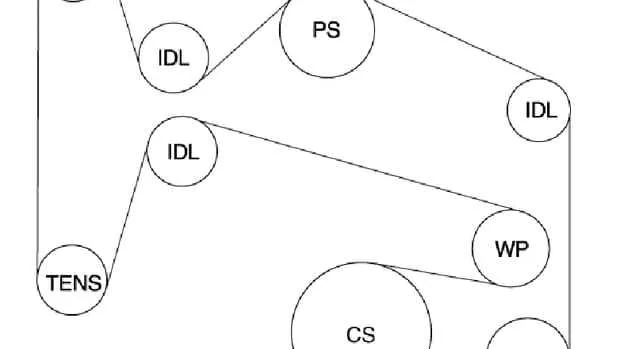
Ensure your engine operates smoothly by correctly identifying and installing the engine pulley system layout. The arrangement of the pulleys and belts plays a critical role in power distribution, influencing both performance and fuel efficiency. It’s essential to follow the exact pattern for optimal tension and alignment, reducing the risk of wear or malfunction.
Examine the position of each driving component before beginning installation. Pay close attention to the orientation of the main drive components, especially the alternator and water pump pulleys. Incorrect placement can cause unnecessary strain, leading to premature component failure. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for precise measurements and routing instructions.
Double-check the tensioning system to ensure proper tension on the components. This adjustment is vital to avoid slippage or excessive wear, which can result in significant damage to the powertrain. Regular maintenance and inspections will prolong the life of the engine’s auxiliary system and prevent costly repairs in the future.
Serpentine System: Practical Guide
For a smooth-running engine, it’s crucial to ensure the drive components are aligned properly. When working on your vehicle, start by checking the routing of the serpentine system. Make sure the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor are all connected correctly. A misaligned or worn-out component can lead to belt slippage, affecting the entire system’s efficiency.
Begin with the tensioner. Its position should be adjusted to maintain the proper tension on the drive system. If it’s too loose or too tight, it can cause premature wear and failure of the connected units. Always replace the tensioner when you notice wear, as it’s an essential part of maintaining optimal function.
Pay close attention to the direction of rotation. The routing should follow the manufacturer’s recommended path to ensure no unnecessary strain is placed on the system. In particular, check that the idler pulley is positioned properly to avoid excessive stress on the belt.
If you’re changing any parts within the system, make sure you inspect all components, including pulleys and tensioners, for any signs of wear or damage. These should be replaced as needed to prevent the system from malfunctioning.
Lastly, always verify the condition of the belt itself. Check for frays, cracks, or any signs of heat damage. Replace the belt immediately if any of these issues are present to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding the Main Components of the 3.5 Impala Belt System
The primary components of the accessory drive system in vehicles equipped with a 3.5-liter engine are the pulleys, tensioners, idlers, and the serpentine loop. Each of these parts plays a crucial role in ensuring that the engine accessories receive the proper amount of power for optimal performance.
Pulleys are essential for transferring mechanical energy from the engine’s crankshaft to components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. These pulleys are designed to maintain consistent speeds for each accessory, which helps prevent wear and ensures smooth operation.
Tensioners are responsible for maintaining the correct tension on the drive loop. Without proper tension, the drive components may slip, leading to inefficiency or failure of the system. Regular inspection of tensioner functionality is recommended to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Idlers are used to guide the drive loop through its correct path, minimizing friction and wear while optimizing the system’s efficiency. These components need to be regularly checked for signs of wear, as a damaged idler can cause the loop to misalign or fail.
Serpentine Loop refers to the continuous loop that connects all the components, from the crankshaft to the various accessories. The loop is usually made from a high-strength rubber material, designed to withstand significant wear and temperature changes. Regular inspections for cracks, frays, or other damage will help extend the life of the entire system.
For long-term durability, it’s essential to replace worn-out components promptly and to perform periodic checks on the alignment and condition of the parts. This ensures that your engine’s performance stays at optimal levels, and accessory failure is minimized.
How to Properly Install the Drive Component on the V6 Sedan for Optimal Performance
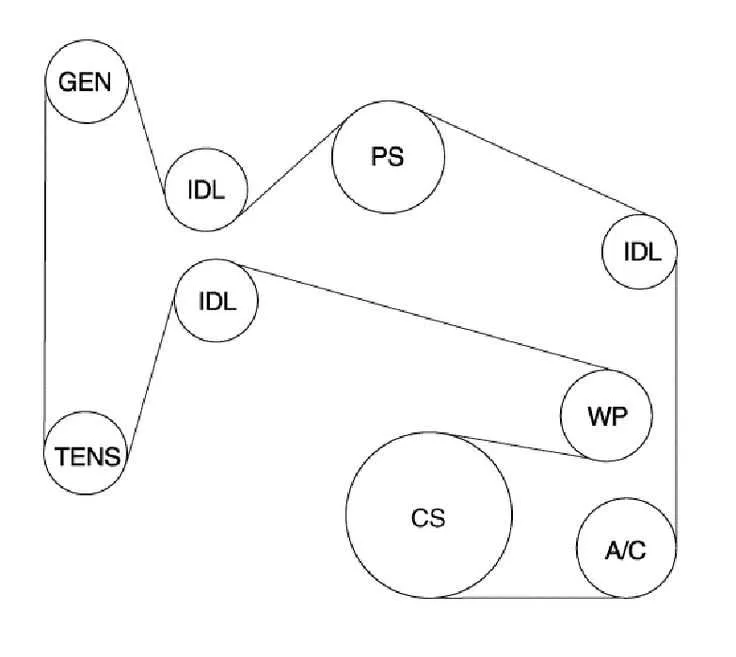
Align the serpentine routing according to the manufacturer’s engine layout. Use a reference guide for the transverse-mounted V6 to identify each pulley location.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal to avoid accidental engagement of electrical systems.
- Locate the automatic tensioner near the alternator bracket. Rotate it clockwise using a 15mm wrench to relieve pressure.
- While holding the tensioner, slide the new ribbed loop over the crankshaft sprocket first. Ensure correct engagement with all grooves.
- Continue routing around the air conditioning compressor, followed by the power steering unit and the idler wheel.
- Wrap the path over the generator pulley, then loop under the water pump drive.
- Finish by sliding the loop over the tensioner while maintaining alignment across all tracks.
- Ensure the ribs sit flush in every channel. Misalignment leads to premature wear.
- Spin each pulley manually to confirm proper seating and detect possible obstructions.
- Reapply tension slowly to avoid slack or twisting.
- Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Observe rotation; any flickering or squealing indicates incorrect setup.
Always verify torque specs on the tensioner bolt and inspect all rotating components for signs of damage before reassembly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in the 3.5 Impala Belt Diagram
Start by checking for misalignment between the crankshaft pulley and the tensioner. A visible offset over 1 mm typically indicates a warped bracket or worn bearing, which must be corrected to prevent uneven wear.
If squealing occurs at startup or under load, inspect the tensioner preload. Factory specification is 15–18 ft-lb; anything below this range can cause slippage, especially in colder climates.
Cracks along the ribbed side of the drive loop suggest overheating. Verify that the water pump rotates freely and doesn’t produce resistance beyond 1.5 Nm when turned by hand. Binding may increase temperature and degrade rubber quickly.
Excessive vibration at idle often points to a deteriorated damper pulley. Use a dial indicator to measure radial wobble; readings over 0.010″ call for immediate replacement.
In cases where the serpentine path is shredding the grooves, inspect each pulley’s edge for burring. Even a 0.5 mm lip can slice the edge under tension, especially near the alternator spindle.
Loss of charging or A/C function without visible fraying usually means insufficient contact pressure. Measure belt deflection at midpoint between the idler and compressor: 10–12 mm under 10 kg force is ideal.