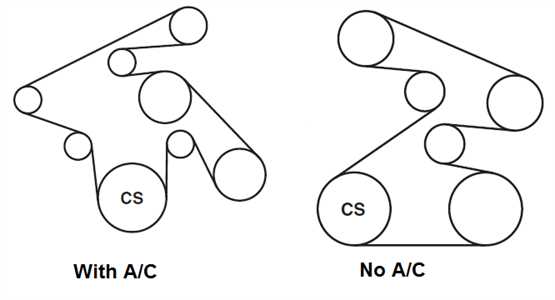
If you own a 2002 Toyota Tacoma, it is important to have a clear understanding of how the various components in your vehicle work together. One such component is the belt system, which plays a crucial role in powering essential parts of the engine.
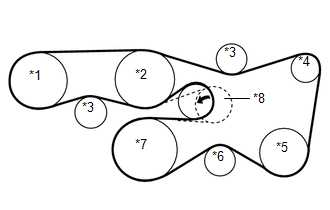
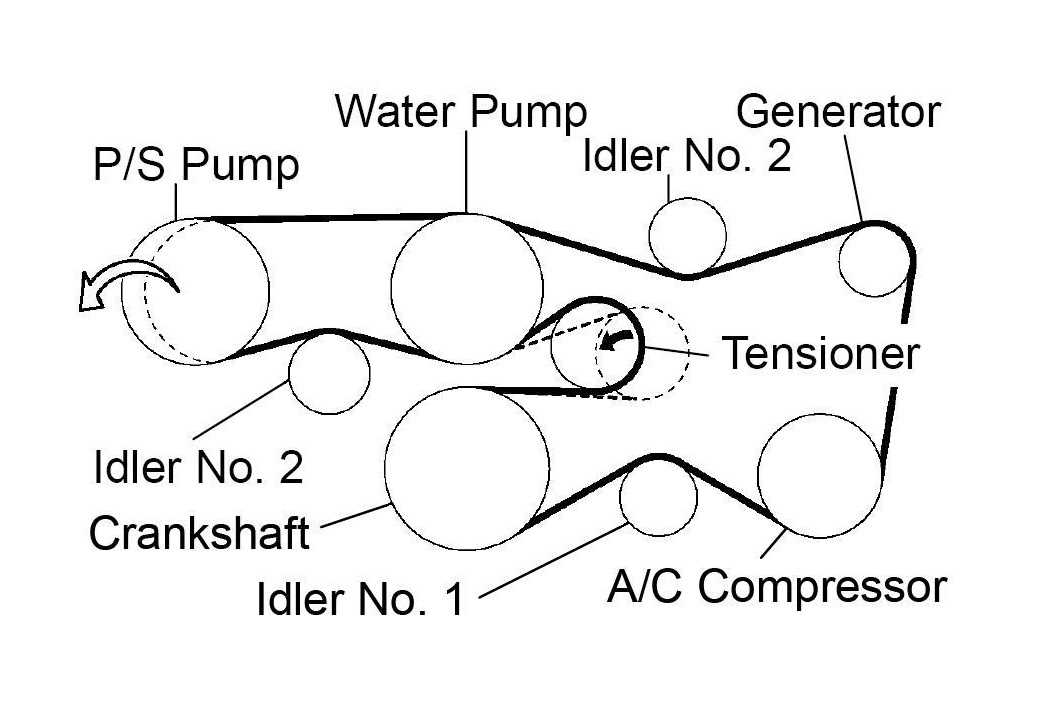
The belt diagram for a 2002 Toyota Tacoma showcases the routing and the position of the various belts in the engine compartment. It provides a visual representation of how the belts loop around various pulleys and accessories, ensuring that everything is functioning properly.
Having a belt diagram can be incredibly helpful when it comes to performing routine maintenance or troubleshooting any issues with the belts. It allows you to follow the correct routing and identify any potential issues, such as misalignment or wear and tear.
Whether you are a seasoned car enthusiast or a DIY mechanic, having access to a belt diagram for your 2002 Toyota Tacoma can save you time and prevent costly mistakes. By understanding how the belts interact with the engine components, you can ensure that your vehicle is running smoothly and efficiently.
Overview of the 2002 Toyota Tacoma Belt Diagram
The 2002 Toyota Tacoma is a reliable and sturdy pickup truck known for its durability and performance. Understanding the belt diagram of this vehicle is important for proper maintenance and repairs. The belt diagram illustrates the routing of various belts in the engine compartment, including the serpentine belt and other accessory belts.
The serpentine belt, also known as the drive belt, is a crucial component that drives multiple accessories in the engine, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and water pump. The belt diagram provides a visual guide on how the serpentine belt should be wrapped around these pulleys to ensure proper functioning of these accessories.
The 2002 Toyota Tacoma belt diagram typically includes the following:
- The serpentine belt, which connects the crankshaft pulley to various engine components.
- Pulleys for the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
- Idler pulleys and tensioner pulleys, which help maintain proper tension on the belts.
Having a clear understanding of the belt diagram is essential for routine maintenance tasks, such as belt inspection, replacement, or adjustment. It allows technicians and DIY enthusiasts to identify the correct routing of the belts, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing the risk of belt failure.
It is important to consult the specific belt diagram for the 2002 Toyota Tacoma model, as belt configurations may vary depending on the engine size and additional accessories installed in the vehicle. Referencing the proper diagram ensures accurate installation and prevents potential damage to the belts and surrounding components.
Overall, the belt diagram for the 2002 Toyota Tacoma serves as a valuable resource for maintaining the vehicle’s belts and ensuring the smooth operation of important engine accessories. Regular inspection and maintenance of the belts based on the diagram’s guidance can help prolong the life of the belts and prevent costly repairs down the road.
Understanding the Importance of the Belt Diagram
When it comes to maintaining your 2002 Toyota Tacoma, understanding the importance of the belt diagram is crucial. The belt diagram provides a visual representation of how the different belts in your vehicle are connected and looped around various pulleys. This diagram is essential for proper belt installation and ensuring that all components are properly aligned.
Proper belt alignment is vital for the efficient operation of your vehicle’s engine and other systems. If the belts are not aligned correctly, they can slip, squeal, or even break, leading to a loss of power and potential damage to important components. The belt diagram serves as a guide to help you route the belts correctly, ensuring that they are properly tensioned and aligned with the pulleys.
When replacing belts on your 2002 Toyota Tacoma, it is crucial to consult the belt diagram specific to your vehicle’s make and model. This diagram can be found in the owner’s manual or online through reliable sources. The diagram will guide you in identifying the correct routing path for each belt and ensure that you do not overlook any necessary adjustments or tensioning.
It is recommended to inspect your belts regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks, fraying, or excessive looseness. If you notice any of these issues, it is essential to address them promptly by referring to the belt diagram and replacing the belt as needed. Regular maintenance and proper belt alignment can help extend the lifespan of your belts, prevent unexpected breakdowns, and maintain the overall performance of your 2002 Toyota Tacoma.
Identifying the Different Belts in the Diagram
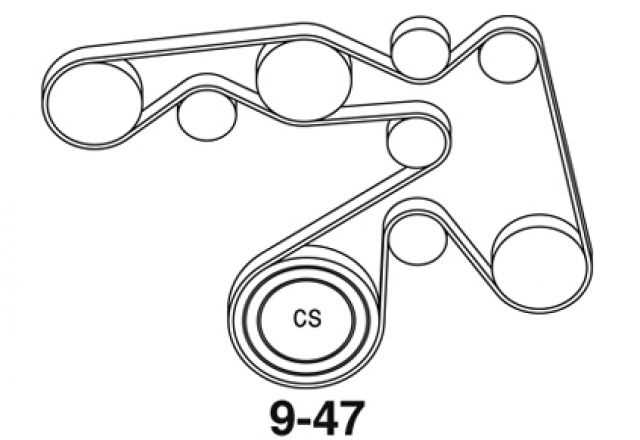
When looking at the 2002 Toyota Tacoma belt diagram, it is important to understand the different belts that are shown. Each belt serves a specific purpose in the vehicle’s engine system, and knowing how to identify them can be helpful for maintenance and repairs.
Main Drive Belt: The main drive belt is the largest belt in the diagram and is responsible for transferring power from the engine to various components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. It is typically located at the front of the engine and is driven by the crankshaft.
Accessory Drive Belt: The accessory drive belt, also known as the serpentine belt, is another important belt shown in the diagram. It is responsible for driving multiple accessories, including the water pump, air conditioning compressor, power steering pump, and alternator. This belt is typically located on the side of the engine and is driven by the crankshaft.
- Power Steering Belt: In some vehicles, there may be a separate belt dedicated solely to the power steering system. This belt is responsible for driving the power steering pump and assisting with the steering mechanism.
- Alternator Belt: The alternator belt is responsible for driving the alternator, which charges the vehicle’s battery and supplies electrical power to the various electrical systems while the engine is running.
- Air Conditioning Belt: If the vehicle is equipped with air conditioning, there may be a separate belt dedicated to driving the air conditioning compressor. This belt is responsible for providing power to the compressor, allowing it to cool the air inside the vehicle.
By understanding the different belts in the 2002 Toyota Tacoma belt diagram, you can easily identify and locate them in your own vehicle. This knowledge can be useful for troubleshooting issues, performing maintenance tasks, or replacing worn or damaged belts.
Exploring the Belt Routing for Specific Engine Components
When it comes to the 2002 Toyota Tacoma, understanding the belt routing for specific engine components is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. The belt routing diagram provides a visual guide to the path that the belt takes around various pulleys and accessories, ensuring proper functionality and performance of the engine.
One of the key components that the belt in the 2002 Toyota Tacoma is responsible for driving is the alternator. The alternator plays a critical role in generating electrical power for the vehicle, including charging the battery. The belt routing diagram will show the path that the belt takes around the alternator pulley, ensuring that it rotates properly and effectively generates electrical power for the vehicle.
Another important component that the belt drives is the power steering pump. The power steering pump provides hydraulic assistance to the steering system, making it easier to turn the wheels. The belt routing diagram will show how the belt connects to the power steering pump pulley, ensuring that there is proper tension and that the pump operates smoothly, allowing for easy steering.
In addition to the alternator and power steering pump, the belt in the 2002 Toyota Tacoma also drives other components such as the air conditioning compressor and the water pump. The air conditioning compressor is responsible for cooling the air inside the vehicle, while the water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine to prevent overheating. The belt routing diagram will provide a clear illustration of how the belt connects to these components, ensuring proper operation and performance.
In conclusion, understanding the belt routing for specific engine components in the 2002 Toyota Tacoma is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. The belt routing diagram provides a visual guide to the path that the belt takes around various pulleys and accessories, ensuring the proper functionality and performance of key components such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replace the Belts
Replacing the belts on a 2002 Toyota Tacoma is a relatively simple process that can be completed in a few steps. By following this step-by-step guide, you can ensure that your belts are properly replaced and your vehicle is operating at its best.
1. Gather the necessary tools: Before you begin, make sure you have all the tools you will need to complete the job. This may include a socket wrench, a belt tensioner tool, and new replacement belts.
2. Locate the belts: The Toyota Tacoma has multiple belts that may need to be replaced, including the serpentine belt and the drive belts. To begin, locate the belts in the engine compartment.
3. Loosen the tension: Using the appropriate tool, loosen the tension on the belt by adjusting the belt tensioner. This will allow you to remove the old belt without any resistance.
4. Remove the old belts: Carefully remove the old belts by sliding them off the pulleys. Make sure to note the routing of the belts, as this will be important when installing the new belts.
5. Install the new belts: Begin by routing the new belts around the pulleys, following the same path as the old belts. Make sure the belts are properly aligned and seated on each pulley.
6. Tighten the tension: Once the new belts are in place, use the belt tensioner tool to tighten the tension on each belt. This will ensure that the belts are securely in place and will not slip or come off while the vehicle is in motion.
7. Test the belts: Start the engine and visually inspect the new belts to ensure they are running smoothly and without any signs of slipping or misalignment. If any issues are detected, adjust the tension accordingly.
8. Check for proper operation: Take the vehicle for a short test drive to confirm that the belts are operating correctly and that all systems are functioning as intended.
By following these steps, you can successfully replace the belts on your 2002 Toyota Tacoma and ensure that your vehicle is running smoothly and efficiently.
Tips and Precautions for Changing the Belts
Changing the belts in a 2002 Toyota Tacoma is an important maintenance task that ensures the proper functioning of various components in the vehicle. Here are some tips and precautions to keep in mind when performing this task:
1. Identify the belt system:
Before starting, it is essential to identify the type and location of the belts in your Toyota Tacoma. Typically, there are multiple belts in the engine compartment, including the serpentine belt, power steering belt, and alternator belt. Refer to the vehicle’s manual or a diagram for accurate identification.
2. Use the right tools:
When changing the belts, make sure to have the necessary tools on hand. These may include a socket wrench, tensioner tool, and a pry bar. Ensure that the tools are of the correct size and type for the specific belt system you are working with.
3. Disconnect the battery:
Before working on any belts or pulleys, it is crucial to disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This prevents accidental engine start-up and keeps you safe from any potential electrical hazards during the repair process.
4. Take note of belt routing:

Before removing the existing belts, carefully observe and take note of their routing pattern. A diagram or photograph of the belt routing can be helpful for reference when installing the new belts. Improper positioning of the belts can lead to their premature wear or even damage to other components.
5. Check belt tension and condition:
Prior to installing new belts, it’s important to inspect the condition and tension of the existing ones. Belts that show signs of fraying, cracking, or excessive wear should be replaced. Additionally, check the tension of the belts by pressing on them firmly with your thumb. If they feel loose or have excessive give, they may need to be adjusted or replaced.
6. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions:
When installing the new belts, carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions and specifications. This includes using the correct tension setting and following the specific routing pattern. Following these instructions ensures proper belt operation and optimal performance of the related components.
By following these tips and precautions, you can confidently change the belts in your 2002 Toyota Tacoma while promoting the longevity and efficiency of your vehicle’s systems.
Common Problems and Solutions Related to the Belt System
The belt system of a 2002 Toyota Tacoma is crucial for the proper functioning of various components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. However, like any other mechanical system, the belt system can experience issues over time. Here are some common problems that can arise with the belt system and solutions to address them:
Belt Misalignment:
If the belt is not properly aligned with the pulleys, it can cause squealing noises, excessive wear on the belt, and may even lead to the belt slipping off the pulley. To fix this problem, the belt should be properly adjusted and aligned. This can be done by loosening the mounting bolts of the affected component and adjusting its position until the belt runs straight and true on the pulleys. Once the alignment is correct, the mounting bolts should be tightened.
Worn or Damaged Belt:
Over time, the belt can become worn or damaged due to constant exposure to heat and friction. Signs of a worn or damaged belt include cracking, fraying, or a glazed appearance. In such cases, it is recommended to replace the belt with a new one. When replacing the belt, it is important to use the correct size and type recommended by the manufacturer to ensure proper fit and function.
Tensioner or Idler Pulley Issues:
The tensioner and idler pulleys play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. If these components become worn or damaged, they can cause the belt to slip or become loose. This can result in noise, reduced performance, and even belt failure. If the tensioner or idler pulleys show signs of wear or damage, they should be replaced with new ones to ensure optimal belt performance.
Lack of Maintenance:
One of the most common reasons for belt system problems is a lack of regular maintenance. It is important to inspect the belt system periodically and check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Additionally, the belt should be properly tensioned as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regular cleaning and lubrication of the pulleys can also help prevent issues with the belt system.
Conclusion:

The belt system in a 2002 Toyota Tacoma is crucial for the proper functioning of various components. However, it can experience problems over time, such as belt misalignment, worn or damaged belts, tensioner or idler pulley issues, and lack of maintenance. By following the appropriate solutions for these problems, one can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the belt system in their vehicle.