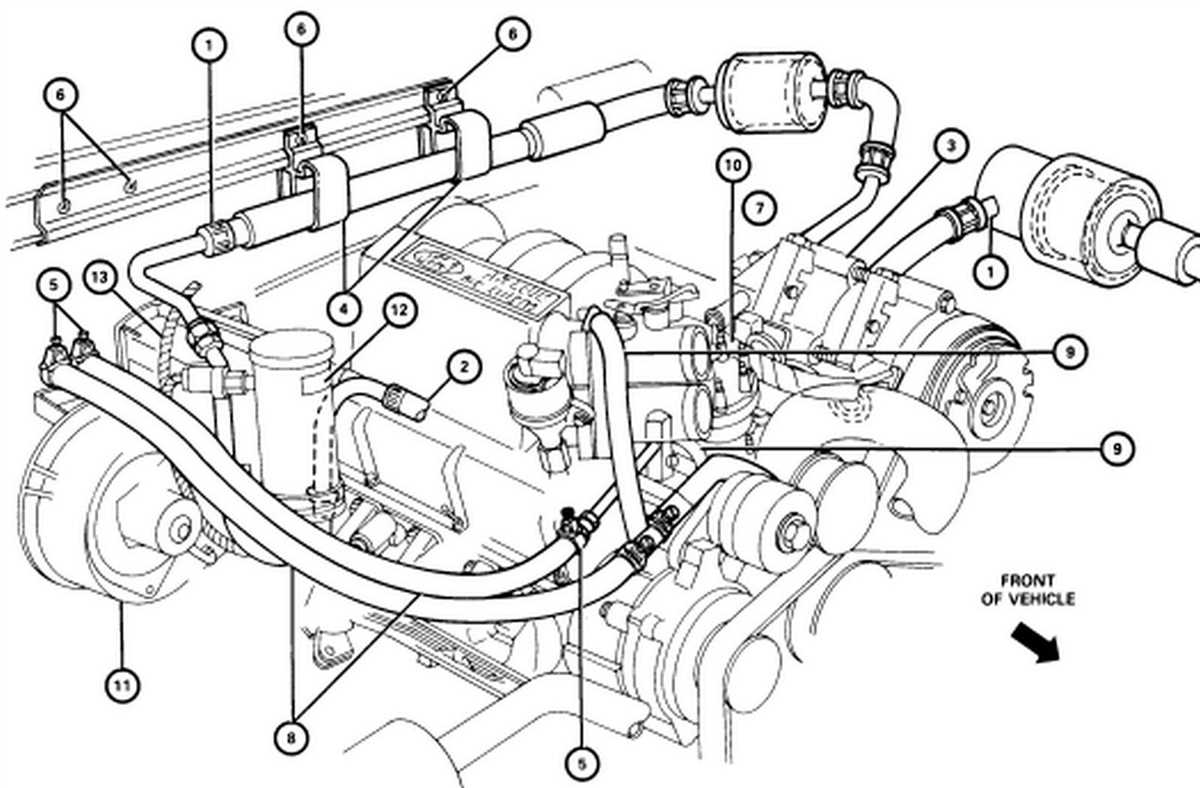
The 2004 Ford F150 is a powerful and reliable truck that has gained a loyal following over the years. One of the standout features of this vehicle is its robust 5.4-liter V8 engine, which provides plenty of horsepower and torque for all your towing and hauling needs. To truly understand the inner workings of this engine, it is essential to have a detailed diagram that breaks down each component and their interconnections.
Firstly, the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine diagram showcases the engine’s main components, such as the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and camshaft. These elements work in harmony to convert the energy from the fuel into mechanical motion. The cylinders provide the space for air and fuel combustion, while the pistons move up and down within the cylinder walls, transferring the force from the combustion to the crankshaft.
Additionally, the diagram also highlights the intake and exhaust systems, which play a crucial role in the engine’s performance. The intake system brings air into the engine, while the exhaust system expels the burnt gases. The diagram shows the paths that the air and gases take, including the intake manifold, throttle body, and exhaust headers.
Furthermore, the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine diagram provides insight into the electrical components that facilitate engine operation. These include the ignition system, which initiates the combustion process by creating a spark, and the fuel injection system, which delivers the fuel to the cylinders. Understanding how these systems interact with the engine’s mechanical components is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
In conclusion, exploring the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine diagram allows enthusiasts and owners to gain a deeper understanding of the inner workings of this powerful truck. From the cylinders to the electrical systems, each component plays a vital role in delivering optimal performance. With this knowledge, owners can better appreciate the craftsmanship and engineering behind the 2004 Ford F150’s impressive engine.
Ford F150 5.4 Engine Diagram: Understanding the Components
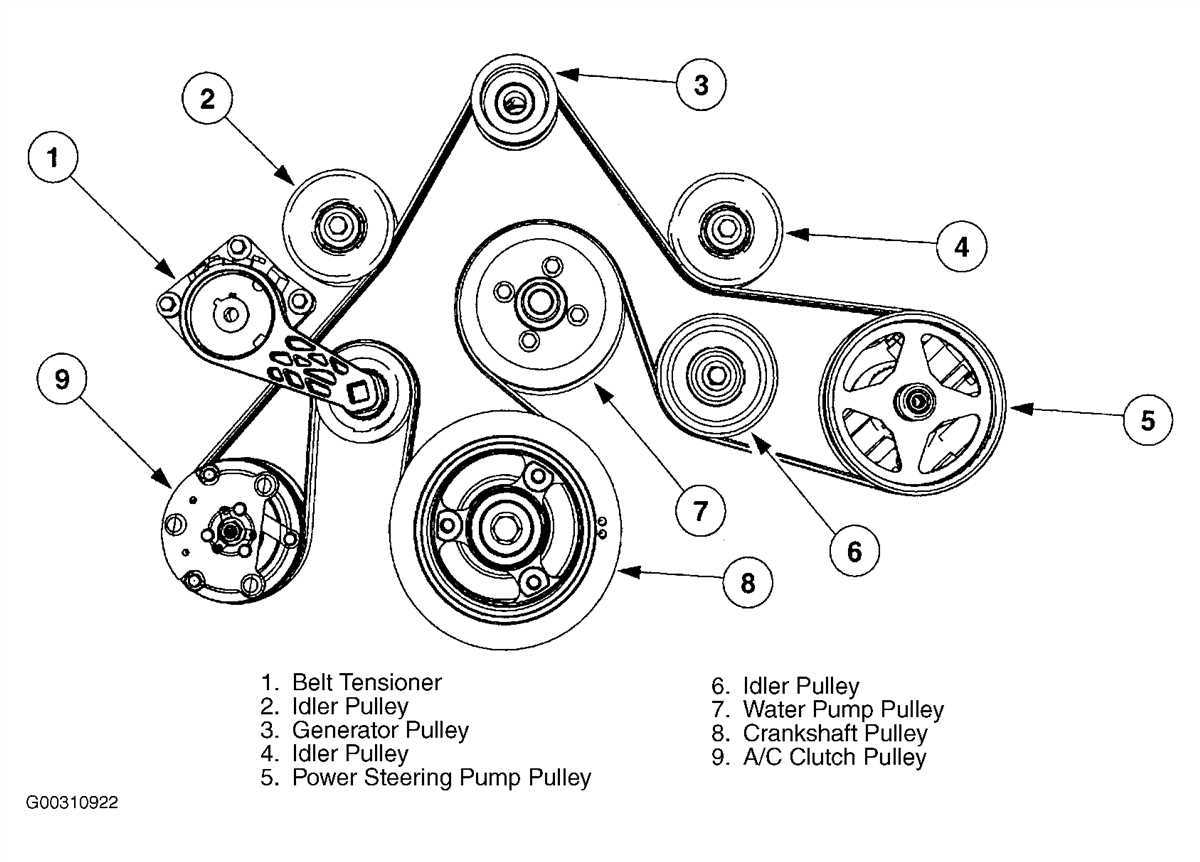
The Ford F150 is a popular truck known for its durability and power. The 5.4-liter engine is one of the options for this vehicle, offering a balance of performance and fuel efficiency. To better understand the inner workings of this engine, it is helpful to examine a diagram that highlights the different components.
Cylinder Block: The cylinder block is the foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders, pistons, and other important components. It is made of cast iron or aluminum and provides the structural integrity needed to handle the powerful combustion forces.
Cylinder Head: Sitting on top of the cylinder block, the cylinder head contains the intake and exhaust valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. It plays a crucial role in the combustion process, ensuring proper air and fuel mixture and efficient exhaust gas evacuation.
Pistons and Connecting Rods: The pistons move up and down inside the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture and generating power. Connected to the pistons are the connecting rods, which transfer the motion to the crankshaft. These components must be strong and precisely balanced to withstand the intense forces.
Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is then transferred to the transmission and wheels. It is a critical component that needs to be precisely machined and balanced to ensure smooth operation and minimize vibrations.
Timing Chain/Belt: The timing chain or belt connects the crankshaft to the camshaft, ensuring proper valve timing. This synchronization is crucial for the engine to operate correctly and efficiently. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent any issues with the timing chain or belt.
Valvetrain: The valvetrain includes the camshafts, valves, and various associated components. The camshafts control the opening and closing of the valves, allowing air and fuel to enter the cylinders and exhaust gases to exit. Proper valve timing and operation are vital for optimal engine performance.
Fuel System: The fuel system supplies the engine with the necessary fuel to operate. It consists of components such as the fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel filter. The 5.4-liter engine utilizes advanced fuel injection technology for precise fuel delivery and improved efficiency.
Ignition System: The ignition system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. It includes components such as spark plugs, ignition coils, and the engine control module (ECM). A reliable ignition system is essential for efficient combustion and overall engine performance.
- Cylinder Block
- Cylinder Head
- Pistons and Connecting Rods
- Crankshaft
- Timing Chain/Belt
- Valvetrain
- Fuel System
- Ignition System
Understanding the components of the Ford F150 5.4 engine diagram provides insight into the engineering behind this powerful and reliable truck engine. Each component has a specific role in the combustion process, and their proper functioning is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the engine.
The Importance of Understanding the Engine Diagram
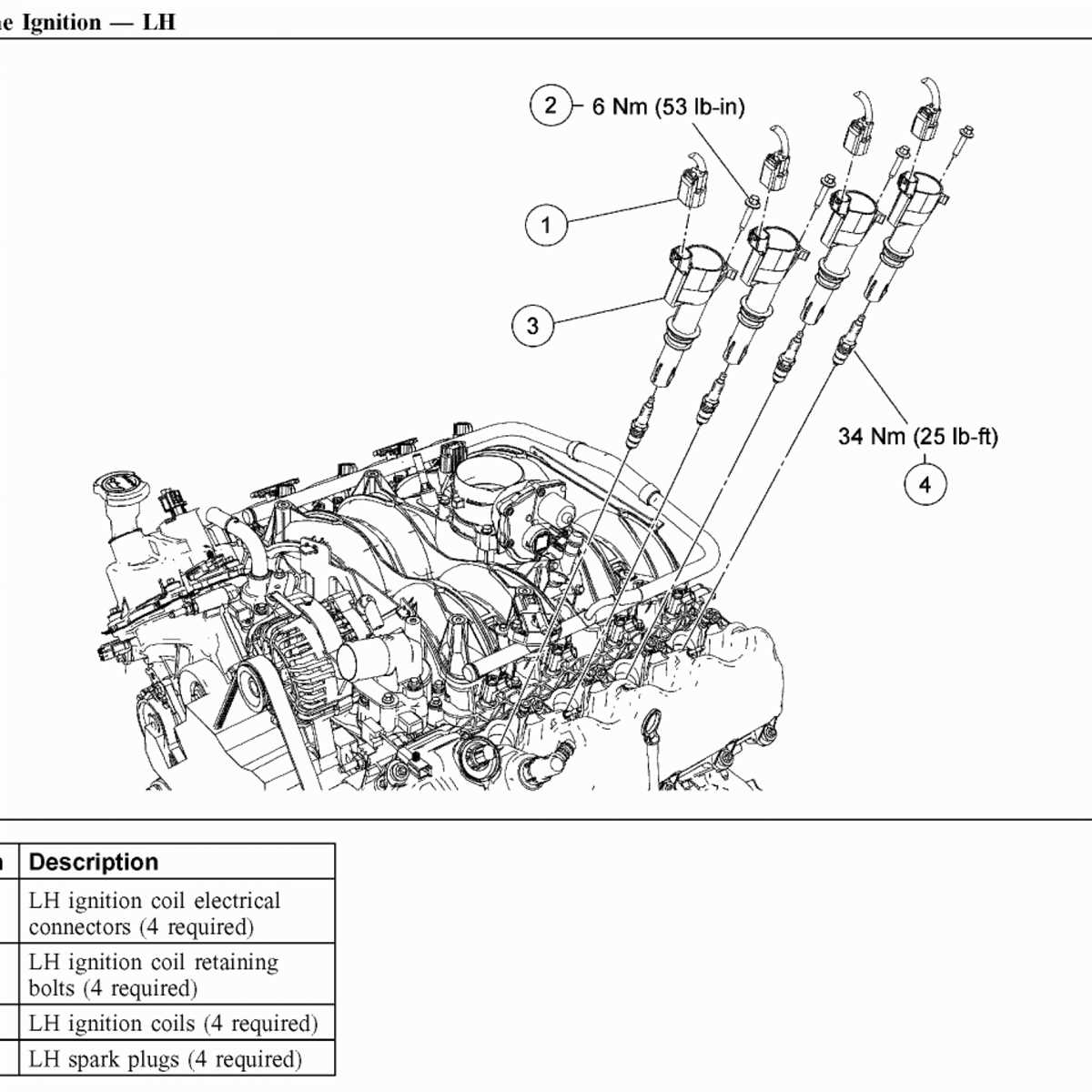
When it comes to troubleshooting and maintaining your vehicle, having a clear understanding of the engine diagram is essential. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, having a visual representation of the engine’s components and their interactions can help you efficiently diagnose problems and perform repairs.
An engine diagram provides a detailed overview of the various parts that make up the engine, including the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and fuel system. It illustrates how these components work together to generate power and propel the vehicle.
Diagnosing Problems: The engine diagram serves as a valuable tool for identifying and addressing issues with your vehicle’s engine. By referencing the diagram, you can easily locate specific parts and understand their function. This knowledge can aid in pinpointing the root cause of the problem and determining the appropriate course of action.
Performing Repairs: Whether you are replacing a faulty part or conducting routine maintenance, an engine diagram can guide you through the process. By following the diagram’s instructions, you can ensure that you disassemble and reassemble the engine correctly, minimizing the risk of errors or damage.
Improving Efficiency: Understanding the engine diagram allows you to gain insights into the engine’s inner workings. This knowledge can help you optimize the engine’s performance and improve fuel efficiency. By knowing how each component affects the engine’s operation, you can make informed decisions regarding modifications or upgrades.
Following Safety Precautions: When working on your vehicle’s engine, safety should always be a top priority. The engine diagram provides information on the location of critical components such as the fuel lines, coolant hoses, and electrical wiring. By familiarizing yourself with these details, you can avoid potential hazards and take appropriate safety measures.
In conclusion, understanding the engine diagram is crucial for efficient troubleshooting, accurate repairs, improved engine performance, and enhanced safety. Whether you own a 2004 Ford F150 with a 5.4 engine or any other vehicle, investing time in studying the engine diagram can pay off in the long run.
Overview of the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 Engine
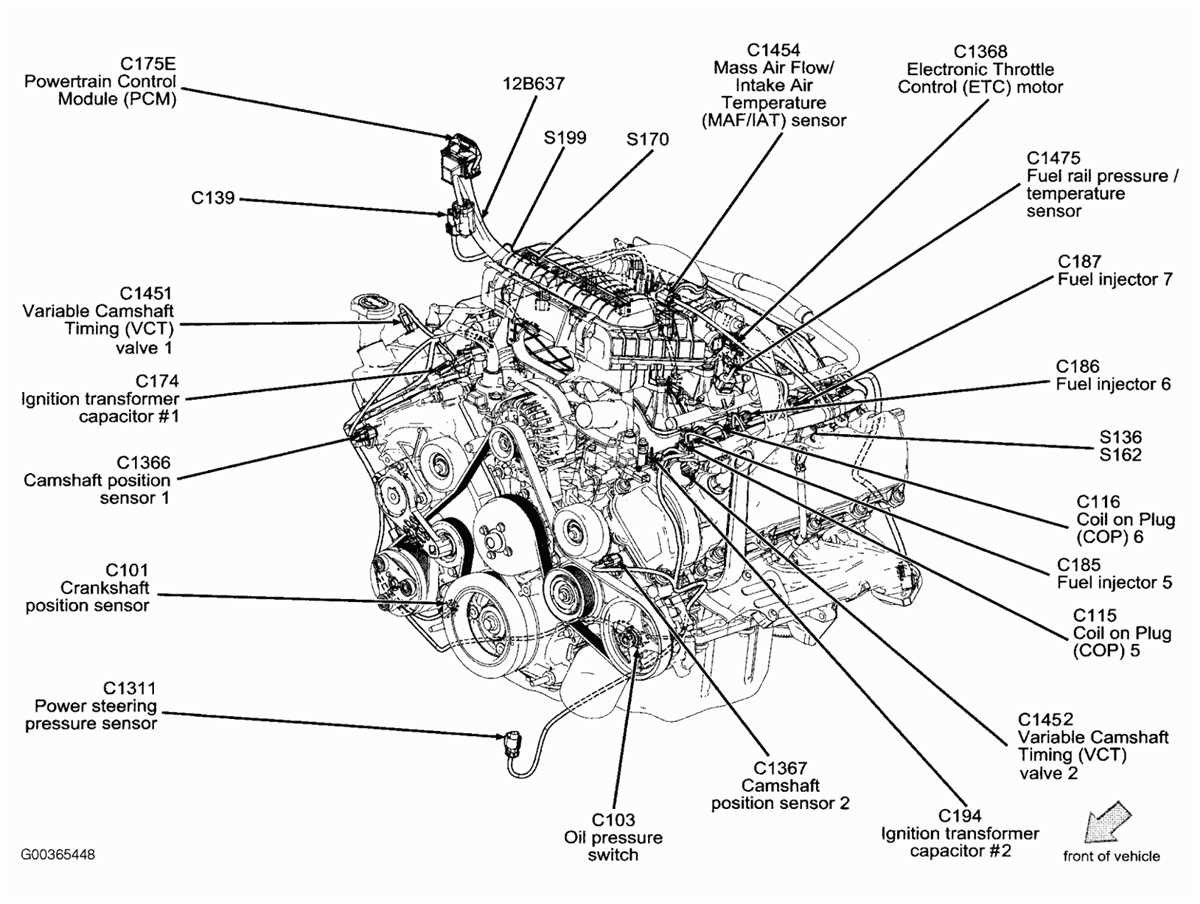
The 2004 Ford F150 is a popular pick-up truck known for its power and reliability. The 5.4-liter engine is one of the engine options available for this model year. It is a V8 engine that provides strong performance and towing capabilities.
This engine is capable of producing up to 300 horsepower and 365 lb-ft of torque, making it a formidable choice for both work and play. It features a cast-iron engine block with aluminum cylinder heads, which helps to reduce weight while maintaining durability.
The 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine also incorporates several advanced technologies to optimize performance and efficiency. It utilizes a multi-point fuel injection system to deliver fuel directly to each cylinder, ensuring precise fuel delivery and combustion.
Additionally, this engine features a variable camshaft timing system, which adjusts valve timing to optimize power output and fuel efficiency across different operating conditions. This technology helps to improve low-end torque and enhance overall engine performance.
In terms of maintenance, the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine requires regular oil changes and inspections to ensure proper functioning. It is also important to check and replace the spark plugs and ignition coils regularly to maintain optimal ignition performance.
Overall, the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine offers a balance of power, durability, and efficiency, making it a reliable choice for those in need of a capable pick-up truck.
Exploring the Engine’s Cylinder Layout
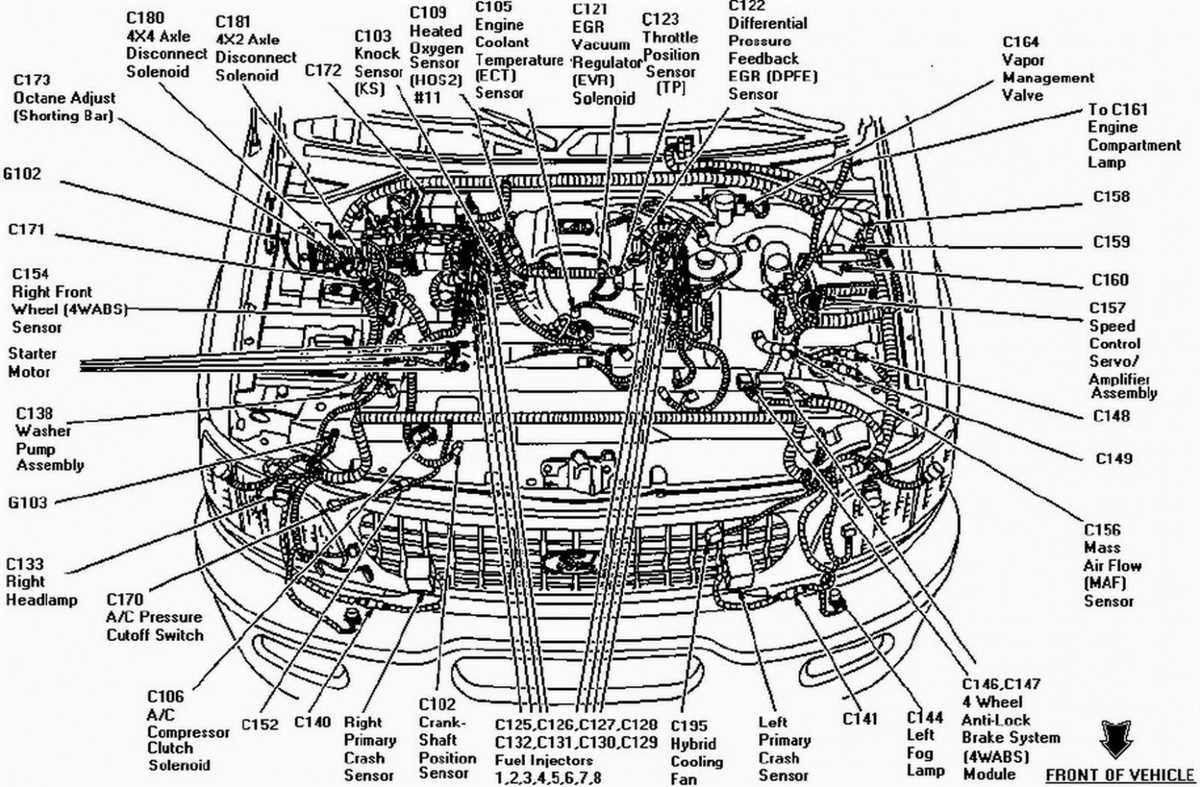
The 2004 Ford F150 is equipped with a 5.4-liter engine, which is known for its power and performance. To understand how this engine operates, it is important to explore its cylinder layout.
The 5.4-liter engine in the 2004 Ford F150 has an eight-cylinder layout, meaning it has eight individual cylinders that work together to power the vehicle. These cylinders are arranged in a V-shape, with four cylinders on each side. This configuration is commonly referred to as a “V8” engine.
The cylinder layout in the 2004 Ford F150’s 5.4-liter engine is as follows:
- Cylinder 1: Located on the driver’s side, front-most cylinder
- Cylinder 2: Located on the driver’s side, second cylinder from the front
- Cylinder 3: Located on the driver’s side, third cylinder from the front
- Cylinder 4: Located on the driver’s side, rear-most cylinder
- Cylinder 5: Located on the passenger side, front-most cylinder
- Cylinder 6: Located on the passenger side, second cylinder from the front
- Cylinder 7: Located on the passenger side, third cylinder from the front
- Cylinder 8: Located on the passenger side, rear-most cylinder
This cylinder layout is important to know when working on the engine, as it determines the firing order and the arrangement of various engine components, such as the spark plugs and fuel injectors. Understanding the layout can also aid in diagnosing and troubleshooting any performance issues that may arise.
Understanding the Fuel Injection System
The fuel injection system in a 2004 Ford F150 with a 5.4 engine is a crucial component that ensures efficient combustion and optimal performance. It is responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine at the right time, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
The fuel injection system consists of several key components, including the fuel injectors, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, and the engine control module (ECM). These components work together to deliver fuel to the engine in a controlled manner, providing the necessary fuel-air mixture for combustion.
Fuel Injectors
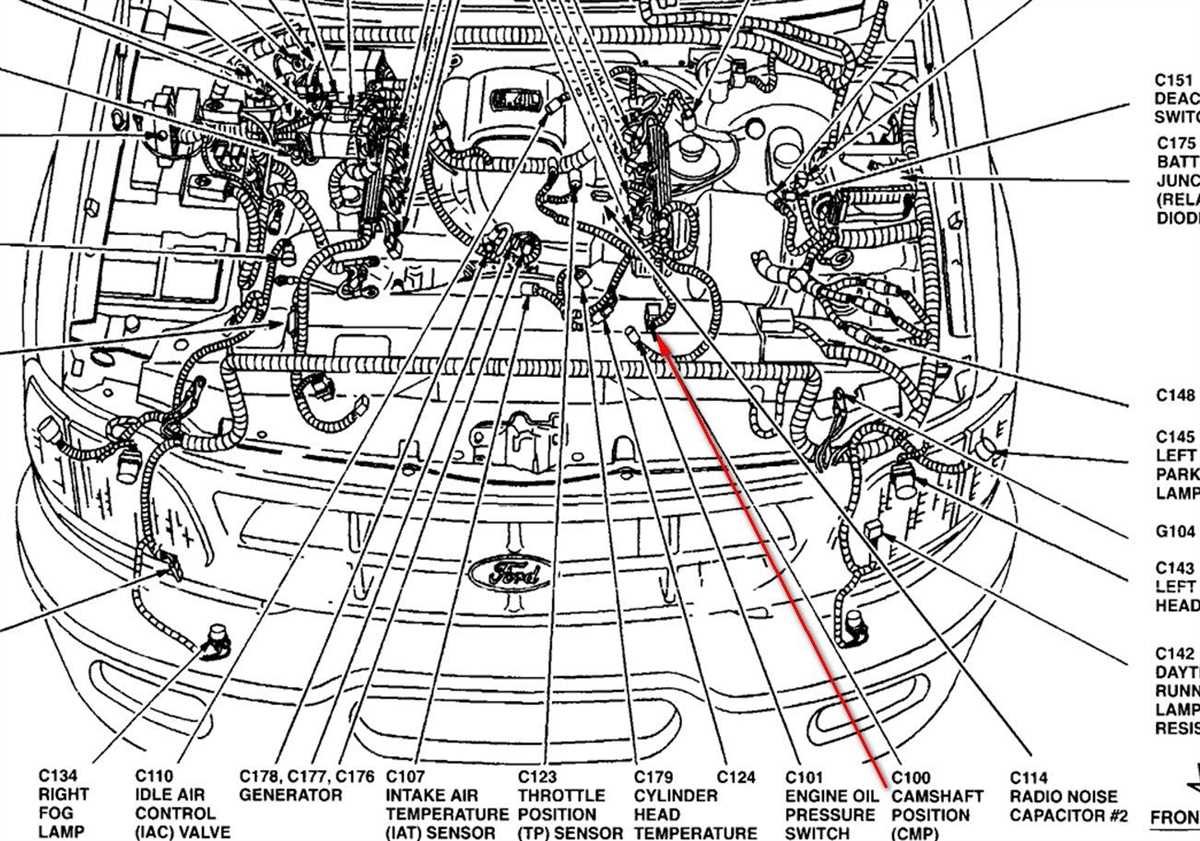
The fuel injectors are responsible for spraying the pressurized fuel into the engine’s intake manifold or directly into the combustion chambers. They are controlled by the ECM, which monitors various engine parameters to determine the amount of fuel to be injected. The fuel injectors ensure that the fuel is atomized into fine particles, allowing for better combustion and power output.
Fuel Pump
The fuel pump is responsible for supplying pressurized fuel from the fuel tank to the fuel injectors. It is typically located inside the fuel tank and is powered by electricity from the vehicle’s battery. The fuel pump maintains a constant fuel pressure, ensuring a steady flow of fuel to the injectors.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
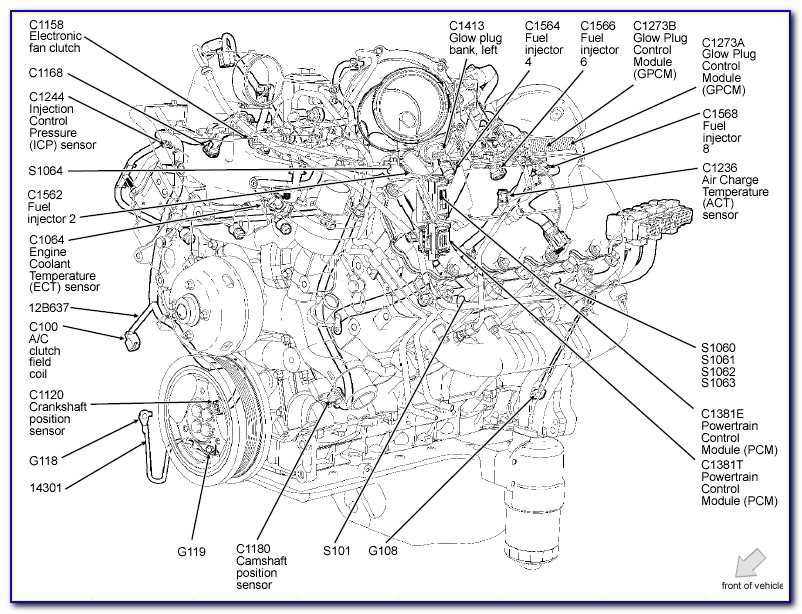
The fuel pressure regulator is responsible for maintaining the correct fuel pressure in the fuel injection system. It is usually located on the fuel rail and regulates the amount of fuel that is returned to the fuel tank. The fuel pressure regulator ensures that the fuel pressure remains within the specified range, allowing for proper fuel delivery and combustion.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is the brain of the fuel injection system. It receives input from various sensors, such as the oxygen sensor and throttle position sensor, and uses this information to determine the fuel injection timing and duration. The ECM also controls other aspects of the engine’s operation, such as ignition timing and idle speed. It constantly adjusts the fuel injection system for optimal performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding the fuel injection system in a 2004 Ford F150 with a 5.4 engine is essential for maintaining and optimizing its performance. The fuel injectors, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, and ECM work together to ensure efficient fuel delivery and combustion, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Examining the Ignition System
The ignition system is a crucial component of the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine, responsible for starting and providing the necessary spark to ignite the fuel mixture in the combustion chambers. Understanding how the ignition system works and its various components can help diagnose and resolve any issues that may arise.
The main components of the ignition system include the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug wires, distributor (for older models), and the ignition control module. These components work together to generate and deliver the high voltage spark required to ignite the air-fuel mixture in each cylinder.
The ignition coil is the heart of the ignition system, converting the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage necessary for spark production. It consists of two coils, a primary and secondary coil, which are wrapped around each other and connected to the battery. When the primary coil receives a current, it generates a magnetic field that causes the secondary coil to produce an even higher voltage.
The spark plugs are responsible for actually igniting the fuel mixture. They are located in each combustion chamber and receive the high voltage spark from the ignition coil via the spark plug wires. The spark created by the spark plug jumps the gap between the center and ground electrode, igniting the compressed fuel mixture and starting the combustion process.
The ignition control module, also known as the ignition module or ignition control unit, plays a critical role in controlling the timing and intensity of the spark. It receives signals from various sensors in the engine, such as the crankshaft position sensor or camshaft position sensor, and uses this information to determine the ideal timing for spark ignition. It then sends the necessary signals to the ignition coil to generate the spark at the precise moment.
Summary:
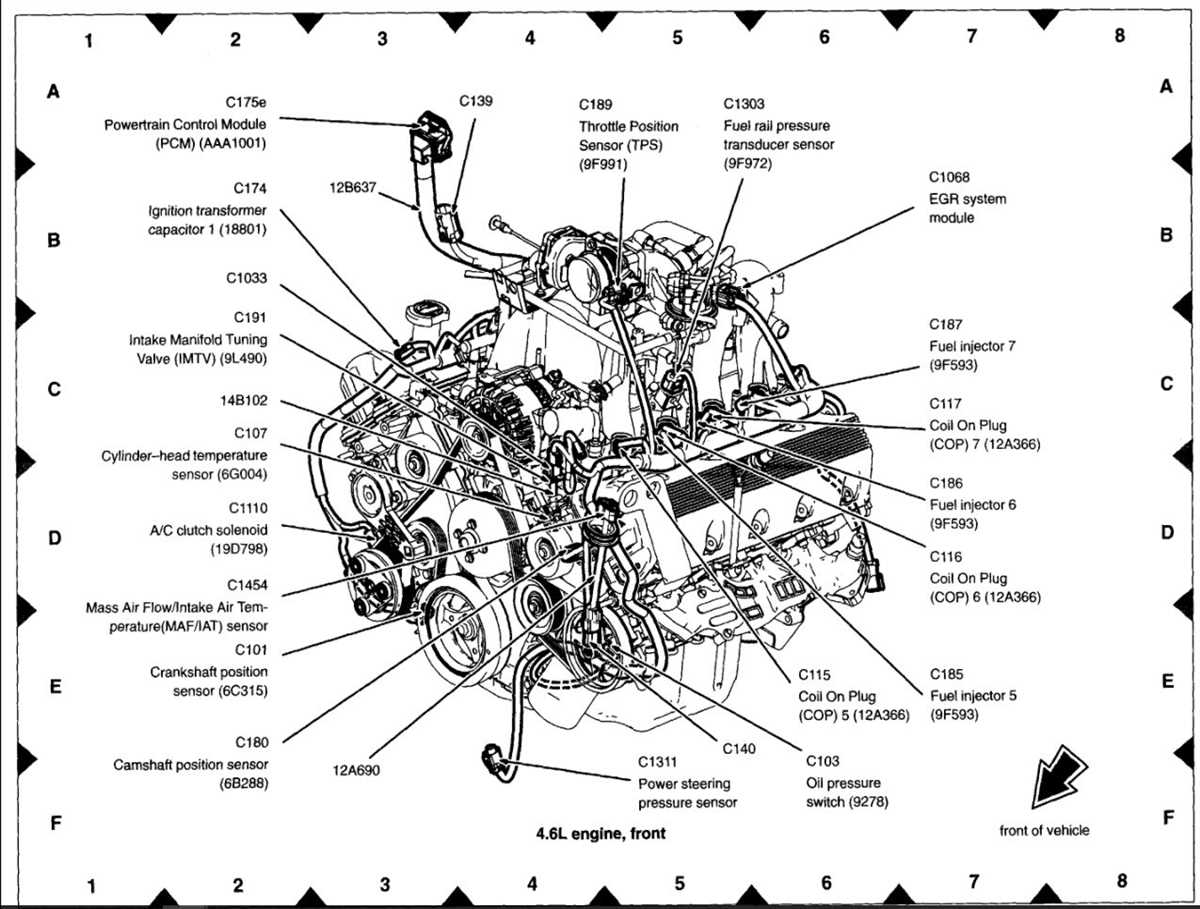
- The ignition system in the 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine consists of several components, including the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug wires, distributor (on older models), and the ignition control module.
- The ignition coil is responsible for converting the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage required for spark production.
- The spark plugs receive the high voltage spark from the ignition coil and ignite the fuel mixture in each combustion chamber.
- The ignition control module plays a vital role in controlling the timing and intensity of the spark, using input from engine sensors to determine the ideal timing for spark ignition.
Diving into the Engine Cooling System
The engine cooling system in a 2004 Ford F150 5.4 engine is a crucial component that helps regulate the engine temperature and prevent overheating. It consists of various parts working together to circulate coolant and dissipate heat generated by the engine.
One of the key components of the cooling system is the radiator, which is responsible for cooling the coolant fluid. The coolant flows through the small tubes inside the radiator, while air passes through the radiator fins, removing heat from the coolant. This process is enhanced by the radiator fan, which helps to increase airflow through the radiator when the vehicle is stationary or moving at low speeds. The radiator also has a pressure cap that maintains the desired pressure in the cooling system.
The water pump is another critical component of the cooling system. It is driven by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft and circulates the coolant through the engine block and cylinder heads. The water pump pushes the coolant into the engine, where it absorbs heat generated during the combustion process, and then returns it to the radiator for cooling.
Other important parts of the cooling system include the thermostat, which regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine temperature, and the heater core, which is responsible for providing warm air to the vehicle’s cabin. The thermostat opens and closes to allow or restrict coolant flow depending on the engine temperature, helping to maintain the optimal operating temperature. The heater core is a small radiator-like component located inside the vehicle’s cabin. Hot coolant flows through it, and air blown over the heater core warms up before entering the cabin.
Overall, the engine cooling system is essential for maintaining the proper operating temperature of the engine. It plays a vital role in preventing overheating, which can lead to severe engine damage. Regular maintenance and inspection of the cooling system, such as checking coolant levels, replacing worn-out components, and cleaning the radiator, are necessary to ensure its efficient operation and prolong the life of the engine.
Q&A:
What is the engine cooling system?
The engine cooling system is a vital component of a vehicle that helps regulate and maintain the optimal temperature of the engine.
How does the engine cooling system work?
The engine cooling system works by circulating coolant through the engine and radiator. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine and then releases it through the radiator, where it is cooled by airflow.
What is coolant?
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, is a liquid that helps regulate the temperature of the engine by absorbing heat and transferring it to the radiator for dissipation.
What are common problems with the engine cooling system?
Common problems with the engine cooling system include coolant leaks, a malfunctioning thermostat, a faulty water pump, and clogged radiator or hoses.
How often should I check and maintain my engine cooling system?
It is important to regularly check and maintain your engine cooling system, including checking the coolant level, inspecting for leaks, and flushing and replacing the coolant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
What is the purpose of the engine cooling system?
The purpose of the engine cooling system is to regulate the temperature of the engine and prevent it from overheating. It helps remove excess heat from the engine and maintain it at an optimal operating temperature.
How does the engine cooling system work?
The engine cooling system typically consists of a radiator, coolant pump, thermostat, and coolant passages. The coolant is circulated through the engine by the pump, absorbing heat. It then flows to the radiator where it is cooled by air or a separate cooling system before being returned to the engine. The thermostat helps regulate the coolant flow and temperature.