The braking system is one of the most critical components of any vehicle, and understanding how it works is essential for both drivers and mechanics alike. In this article, we will be focusing on the drum brake system used in the 1993 Ford Ranger. This system, while not as commonly used today as disc brakes, is still relied upon in many older vehicles, including the Ford Ranger.
The drum brake system consists of several key components that work together to slow down and stop the vehicle. These components include the brake drum, brake shoes, wheel cylinders, and various springs and clips. Each component plays a vital role in the overall function of the drum brake system.
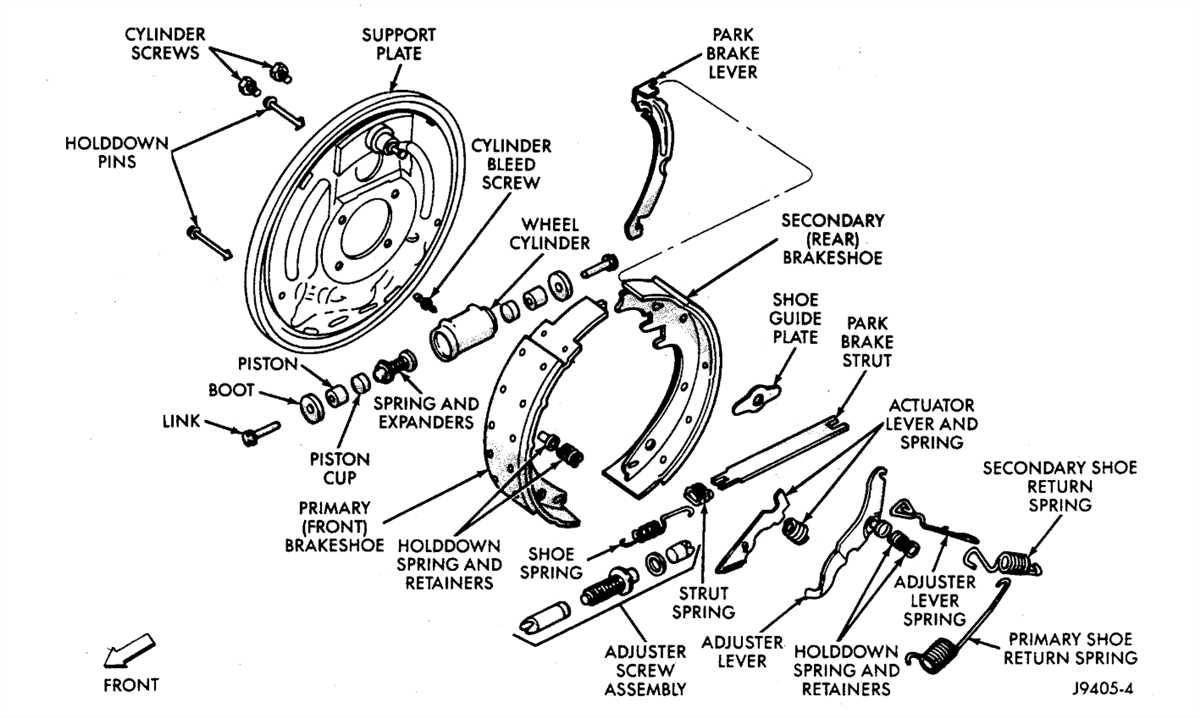
To fully understand how the drum brake system works in the 1993 Ford Ranger, it’s important to have a visual representation. The drum brake diagram provides a detailed illustration of all the components and their positions within the system. This diagram serves as a valuable tool for mechanics who are troubleshooting brake issues or for anyone looking to gain a better understanding of how the system operates.
In this article, we will examine each component of the drum brake system in the 1993 Ford Ranger, discussing their function and how they work together to provide effective braking power. By understanding the drum brake system, you will be better equipped to identify and resolve any potential issues that may arise.
What Is a Drum Brake?
A drum brake is a type of braking system used in vehicles, particularly older models. It is composed of various components that work together to slow down or stop the rotation of the wheels. This type of brake system is commonly found in the rear wheels of a vehicle.
The main components of a drum brake include brake shoes, brake drums, wheel cylinders, and return springs. When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, hydraulic fluid is sent to the wheel cylinders, causing them to push the brake shoes against the inside surface of the brake drum. This friction between the brake shoes and the drum slows down the rotation of the wheel, eventually bringing the vehicle to a stop.
Brake shoes: Brake shoes are curved metal plates that contain friction material or brake lining on the outer surface. When the wheel cylinders apply pressure, the brake shoes are forced against the drum, creating friction to slow down the wheel.
Brake drums: Brake drums are large, cylindrical metal components that are attached to the wheel hubs. They provide a surface for the brake shoes to press against, generating the necessary friction to slow down the wheels.
Wheel cylinders: Wheel cylinders are hydraulic devices that convert the pressure from the brake pedal into a mechanical force. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic fluid is directed to the wheel cylinders, causing them to extend and push the brake shoes against the drum.
Return springs: Return springs are used to retract the brake shoes away from the drum when the brake pedal is released. They ensure that the brake shoes do not remain in constant contact with the drum, preventing unnecessary wear and heat buildup.
In summary, a drum brake is a braking system that uses friction to slow down or stop the rotation of the wheels. It is composed of brake shoes, brake drums, wheel cylinders, and return springs, all working together to provide effective braking performance.
Components of a 1993 Ford Ranger Drum Brake

The drum brakes on a 1993 Ford Ranger consist of several key components that work together to provide efficient braking performance. Understanding these components and their functions is essential for proper maintenance and repairs.
1. Brake Drum: The brake drum is a cylindrical component that is mounted onto the wheel hub. When the brake pedal is pressed, the brake shoes inside the drum come into contact with the drum, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle.
2. Brake Shoes: The brake shoes are curved metal plates that are lined with friction material. They are located inside the brake drum and are attached to the backing plate. When the brake pedal is engaged, the hydraulic pressure forces the brake shoes against the drum, creating the necessary friction to stop the vehicle.
3. Wheel Cylinder: The wheel cylinder is responsible for applying pressure to the brake shoes. It is located at the top of the brake assembly and is connected to the hydraulic brake system. When hydraulic pressure is applied, the wheel cylinder extends and pushes the brake shoes against the drum.
4. Brake Springs: Brake springs play a crucial role in the operation of drum brakes. They help to return the brake shoes to their original position after the brake pedal is released. They also provide tension to keep the brake shoes in contact with the drum when the brakes are not being applied.
5. Self-Adjuster Mechanism: The self-adjuster mechanism is designed to automatically adjust the clearance between the brake shoes and the drum as the friction material wears down over time. This ensures consistent braking performance and reduces the need for manual adjustment.
6. Adjusting Lever: The adjusting lever is a component that connects the self-adjuster mechanism to the brake shoes. It helps to activate the self-adjuster when the brake pedal is released, allowing for proper adjustment of the brake shoes.
By understanding the purpose and function of these components, drivers and mechanics can effectively maintain and service the drum brakes on a 1993 Ford Ranger, ensuring optimal braking performance and safety on the road.
Brake Drum
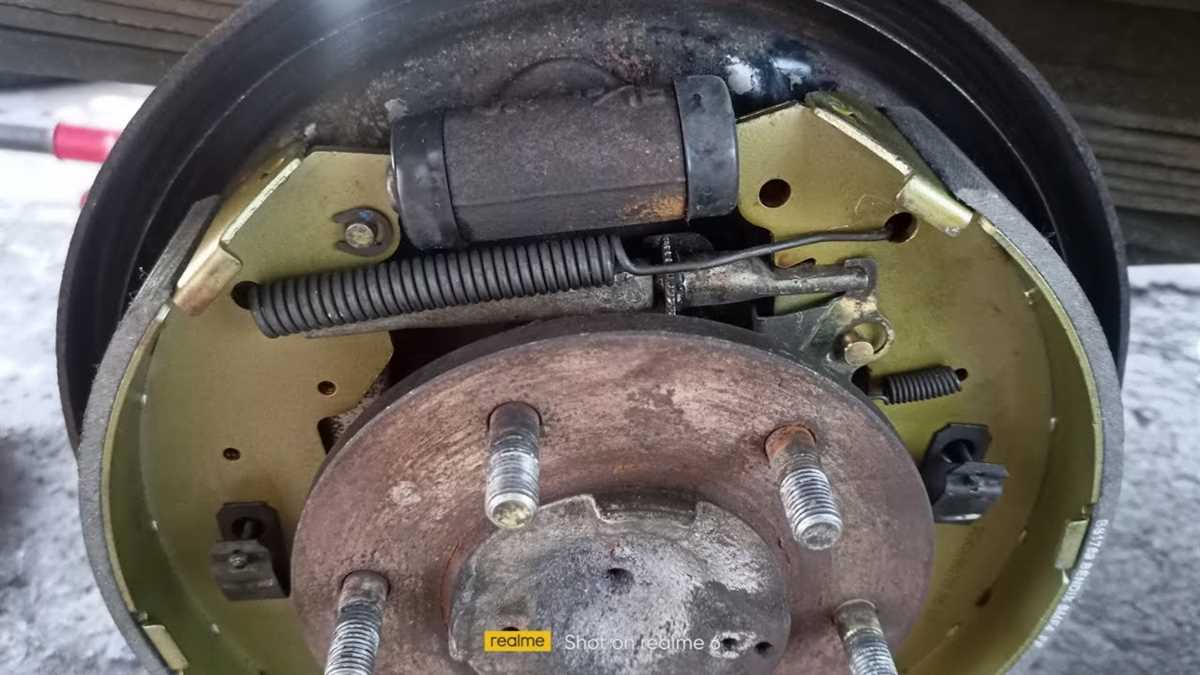

A brake drum is a part of the drum braking system used in many vehicles, including the 1993 Ford Ranger. It is a large cylinder-shaped component located on each of the rear wheels. The brake drum is an essential part of the drum brake system, which is responsible for stopping or slowing down the vehicle.
The brake drum works in conjunction with other components, such as brake shoes, wheel cylinders, and springs, to create the necessary friction to stop the vehicle. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is applied to the wheel cylinders, which then pushes the brake shoes against the inner surface of the brake drum.
The inner surface of the brake drum is lined with brake linings, which provide the necessary friction to stop the rotation of the drum and, consequently, the vehicle. As the brake shoes press against the brake linings, the friction generates heat, which is dissipated through the brake drum, preventing overheating of the braking system.
The brake drum is designed to be strong and durable, as it is subjected to high levels of heat and friction during braking. However, over time, the brake drum can wear out or become damaged, which may affect the performance of the braking system. Regular inspection and maintenance of the brake drum, including checking for signs of wear, cracks, or warping, are essential to ensure optimal braking performance and safety.
Overall, the brake drum plays a critical role in the drum braking system of the 1993 Ford Ranger. It is a vital component that, when properly maintained, helps ensure safe and effective braking performance for the vehicle.
Brake Shoes
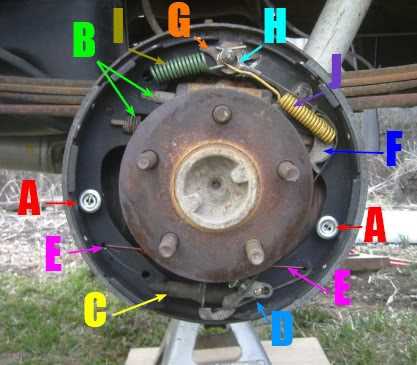
Brake shoes are an essential component of the drum brake system in a 1993 Ford Ranger. They are responsible for applying pressure to the brake drum, which causes friction and slows down the vehicle. The brake shoes are typically made of a heat-resistant material, such as steel or aluminum, and are designed to withstand the high temperatures generated during braking.
When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is applied to the brake shoes, causing them to move outward and make contact with the brake drum. The friction generated between the brake shoes and the drum converts the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into thermal energy, dissipating the heat through the brake drum and causing the vehicle to slow down or come to a complete stop.
In the case of a 1993 Ford Ranger, the drum brake system consists of two brake shoes per wheel, one primary and one secondary. The primary shoe is located towards the front of the vehicle and receives the most force during braking. The secondary shoe is located towards the rear and assists in providing additional braking power.
The brake shoes in a 1993 Ford Ranger should be regularly inspected for wear and tear. If the brake shoes are too thin or damaged, they should be replaced to ensure optimal braking performance. Additionally, the brake shoes should be properly lubricated to reduce friction and avoid premature wear. It is crucial to maintain the drum brake system in good condition to ensure the safety and reliability of the vehicle.
Wheel Cylinder
The wheel cylinder is an essential component of the drum brake system in a 1993 Ford Ranger. It plays a crucial role in transferring hydraulic pressure to the brake shoes, causing them to press against the drum and create friction for braking.
Function: The wheel cylinder is responsible for converting hydraulic pressure from the brake master cylinder into mechanical force. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic fluid is forced into the wheel cylinder, causing the pistons inside to push the brake shoes against the drum. The resulting friction slows down or stops the rotation of the wheel.
Location: In a 1993 Ford Ranger, there is a wheel cylinder for each wheel. They are typically located on the backside of the brake assembly, near the bottom of the drum. Each wheel cylinder is connected to the brake shoes by a series of rods and springs.
Components: The wheel cylinder consists of several important components. These include the cylinder body, which houses the pistons, rubber seals, and springs. The pistons move back and forth within the cylinder, applying pressure to the brake shoes. The rubber seals help to prevent leaks and maintain hydraulic pressure, while the springs provide tension to retract the brake shoes when pressure is released.
Maintenance and Replacement: Over time, the wheel cylinder can become worn or damaged due to the high heat and pressure involved in braking. Common issues include leaking seals and corroded pistons. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting for leaks and replacing worn components, is essential to ensure the proper functioning of the wheel cylinder. If a wheel cylinder is found to be faulty, it should be replaced promptly to prevent brake failure.
Return Springs
In the drum brake system of a 1993 Ford Ranger, return springs play a crucial role in ensuring proper brake operation. These springs are responsible for retracting the brake shoes after the brakes are applied, allowing the wheels to rotate freely.
The return springs in the drum brake assembly are typically positioned between the brake shoes and the anchor pin or the backing plate. They are designed to exert a force that pulls the brake shoes away from the brake drum, creating a small air gap between the shoes and the drum when the brakes are not applied.
Function of Return Springs:
- Providing brake shoe retraction: When the brakes are released, the return springs pull the brake shoes away from the brake drum. This retraction is necessary to prevent the shoes from dragging on the drum, which can cause excessive heat buildup and premature wear.
- Ensuring proper clearance: The return springs help maintain the proper clearance between the brake shoes and the drum, allowing for smooth and efficient braking performance. This clearance ensures that the shoes do not contact the drum when the brakes are not applied, minimizing friction and extending the life of the brake components.
- Assisting in brake shoe centering: Return springs also assist in centering the brake shoes within the drum, ensuring even braking pressure on both sides of the drum. This helps prevent uneven wear and promotes balanced braking performance.
It is important to regularly inspect and maintain the return springs in a 1993 Ford Ranger drum brake system. Over time, these springs can weaken or become damaged, compromising their ability to properly retract the brake shoes. If a return spring shows signs of wear or is broken, it should be replaced to maintain the safety and effectiveness of the vehicle’s braking system.
How Does a Drum Brake Work?
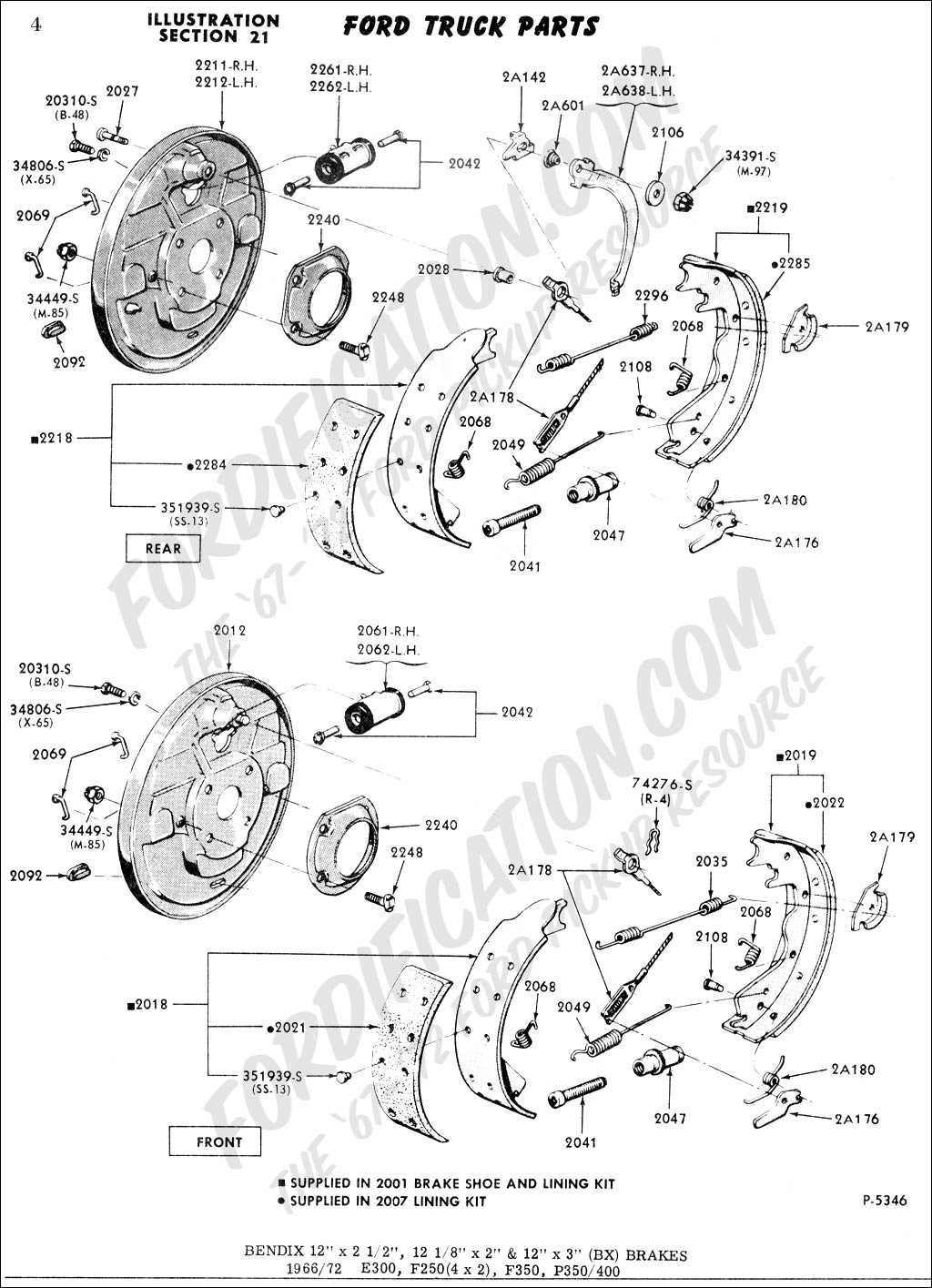
A drum brake is a type of braking system commonly found in older vehicles, such as the 1993 Ford Ranger. It consists of several components, including the brake drum, brake shoes, wheel cylinder, and brake hardware. Understanding how a drum brake works is essential for proper maintenance and repair.
When the driver applies the brakes, hydraulic pressure is exerted on the wheel cylinder, which in turn pushes the brake shoes against the brake drum. The brake drum is a circular metal housing attached to the wheel hub. As the brake shoes press against the inside surface of the drum, friction is created, resulting in a slowing or stopping of the vehicle.
- Brake drum: The brake drum is a large metal cylinder with a hollow center that fits over the wheel hub. Its purpose is to provide a surface for the brake shoes to press against.
- Brake shoes: The brake shoes are curved metal plates lined with friction material. They are attached to the backing plate and move in response to hydraulic pressure from the wheel cylinder.
- Wheel cylinder: The wheel cylinder is a hydraulic device that converts the pressure from the brake pedal into the force that pushes the brake shoes against the drum. It consists of two pistons and a seal that maintains hydraulic pressure.
- Brake hardware: The brake hardware includes various springs, clips, and adjusters that hold the brake shoes in place and allow for proper adjustment.
As the brake shoes press against the drum, friction is generated, causing the vehicle to slow down or stop. However, over time, the friction material on the brake shoes wears down, requiring regular maintenance and replacement. It is important to inspect and service drum brakes regularly to ensure optimal braking performance and safety on the road.
How to Replace Drum Brakes on a 1993 Ford Ranger
Replacing the drum brakes on a 1993 Ford Ranger is an important maintenance task that should be done regularly to ensure the safety and efficiency of your vehicle’s braking system. By following a few simple steps, you can replace the drum brakes on your 1993 Ford Ranger and restore optimal braking performance.
Steps to Replace Drum Brakes:
1. Prepare for the Task: Before starting the replacement process, gather all the necessary tools and equipment, including a jack, jack stands, lug wrench, brake cleaner, brake parts cleaner, brake lubricant, new brake shoes, and any additional hardware if needed. Park the vehicle on a flat and level surface and engage the parking brake.
2. Remove the Wheel and Drum: Begin by loosening the lug nuts on the wheel where you will be replacing the drum brakes. Lift the vehicle using a jack and secure it with jack stands. Remove the lug nuts and carefully take off the wheel. Using a rubber mallet, tap the drum to loosen it and remove it from the wheel hub.
3. Inspect and Clean the Brake Components: Inspect the brake components for any signs of damage or excessive wear. If necessary, replace any damaged parts. Use brake cleaner and a wire brush to clean the drum, wheel hub, and any other brake parts. Ensure that all dirt, debris, and old brake lining are thoroughly removed.
4. Install the New Brake Shoes: Apply a thin layer of brake lubricant to the contact points of the brake shoes. Install the new brake shoes into the drum, making sure they are aligned correctly. Attach any required hardware and ensure that everything is securely in place.
5. Reassemble the Drum: Slide the drum back onto the wheel hub and make sure it is properly seated. Use a rubber mallet to tap it gently into place if necessary. Reinstall the wheel onto the wheel studs and hand-tighten the lug nuts.
6. Adjust the Brakes: Use a brake adjustment tool or a flathead screwdriver to adjust the brake shoes until they lightly brush against the drum. Ensure that the brake shoes are properly aligned and adjusted for optimal braking performance.
7. Repeat the Process: Repeat the above steps for the remaining wheels that require drum brake replacement.
8. Test the Brakes: After replacing the drum brakes on all wheels, lower the vehicle from the jack stands and remove the jack. Start the engine and pump the brake pedal several times to restore hydraulic pressure. Test the brakes by driving the vehicle at a low speed and performing a series of stops to ensure they are functioning properly.
Conclusion:
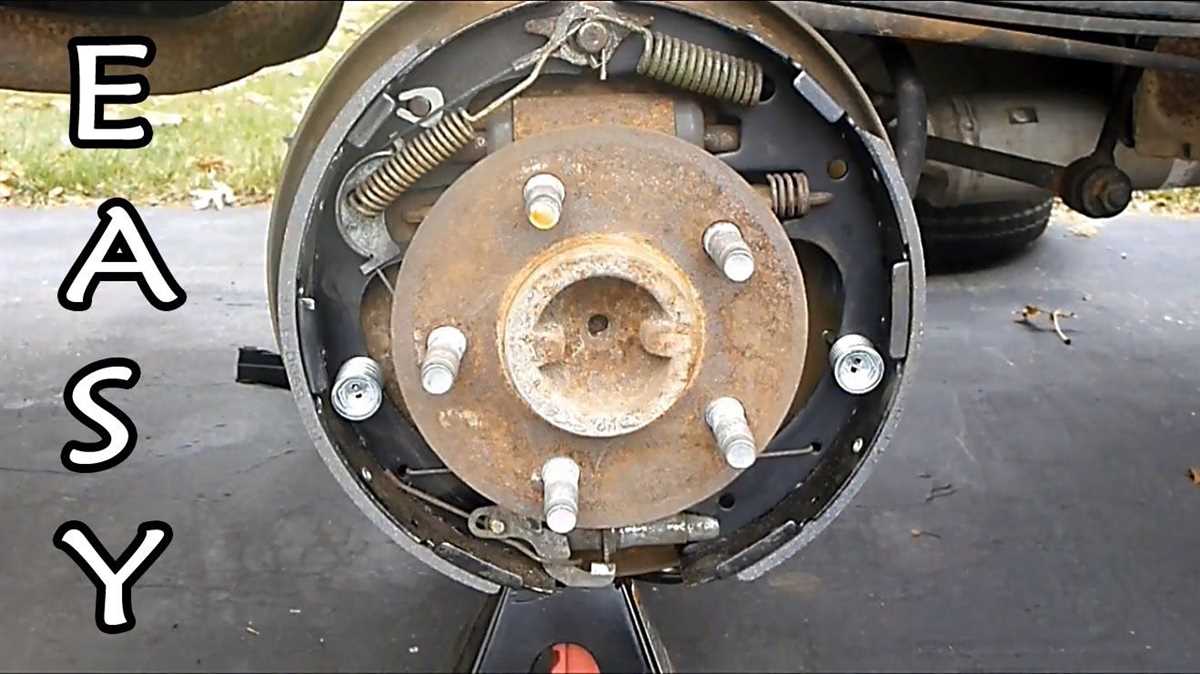

Replacing drum brakes on a 1993 Ford Ranger is a relatively straightforward process that can be completed with basic mechanical skills and tools. Regular maintenance of your vehicle’s braking system is crucial for safety and optimal performance. By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure that your 1993 Ford Ranger’s drum brakes are in good condition and functioning properly.