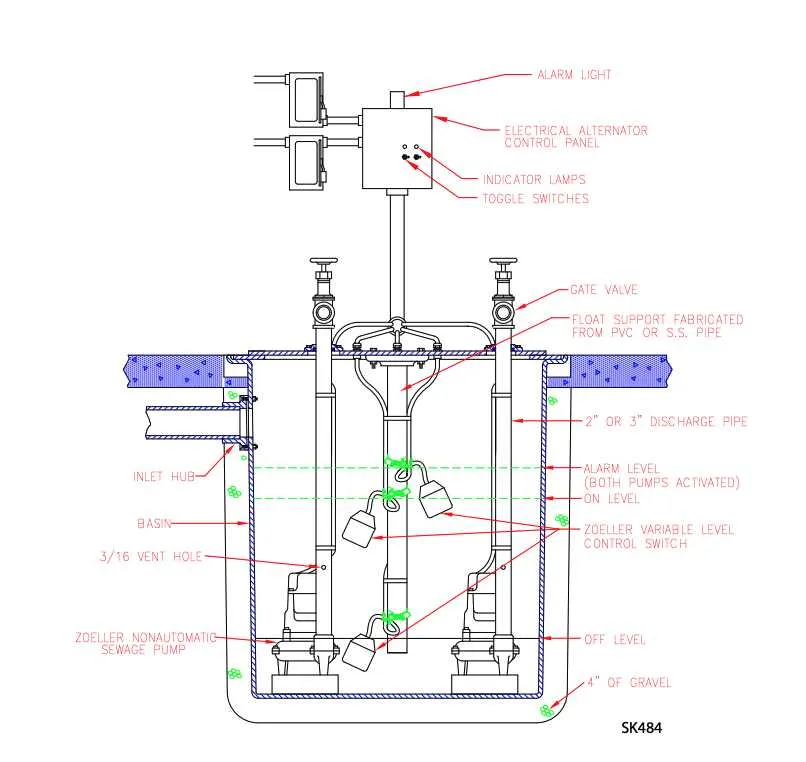
Ensure proper air circulation for optimal performance. The ventilation system must be carefully designed to prevent airlocks and ensure smooth fluid flow. Always position the vent line at a high point in the installation to avoid interference with waste material movement. This helps prevent any unwanted pressure build-up, which can cause malfunctions or inefficient operation.
Vent pipe sizing is critical. Select the correct diameter for the vent pipe based on the specific requirements of the system. A pipe that is too small can restrict airflow, leading to increased pressure and potential system failures. A larger diameter, however, may be necessary for longer or more complex setups to maintain an effective venting process.
Proper placement is crucial. Ensure that the vent outlet is directed away from areas with high foot traffic or sensitive equipment. It is also important to place the vent outlet above the highest point of the system to allow proper air expulsion. A suitable location will minimize the chance of odor leakage and keep the system functioning optimally.
Detailed Guide to Wastewater Disposal System Airflow Management
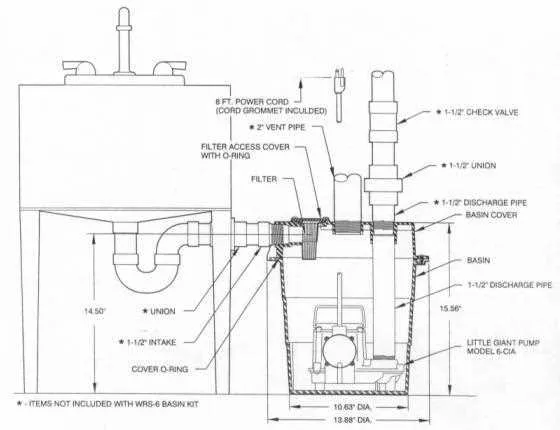
Proper airflow management is crucial for ensuring that wastewater removal systems operate efficiently and without issues. Here are the key considerations to effectively manage air circulation in these systems:
- Ensure the discharge line includes a vent pipe that extends well above ground level, promoting adequate air release from the system.
- Position the air vent near the highest point of the system to allow trapped air to escape and prevent blockages.
- Use a vent cap to prevent debris and rainwater from entering the pipe, which could impede air flow.
- Install a vent with the appropriate diameter to match the capacity of the system, ensuring air pressure is balanced.
- Avoid placing vent openings near windows, vents, or air intake areas to prevent unpleasant odors from entering the living spaces.
When selecting materials for the venting components, opt for durable, corrosion-resistant piping to avoid degradation over time. Schedule regular inspections to ensure there are no clogs or obstructions in the venting system.
- Install an anti-backflow valve to prevent gases from entering the interior spaces in case of pressure imbalances.
- Use cleanouts at strategic points along the venting system to allow for easy maintenance and clearing of any potential blockages.
In complex installations, consider hiring a professional to ensure compliance with local building codes and to optimize airflow functionality. Proper installation and regular maintenance are the keys to long-term system performance.
Understanding the Basic Principles of Wastewater System Airflow Control
Ensure proper airflow by installing a venting system that allows air to enter the chamber when the system operates. A closed system can lead to pressure build-up, preventing optimal function. A well-designed air inlet reduces resistance and promotes smooth discharge, allowing waste materials to flow efficiently.
For effective operation, select vent pipes that match the capacity of the system. A pipe too narrow will restrict airflow, while one too wide may fail to maintain necessary pressure balance. Typically, a 2- or 3-inch pipe works best for standard setups.
Install the vent at an appropriate height to avoid clogging or blockages from external debris. Position the vent outlet above the system’s highest point to allow air to escape easily, preventing siphoning effects that can disrupt operation.
Maintenance is critical; inspect the vent regularly to ensure no obstructions are present. Even small blockages, such as dirt or leaves, can lead to significant performance issues. Always check that the vent remains clear, particularly after heavy rainfall or storms.
Consistency in checking for leaks around the vent connections will help maintain system integrity. Small leaks can lead to air pressure imbalances, which may result in inefficient waste disposal and damage to the components over time.
Step-by-Step Process of Installing Vent Pipes for Wastewater Pumps
Ensure the vent pipes are placed vertically, extending from the system to above the roofline, to allow for proper airflow. This will help in preventing airlock situations and ensure efficient pressure regulation.
Start by cutting the vent pipe to the required length. The ideal height should be a minimum of 6 inches above the roof. Use a level to ensure the pipe remains straight during installation.
Install a coupling at the connection point between the discharge and the vent pipe to ensure a secure and leak-free attachment. Make sure to check the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended coupling size.
When positioning the pipe, avoid sharp bends, as they can restrict airflow. Instead, use gradual angles when necessary. Avoid using more than two 45-degree bends in a single line of piping to maintain efficient flow.
Ensure the pipe is securely fastened to prevent shifting. Use pipe straps or brackets to hold the vent pipe in place along its length, checking that the pipe is not under tension or stress.
After installation, test the airflow by running water through the system. Listen for any unusual noises or air pressure changes that could indicate blockages or improper installation. This ensures that the pipe is functioning as expected.
Common Issues and Solutions in Wastewater System Airflow
Ensure proper air circulation to prevent pressure build-up and maintain efficient system operation. A clogged vent can lead to slow drainage or backups. Regularly check the air intake for obstructions, such as debris or nests, which can block airflow.
If the ventilation pipe is improperly sized, the system may not function optimally. It is essential to match the pipe diameter to the capacity of the system. If the pipe is too small, air won’t circulate efficiently, leading to sluggish performance.
Inadequate venting can also cause odor issues. A poorly installed or damaged vent pipe might allow odors to escape. Inspect the piping for leaks or cracks, especially at connection points. Replacing or sealing damaged sections can restore proper airflow and eliminate unpleasant smells.
Excessive condensation in vent pipes can occur in cold climates. To prevent water from accumulating and freezing, ensure the vent is properly insulated. This will maintain consistent airflow and prevent blockage from ice build-up during winter months.
Ensure that the vent pipe extends above the roofline to avoid negative pressure and allow gases to escape. A vent positioned too low can restrict airflow and lead to system malfunctions. Regular inspections of the pipe height and alignment can prevent these issues.