
When connecting a towing safety system to your vehicle, it is crucial to follow the precise setup to ensure proper functionality. The system’s connection to the vehicle’s electrical circuit must be correct to avoid malfunctions. Start by ensuring all terminals are clean and corrosion-free. It’s advisable to use a multimeter to verify that each terminal provides a consistent and reliable signal.
Key Considerations: Ensure that the power input matches the system’s required voltage. Incorrect voltage can damage the system or cause it to malfunction. Double-check the continuity of the connections to prevent electrical shorts, which can lead to further issues. It’s also essential to confirm that the ground connection is solid and free from interference.
Common Troubleshooting Tip: If the safety system fails to activate, inspect the connection for any loose or damaged wires. Re-secure or replace any faulty wires to restore proper functionality.
Electrical Connections for Trailer Safety System
Ensure proper connection between the power source and the towing vehicle by linking the designated input to the vehicle’s electrical system. The positive terminal should be wired to the vehicle’s battery, while the ground terminal is connected to a metal part of the chassis. This establishes a secure path for the current to flow during operation.
Next, connect the signal line from the towing vehicle’s braking mechanism to the corresponding input of the device. Use heavy-duty, insulated wiring to avoid any short circuits. The connection should be made with solid terminals for reliability, minimizing any chance of loose connections that could result in failure during towing.
For the additional safety features, include a safety override connection, which will engage the system even if the main signal fails. It is recommended to use a separate fuse for this circuit to prevent any system-wide damage. Ensure that each connection is tight and well-insulated to avoid any exposure to moisture or elements that could corrode the wires over time.
Test the system thoroughly after installation. Make sure that each component functions correctly by checking that the signal is sent from the towing vehicle and the device responds properly under varying load conditions. Adjust the sensitivity to suit the specific requirements of your trailer.
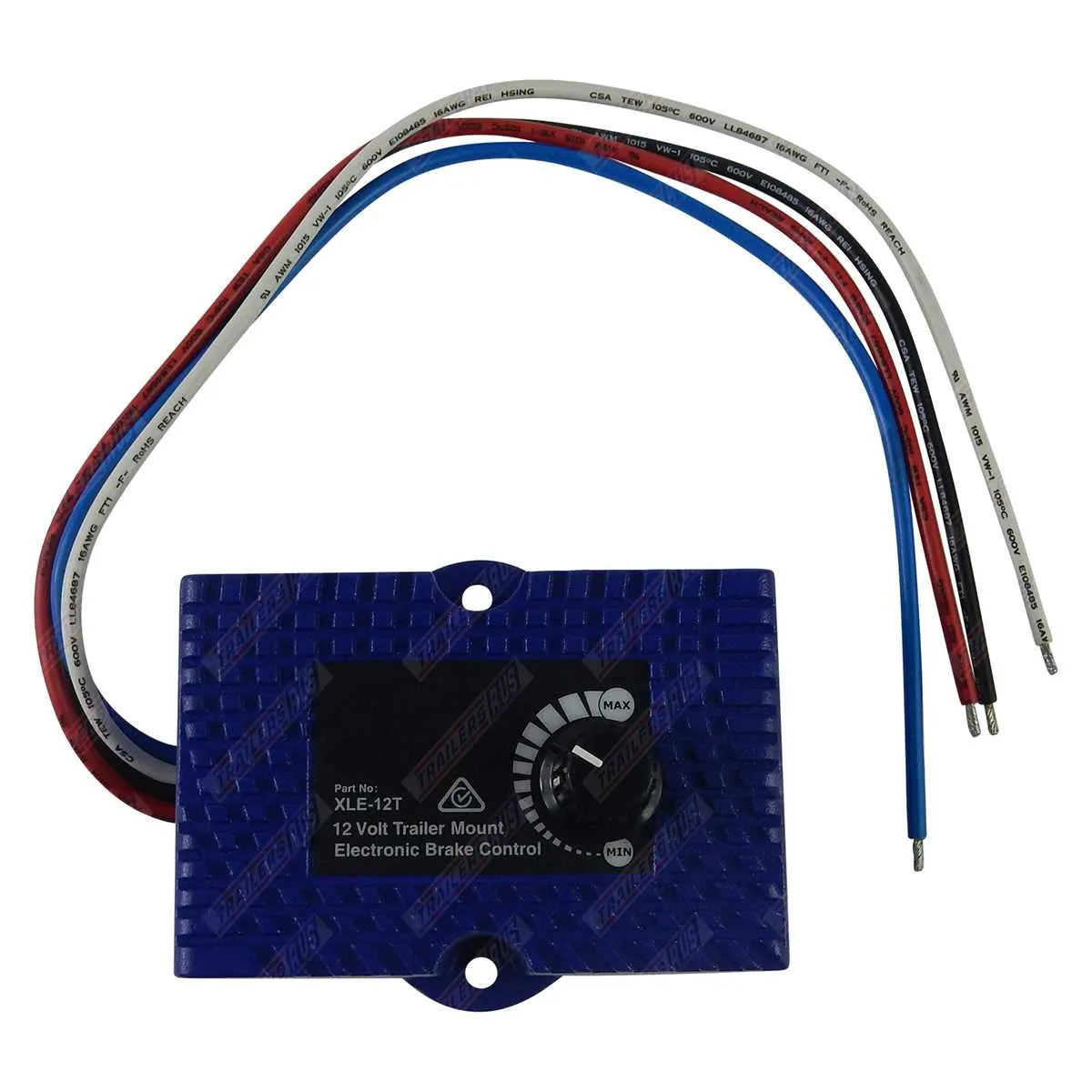
How to Identify and Connect the Power Supply Wires in Electric Braking Systems
Start by locating the power supply cable that provides the necessary voltage for the system. This is typically a thicker wire, often color-coded, which connects to the main electrical circuit. Ensure the wire is routed through a secure channel, avoiding areas of high heat or potential interference.
The positive terminal is usually marked with a red wire or a “+” symbol. Use a multimeter to verify the voltage if unsure. The negative terminal, typically indicated with a black wire or “-” symbol, should be securely connected to the grounding point of the vehicle’s electrical system. Check that the connection is tight and there is no corrosion.
If your system requires an additional power source for auxiliary functions, look for a separate wire labeled for auxiliary power or “ACC”. Connect this to a switched power source, ensuring that the system will only activate when the vehicle is running, preventing any drain when off.
After identifying the wires, make the connections using high-quality connectors that ensure a stable and secure link. If crimp connectors are used, ensure the crimp is firm enough to prevent accidental disconnection. Finally, inspect all connections for signs of wear or exposure to moisture, and use electrical tape or heat shrink tubing to prevent any potential short circuits.
Step-by-Step Guide for Connecting a Trailer to the Vehicle’s Stopping System

1. Begin by selecting the correct connection kit for your vehicle and trailer. Ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system and the trailer’s needs.
2. Locate the vehicle’s connection port, typically near the rear bumper or inside the cabin. This is where you will attach the necessary cables.
3. Attach the ground wire from the vehicle’s power source to the trailer’s designated grounding point. This ensures that the system functions properly and prevents electrical malfunctions.
4. Identify the signal wires in the vehicle’s electrical system. These will transmit the necessary signals to the trailer’s stopping components. Connect each wire to the corresponding terminals on the trailer. Make sure to securely fasten each connection to avoid loose contacts.
5. For the signal wires, follow the vehicle’s manual to determine the correct sequence. Typically, these signals include the stop-light, turn signals, and auxiliary signals for additional features such as hazard lights or trailer stability systems.
6. Once all wires are connected, verify that each signal is correctly transmitted by testing each function individually. Turn on the vehicle and check the trailer’s lighting and stopping systems to ensure they react as intended when activated.
7. If everything is properly connected and functioning, secure any exposed wires to prevent damage from road conditions. Use cable ties or appropriate insulation to protect the wiring from abrasion or environmental elements.
8. Finally, perform a full system check to confirm that the vehicle’s and trailer’s systems work seamlessly together. If any discrepancies are found, review your connections to identify and fix any issues.
Common Issues with Brake Controller Wiring and How to Resolve Them
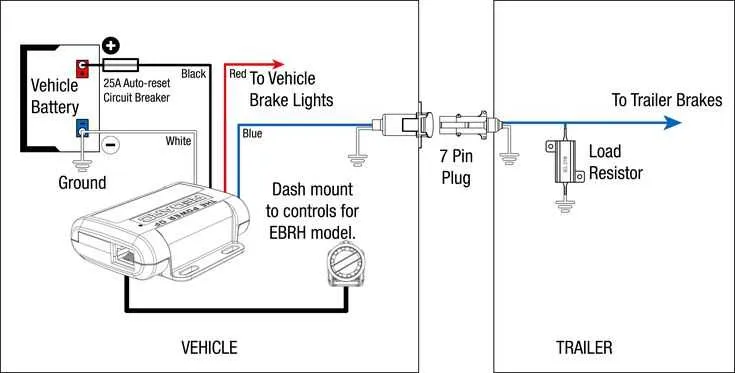
Incorrect connections are the primary cause of malfunction in these systems. Always verify that the terminals are correctly matched to their respective wires.
- Loose Connections: Ensure all terminals are securely tightened. Loose connections can result in intermittent power loss. Check each terminal and replace any worn-out connectors.
- Grounding Problems: An improper ground connection can prevent the system from functioning. Inspect the grounding point for corrosion or looseness. Clean or replace the ground terminal if needed.
- Corroded or Damaged Wires: Over time, wires may deteriorate, especially if exposed to moisture. Replace any frayed or corroded wires immediately to prevent further issues.
- Power Overload: Too much power drawn from the unit can cause overheating and malfunctions. Use a fuse rated for the system’s specifications to prevent overloading.
- Misplaced Connections: Incorrectly connected wires can disrupt the system’s function. Double-check the manufacturer’s guide to ensure that each wire is correctly placed according to the vehicle’s setup.
By addressing these common issues, the system can operate effectively and safely, ensuring that the vehicle functions as expected.