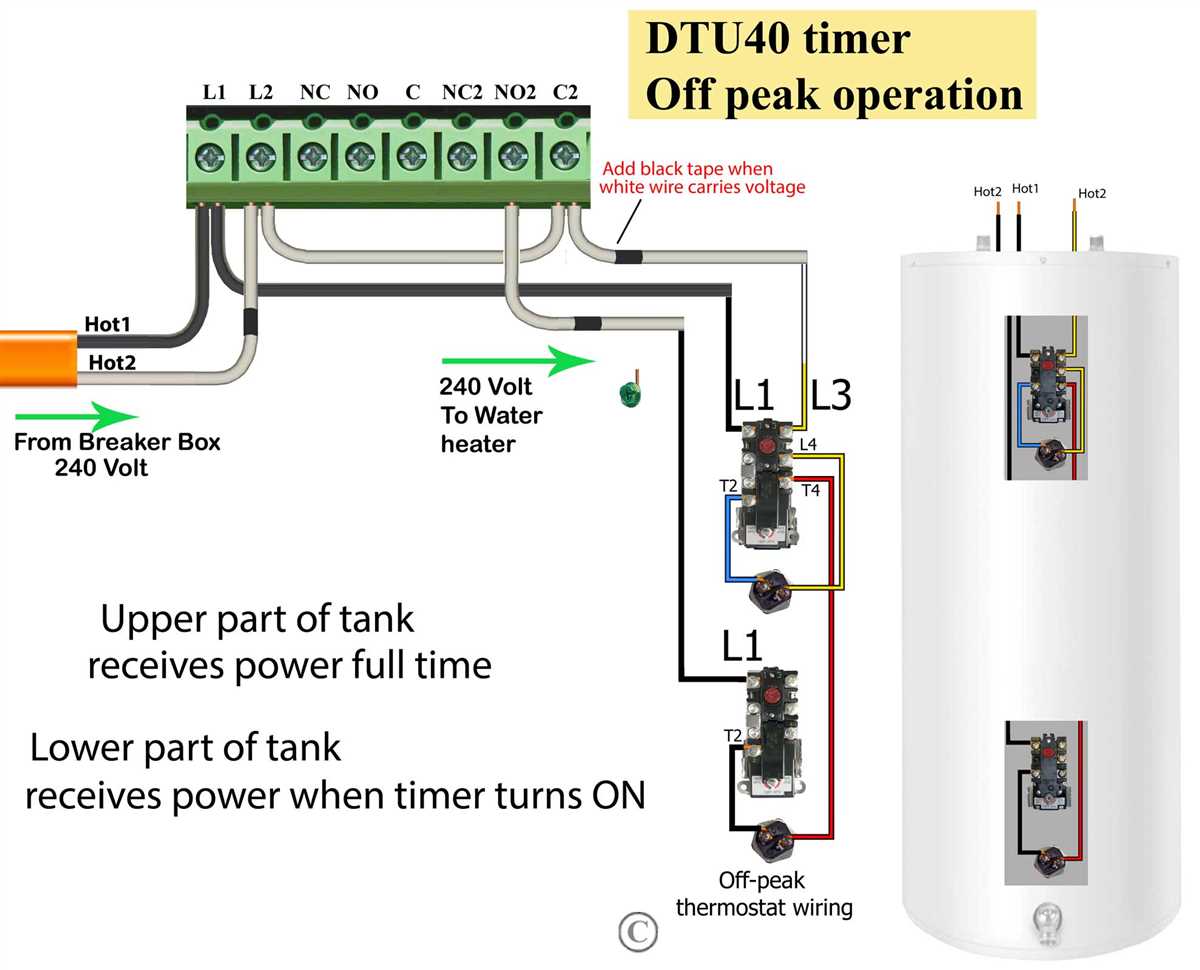
When it comes to installing a heater in your home, it’s important to understand the wiring diagram to ensure that everything is connected correctly. One common type of heater is a 220 volt heater, which requires a higher voltage than a standard 120 volt heater. Understanding the wiring diagram for a 220 volt heater is essential for a safe and effective installation.
A 220 volt heater is typically used for larger spaces or heating systems that require more power. This type of heater uses two hot wires and a ground wire. The hot wires carry the current to the heater, while the ground wire provides a path for any excess current to safely dissipate. The wiring diagram will show you how to connect these wires to the proper terminals.
When working with electricity, it’s important to follow safety guidelines and to turn off the power before beginning any installation or wiring work. It’s also a good idea to consult a professional electrician if you’re unsure about any aspect of the installation process. With the right knowledge and precautions, you can safely install a 220 volt heater and enjoy the benefits of effective and efficient heating in your home.
Understanding 220 Volt Heater Wiring Diagram

When installing a 220 volt heater, it is essential to understand the wiring diagram to ensure safe and proper installation. A 220 volt heater operates at a higher voltage than standard household appliances, making it crucial to follow the correct wiring procedures.
The wiring diagram for a 220 volt heater typically consists of four wires: two hot wires, one neutral wire, and one ground wire. The hot wires are usually black and red, the neutral wire is typically white, and the ground wire is usually green or bare copper. Each wire has a specific purpose in the electrical circuit.
- Hot wires: The hot wires carry the electrical current from the circuit breaker to the heater. These wires are connected to the two hot terminals on the heater. It is important to make sure the hot wires are properly sized to handle the load of the heater.
- Neutral wire: The neutral wire acts as a return path for the electrical current. It is connected to the neutral terminal on the heater. The neutral wire is crucial for balancing the electrical load in the circuit.
- Ground wire: The ground wire is a safety feature that provides a path for excess electrical current to flow away from the heater and into the ground. It is connected to the ground terminal on the heater and should be properly grounded to prevent electrical shock.
It is important to carefully follow the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer of the 220 volt heater. This diagram will show the specific connections for each wire and any additional requirements, such as wire sizing or the use of a separate disconnect switch. Failure to follow the correct wiring diagram can result in electrical hazards, damage to the heater, or even fire.
If you are not comfortable or experienced with electrical wiring, it is recommended to hire a licensed electrician to install the 220 volt heater. They will have the knowledge and expertise to ensure a safe and proper installation, following all applicable codes and regulations.
What is a 220 Volt Heater?
A 220 volt heater is an electrical heating device that operates on a 220 volt power supply. It is commonly used in residential and commercial settings to provide warmth and comfort in colder climates. Unlike standard 110 volt heaters, which are commonly used for small spaces or temporary heating needs, 220 volt heaters are designed for larger areas and provide a more powerful heat output.
220 volt heaters come in various types and styles, including baseboard heaters, wall heaters, radiant heaters, and portable heaters. They can be powered by either gas or electricity, with electric heaters being the most common in residential settings. These heaters typically require a dedicated circuit and heavy-duty wiring to safely handle the higher voltage and power requirements.
- Baseboard heaters: These heaters are installed along the baseboard of a room and are a popular choice for providing supplemental heat. They are typically controlled by a built-in thermostat and can be easily adjusted to maintain a desired temperature.
- Wall heaters: Wall heaters are mounted on the wall and are a space-saving option for heating larger areas. They are often installed in bathrooms, bedrooms, or living rooms where additional heat is needed.
- Radiant heaters: Radiant heaters use infrared technology to heat objects and people directly, rather than heating the air. They are often used in outdoor spaces or garages where conventional heating methods may not be effective.
- Portable heaters: Portable 220 volt heaters are versatile and can be moved from room to room as needed. They are often equipped with wheels or handles for easy transportation and are a convenient solution for heating specific areas.
In conclusion, a 220 volt heater is a powerful heating device that operates on a 220 volt power supply. It is designed for larger areas and provides a more efficient and effective heat output compared to standard 110 volt heaters. With various types and styles available, 220 volt heaters offer versatility and comfort in colder climates.
The Importance of Proper Wiring for a 220 Volt Heater
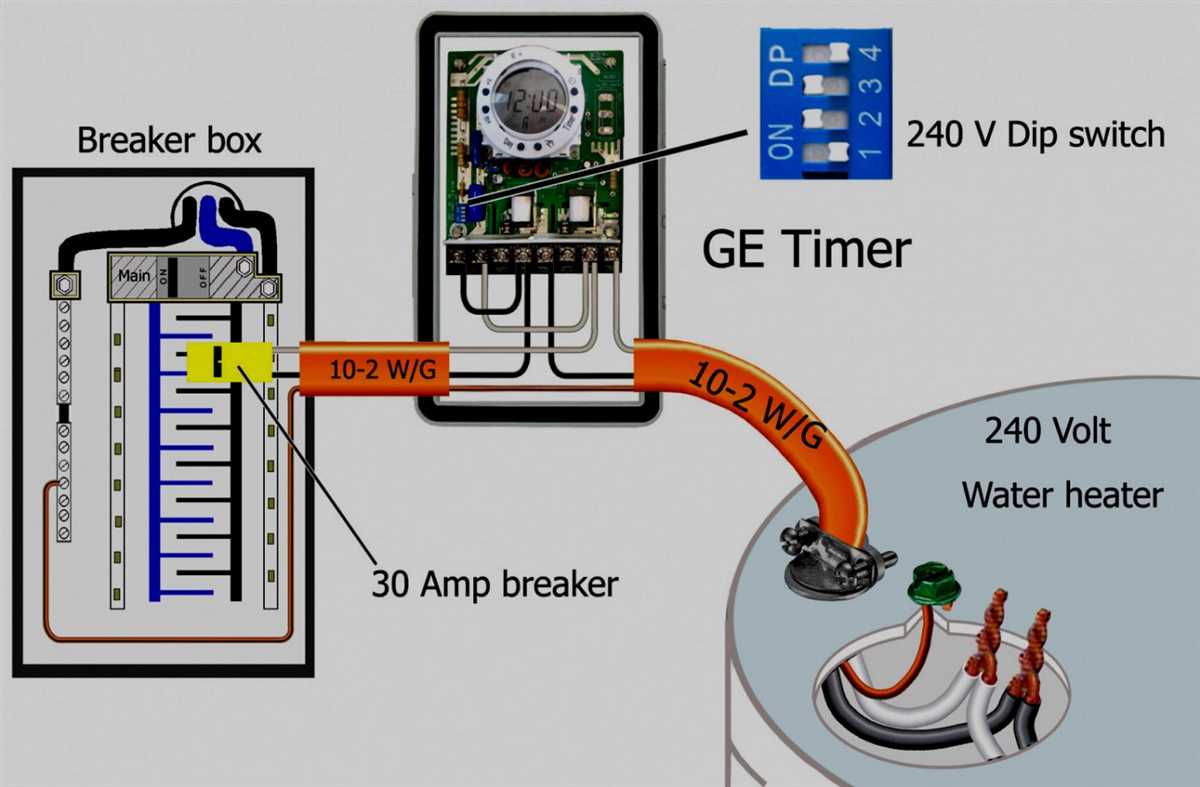
Proper wiring is crucial when installing a 220 volt heater. This type of heater requires a dedicated circuit with the appropriate gauge of wire and proper connections to ensure safe and efficient operation. Failing to adhere to proper wiring practices can result in electrical hazards, inefficient heating, and potential damage to the heater.
One of the key considerations when wiring a 220 volt heater is the selection of the correct wire gauge. The wire size should be chosen based on the heater’s electrical requirements, taking into account factors such as the heater’s wattage and the distance from the electrical panel. Using wire that is too small can cause excessive voltage drop, resulting in decreased heat output and potential damage to the heater. On the other hand, using wire that is too large can be unnecessary and costly.
Another important aspect of proper wiring for a 220 volt heater is making sure the connections are secure and properly insulated. Loose or improper connections can lead to overheating, sparking, and electrical fires. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and any applicable electrical codes when making these connections. Additionally, using wire connectors, junction boxes, and electrical tape can help ensure that the connections are protected and secure.
In summary, proper wiring is essential for the safe and efficient operation of a 220 volt heater. By selecting the correct wire gauge and ensuring secure connections, the risk of electrical hazards and inefficient heating can be minimized. Following the manufacturer’s instructions and any applicable electrical codes is crucial to ensure a properly wired 220 volt heater.
Basic Components of a 220 Volt Heater Wiring Diagram
A 220 volt heater wiring diagram consists of several basic components that are necessary for proper installation and operation of the heater. These components include:
- Heater – The main element of the system, the heater is the device that generates heat. It can be an electric resistance coil, a heat pump, or any other type of heating element.
- Power Supply – The power supply is responsible for providing the 220-volt electrical current needed to operate the heater. It typically includes a circuit breaker or fuse for protection against electrical overload.
- Thermostat – The thermostat is a control device that regulates the temperature of the heater. It senses the current temperature and sends signals to turn the heater on or off to maintain the desired temperature.
- Wiring – The wiring connects all the components of the heater system together. It includes electrical cables, connectors, and switches that transmit the electrical current from the power supply to the heater and other components.
- Safety Devices – The wiring diagram may also include safety devices such as thermal overload protectors, pressure switches, or temperature limiters to prevent overheating or other hazards.
In addition to these basic components, a 220 volt heater wiring diagram may also include additional features specific to the type and model of the heater. These can include fan motors, control panels, timers, and other accessories.
Overall, a 220 volt heater wiring diagram serves as a blueprint for proper installation and understanding of the electrical connections required for a heater system to function safely and efficiently.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a 220 Volt Heater
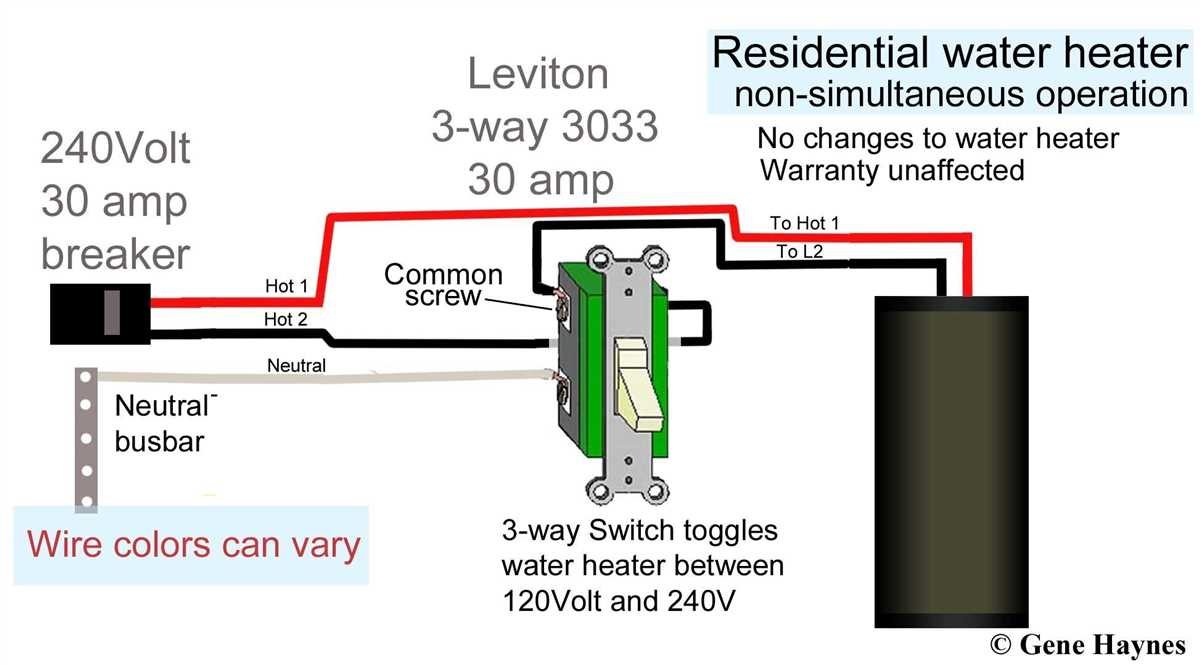
Wiring a 220 volt heater requires careful attention to ensure proper installation and adherence to safety guidelines. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you wire a 220 volt heater:
1. Gather the necessary tools and materials:
Before starting the wiring process, gather all the necessary tools and materials. This includes a voltage tester, wire strippers, electrical tape, wire nuts, a screwdriver, and the appropriate gauge wire for your heater.
2. Turn off the power:
Before working on any electrical wiring, it is essential to turn off the power to the circuit you will be working on. Locate the circuit breaker in your electrical panel and switch it off to ensure your safety. Use a voltage tester to double-check that there is no electrical current running through the wires.
3. Install a double pole circuit breaker:
To handle the 220 volt power supply, you will need a double pole circuit breaker. Install the circuit breaker in your electrical panel by removing the appropriate knockout and connecting the wires to the breaker. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
4. Run the appropriate gauge wire:
Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your heater to determine the appropriate gauge wire to use. Run the wire from the circuit breaker to the location where you will install the heater, ensuring that it is the correct size for the amperage and length required.
5. Connect the wires:
Strip the ends of the wire to expose the copper conductors. Connect the wires from the circuit breaker to the heater, ensuring that the hot wires are connected to the appropriate terminals. Use wire nuts to secure the connections and wrap them with electrical tape for added safety.
6. Double-check the connections:
After connecting the wires, double-check all the connections to ensure they are secure and properly connected. Verify that there are no loose wires or exposed copper. It is crucial to have a tight and secure connection to prevent any electrical hazards.
7. Test the heater:

Before turning on the power, verify that the heater is installed correctly and securely. Make sure all connections are tightened and secure. Once everything is in order, turn on the circuit breaker and test the heater to ensure it is functioning properly.
Following these step-by-step instructions will help you safely and correctly wire a 220 volt heater. It is essential to adhere to all safety guidelines and consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific heater model. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with electrical wiring, it is recommended to seek professional assistance.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting for 220 Volt Heater Wiring
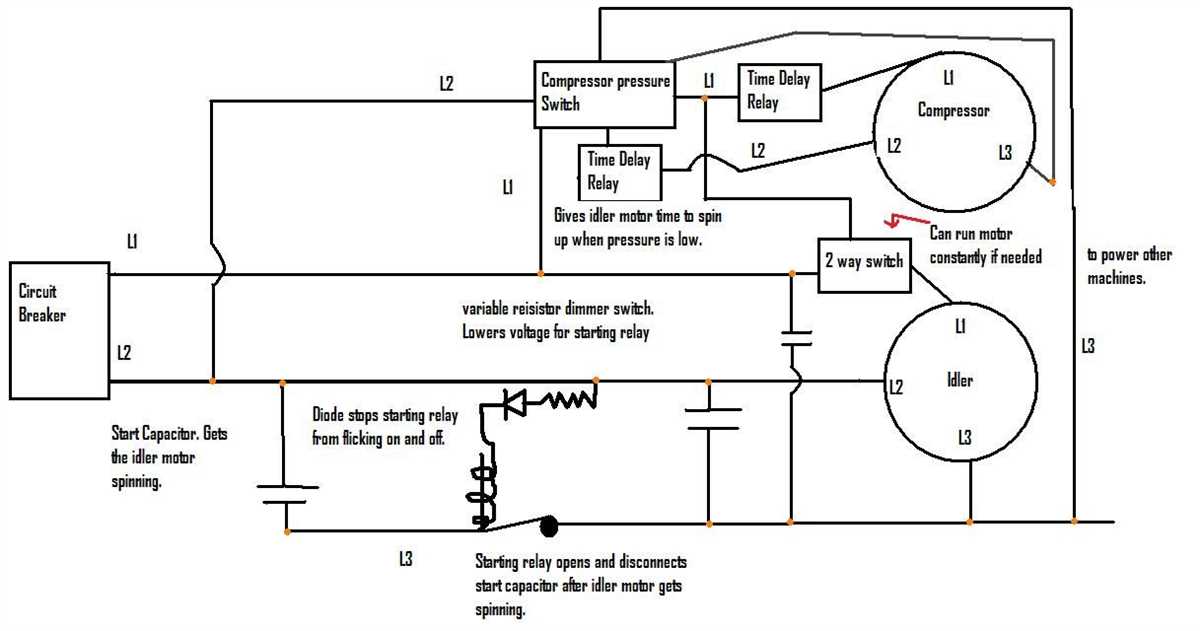
Wiring a 220-volt heater can be a complex task, and sometimes issues may arise that prevent the heater from working properly. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them:
1. Incorrect wiring connections:
One of the most common issues with 220 volt heater wiring is incorrect or loose wiring connections. Make sure to double-check all the connections and ensure that they are securely tightened. If any wires are damaged or frayed, they should be replaced. Incorrect wiring connections can cause the heater to malfunction or not work at all.
2. Faulty circuit breaker:
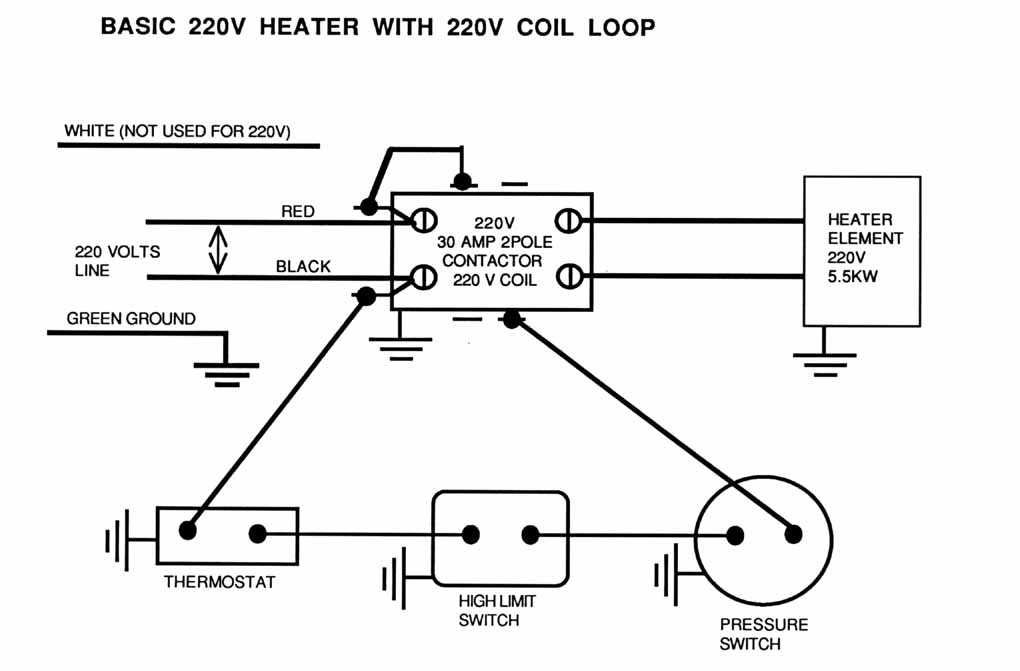
If the heater is not receiving power, it could be due to a faulty circuit breaker. Check the circuit breaker panel and make sure the breaker for the heater is in the “ON” position. If it has tripped, reset it and test the heater again. If the breaker continues to trip, there may be an underlying electrical issue that needs to be addressed by a professional.
3. Overloaded circuit:
If the heater is causing the circuit breaker to trip repeatedly, it may be due to an overloaded circuit. Check the amp rating of the heater and make sure it is compatible with the circuit’s capacity. If the heater is drawing too much power for the circuit, it may be necessary to upgrade the wiring or install a dedicated circuit for the heater.
4. Incorrect voltage:
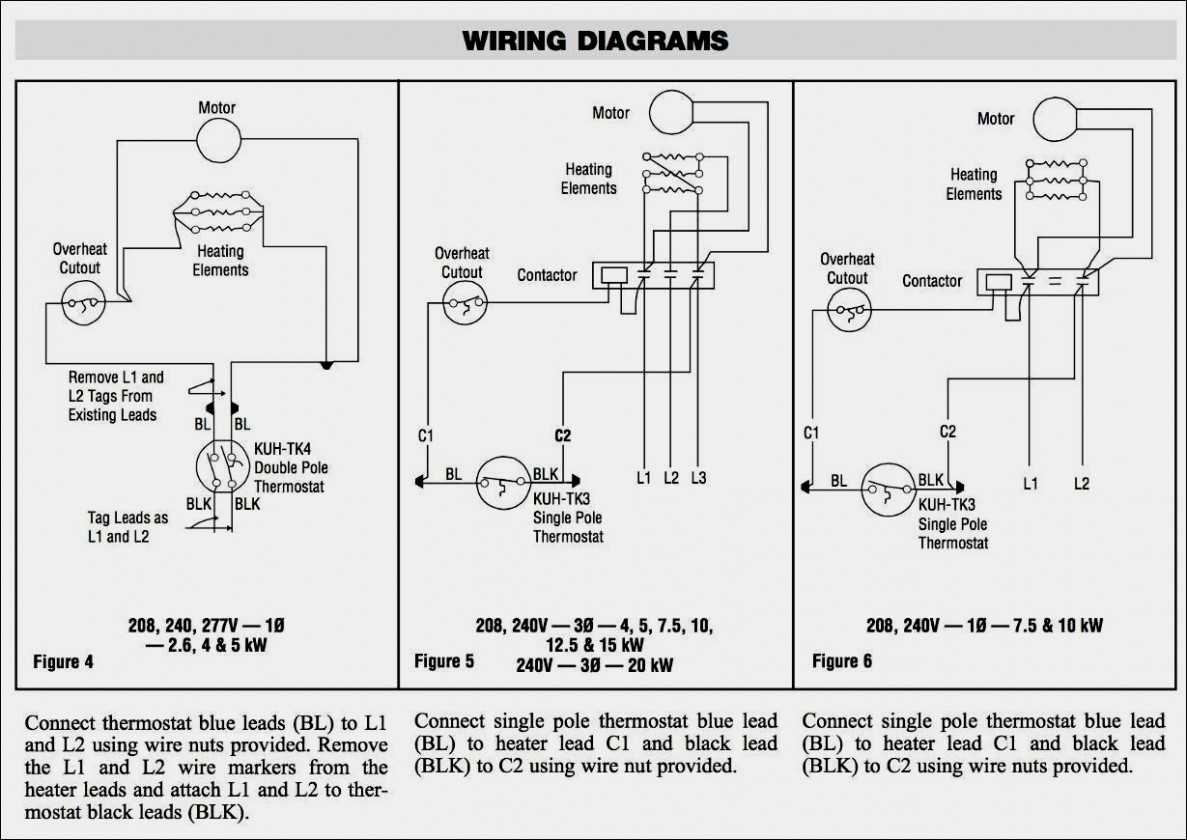
Verify that the heater is designed to operate at 220 volts. Using a heater that requires a different voltage can result in damage to the heater and pose a safety hazard. Check the heater’s user manual or consult with a professional to ensure that the voltage requirements match the electrical supply.
5. Defective thermostat or heating element:
If the heater is not producing heat or is not cycling on and off correctly, there may be an issue with the thermostat or heating element. Test the thermostat for continuity using a multimeter, and if it is not functioning properly, it may need to be replaced. Similarly, a heating element that is burnt out or damaged will need to be replaced to restore the heater’s functionality.
It is important to note that working with electrical wiring can be dangerous, especially if you are not familiar with electrical systems. If you are unsure about any aspect of wiring a 220-volt heater or troubleshooting any issues, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician.