
Start by identifying the six necessary connections to ensure proper functionality of your surveillance setup. First, focus on providing power to the unit through a direct link from your power source to the device. The second connection involves the transmission of video data, which should be established through the correct signal path to avoid interference or poor-quality footage.
Make sure to connect the ground system properly, as this will minimize electrical noise and potential damage. For the fourth link, ensure the data transmission is stable and secure by using high-quality cables. The fifth connection involves the additional channels that enhance the range and quality of your system. Finally, make sure to link your setup to the monitoring hub, ensuring each segment is functioning independently but within the network.
Using these six essential connections, you can create a reliable and efficient surveillance network. Double-check each step, and always use the appropriate connectors and power sources to avoid complications.
6-Conductor Setup for Monitoring Systems
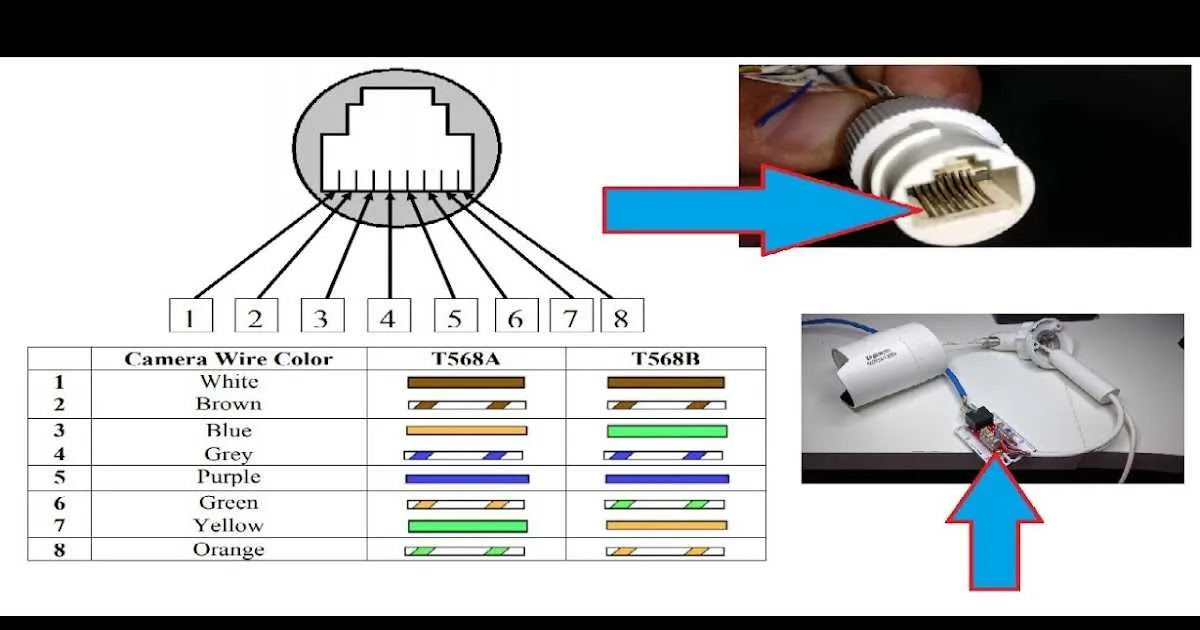
For a robust installation of a surveillance system with six connections, ensure the following sequence: connect the power, video output, ground, and control lines to the respective terminals. The fifth conductor should be assigned to transmit audio signals, while the sixth will handle the trigger or alarm output, depending on your model.
Start by securely linking the positive and negative power lines to ensure proper energy flow. Then, connect the video output to the display unit for real-time monitoring. A solid ground connection is crucial to prevent interference.
Next, use the fifth cable for transmitting audio if your unit supports two-way communication. This line should be routed to the appropriate audio receiver, ensuring proper synchronization between video and sound.
Lastly, the sixth conductor will either manage alarm triggers or activate preset recording actions. Depending on your setup, this could be configured to alert you of detected motion or to initiate remote monitoring features.
Keep all connections well-organized and insulated to avoid signal degradation and ensure long-term functionality. Proper grounding is essential to maintain stability and clarity across all channels.
How to Connect Power and Video Cables for a 6-Wire System
For optimal setup, ensure that the power cable is securely connected to the main unit, with a solid ground connection. This is crucial for consistent voltage flow to all components.
The video signal needs to be transmitted through a dedicated channel, with each line clearly marked for positive and negative polarity. Match the terminals accordingly to avoid signal loss or interference.
Use a power injector if required, to boost the voltage, ensuring that the system runs smoothly without flickering or interruptions. This is especially useful for long-distance connections.
For a clean setup, ensure that the video and power lines are run separately, keeping them away from each other to minimize the risk of cross-talk or electrical interference.
Lastly, always verify that the connection points are secure, and there are no exposed ends that could lead to shorts or degraded performance.
Identifying and Installing the 6-Wire Connections in Your Setup
Begin by clearly distinguishing each of the six essential conductors. You will typically encounter the following types:
- Power (12V DC or 24V AC) – This is essential for operation. Ensure correct polarity when connecting.
- Ground – Commonly marked as “GND,” this provides a return path for current.
- Video Signal – Usually the main feed, this transports the visual data from the device to the recorder or monitor.
- Audio Signal – If supported, this line carries sound information. It may be optional depending on your setup.
- Data/Control – This channel is responsible for communication between components, such as PTZ controls or motion detection signals.
- Alarm or Trigger – This line is often used to send an alert or activate other systems based on a specific event.
To properly connect these elements, follow these steps:
- Start with the power and ground connections, ensuring they are firmly secured. Incorrect connections here may cause malfunction.
- Next, identify the video and audio conductors. Connect the video cable to the main display or recorder port, and if necessary, link the audio to the appropriate input.
- For data or control lines, refer to your equipment’s manual to determine the exact pinout for specific functionality. Proper handling of these is critical for communication accuracy.
- The alarm or trigger cable should be connected to a relay or alarm system, if applicable. This allows for event-based notifications.
- Once all cables are linked, double-check each connection for stability and accuracy, ensuring none of the contacts are loose.
Testing the system before finalizing the installation is crucial. Verify each element by powering up and ensuring all signals are transmitted correctly to the monitoring stations or recorders.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues in 6-Conductor Systems
Ensure all connections are tightly secured. Loose terminals or improperly inserted plugs can cause intermittent signals or complete failure. Double-check each terminal to confirm proper attachment.
If there’s no power, inspect the power source and connections leading to the unit. Low voltage or unstable power can result in malfunction. Use a multimeter to verify voltage at the source and along the connections.
For distorted images or blackouts, check for any short circuits. If any conductor is frayed or touching another, this may create interference. Replace damaged sections and isolate wires to avoid contact.
Signal loss between units may be due to poor grounding. Test the grounding of the system to ensure it’s properly connected to the earth. If grounding is inconsistent, try using a dedicated grounding wire to improve performance.
Examine the connectors for any oxidation or corrosion. If present, clean the metal surfaces or replace damaged parts. Corroded connectors can significantly degrade performance, leading to poor signal integrity.
If there is poor image quality or pixelation, consider checking the distance between components. Excessive length of conductors can reduce signal strength. If needed, reduce the distance or use signal amplifiers to compensate for the loss.
For intermittent functionality, it’s essential to verify the integrity of the power and data connections. Fluctuating connections or fluctuating power levels can disrupt operation. Ensure these components are securely connected and free of damage.