
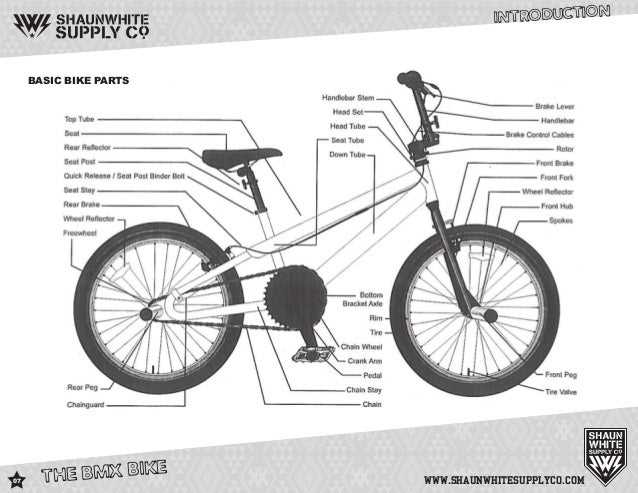
A BMX bike diagram is a visual representation that breaks down the different parts of a BMX bike and explains their functions. BMX, short for Bicycle Motocross, is a type of bike that is designed for off-road racing and freestyle stunts. It has gained popularity over the years, and many people enjoy riding and performing tricks on these bikes.
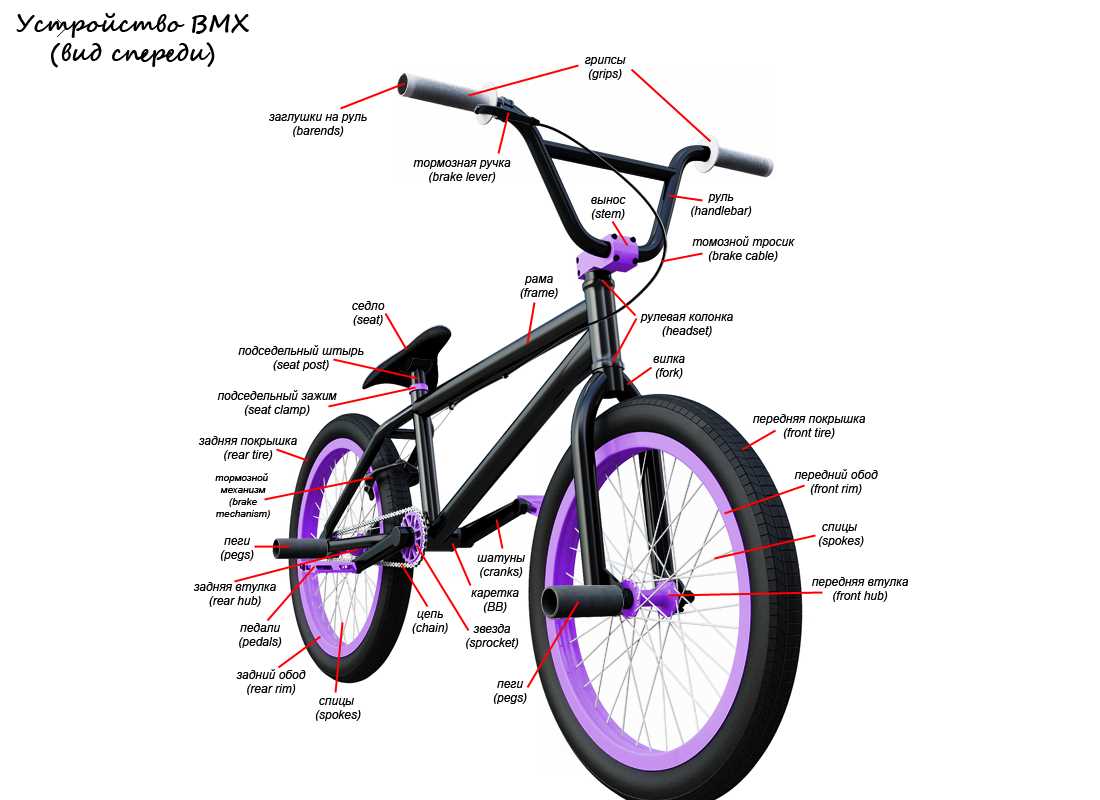
The diagram typically includes labeled images of the frame, wheels, handlebars, pedals, brakes, and other components. Each part has a specific purpose and contributes to the overall performance and functionality of the bike. Understanding the different parts of a BMX bike is essential for riders, as it helps them maintain and repair their bikes, as well as choose the right components for upgrades.
The frame is the backbone of the bike and provides structural support and stability. It is typically made of steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber and comes in various sizes and geometries to accommodate different riding styles and preferences. The wheels are another crucial component, as they determine the bike’s speed, maneuverability, and overall ride quality. Most BMX bikes have 20-inch wheels, but there are also bikes with larger or smaller wheels depending on the rider’s needs.
BMX Bike Diagram: Understanding the Anatomy of a BMX Bike
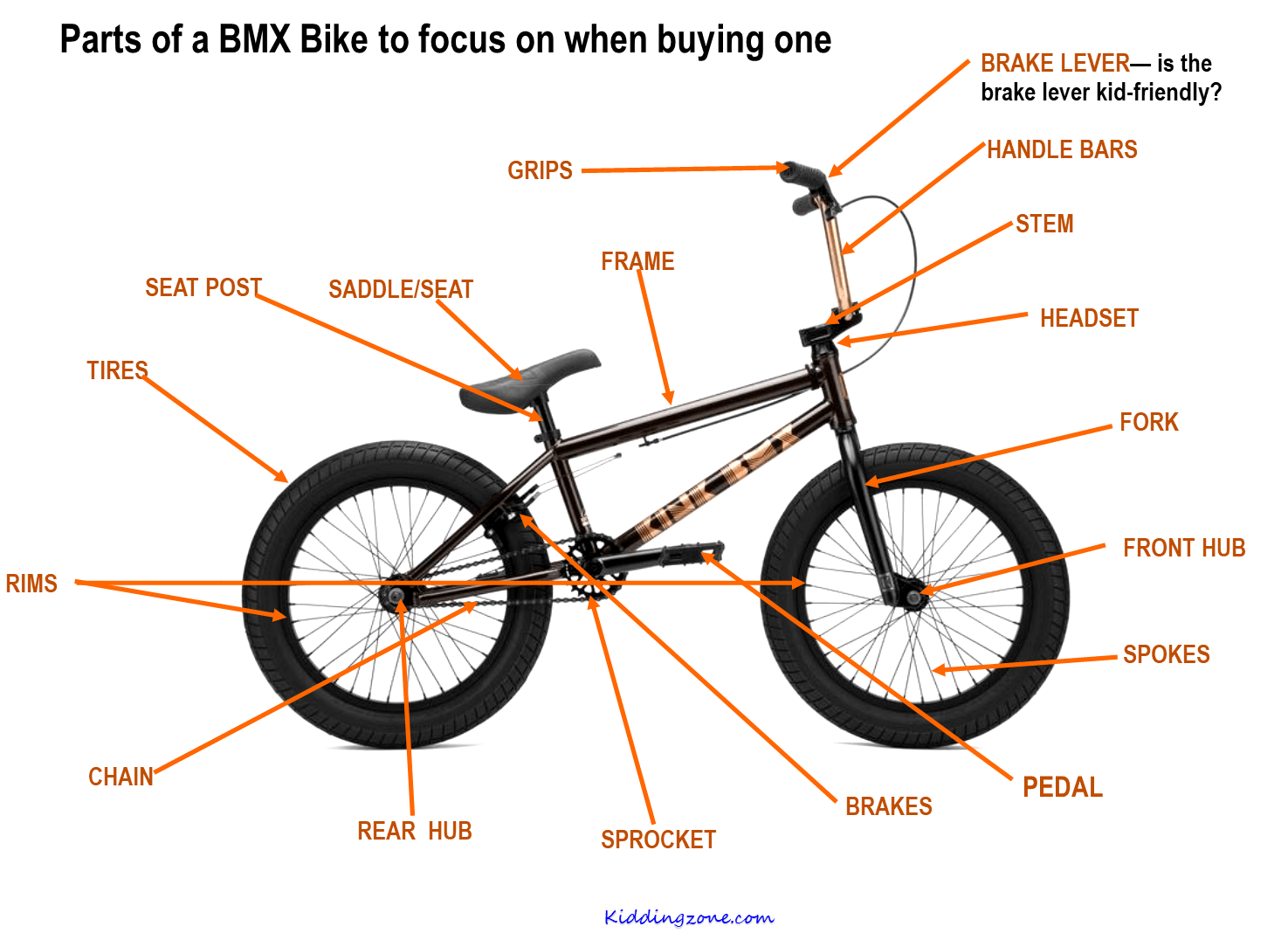
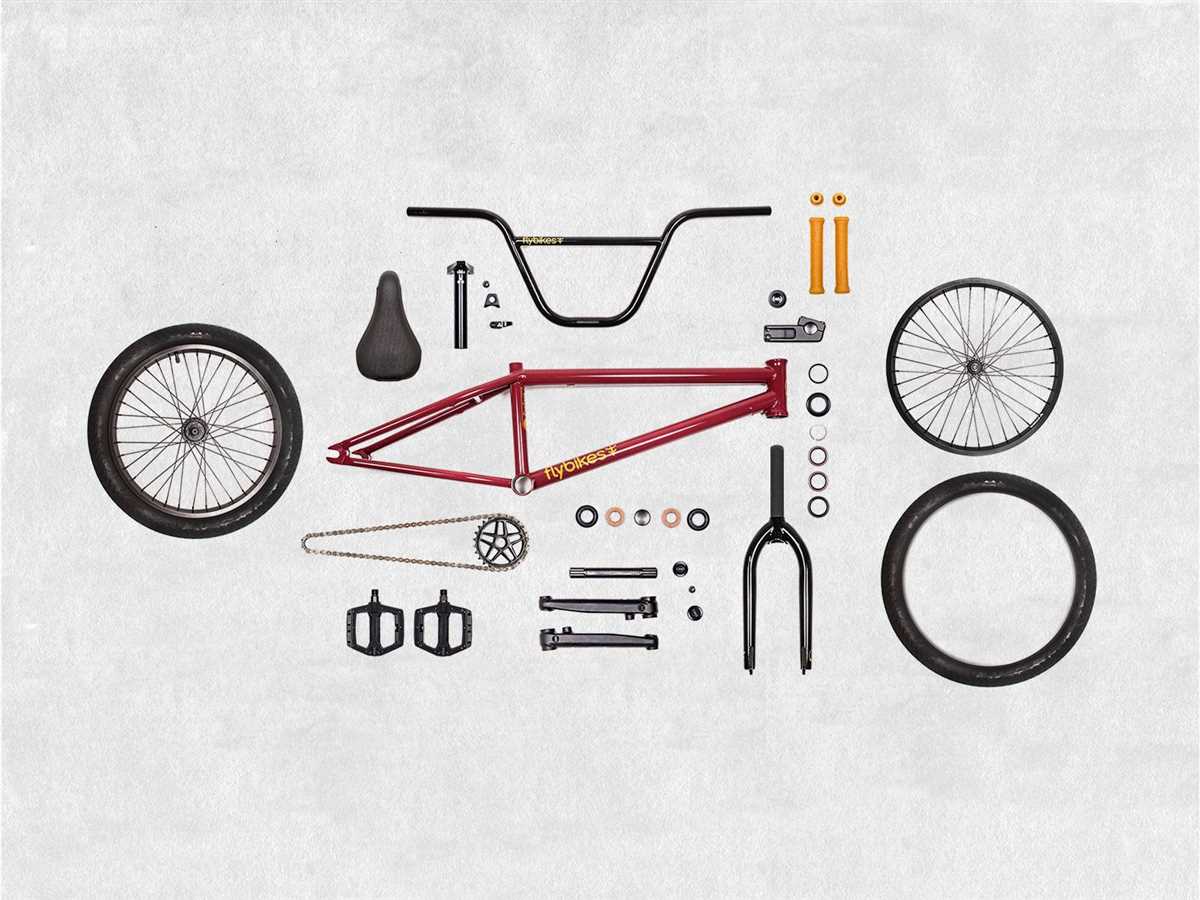
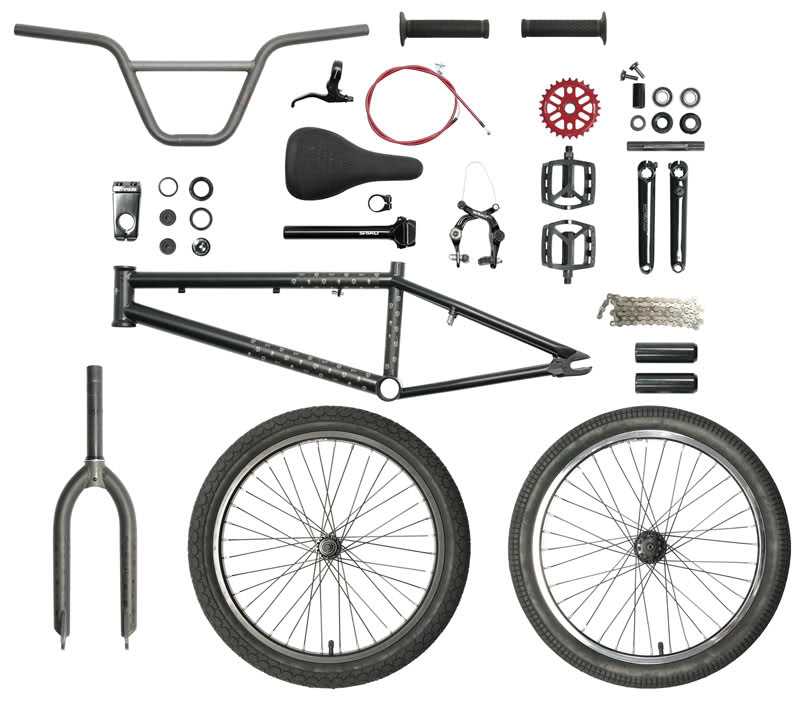
When it comes to understanding the anatomy of a BMX bike, there are several key components that make up this high-performance bicycle. Whether you’re a seasoned rider or just starting out, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a BMX bike to have better control, maintain your bike, and ensure your safety.
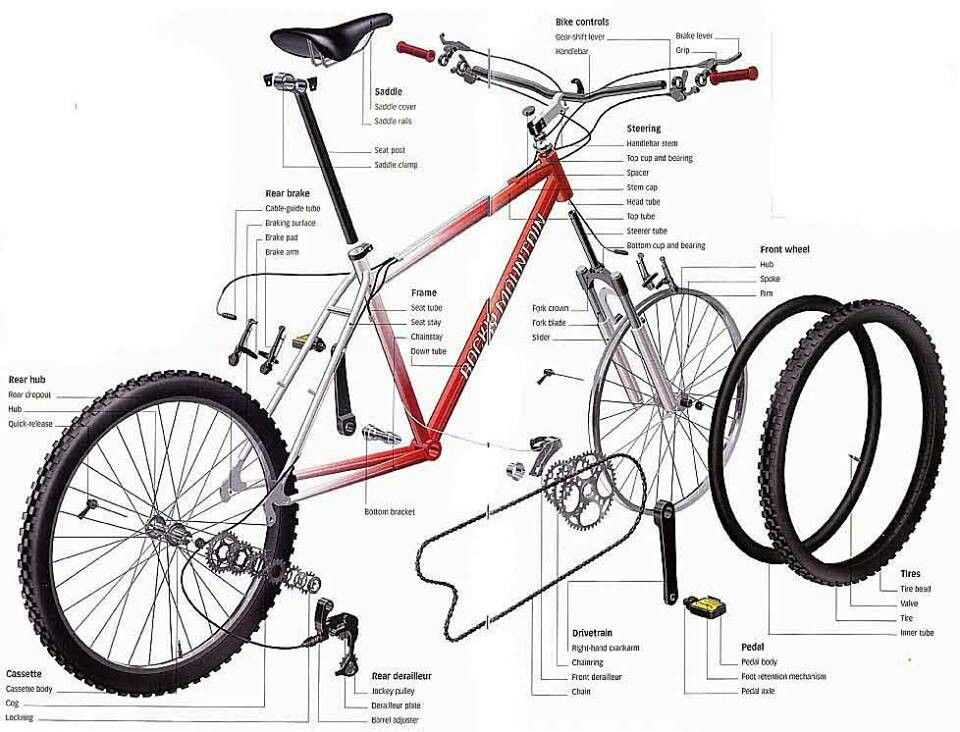
One of the most important components of a BMX bike is the frame. The frame is the main structure that holds all the other parts together. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and comes in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different riding styles and body types. The top tube, down tube, seat tube, and chain stays are the main sections of the frame that give it strength and stability.
Handlebars
Another important part of a BMX bike is the handlebars. The handlebars provide the rider with control and steering. They are usually made of chromoly steel or aluminum and come in different widths and heights. BMX handlebars have crossbars for added strength and stability. Grips are attached to the handlebars to provide a comfortable and secure grip for the rider.
Wheels and Tires
The wheels and tires of a BMX bike play a crucial role in its performance. BMX bikes usually have 20-inch wheels, which are smaller and stronger than those found on other types of bicycles. The tires are wider and have a knobby tread pattern for better traction and grip on various surfaces. The rims of the wheels are also designed to withstand the impact of jumps and tricks.
Brakes

Brakes are an essential safety feature on a BMX bike. BMX bikes typically use U-brakes or caliper brakes, which provide quick and reliable stopping power. The brake lever is attached to the handlebars, and when squeezed, it activates the brake pads, which press against the rim of the wheel to slow down or stop the bike. Some BMX bikes also have a rear brake for additional stopping power.
Other components of a BMX bike include the cranks, pedals, sprocket, chain, seat, and seat post. These parts all work together to ensure proper power transfer, stability, and comfort while riding. Understanding how these components function and how they interact with each other is essential for any BMX rider.
In summary,

- The frame is the main structure of a BMX bike.
- The handlebars provide control and steering.
- The wheels and tires are designed for performance and traction.
- Brakes are an important safety feature.
By familiarizing yourself with the anatomy of a BMX bike, you can make informed decisions when it comes to choosing and maintaining your bike, as well as understanding how to optimize your riding experience.
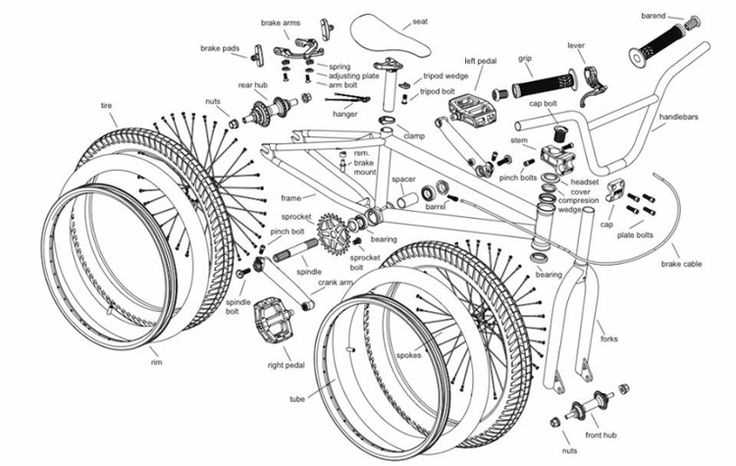
Frame
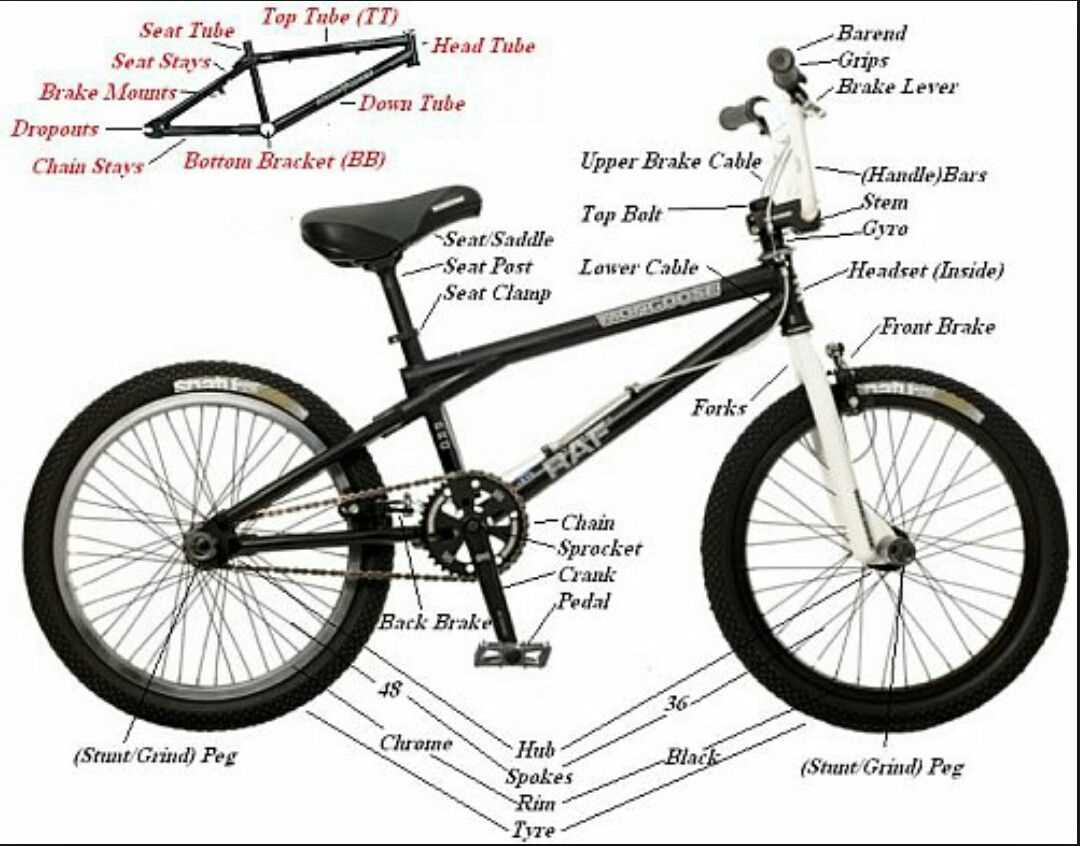
The frame is the backbone of a BMX bike. It is the central component that holds all the other parts together and provides stability and strength. A BMX frame is usually made of steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber, depending on the rider’s preferences and intended use.
BMX frames come in different sizes and designs to accommodate riders of various heights and riding styles. The most common frame sizes are mini, junior, expert, expert xl, pro, and pro xl. Each size has specific dimensions and proportions to ensure a comfortable and efficient riding experience.
Key components of a BMX frame include the top tube, down tube, seat tube, head tube, chainstays, and seat stays. The top tube connects the head tube to the seat post, providing the rider with space to stand and balance. The down tube connects the head tube to the bottom bracket and provides additional strength and stability. The seat tube holds the seat post and saddle, allowing the rider to sit and pedal comfortably. The head tube houses the headset, which connects the forks to the frame and allows for steering. The chainstays and seat stays connect the bottom bracket to the rear dropouts, providing support and stability for the rear wheel.
Some BMX frames feature additional design elements to enhance performance, such as gussets or braces, which reinforce key areas of the frame to withstand the impacts and stresses of BMX riding. These reinforcements can be found near the head tube, bottom bracket, and seat tube junctions. BMX frames may also have various types of dropouts, such as standard dropouts, integrated dropouts, or removable dropouts, which affect wheel installation and chain tension.
Overall, the frame is a crucial component of a BMX bike, providing the foundation for all other parts and determining the bike’s strength, stability, and maneuverability. Riders should choose a frame that matches their riding style and preferences, ensuring an optimal riding experience.
Fork

The fork is an essential component of a BMX bike. It is the part that connects the front wheel and the handlebars to the rest of the frame. The fork is responsible for supporting the weight of the rider and absorbing shocks and impacts during riding, making it an important part for maintaining control and stability.
BMX forks are typically made of high-strength steel or carbon fiber to ensure durability and strength while keeping the weight low. They come in different lengths and designs, depending on the specific type of riding and personal preference. Some forks have a straight design, while others have a curved shape for added strength and agility.
A key feature of BMX forks is the steerer tube. This is the part of the fork that extends up through the frame and connects to the stem, allowing the rider to steer the bike by turning the handlebars. The steerer tube may be threaded or threadless, depending on the type of headset used.
Most BMX forks are designed to accommodate a 20-inch wheel, which is the standard size for BMX bikes. However, there are also forks available for larger wheel sizes, such as 24-inch and 26-inch, for riders who prefer a different riding style or terrain.
Overall, the fork is an integral part of a BMX bike that plays a crucial role in providing control, stability, and durability. It is important to choose a fork that matches the specific requirements of the rider’s riding style and preferences to ensure optimal performance and safety on the bike.
Handlebars
The handlebars on a BMX bike play a crucial role in controlling the direction and stability of the bike. They are the main component that the rider uses to steer and maneuver the bike. BMX handlebars are typically made out of steel or aluminum alloy, which provides strength and durability while keeping the weight of the bike relatively light.
The handlebars on a BMX bike are designed to provide the rider with a comfortable and secure grip. They are usually straight or slightly curved, with a width that is suited to the rider’s preference and riding style. Some riders prefer wider handlebars for more stability, while others prefer narrower ones for better maneuverability.
BMX handlebars are attached to the bike’s stem, which is connected to the fork of the bike. The stem allows the rider to adjust the height and angle of the handlebars, making it possible to find the most comfortable riding position. The handlebars are often equipped with grips made of rubber or foam, which provide cushioning and enhance the rider’s grip on the handlebars.
Many BMX riders also choose to customize their handlebars by adding bar ends. Bar ends are small extensions that are inserted into the ends of the handlebars and provide additional grip and protection in case of a fall. Some riders also choose to add a crossbar to their handlebars, which can help improve stability and control during certain tricks and maneuvers.
- Handlebars play a crucial role in controlling the direction and stability of a BMX bike.
- They are typically made of steel or aluminum alloy for strength and durability.
- BMX handlebars come in different widths to suit rider preferences.
- They are attached to the stem, which allows for height and angle adjustments.
- Grips made of rubber or foam provide cushioning and enhance grip.
- Some riders choose to add bar ends or a crossbar for customization and additional functionality.
Wheels
The wheels of a BMX bike are one of its most crucial components. They are responsible for providing stability, support, and maneuverability. The wheels consist of several parts, including the rim, spokes, and hub.
The rim is the outer circle of the wheel that holds the tire in place. It is typically made of aluminum or carbon fiber, which makes it lightweight and durable. The rim’s size and design may vary depending on the specific BMX discipline, such as racing or freestyle.
The spokes are thin metal rods that connect the rim to the hub. They provide support and help distribute the rider’s weight evenly across the wheel. The number of spokes can vary, with some wheels having as few as 36 and others having up to 48 or more. The spokes are typically made of stainless steel, which is strong and resistant to corrosion.
The hub is the center part of the wheel that houses the axle and bearings. It allows the wheel to rotate smoothly and provides a connection point for the spokes. The hub can be either freewheel or cassette type, depending on the bike’s drivetrain. Freewheel hubs allow the rider to coast, while cassette hubs provide multiple gear options.
In addition to these main components, BMX wheels may also have other features such as rim tape, which protects the inner tube from punctures, and wheel nuts or quick-release levers, which secure the wheel to the frame. Proper maintenance and regular inspection of the wheels are essential to ensure safe and optimal performance on the BMX bike.
Brakes
The brakes on a BMX bike are an essential component that ensures the rider’s safety. They allow the rider to slow down or bring the bike to a complete stop when necessary. There are two main types of brakes used on BMX bikes: caliper brakes and disc brakes.
Caliper brakes are the most common type of brakes found on BMX bikes. They consist of a set of brake pads that squeeze against the rim of the wheel to create friction and slow down the bike. Caliper brakes are lightweight and easy to maintain, making them a popular choice among BMX riders.
Disc brakes are becoming increasingly popular on BMX bikes, especially in the freestyle discipline. These brakes use a rotor attached to the hub of the wheel and a caliper mechanism that squeezes the rotor to provide stopping power. Disc brakes offer better modulation and stopping power, making them ideal for riders who perform tricks and stunts that require precise control.
Both caliper brakes and disc brakes can be operated using a mechanical system or a hydraulic system. Mechanical brakes use a cable to transfer the force from the brake lever to the brake caliper, while hydraulic brakes use fluid to transmit the force. Hydraulic brakes generally offer better performance and more consistent braking power, but they require more maintenance and can be more expensive to repair.
Regardless of the type of brake system used, it is important to regularly check and maintain the brakes on a BMX bike. This includes inspecting the brake pads for wear, adjusting the brake tension, and ensuring that the brake cables are properly lubricated. Properly functioning brakes are essential for safe riding and full control over the bike.
Conclusion: Pedals and Cranks
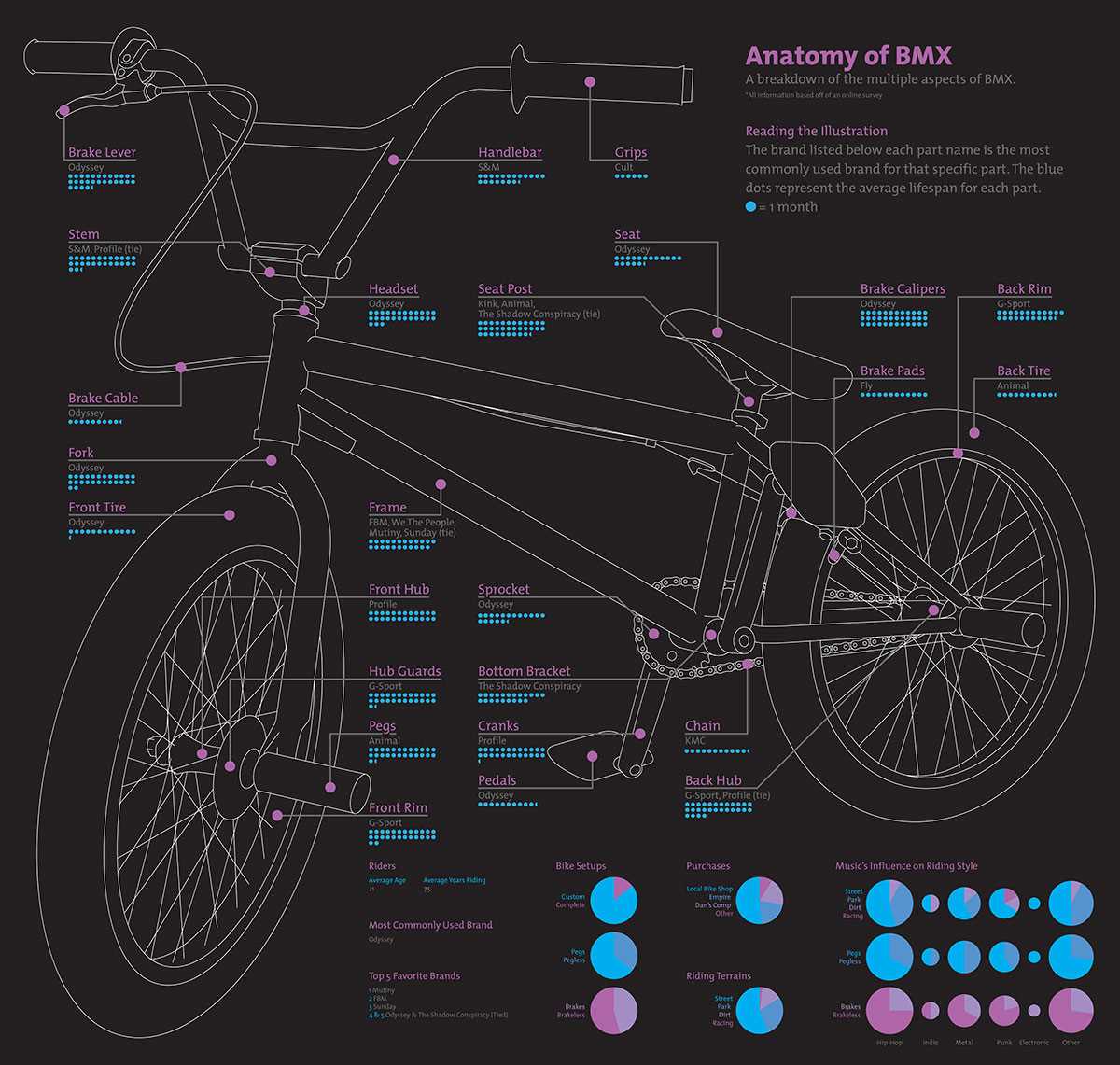
In conclusion, pedals and cranks are essential components of a BMX bike that allow the rider to generate power and transfer it to the drivetrain. The pedals provide a platform for the rider’s feet and are designed to maximize grip and control. Cranks, on the other hand, connect the pedals to the chainring, enabling the rider to convert their pedaling motion into forward propulsion.
When choosing pedals and cranks for a BMX bike, it is important to consider factors such as material, durability, and weight. Aluminum alloy, titanium, and carbon fiber are popular materials used for both pedals and cranks, as they offer a good balance between strength and weight. It is also important to select pedals and cranks that are compatible with the rider’s riding style, preferences, and the type of terrain they will be riding on.
To summarize:
- Pedals provide a platform for the rider’s feet and maximize grip and control.
- Cranks connect the pedals to the chainring, converting pedaling motion into forward propulsion.
- Choosing pedals and cranks involves considering factors such as material, durability, and weight.
- Aluminum alloy, titanium, and carbon fiber are popular materials for pedals and cranks.
- Selecting compatible pedals and cranks based on riding style and terrain is important.
By understanding the importance of pedals and cranks in a BMX bike, riders can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting these components for their bikes. Whether it’s for racing, freestyle, or casual riding, having the right pedals and cranks can greatly enhance the overall riding experience and performance.