An air conditioner control system is a crucial component of any air conditioning unit. It is responsible for regulating the temperature, humidity, and airflow within a building or vehicle to ensure maximum comfort for occupants. The control system consists of various components working together in a block diagram arrangement to achieve these objectives.
The primary function of the control system is to receive input from various sensors and adjust the operation of the air conditioning unit accordingly. These sensors include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, and airflow sensors, which provide real-time data on the current conditions. The control system then analyzes this information and sends instructions to the different components of the air conditioner, such as the compressor, fan, and damper, to achieve the desired temperature, humidity, and airflow.
The block diagram of an air conditioner control system typically includes several key components. These include the microcontroller, which serves as the brain of the system and processes the input data from the sensors. The microcontroller also sends signals to the different components of the air conditioner to control their operation. Additionally, the control system may include a user interface, such as a thermostat or control panel, which allows users to adjust the settings and preferences of the air conditioner.
Other components of the control system may include relays, which are used to switch power to different components, and power supplies, which provide the necessary electrical energy for the system to function. The control system may also include a feedback loop, which continuously monitors the output of the air conditioner and adjusts the operation accordingly to maintain the desired conditions. Overall, the block diagram of an air conditioner control system provides an overview of how the different components work together to regulate the indoor climate and ensure optimal comfort for occupants.
Overview
An air conditioner control system block diagram provides a high-level overview of the various components and their interactions in an air conditioning system. It showcases the complexity of the system and illustrates how different parts work together to deliver cool air and maintain desired indoor temperature.
In a typical air conditioner control system, there are several key components including the thermostat, the control board, the compressor, the condenser, and the evaporator. These components work together to regulate the temperature, manage the refrigerant flow, and control the fan speed to achieve the desired cooling effect.
The thermostat is the primary input device for the system. It allows users to set the desired temperature and mode of operation. The information from the thermostat is passed to the control board, which acts as the central processing unit of the system. The control board receives input from the thermostat and other sensors, and it sends signals to the various components to regulate their operation.
The compressor is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas and raising its temperature before it enters the condenser. The condenser then cools down the refrigerant, causing it to condense into a liquid state. The liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve and enters the evaporator, where it evaporates, absorbing heat from the surrounding air in the process. The cooled air is then circulated back into the room, while the warm refrigerant is sent back to the compressor to start the cycle again.
The air conditioner control system block diagram provides a visual representation of the interplay between these components and their respective roles in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. It serves as a valuable tool for engineers and technicians to understand the system design, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance.
Components of the air conditioner control system
The air conditioner control system is composed of several interconnected components that work together to ensure the comfortable and efficient operation of the air conditioning unit. These components include:
- Thermostat: The thermostat is a temperature-sensitive device that allows the user to set the desired temperature of the room. It acts as the main control interface for the air conditioning system.
- Temperature sensor: The temperature sensor is used to measure the current temperature of the room. It provides feedback to the control system, allowing it to adjust the cooling or heating output accordingly.
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the cooling system. It compresses refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure, before sending it to the condenser.
- Condenser: The condenser is a heat exchanger that cools down the high-temperature refrigerant gas and converts it into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It helps to lower the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to absorb heat from the surrounding environment.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is another heat exchanger that absorbs heat from the room and releases cool air into the environment. It cools down the low-pressure liquid refrigerant, converting it back into a gas.
- Blower fan: The blower fan is responsible for circulating the cooled air throughout the room. It helps to maintain a consistent temperature and airflow, ensuring optimal comfort.
- Control board: The control board is the brain of the air conditioner control system. It receives inputs from the thermostat and temperature sensor, and sends commands to the compressor, blower fan, and other components to achieve the desired temperature.
By integrating these components, the air conditioner control system can effectively regulate the temperature of the room, providing a comfortable and energy-efficient cooling or heating solution for the users.
Sensing and Feedback Devices
In an air conditioner control system, sensing and feedback devices play a crucial role in monitoring and regulating various parameters to ensure optimal performance and user comfort. These devices provide real-time data and enable the system to make necessary adjustments based on the feedback received.
Temperature Sensors: One of the key sensing devices in an air conditioner control system is the temperature sensor. It accurately measures the ambient temperature and provides this information to the control unit. Based on the feedback from the temperature sensor, the air conditioner can adjust the cooling or heating output to maintain the desired temperature set by the user.
Humidity Sensors: Humidity sensors are another important component in an air conditioner control system. These sensors measure the amount of moisture in the air and provide feedback to the control unit. With this information, the system can adjust the dehumidification or humidification processes to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Occupancy Sensors: Occupancy sensors are used to detect the presence of people in a room or space. These sensors help the air conditioner control system determine whether a room is occupied or vacant. If a room is unoccupied for a certain period, the system can adjust the temperature settings or switch to an energy-saving mode to conserve energy.
Airflow Sensors: Airflow sensors measure the velocity and direction of air movement within the air conditioning system. These sensors help in regulating the airflow, ensuring that the right amount of air is distributed to different zones or rooms. By monitoring the airflow, the system can adjust the fan speed or damper position to achieve optimal airflow and maintain a consistent temperature throughout the space.
Outdoor Weather Sensors: Outdoor weather sensors provide information about external weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and solar radiation. This data helps the air conditioner control system adapt to changes in the outdoor environment and adjust its operation accordingly. For example, if it’s a hot sunny day, the system may increase the cooling output to compensate for the additional heat load.
Remote Control: A remote control device allows users to adjust the settings of the air conditioner from a distance. It provides a convenient way for users to change the temperature, fan speed, or mode of operation without having to physically interact with the control unit. The remote control sends signals to the control unit, which then executes the desired commands.
In summary, sensing and feedback devices in an air conditioner control system play a critical role in monitoring and regulating various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, airflow, and outdoor weather conditions. These devices enable the system to make automatic adjustments based on real-time feedback, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and user comfort.
Controller
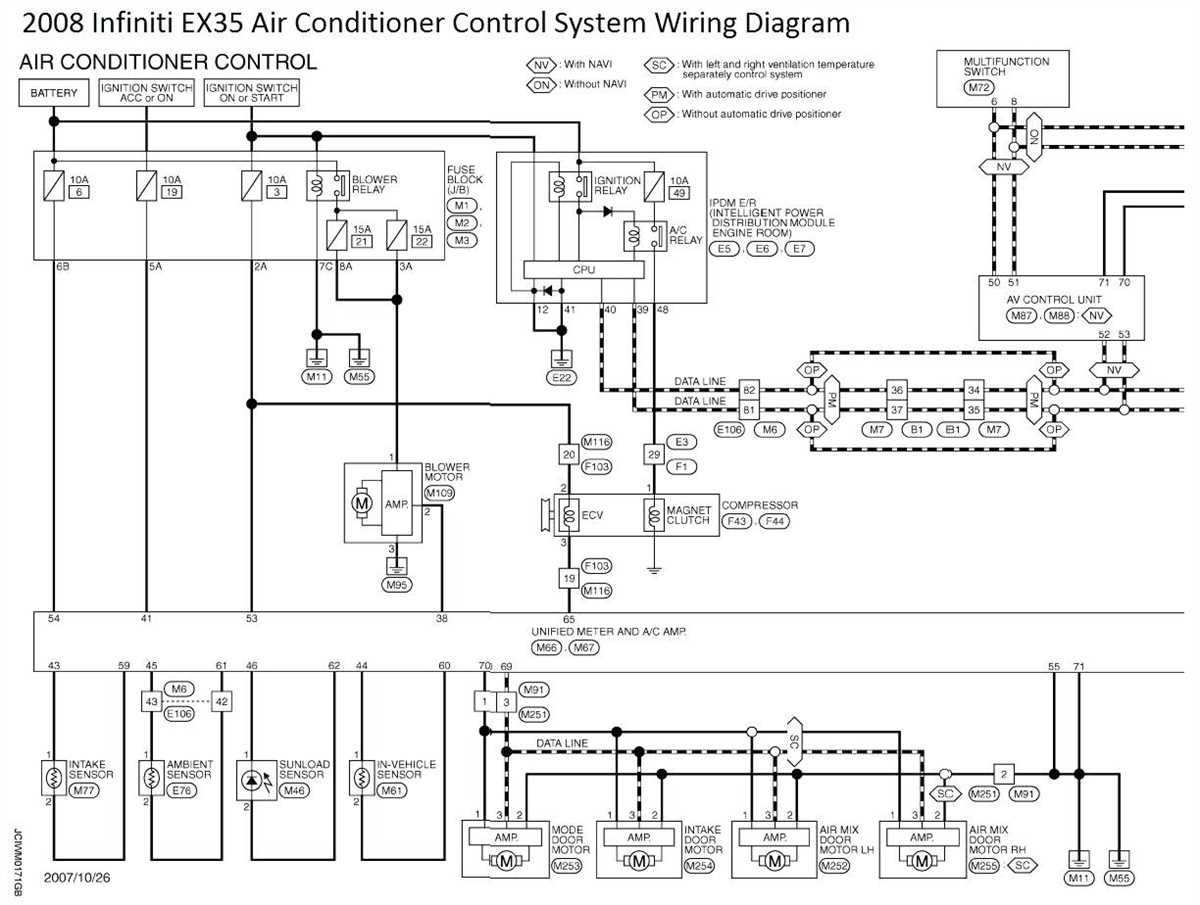
The controller is the central component of the air conditioner control system. It is responsible for processing input signals from various sensors and user interfaces, and generating output signals to control the operation of different components of the air conditioner.
The controller typically consists of a microcontroller or microprocessor, memory, and input/output interfaces. It receives input signals from temperature sensors, humidity sensors, and user interfaces such as a thermostat or a remote control. These input signals provide information about the current conditions and desired settings for the air conditioner.
- The temperature sensors measure the ambient temperature and provide feedback to the controller. Based on this input, the controller can determine whether the air conditioner needs to be turned on or off, or adjust the temperature setting accordingly.
- The humidity sensors measure the humidity level in the room and provide feedback to the controller. This information is used to determine whether the air conditioner needs to adjust the dehumidification or humidification process.
- The user interfaces allow the user to control the air conditioner settings. The thermostat, for example, allows the user to set the desired temperature and mode of operation (cooling, heating, or fan only).
Based on the input signals, the controller uses an algorithm or a set of control rules to determine the appropriate action to be taken. For example, if the ambient temperature is higher than the desired temperature, the controller may turn on the compressor and activate the cooling process. Conversely, if the temperature is lower than the desired temperature, the controller may turn off the compressor and activate the heating process.
The controller also communicates with other components of the air conditioner, such as the compressor, fan motors, and valves, by sending output signals. These signals control the operation of these components, ensuring that the air conditioner functions according to the desired settings and environmental conditions. The controller may also provide feedback signals to the user interfaces, such as indicating the current operating mode or displaying error messages.
Actuators
Actuators are essential components in an air conditioner control system. They are responsible for converting electrical or mechanical energy into physical motion, which controls various operations such as airflow, temperature, and direction of air. Actuators play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of the air conditioning system.
There are several types of actuators commonly used in air conditioner control systems:
- Motorized dampers: These actuators control the airflow by adjusting the position of dampers in the air conditioning ducts. They can open or close the dampers to regulate the amount of air entering different zones of the building. Motorized dampers are typically controlled by signals from the thermostat or the control system.
- Thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs): TXVs are used in refrigeration systems to regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. They adjust the refrigerant flow based on the temperature and pressure conditions, ensuring optimal cooling performance and energy efficiency.
- Compressor motors: The compressor motor is one of the most critical actuators in an air conditioner system. It compresses the refrigerant gas and circulates it through the condenser and evaporator coils. The compressor motor is responsible for maintaining the desired temperature in the conditioned space.
- Fan motors: Fan motors are used to drive the fans that circulate the air within the air conditioning system. They can be controlled to vary the speed of the fans based on the cooling demand, providing precise airflow control and energy efficiency.
In summary, actuators are essential components in an air conditioner control system, enabling precise control over various parameters such as airflow, temperature, and refrigerant flow. By converting electrical or mechanical energy into physical motion, actuators play a crucial role in maintaining optimal comfort and energy efficiency in air conditioning systems.