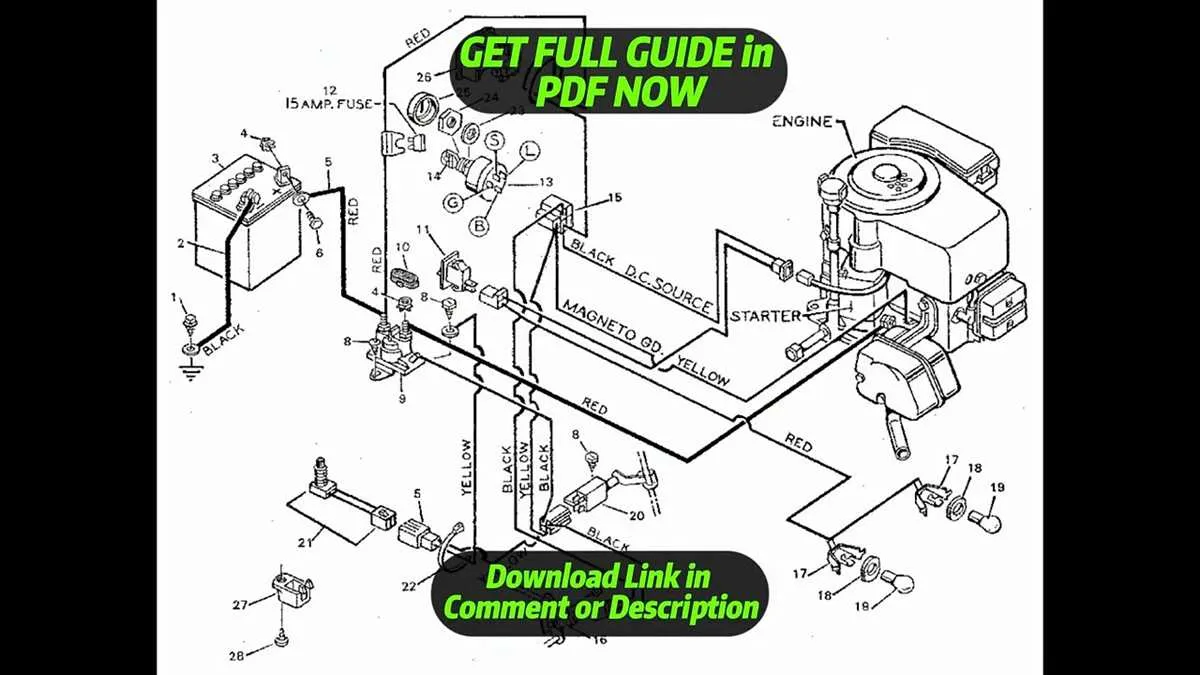
To efficiently troubleshoot or repair the electrical components of your lawn tractor, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of its power system. Focus on the key connections such as the battery, ignition switch, and motor terminals. A reliable system ensures smooth operation and prevents frequent breakdowns.
Identify the Battery Connections: Begin by examining the positive and negative terminals. Ensure that both are properly connected to prevent power issues. A loose or corroded terminal can disrupt the tractor’s performance.
Check the Safety Switch Wiring: Verify that the safety switches are linked correctly to the ignition circuit. These switches are essential to start and stop the engine safely, cutting power when necessary. Malfunctioning safety switches are often a common cause of starting problems.
Inspect Ground Connections: Ensure that all ground points are tightly secured to the frame of the machine. A weak ground connection can lead to irregular electrical behavior, causing intermittent faults.
Understand the Motor and Solenoid Links: The solenoid plays a crucial role in transferring current to the engine’s starter motor. Make sure all links between the starter solenoid and the engine are intact to avoid stalling or failure to start.
By focusing on these areas, you’ll be able to effectively diagnose and address issues with your machine’s power system, ensuring it operates at peak efficiency.
Understanding the Electrical Layout for Your Lawn Equipment
Start by identifying the key components: ignition switch, battery, solenoid, and starter motor. Ensure each part is properly connected according to the manufacturer’s guide to prevent malfunctions.
For optimal performance, the battery terminals must be clean and tightly secured to avoid electrical loss. If you notice dim lights or slow engine cranking, inspect the battery for corrosion or loose connections.
The solenoid is crucial for initiating the engine. Test it by connecting a multimeter to the terminal while attempting to start. If there’s no voltage change, replacing the solenoid may be necessary.
Check all fuse connections, especially if you experience electrical failures. A blown fuse often indicates a short circuit or overcurrent, so use the proper rating to avoid damage to the system.
Finally, ensure that all ground connections are intact. A poor ground can lead to irregular electrical flow, affecting engine start-up or operation. Clean the ground points and make sure they’re tightly connected to the frame.
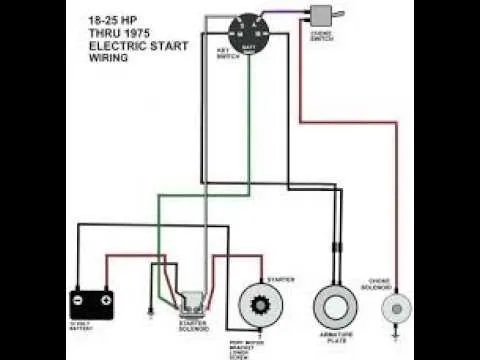
Understanding the Main Power System
The main power system in these machines is essential for ensuring smooth operation and effective engine performance. Start by checking the battery, as it supplies the necessary voltage to start the engine. A fully charged, properly installed battery is crucial for preventing starting issues. Pay close attention to the battery terminals, ensuring they are clean and free from corrosion.
The alternator plays a key role in maintaining battery charge while the engine runs. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, keeping the battery at an optimal level. If the alternator malfunctions, it could result in the battery draining quickly, leading to starting problems or complete power failure.
Inspect the fuses regularly, as these protect the electrical components from overloading. A blown fuse can disrupt power flow, leading to malfunctioning electrical systems. Always replace fuses with the correct amperage to avoid further damage.
Another critical element is the starter solenoid, which controls the power flow to the starter motor. When the key is turned, the solenoid sends current to the starter motor, engaging the engine. A faulty solenoid can prevent the engine from turning over, so be sure to test and replace it if necessary.
Finally, check the grounding connections. A poor ground connection can lead to electrical surges or failure to power on. Clean the ground wire connections and make sure they are securely attached to the frame of the machine.
Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting Electrical Issues on Lawn Equipment
Start by checking the battery voltage with a multimeter. A fully charged battery should read between 12.6 and 12.8 volts. If the reading is lower, recharge or replace the battery.
- Inspect the fuses: Identify the location of the fuse box. Replace any blown fuses with the correct amperage rating.
- Examine the ignition switch: Ensure the ignition switch is functioning. If the engine won’t start, test the switch with a multimeter for continuity.
If the engine does not crank, the solenoid might be faulty. Test it by checking for voltage at the starter terminal when turning the ignition key.
- Check the connections: Inspect all wiring connections for corrosion, loose terminals, or frayed wires. Tighten and clean all connections where necessary.
- Test the safety switches: Safety switches on the seat, parking brake, and blades are crucial. Ensure all switches are engaged properly, as a faulty switch can prevent the engine from starting.
Use a test light to confirm power is reaching the starter motor. If the starter doesn’t engage despite having power, it could be worn out.
- Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental starting.
- Remove the starter motor and test it by bypassing the switch.
- If the starter turns over, replace the solenoid. If it doesn’t, replace the starter motor.
Lastly, ensure the charging system is functioning by testing the alternator. If the voltage exceeds 13.5 volts with the engine running, the alternator is working. If not, it may need to be replaced.
How to Replace or Repair the Electrical System Harness on Lawn Tractors
Start by disconnecting the battery to avoid any accidental shorts or electrical shocks. Locate the faulty harness and identify the damaged wires. Use a multimeter to check for continuity or any breaks in the circuit. If you find a short or damaged wire, carefully cut it out using wire cutters.
Next, strip the insulation from the wire ends that need replacement. Match the replacement wire with the same gauge to maintain proper current flow. Solder the new wire securely and cover the joint with heat shrink tubing to prevent further damage. Use electrical tape to reinforce any connections that might be exposed to moisture or friction.
Ensure that the new harness matches the original one in terms of length and routing. Avoid pinching wires or leaving them exposed to moving parts, which can lead to further issues down the road. After securing the harness in place, reconnect the battery and test all electrical components to verify proper functionality.
If the damage is widespread, replacing the entire system may be necessary. In that case, follow the same procedures, but be sure to remove the old system completely before installing the new one. Always follow manufacturer specifications for wire gauges and routing to ensure safety and optimal performance.