Having a reliable and stable power supply is crucial in today’s world of electronic devices. Whether you are working on a small DIY project or a complex electronic circuit, a regulated power supply is essential to ensure proper functionality and performance. One of the most commonly used power supply circuits is the 12v DC regulated power supply circuit.
This circuit is designed to provide a constant voltage of 12 volts DC, regardless of load variations or input voltage fluctuations. It is widely used in various electronic applications, such as automotive electronics, robotics, and telecommunications.
The working principle of the 12v DC regulated power supply circuit involves converting the AC voltage from the mains into a stable DC voltage. This is achieved through a series of components, including a transformer, rectifier, and regulator. The transformer steps down the high voltage from the mains to a lower voltage, typically around 12 volts. The rectifier converts the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), and the regulator ensures a constant output voltage regardless of load changes.
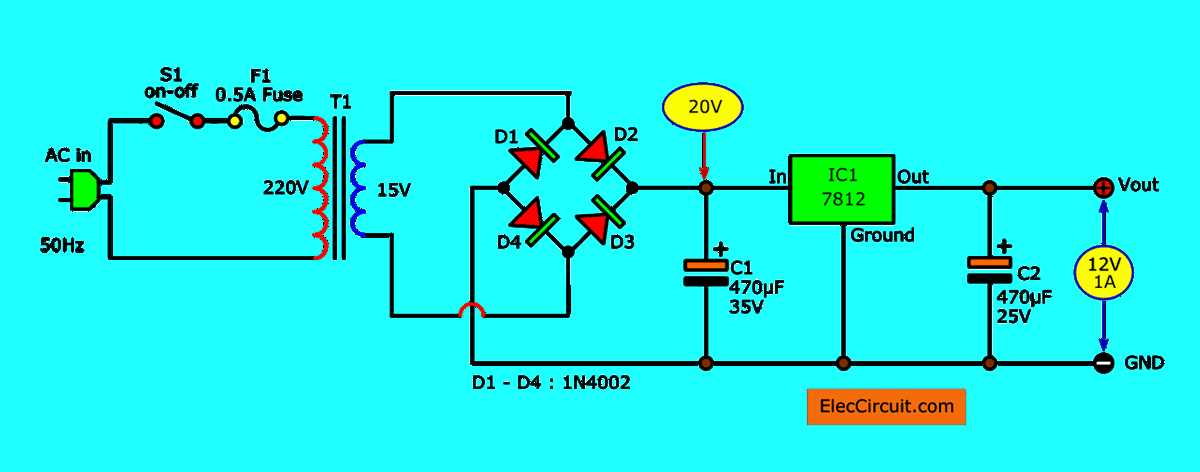
The circuit diagram of the 12v DC regulated power supply typically includes components such as a transformer, rectifier bridge, filter capacitor, and voltage regulator IC. The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains and provides an output voltage of around 12 volts. The rectifier bridge converts the AC voltage to DC voltage, and the filter capacitor smoothens the output voltage by removing any ripples. The voltage regulator IC ensures a constant output voltage of 12 volts, even with load variations or input voltage fluctuations.
12V DC Regulated Power Supply Circuit Diagram
A regulated power supply is an essential component in many electronic devices and circuits as it provides a stable and constant voltage to power them. One commonly used circuit is the 12V DC regulated power supply. This circuit diagram shows the components and connections needed to create such a power supply.
The circuit begins with a transformer that converts the incoming AC voltage to a lower AC voltage. This lower voltage is then rectified using a bridge rectifier, which converts it to a pulsating DC voltage. The rectified voltage is then smoothed using a capacitor, which makes it into a more stable DC voltage.
Components:
- Transformer: This component steps down the AC voltage from the mains to a lower voltage.
- Bridge rectifier: The rectifier converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC voltage.
- Filter capacitor: The capacitor smooths the rectified voltage and makes it more stable.
- Regulator: This component regulates the voltage to a constant 12V DC.
- Output capacitor: The output capacitor filters any remaining ripples in the voltage.
Circuit Operation:

The transformer steps down the mains AC voltage to a lower voltage suitable for rectification. The bridge rectifier then converts this lower AC voltage to pulsating DC voltage, which consists of positive and negative half cycles. The filter capacitor smooths out these half cycles, making the rectified voltage more stable.
The regulated voltage is achieved by using a voltage regulator in the circuit. The regulator ensures that the output voltage remains constant at 12V DC, regardless of any fluctuations in the input voltage or load conditions. It achieves this by controlling the current flowing through a series pass transistor or integrated circuit.
The output capacitor connected in parallel to the load serves as a filter to remove any remaining ripples in the voltage, providing a clean and stable 12V DC output. This ensures that the connected electronic devices or circuits receive a consistent and reliable power supply.
Components Needed for the Circuit
In order to build a 12V DC regulated power supply circuit, several components are required. These components play crucial roles in regulating the voltage and ensuring the stability of the power supply. The following is a list of the key components needed:
- Transformer: The transformer is responsible for converting the input voltage to the desired output voltage. In this case, a step-down transformer is required to reduce the voltage from the mains supply to the desired 12V DC output.
- Rectifier: The rectifier circuit is used to convert the AC voltage from the transformer to a pulsating DC voltage. This is achieved through the use of diodes that allow current to flow in only one direction.
- Filter Capacitor: The filter capacitor is used to smoothen the pulsating DC voltage from the rectifier, resulting in a more stable DC output. It helps to reduce the ripple voltage and improve the overall performance of the power supply.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator is the most important component in the circuit as it ensures a constant output voltage regardless of any fluctuations in the input voltage or load variations. There are different types of voltage regulators available, such as linear and switching regulators, which can be selected based on the specific requirements of the power supply.
- Pass Transistor: In some designs, a pass transistor is used together with the voltage regulator to increase the current-handling capacity of the power supply. The pass transistor is responsible for carrying the load current and reducing the stress on the voltage regulator.
- Heat Sink: A heat sink is an essential component to dissipate heat generated by the voltage regulator and pass transistor (if used). It helps to maintain the temperature within acceptable limits and prevent overheating, which can lead to malfunction or damage.
- Circuit Protection Devices: To ensure the safety of the circuit and prevent damage from voltage spikes or short circuits, circuit protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers can be included.
With these components assembled and connected properly, a 12V DC regulated power supply circuit can be constructed that provides a stable and reliable power source for various electronic devices.
Connecting the Components
When building a 12V DC regulated power supply circuit, it is important to connect the components properly in order to ensure the circuit functions correctly. Here are the steps to connect the different components:
1. Connect the Transformer:
Start by connecting the primary winding of the transformer to the AC power source. The secondary winding of the transformer will provide the required 12V DC output.
2. Connect the Bridge Rectifier:
Next, connect the bridge rectifier to the secondary winding of the transformer. The bridge rectifier is responsible for converting the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC).
3. Connect the Filter Capacitor:
After the bridge rectifier, connect the filter capacitor to smooth out the DC output. The filter capacitor helps remove any remaining AC ripple from the rectified DC voltage.
4. Connect the Voltage Regulator:
Once the DC voltage is filtered, connect the voltage regulator to regulate the output voltage to a stable 12V DC. The voltage regulator ensures that the output voltage remains constant, regardless of any fluctuations or changes in the input voltage.
5. Connect the Load:
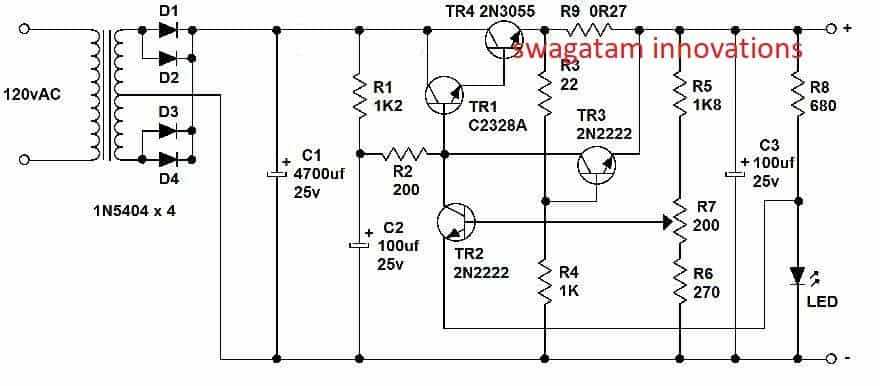
Finally, connect the load to the output of the voltage regulator. The load can be any device or circuit that requires a 12V DC power supply. Make sure to properly size the load and ensure it does not exceed the maximum current rating of the power supply.
Additional Tips:
- Double-check all connections to ensure they are properly secured.
- Use appropriate wire gauges to handle the current requirements of the circuit.
- Consider adding additional protection components, such as fuses or circuit breakers, to protect against overcurrent or short circuits.
Following these steps and taking the necessary precautions will help in successfully connecting the components of a 12V DC regulated power supply circuit.
Working of the Circuit
The 12V DC regulated power supply circuit diagram operates based on the principle of rectification and voltage regulation. The main components of the circuit include a transformer, diodes, capacitors, and voltage regulators.
When the input AC voltage is applied to the transformer, it steps down the voltage to a lower value suitable for the circuit. The transformer’s secondary winding output is then rectified by a bridge rectifier circuit composed of diodes. This converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC voltage.
The rectified DC voltage is then filtered using a capacitor, which smoothens out the voltage waveform and reduces the ripple. The filtered DC voltage is then fed to a voltage regulator circuit, which maintains the output voltage at a constant 12V. The voltage regulator circuit consists of a regulator IC along with capacitors for stability and filtering.
In addition to the voltage regulation, the circuit also includes protection features such as a fuse and a voltage surge suppressor. The fuse protects the circuit from excessive current flow, while the surge suppressor protects against voltage spikes.
The regulated 12V DC output can be used to power various electronic devices and circuits, providing a stable and reliable power source. It is commonly used in applications such as battery chargers, Arduino projects, and automotive electronics.
Advantages of Using a Regulated Power Supply
A regulated power supply offers several advantages over an unregulated power supply:
- Stability: A regulated power supply provides a stable output voltage, even when there are fluctuations in the input voltage or changes in the load. This ensures consistent and reliable operation of electronic devices.
- Protection: Regulated power supplies often include built-in protection mechanisms, such as overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, and short-circuit protection. These safeguards help prevent damage to the power supply and the connected devices.
- Low ripple: Regulated power supplies typically have low ripple and noise levels in their output voltage. This is important for sensitive and analog electronic circuits that require precise and clean power sources.
- Efficiency: Regulated power supplies are designed to be highly efficient, converting the input voltage to the desired output voltage with minimal power loss. This helps reduce energy waste and saves on electricity costs.
- Versatility: A regulated power supply can be easily adjusted or set to different output voltages within its range to accommodate various devices and applications. This makes it a versatile choice for powering a wide range of electronics.
- Reliability: Due to their stable operation and built-in protection features, regulated power supplies are generally more reliable and less prone to failure compared to unregulated power supplies.
In conclusion, using a regulated power supply offers numerous benefits including stability, protection, low ripple, efficiency, versatility, and reliability. Whether it’s for hobby electronics or professional applications, a regulated power supply is an essential component for providing reliable and consistent power to electronic devices.