
The 6.0 Powerstroke engine is a popular choice among truck enthusiasts for its power and performance. However, like any engine, it requires proper maintenance and care to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. One of the crucial components of the 6.0 Powerstroke engine is the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system, which plays a significant role in reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency.
The EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine works by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. This process helps lower the combustion temperature by diluting the amount of fresh oxygen entering the combustion chamber. As a result, it reduces the formation of harmful nitrous oxides (NOx) emissions, which can be detrimental to the environment and human health.
To understand the functioning of the EGR system better, it’s crucial to have a clear diagram that illustrates the connections and components involved. The 6.0 Powerstroke EGR diagram provides a visual representation of the entire system, including the EGR valve, EGR cooler, and associated hoses and pipes. This diagram helps technicians and DIY enthusiasts alike to diagnose and troubleshoot any issues related to the EGR system effectively.
Overview of the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system
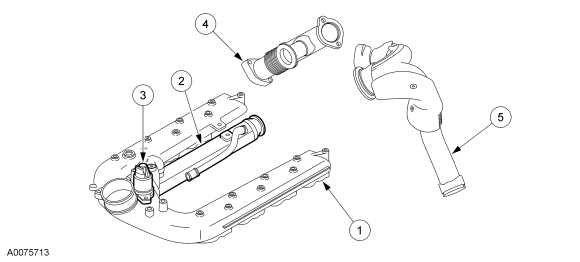
The 6.0 Powerstroke EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system is an important component of the engine’s emissions control system. It is designed to reduce the amount of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions that are released into the atmosphere by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake manifold.
The EGR system consists of several key components, including the EGR valve, cooler, and piping. The EGR valve is responsible for controlling the flow of exhaust gas into the intake manifold. It opens and closes based on input from the engine’s control module, allowing a precise amount of exhaust gas to be recirculated.
The EGR cooler is a heat exchanger that cools the recirculated exhaust gas before it is reintroduced into the engine. This helps to reduce the temperature of the combustion process and prevent the formation of harmful pollutants. The cooler is typically made of stainless steel or aluminum and is located near the intake manifold.
The EGR piping connects the EGR valve to the cooler and allows the exhaust gas to flow between the two components. It is made of durable materials, such as stainless steel or high-density polyethylene, to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the exhaust gases.
Overall, the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system plays a crucial role in reducing emissions and improving the engine’s efficiency. However, it can also be a common source of problems, such as clogging or leaking, which can lead to engine performance issues. Regular maintenance and inspection of the EGR system is recommended to ensure its proper operation.
What is the EGR system and how does it work in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine?
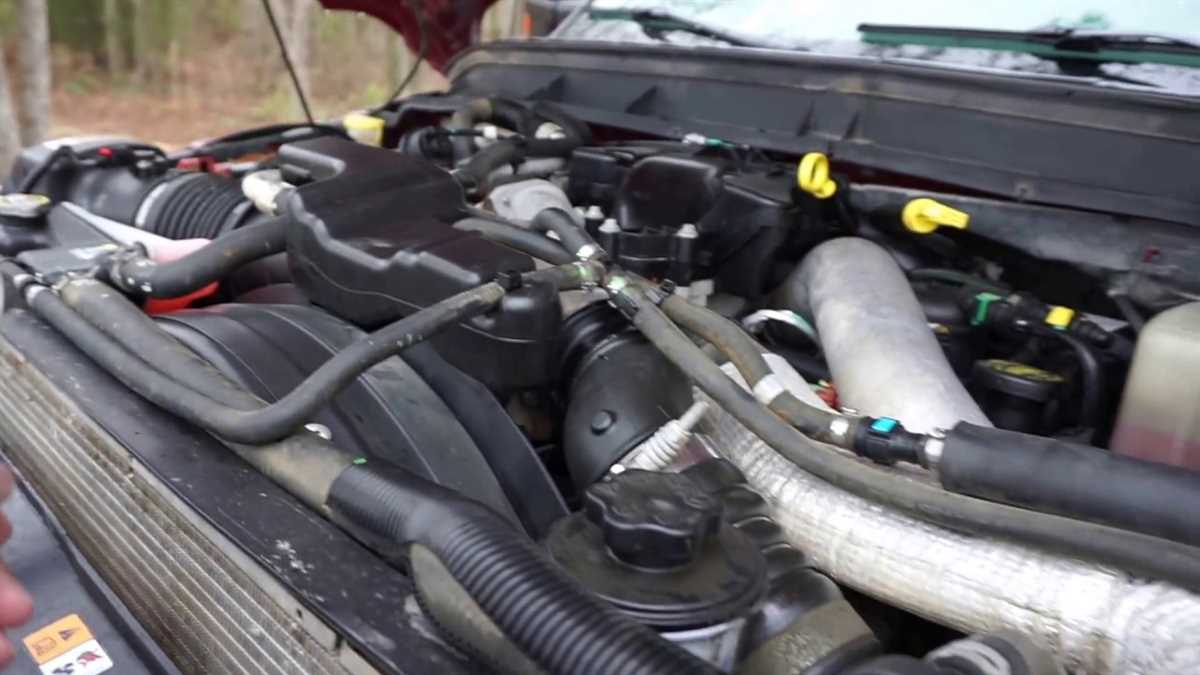

The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is an emission control technology that is used in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine to reduce the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) during combustion. The EGR system works by recirculating a portion of the engine’s exhaust gas back into the intake manifold, where it mixes with the fresh air and fuel before entering the combustion chamber.
The EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine consists of several components, including an EGR cooler, EGR valve, EGR temperature sensor, and EGR control solenoid. The EGR cooler is responsible for reducing the temperature of the recirculated exhaust gas before it is sent back into the intake manifold. This helps prevent excessive heat buildup in the engine and ensures optimal performance.
The EGR valve controls the flow of the recirculated exhaust gas into the intake manifold. It opens and closes as needed to maintain the proper balance between fresh air and recirculated exhaust gas in the combustion chamber. The EGR temperature sensor monitors the temperature of the recirculated exhaust gas, while the EGR control solenoid regulates the operation of the EGR valve based on various engine parameters.
The EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine is designed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the intake manifold, the EGR system helps lower the combustion temperature, which reduces the formation of NOx. This is especially important in diesel engines, as they tend to produce higher levels of NOx compared to gasoline engines.
However, the EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine has been known to have reliability issues. The EGR cooler, in particular, is prone to clogging and failure, which can lead to coolant leaks and engine overheating. Additionally, carbon buildup in the EGR system can cause reduced engine performance and increased emissions. Regular maintenance and proper care are crucial to ensuring the longevity and proper functioning of the EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine.
Components of the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system
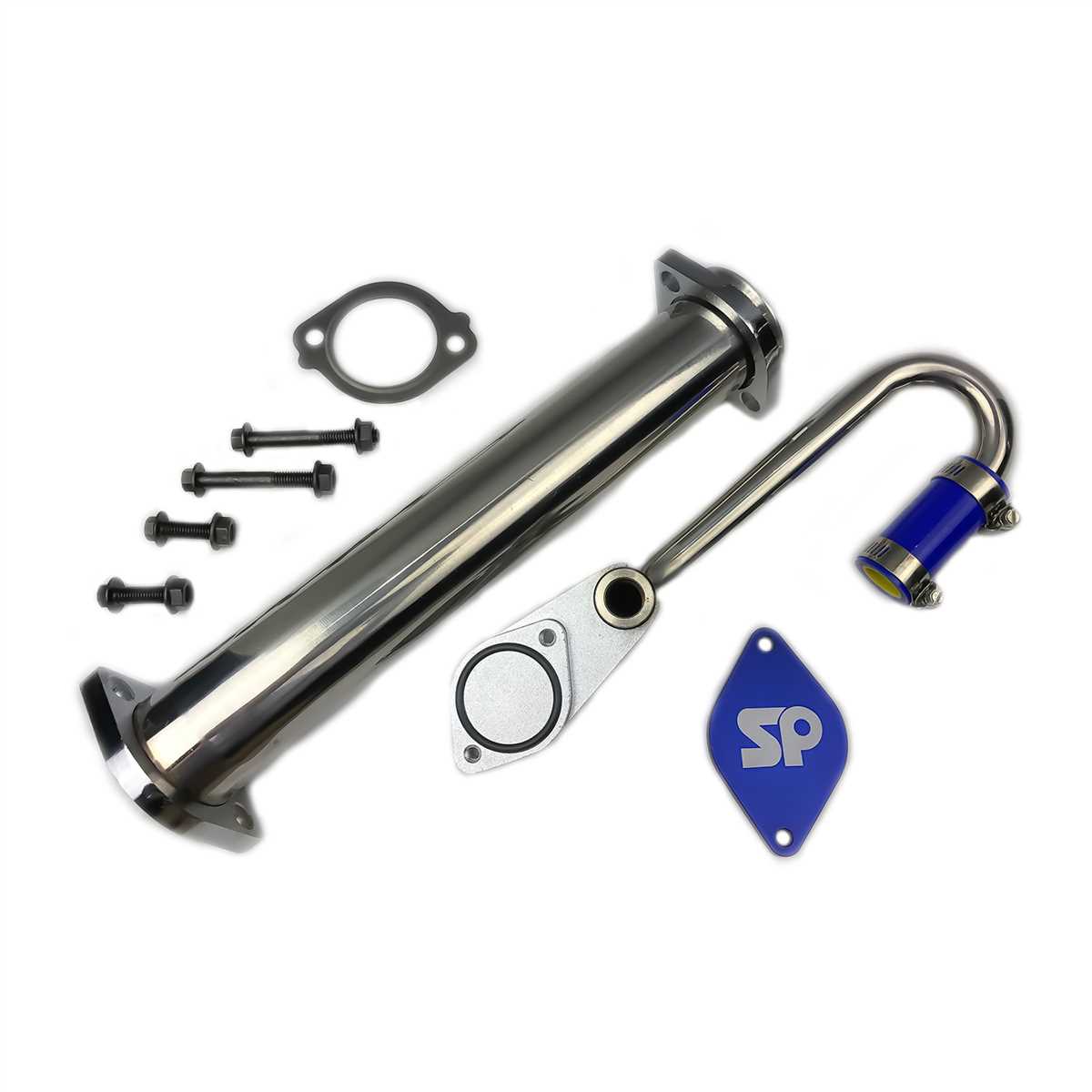

The 6.0 Powerstroke EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system is an important component of the engine’s emission control system. It works by recirculating a portion of the engine’s exhaust gases back into the intake manifold, reducing the amount of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions produced by the engine.
The EGR system consists of several key components that work together to achieve this goal. One of the main components is the EGR valve. The EGR valve is responsible for controlling the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. It is typically located on the engine’s intake manifold and is controlled by the engine control module (ECM).
Another important component of the EGR system is the EGR cooler. The EGR cooler is responsible for cooling the exhaust gases before they are reintroduced into the intake manifold. This is important because the exhaust gases can reach extremely high temperatures, and if they are not cooled down, they can cause damage to the engine. The EGR cooler is typically made of metal and is connected to the EGR valve and the engine’s cooling system.
In addition to the EGR valve and EGR cooler, the EGR system also includes various sensors and hoses. These sensors monitor the EGR system’s performance and provide feedback to the ECM. They can measure parameters such as the temperature and pressure of the exhaust gases, as well as the flow of gases through the system. The hoses, on the other hand, are used to connect the different components of the EGR system together and ensure the proper flow of exhaust gases.
Summary:

- The 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system helps reduce nitrogen oxide emissions.
- The EGR valve controls the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold.
- The EGR cooler cools down the exhaust gases before reintroducing them into the intake manifold.
- Sensors and hoses are used to monitor and connect the different components of the EGR system.
Common issues with the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system
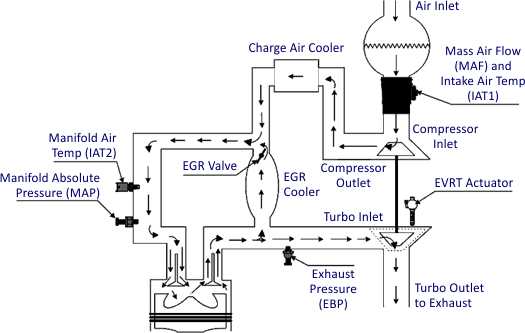
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is an essential component of the 6.0 Powerstroke engine in reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency. However, like any system, it is prone to issues that can lead to performance problems and even engine failure if not addressed promptly.
One of the most common issues with the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system is the buildup of carbon deposits. Over time, the recirculated exhaust gases can leave behind carbon deposits in the EGR cooler, EGR valve, and intake manifold. These deposits can restrict airflow, causing reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and even engine overheating. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the EGR system can help prevent these issues.
EGR cooler failure is another common problem with the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system. The cooler is responsible for cooling down the recirculated exhaust gases before they are reintroduced into the combustion chamber. However, the high temperatures and pressure can cause the cooler to crack, leading to coolant leaks or exhaust gas leaks. These leaks can result in white smoke from the exhaust, coolant loss, and engine coolant contamination. Replacing the EGR cooler is necessary to resolve this issue.
EGR valve malfunction is also a common issue that can affect the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system. The valve regulates the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. If the valve becomes stuck or fails to open or close properly, it can disrupt the EGR system’s operation. This can lead to rough idling, engine misfires, reduced power, and increased emissions. Cleaning or replacing the EGR valve is typically required to fix this problem.
Additionally, the EGR pressure sensor can fail on the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system. The sensor is responsible for monitoring the pressure of the exhaust gases within the system. If the sensor malfunctions, it can cause incorrect readings and improper operation of the EGR system. This can result in decreased engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and even triggering the check engine light. Replacing the faulty EGR pressure sensor is necessary to resolve this issue.
In summary, the 6.0 Powerstroke EGR system can experience various issues, including carbon deposit buildup, EGR cooler failure, EGR valve malfunction, and EGR pressure sensor failure. Regular maintenance, cleaning, and timely replacement of faulty components are essential in ensuring the proper operation of the EGR system and maintaining the performance of the engine.
How to diagnose EGR system problems in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine

The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system plays a crucial role in the operation of the 6.0 Powerstroke engine. However, like any other component, it can experience problems over time. It is important to be able to diagnose these problems in order to ensure that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
1. Check for engine performance issues: One of the first signs of an EGR system problem is a decrease in engine performance. If you notice a lack of power, rough idling, or poor fuel efficiency, these could be indicators of a faulty EGR system. It is important to take note of any changes in engine performance and address them promptly.
2. Inspect the EGR valve: The EGR valve is a key component of the EGR system and can often be the source of problems. Inspect the valve for any signs of wear, damage, or carbon buildup. A stuck or clogged EGR valve can prevent the proper recirculation of exhaust gases, leading to engine issues. Clean or replace the valve as necessary.
3. Check for EGR cooler leaks: The EGR cooler is responsible for cooling the exhaust gases before they are recirculated back into the engine. Over time, the cooler can develop leaks, causing a loss of coolant and potential engine damage. Inspect the cooler for any signs of leakage and repair or replace it if necessary.
4. Scan for error codes: Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostic systems that can provide valuable information about the condition of various engine components, including the EGR system. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any error codes related to the EGR system. These codes can help pinpoint the source of the problem and guide the diagnostic process.
5. Check for clogged EGR passages: The EGR system relies on a series of passages to direct the exhaust gases to the intake manifold. Over time, these passages can become clogged with carbon deposits, obstructing the flow of gases. Use a suitable cleaner or a brush to remove any buildup from the EGR passages and ensure proper flow.
6. Inspect the EGR pressure sensor: The EGR pressure sensor monitors the pressure of the exhaust gases in the EGR system. If the sensor is malfunctioning, it can cause incorrect readings and result in engine performance issues. Inspect the sensor for any signs of damage or corrosion and replace it if necessary.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose EGR system problems in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine. Addressing these issues promptly will help maintain the engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall reliability.
Steps to clean or replace the EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine
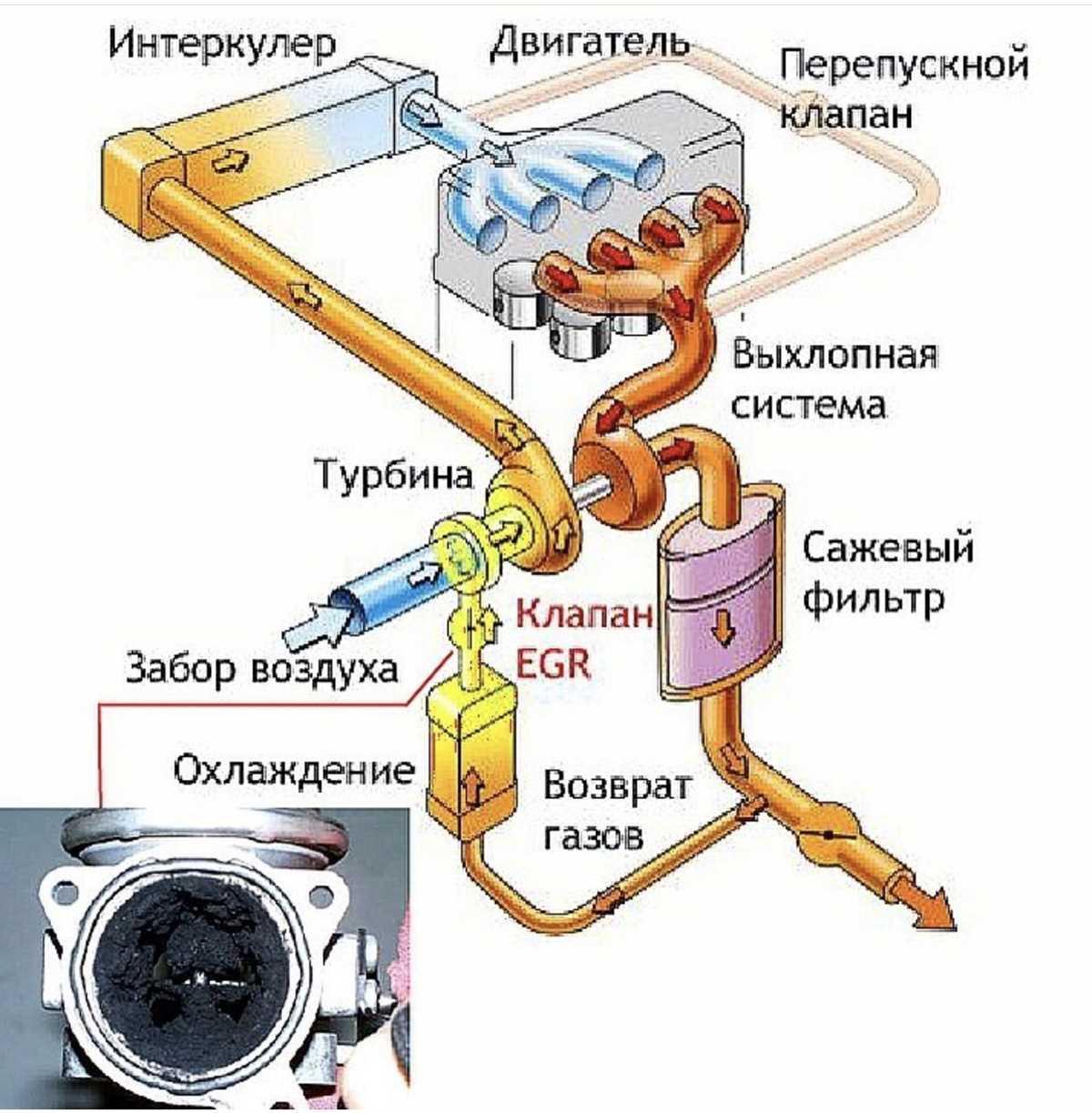
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine plays a crucial role in reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency. However, over time, carbon deposits can build up in the EGR system, leading to reduced performance and potentially causing engine problems. Cleaning or replacing the EGR system is an important maintenance task to ensure the optimal operation of the engine.
Step 1: Identify the EGR system components
Before cleaning or replacing the EGR system, it is essential to locate and identify the different components. The EGR valve, EGR cooler, EGR tube, and associated hoses are the main parts of the system that need attention. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or an EGR system diagram specific to the 6.0 Powerstroke engine for guidance.
Step 2: Remove the EGR valve
To clean or replace the EGR valve, start by disconnecting the negative battery cable to ensure safety. Locate the EGR valve and disconnect any electrical connectors or vacuum lines attached to it. Remove the bolts or screws securing the EGR valve in place, and gently pull the valve out of its mounting. Inspect the valve for any damage or signs of carbon buildup.
Step 3: Clean or replace the EGR valve
If the EGR valve is still in good condition, it can be cleaned by using an appropriate cleaner, such as a carburetor or EGR cleaner. Follow the instructions on the cleaner’s packaging and use a brush or cloth to remove carbon deposits from the valve. If the valve is damaged or heavily clogged, it is advisable to replace it with a new one to ensure optimal performance.
Step 4: Clean the EGR cooler and tube
The EGR cooler and tube can also accumulate carbon deposits over time, affecting their efficiency. Remove the EGR cooler and tube by disconnecting any mounting hardware and hoses. Use a brush and cleaner to remove carbon buildup from the surfaces and passages. Pay attention to any signs of damage or leaks, and replace the components if necessary.
Step 5: Reassemble the EGR system
After cleaning or replacing the necessary components, reassemble the EGR system in the reverse order of disassembly. Make sure all connections are secure and properly tightened. Reconnect any electrical connectors or vacuum lines to the EGR valve, and don’t forget to reconnect the negative battery cable.
Step 6: Test the EGR system
Before considering the cleaning or replacement process complete, it is essential to test the EGR system for proper operation. Start the engine and let it idle, and listen for any unusual noises or vibrations. Monitor the engine’s performance and check for any error codes using a diagnostic tool. If everything appears to be working correctly, the EGR system cleaning or replacement is considered successful.
Tips for maintaining the EGR system in the 6.0 Powerstroke engine
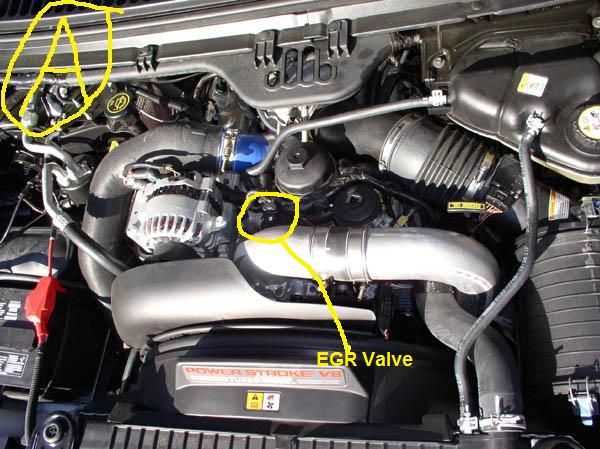

The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is an important component of the 6.0 Powerstroke engine, helping to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. However, it is also prone to issues and can cause various problems if not properly maintained. Here are some tips to ensure the EGR system in your 6.0 Powerstroke engine remains efficient and trouble-free:
- Regular Inspection: It is important to regularly inspect the EGR system for any signs of wear, damage, or buildup. Look for leaks, cracks, or loose connections in the EGR valve, cooler, and tubing. Clean or replace any components that show signs of clogging or contamination.
- Clean or Replace the EGR Valve: The EGR valve is a critical part of the system and can get clogged with carbon deposits over time. Regularly clean or replace the EGR valve to maintain its proper functioning. Use an EGR valve cleaner or follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for cleaning.
- Keep the EGR Cooler Clean: The EGR cooler can also accumulate carbon deposits and become clogged, affecting the performance of the EGR system. Regularly clean the EGR cooler using a suitable cleaning solution and ensure it is free from obstructions.
- Monitor Coolant and Oil Quality: The EGR system relies on the proper flow of coolant and lubrication oil. Monitor the coolant and oil quality regularly and ensure they are within the recommended levels and free from contamination. Replace coolant and oil as needed and address any cooling system or oil leak issues promptly.
- Consider EGR Delete: If you frequently experience problems with the EGR system or are looking for improved performance, consider installing an EGR delete kit. This modification removes the EGR system from the engine, eliminating potential issues associated with it.
By following these tips for maintaining the EGR system in your 6.0 Powerstroke engine, you can ensure its efficient operation, reduce the risk of breakdowns, and prolong the engine’s lifespan. Regular inspection, cleaning, and proper fluid maintenance are key to keeping the EGR system in optimal condition.