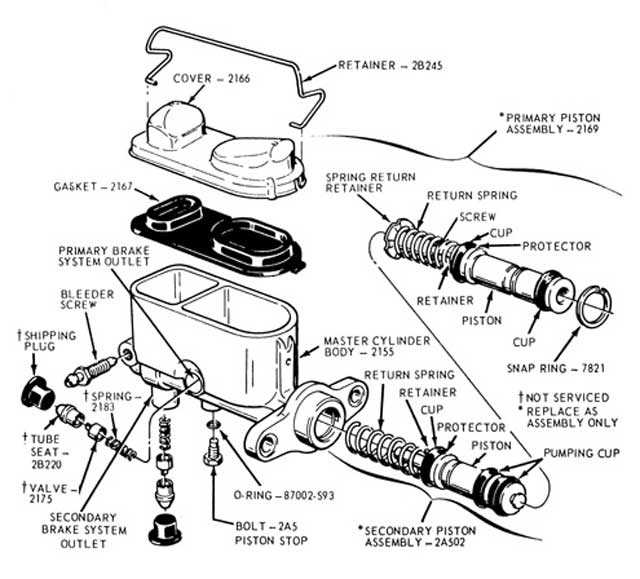
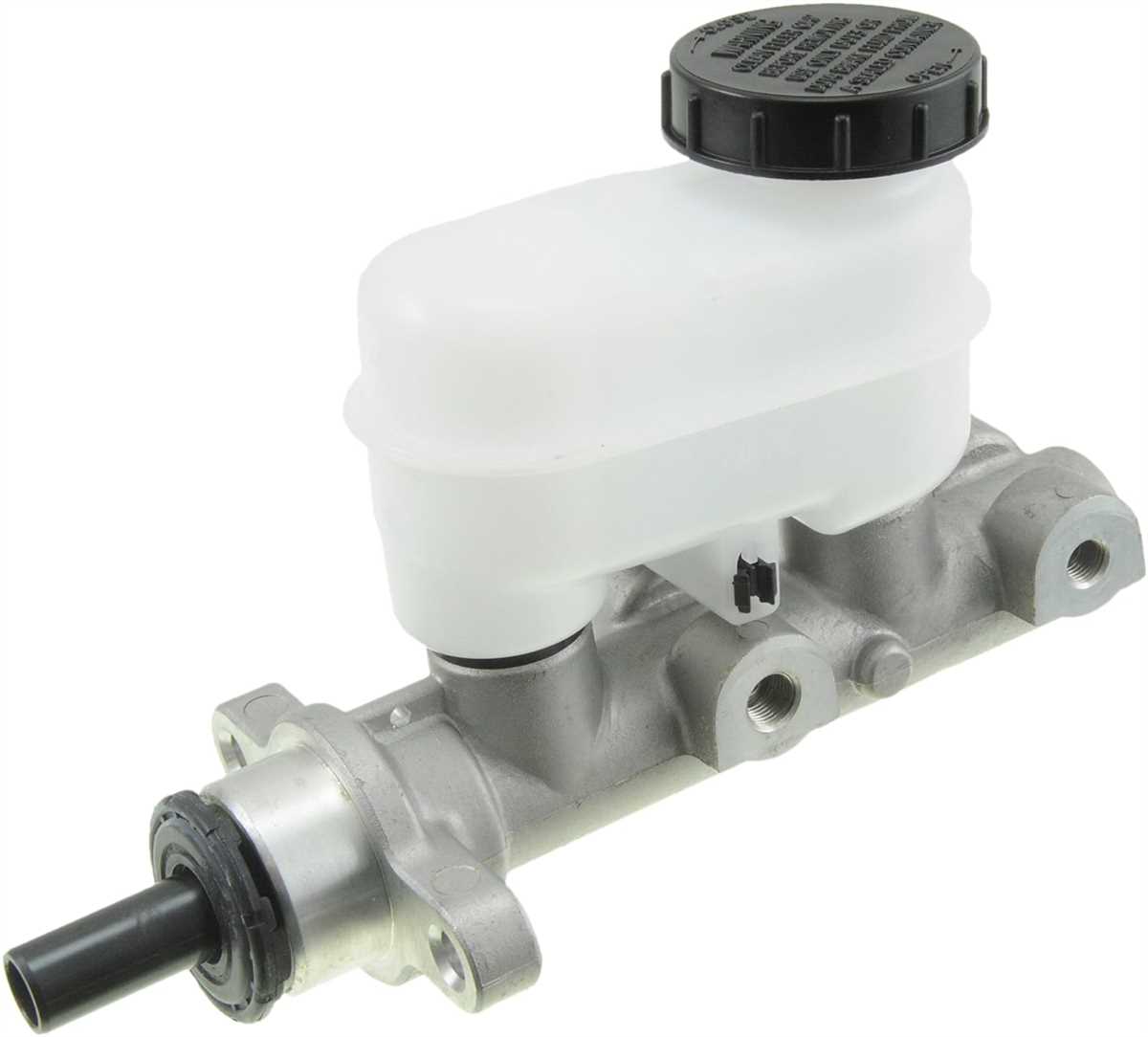
The brake master cylinder is an essential component of a vehicle’s braking system, responsible for converting the pressure applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure that is then transferred to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. One of the most well-known manufacturers of brake master cylinders is Lockheed.
A brake master cylinder diagram helps in understanding the internal components and their functions within the brake master cylinder. It provides a visual representation of how the master cylinder works, allowing technicians and enthusiasts to diagnose and troubleshoot brake issues effectively.
The diagram typically shows the main parts of the master cylinder, including the reservoir, cylinder bore, piston, seals, and ports. By understanding how these components interact, it becomes easier to identify potential problems such as leaks, air bubbles, or inadequate pressure within the braking system.
Lockheed brake master cylinder diagrams are also useful for those who are interested in learning more about the inner workings of a vehicle’s braking system. Whether it’s for educational purposes or to gain a better understanding of one’s own vehicle, studying the diagram can provide valuable insights into the mechanics of hydraulic braking systems and their maintenance.
What is a Brake Master Cylinder?
A brake master cylinder is a crucial component of a vehicle’s braking system. It is responsible for converting the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which then activates the brake calipers or wheel cylinders to apply the brakes.
The brake master cylinder consists of a reservoir that stores brake fluid, a piston, and a cylinder. When the driver presses the brake pedal, it pushes a rod connected to the piston of the master cylinder. This action creates pressure within the cylinder, which forces the brake fluid to move through the brake lines to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders.
The brake master cylinder plays a vital role in ensuring safe and effective braking. It enables the driver to control and modulate the braking force applied to the vehicle’s wheels. Without a properly functioning master cylinder, the vehicle may experience a loss of braking power, resulting in compromised safety on the road.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake master cylinder are essential to ensure its proper functioning. This includes checking the fluid level, inspecting for any leaks, and monitoring the condition of the brake fluid. If any issues or abnormalities are detected, it is crucial to address them promptly to maintain optimal braking performance.
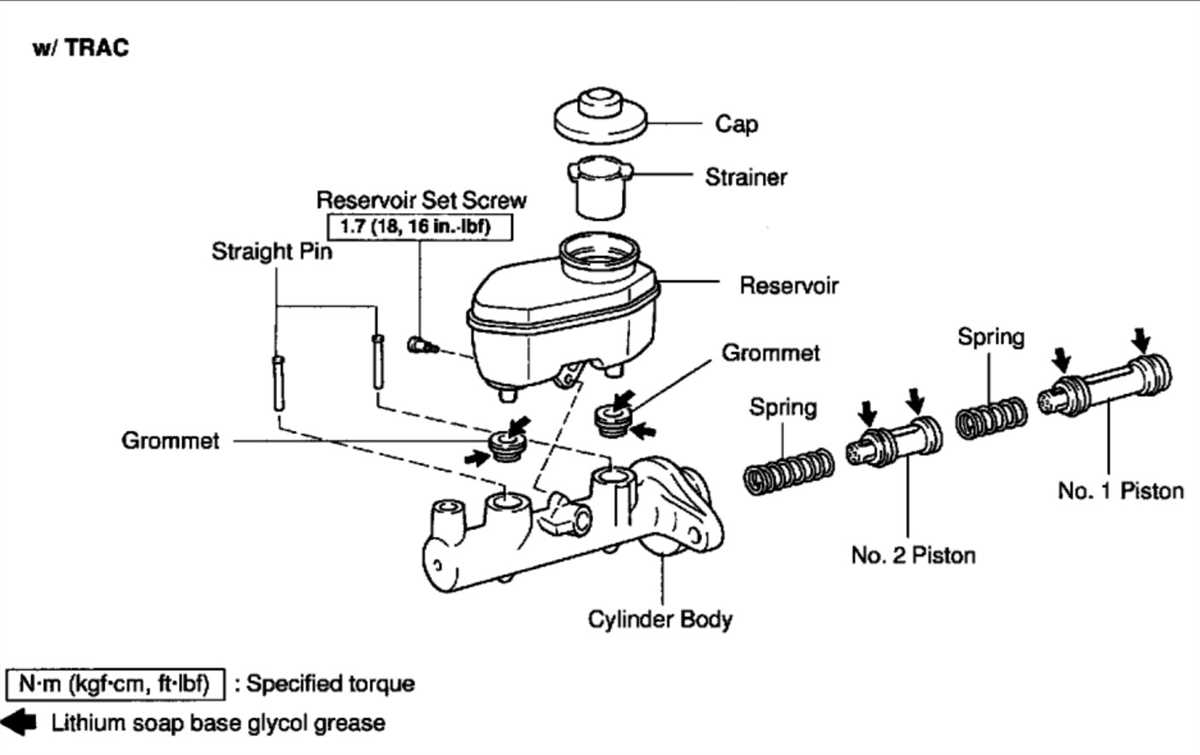
Understanding the Function and Importance of the Lockheed Brake Master Cylinder Diagram
The Lockheed brake master cylinder diagram is an essential tool for understanding the function and importance of this critical component in a vehicle’s braking system. The diagram visually represents the inner workings of the brake master cylinder and provides a clear understanding of how it functions to ensure safe and reliable braking performance.
The brake master cylinder is a key component of the hydraulic braking system, responsible for converting the driver’s input on the brake pedal into the hydraulic pressure required to engage the brakes. The diagram showcases the different components of the master cylinder, including the reservoir, piston, seals, and valves, and illustrates how they work together to generate and control hydraulic pressure.
- Reservoir: The diagram shows the reservoir, which holds the brake fluid. It provides a constant supply of fluid to the master cylinder for brake operation.
- Piston: The diagram demonstrates the piston, which is connected to the brake pedal. When the driver applies pressure to the pedal, the piston moves forward, pressurizing the brake fluid.
- Seals: The diagram highlights the seals, which prevent the brake fluid from leaking out of the master cylinder and maintain pressure within the system.
- Valves: The diagram depicts the valves, which control the flow of brake fluid to the brake lines, allowing the brakes to engage and disengage.
Understanding the function and importance of the brake master cylinder is crucial for maintaining a vehicle’s braking system. The diagram serves as a valuable reference tool for mechanics, technicians, and enthusiasts, enabling them to identify potential issues, troubleshoot problems, and make necessary repairs. It also helps drivers better comprehend the complexities of their vehicle’s braking system, allowing them to appreciate the importance of regular maintenance and prompt servicing.
Components of a Brake Master Cylinder
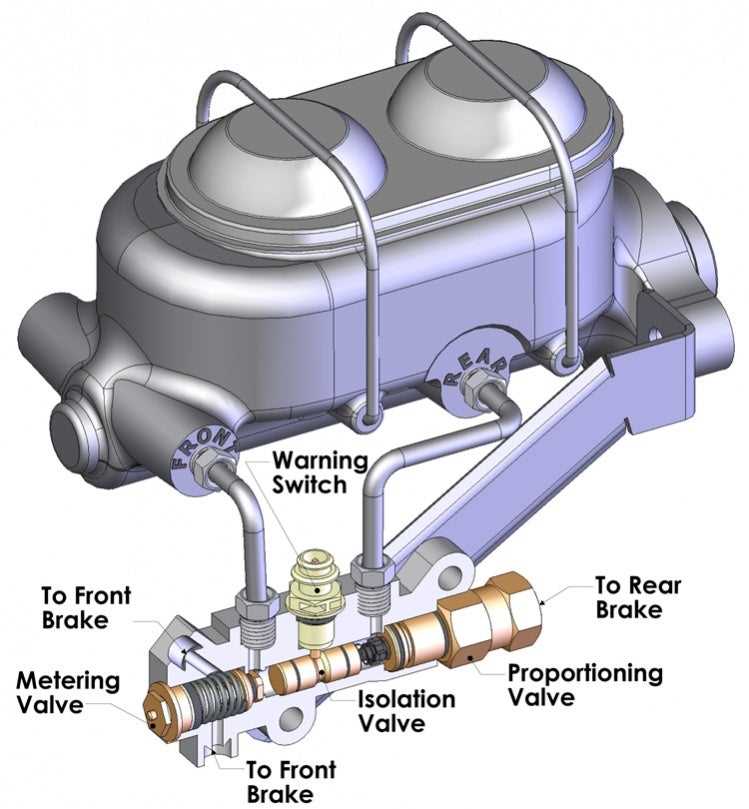
The brake master cylinder is an essential component of any vehicle’s braking system. It plays a crucial role in converting the pressure applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which then activates the brakes. Understanding the components of a brake master cylinder is important for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Cylinder Barrel: The main body of the brake master cylinder is known as the cylinder barrel. It houses the other components and provides the structure for the entire assembly. The cylinder barrel is typically made of cast iron or aluminum to withstand the high pressures within the system.
Piston: The brake master cylinder contains one or multiple pistons, depending on the design. These pistons are responsible for generating the hydraulic pressure required to activate the brakes. When the brake pedal is pressed, it pushes the piston(s) forward, exerting force on the brake fluid.
Reservoir: The brake master cylinder has a built-in reservoir that holds the brake fluid. It is usually located on top of the cylinder and is easily accessible for fluid checks and top-ups. The reservoir ensures a constant supply of brake fluid for the hydraulic system.
Fluid Lines: Fluid lines connect the brake master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders in a hydraulic braking system. These lines transport the pressurized brake fluid, allowing it to reach the braking components and activate them. Properly installed and maintained fluid lines are crucial for effective brake operation.
Check Valve: Some brake master cylinders include a check valve, which prevents the backflow of brake fluid. This valve ensures that pressure applied to the brakes is not lost when the pedal is released, maintaining a firm brake pedal feel and allowing for quicker subsequent brake applications.
Seals and O-rings: To maintain proper pressure and prevent fluid leaks, the brake master cylinder is equipped with seals and o-rings. These components create a tight seal between moving parts, preventing loss of hydraulic pressure and ensuring efficient brake operation.
In summary, the brake master cylinder consists of multiple key components, including the cylinder barrel, pistons, reservoir, fluid lines, check valve, and seals. Together, these components work in harmony to generate and maintain the necessary hydraulic pressure for effective braking.
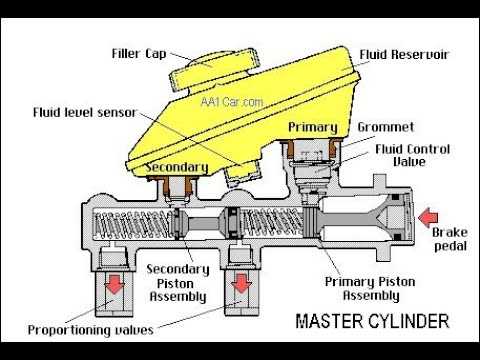
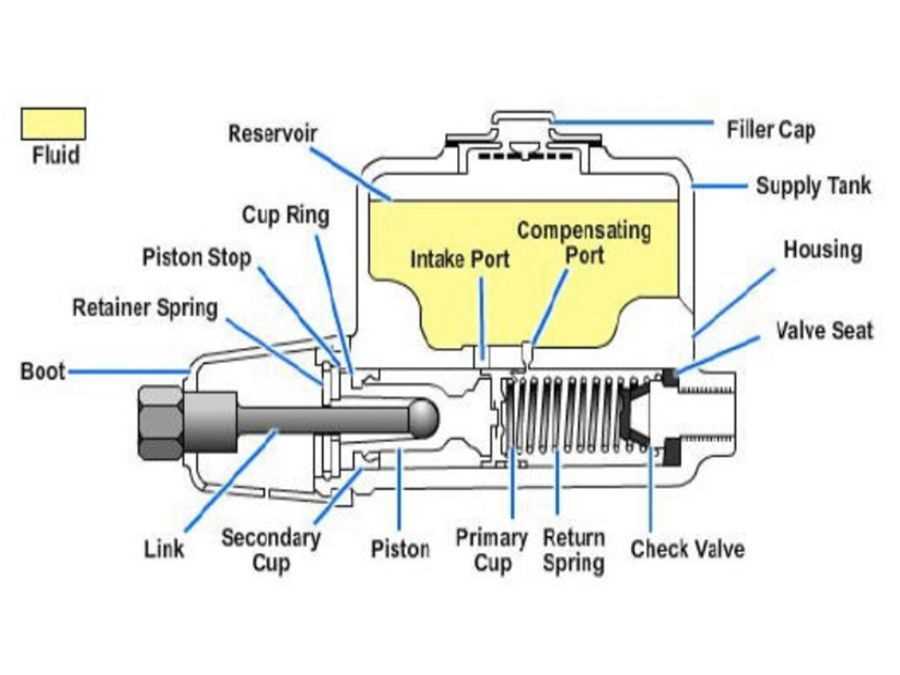
Exploring the Internal Structure and Parts of a Lockheed Brake Master Cylinder
The Lockheed brake master cylinder is a vital component of a vehicle’s braking system. It plays a crucial role in converting the pressure applied to the brake pedal by the driver into hydraulic pressure, which in turn activates the brakes. Understanding its internal structure and parts can provide valuable insights into its functionality.
1. Piston
At the heart of the Lockheed brake master cylinder is the piston, which is responsible for creating the hydraulic pressure. When the brake pedal is pressed, it pushes the piston forward, forcing brake fluid into the brake lines and activating the brakes. The piston is typically made of durable materials such as steel or aluminum to withstand the high pressures generated during braking.
2. Cylinder Bore
The cylinder bore houses the piston and provides the space for its movement. It is a cylindrical cavity within the master cylinder body. The diameter and length of the cylinder bore determine the braking force that can be generated by the master cylinder. A larger bore diameter allows for greater brake pressure, while a longer bore can accommodate a larger piston for increased fluid displacement.
3. Reservoir
The reservoir is a crucial part of the brake master cylinder, as it stores the brake fluid required for the system’s operation. It is typically located on top or mounted adjacent to the cylinder body. The reservoir is equipped with a cap or a lid to prevent contamination of the brake fluid by dirt, moisture, or other foreign substances. Inspecting and maintaining an adequate brake fluid level in the reservoir is essential for safe braking performance.
4. Check Valves
Check valves are used in the Lockheed brake master cylinder to control the flow of brake fluid. There are typically two check valves: the inlet valve and the outlet valve. The inlet valve allows brake fluid to enter the master cylinder from the reservoir, while the outlet valve ensures that the hydraulic pressure generated by the piston is directed towards the brake lines. Check valves are designed to prevent backflow and maintain the integrity of the hydraulic system.
5. Seals and O-Rings
Seals and o-rings are crucial for preventing fluid leaks and maintaining the hydraulic integrity of the braking system. They are located in various parts of the master cylinder, including the piston, reservoir, and cylinder bore. These seals and o-rings ensure that the brake fluid is contained within the system, preventing loss of pressure and potential brake failure. Regular inspection and replacement of worn seals and o-rings are essential for optimal braking performance.
- Piston: Creates hydraulic pressure to activate the brakes.
- Cylinder Bore: Houses the piston and determines braking force.
- Reservoir: Stores brake fluid for the system’s operation.
- Check Valves: Control the flow of brake fluid.
- Seals and O-Rings: Prevent fluid leaks and maintain hydraulic integrity.
Understanding the internal structure and parts of a Lockheed brake master cylinder provides insights into its intricate workings. The piston, cylinder bore, reservoir, check valves, seals, and o-rings all play vital roles in ensuring safe and reliable braking performance.
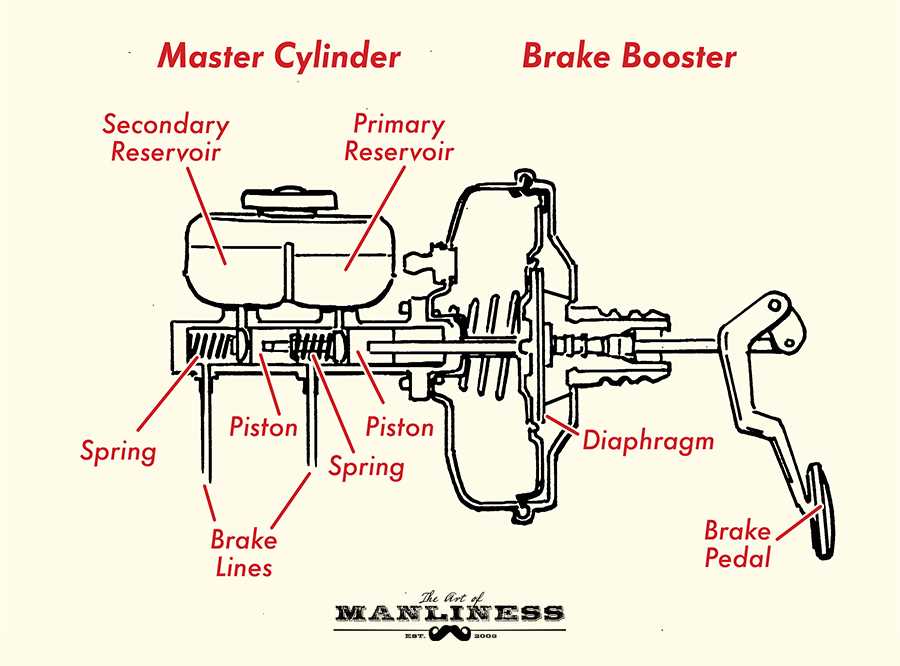
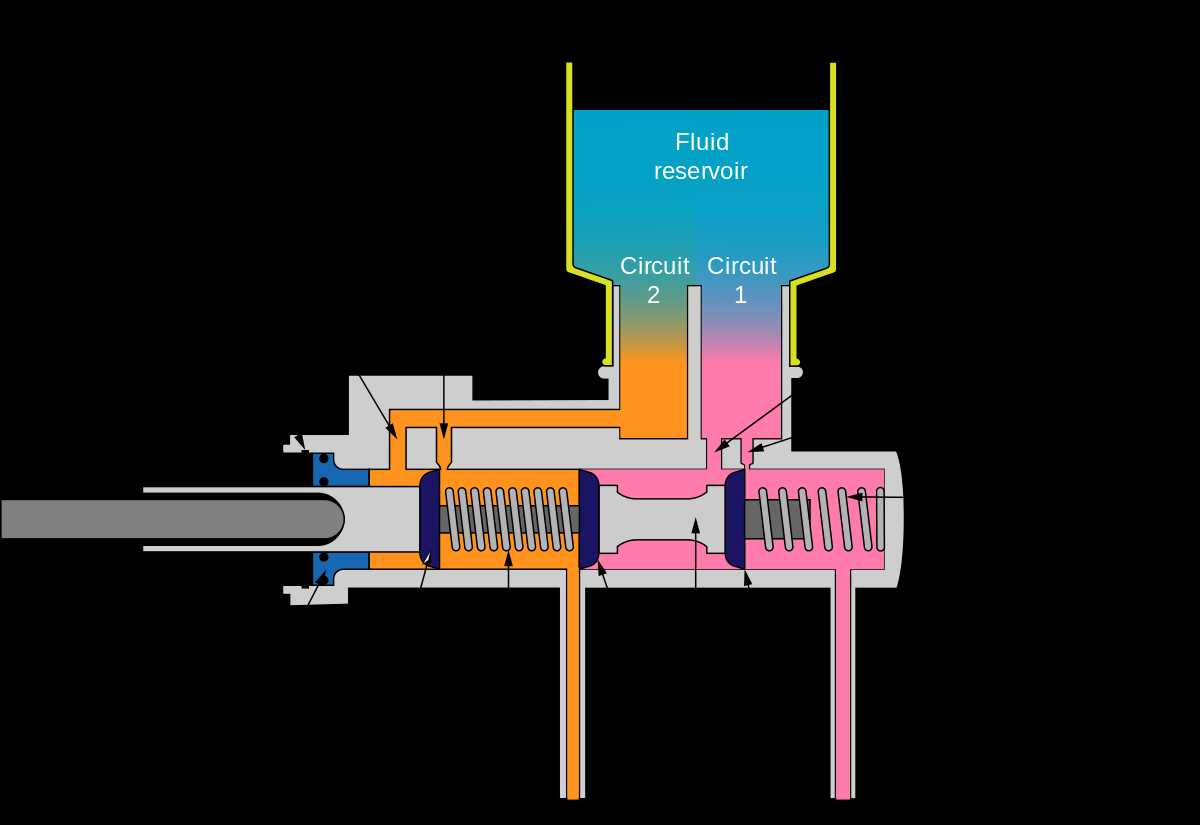
Working Principle of a Brake Master Cylinder
The brake master cylinder is a crucial component in a hydraulic braking system, responsible for converting the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which then activates the brake calipers or drums. Understanding the working principle of a brake master cylinder is essential for ensuring safe and reliable braking performance.
At its core, a brake master cylinder consists of a piston, a cylinder, and two fluid reservoirs–an upper reservoir for the brake fluid supply and a lower reservoir for compensating the fluid level as the brake pads or shoes wear down. When the brake pedal is pressed, it acts on the piston inside the cylinder, creating a hydraulic force that moves the piston forward.
This forward movement of the piston increases the pressure in the cylinder, causing the brake fluid to be forced out of the cylinder and into the brake lines. The brake fluid then travels through the brake lines to the brake calipers or drums, applying pressure to the brake pads or shoes, which ultimately slows down or stops the vehicle. The size of the piston, cylinder diameter, and the force applied to the brake pedal determine the hydraulic pressure generated by the brake master cylinder.
How the Cylinder Generates Hydraulic Pressure
The Lockheed brake master cylinder is an essential component of the hydraulic brake system in vehicles. It plays a crucial role in converting mechanical force into hydraulic pressure, which in turn activates the brake calipers or wheel cylinders to apply the brakes.
At its core, the brake master cylinder consists of a cylindrical housing with a piston and a reservoir filled with brake fluid. When the brake pedal is pressed, it applies mechanical force to the piston, which then moves forward within the cylinder. As the piston moves forward, it creates pressure in the brake fluid by compressing it.
This increase in pressure is essential for generating hydraulic force, which is transmitted through the brake lines to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. The hydraulic force then pushes the brake pads or brake shoes against the rotors or drums, resulting in the vehicle’s deceleration or stopping.
The design of the Lockheed brake master cylinder ensures that the force applied at the brake pedal is efficiently converted into hydraulic pressure. It utilizes a series of seals and valves to prevent brake fluid from leaking and maintain consistent pressure within the system. The reservoir within the master cylinder also allows for the replenishment of brake fluid as it is consumed during braking.
Overall, the Lockheed brake master cylinder’s ability to generate hydraulic pressure is crucial for the proper functioning of the vehicle’s braking system. Without this pressure, the brakes would not be able to engage effectively, compromising the safety and performance of the vehicle.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
The Lockheed brake master cylinder diagram is a crucial component of the brake system in various vehicles. However, like any mechanical component, it can encounter issues that may affect its performance. Understanding these common problems and troubleshooting methods can help you maintain and repair your brake master cylinder.
1. Brake Fluid Leaks
One of the most common issues with the brake master cylinder is brake fluid leaks. Leaks can occur due to worn-out seals, damaged pistons, or corroded brake lines. These leaks can lead to a loss of brake fluid, which can affect the performance and safety of your vehicle. If you notice any signs of fluid leaks, such as puddles under your vehicle or a low brake fluid level, it is essential to address the issue promptly. You may need to replace the faulty seals, pistons, or brake lines to fix the leak.
2. Brake Pedal Softness or Sponginess
If you experience a soft or spongy brake pedal, it could be an indication of air in the brake system. Air can enter the system through a damaged or faulty brake master cylinder, brake lines, or during brake fluid replacement. To troubleshoot this issue, you may need to bleed the brake system to remove any air bubbles. Start by bleeding the brake line at the wheel furthest from the master cylinder and work your way to the closest. This process will help remove any trapped air and restore the firmness of the brake pedal.
3. Inconsistent or Uneven Braking
Another common issue with the brake master cylinder is inconsistent or uneven braking. This problem can occur due to unequal pressure distribution caused by a faulty master cylinder. Inspect the brake lines and hoses for any signs of damage, such as leaks or blockages. If everything appears to be in working order, the issue may lie with the master cylinder itself. In such cases, it is recommended to replace the master cylinder to ensure proper brake performance.
4. Brake Warning Light On
If the brake warning light on your vehicle’s dashboard illuminates, it could indicate a problem with the brake master cylinder. This warning light can be triggered by various issues, such as low brake fluid level, brake fluid contamination, or a malfunctioning master cylinder. Check the brake fluid level and inspect it for any signs of contamination. If the level is low or the fluid appears dirty, it may be necessary to replace the brake fluid and address any underlying issues. If the problem persists, it is advisable to have a professional inspect the master cylinder for any faults.
Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting of the brake master cylinder can help ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle’s braking system. If you encounter any of these common issues, it is essential to address them promptly to maintain the safety and performance of your vehicle.
Identifying and Resolving Brake Master Cylinder Problems

Brake master cylinders play a crucial role in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s braking system. When a problem arises with the master cylinder, it can affect the overall performance and safety of the vehicle. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a faulty master cylinder is important for timely identification and resolution of the issue.
The most common signs of a brake master cylinder problem include a spongy or soft brake pedal, a low brake fluid level, and leaking brake fluid. Additionally, a faulty master cylinder may result in a loss of brake pressure, difficulty in applying or releasing the brakes, and a pulsating brake pedal during braking.
To resolve brake master cylinder problems, it is recommended to first check the brake fluid level. If it is low, adding more brake fluid may solve the issue. However, if the fluid level is consistently dropping or if there is a noticeable leak, it is important to inspect the master cylinder for any signs of damage or wear. If any leaks or damage are found, replacing the master cylinder is often necessary.
In some cases, the problem may lie with the brake booster or other components of the braking system. It is important to thoroughly inspect these components before assuming that the master cylinder is the sole source of the problem.
When replacing the brake master cylinder, it is recommended to use a high-quality, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part to ensure proper fit and functionality. Additionally, bleeding the brake system after installation is necessary to remove any air pockets and ensure proper brake operation.
In conclusion, identifying and resolving brake master cylinder problems is crucial for maintaining the safety and performance of a vehicle’s braking system. Regular inspection and timely resolution of any issues can help prevent accidents and ensure optimal braking performance.