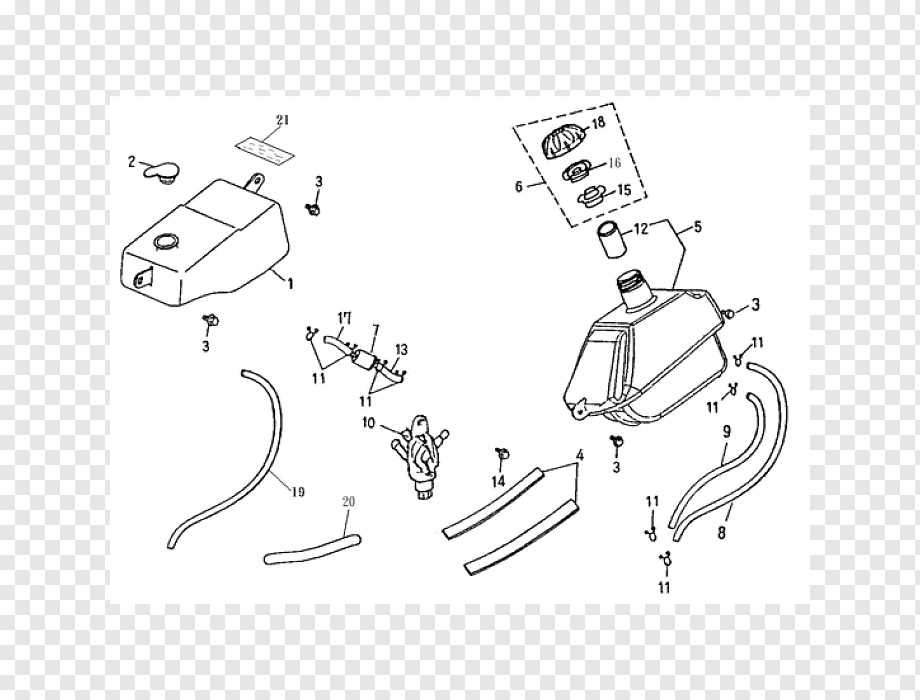
When it comes to maintaining your ATV, understanding how the fuel system works is essential. One key component of this system is the fuel line. The fuel line is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, making it an integral part of the ATV’s operation.
Having a clear understanding of the ATV fuel line diagram can help you diagnose and fix any issues that may arise. This diagram typically includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and carburetor, showcasing the pathway the fuel takes through these components. Additionally, it may also illustrate the connections between various hoses and fittings.
By familiarizing yourself with this diagram, you’ll be better equipped to troubleshoot and identify any potential problems with your ATV’s fuel system. Whether you’re experiencing fuel leaks or engine misfires, understanding the path of fuel flow can help you pinpoint the issue and make the necessary repairs.
Understanding the Fuel Line System in an ATV: A Comprehensive Diagram
When it comes to the proper functioning of an ATV, understanding its fuel line system is essential. The fuel line system is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring a steady supply of fuel and optimal performance. To help visualize this complex system, let’s explore a comprehensive diagram that breaks down its key components and their connections.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank is where the ATV’s fuel is stored. It is typically located at the front or rear of the vehicle and is connected to the rest of the fuel line system through an outlet or fuel pump. A fuel cap ensures the tank remains sealed and prevents fuel leakage.
Fuel Pump: In some ATVs, a fuel pump is used to transfer fuel from the tank to the engine. The pump is powered by electricity and creates the necessary pressure to propel fuel through the system. It is often located inside the fuel tank or near it, and it may have an inlet strainer to filter out impurities from the fuel.
Fuel Filter: To ensure clean fuel reaches the engine, a fuel filter is installed in the fuel line. The filter traps debris, dirt, and other contaminants, preventing them from entering the engine and causing damage. It is usually located between the fuel tank and the carburetor or fuel injector.
Carburetor or Fuel Injector: The carburetor or fuel injector is where the fuel is mixed with air to create a combustible mixture that powers the engine. In a carbureted ATV, the carburetor adjusts the fuel-air mixture manually, while in a fuel-injected ATV, the fuel injector automatically controls the mixture based on engine requirements.
Fuel Lines: The fuel lines are the conduits that carry fuel from the tank to the engine and back. They are typically made of rubber or plastic and are designed to withstand the pressure and chemicals present in the fuel. The lines are connected to various components using hose clamps, fittings, and connectors.
Vent Lines: In addition to the main fuel lines, ATVs also have vent lines. These lines allow air to enter or escape from the fuel tank, depending on the fuel consumption. Vent lines prevent a vacuum from forming in the tank and ensure a smooth flow of fuel.
In summary, the fuel line system in an ATV is a crucial component that enables the vehicle to run smoothly. Understanding the system’s key components, such as the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, carburetor or fuel injector, fuel lines, and vent lines, is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. By referring to a comprehensive diagram, ATV owners and enthusiasts can gain a better understanding of how the fuel line system works and how its various parts are interconnected, leading to a more efficient and reliable ATV.
What is an ATV Fuel Line System?
An ATV fuel line system is a crucial component in the proper functioning of an all-terrain vehicle (ATV). It is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring that the vehicle has a continuous and steady supply of fuel for optimal performance. The fuel line system consists of various components, including the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel filter, and fuel pump.
The fuel tank is where the fuel is stored and is typically located at the rear of the ATV. The fuel lines connect the fuel tank to the engine, allowing fuel to flow through the system. The fuel filter is an essential part of the fuel line system as it removes any impurities or debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine. This helps to prevent damage to the engine and ensures that only clean fuel is being used.
The fuel pump is responsible for pumping the fuel from the tank to the engine. It creates the necessary pressure to push the fuel through the lines and into the engine. The fuel pump can be either mechanical or electric, depending on the ATV’s design. Mechanical fuel pumps are driven by the engine’s motion, while electric fuel pumps are powered by the vehicle’s electrical system.
In addition to these main components, the fuel line system may also include other parts such as fuel injectors, carburetors, and fuel pressure regulators, depending on the ATV’s specific design. These components work together to ensure that the fuel is properly delivered to the engine, allowing the ATV to operate efficiently and reliably.
Overall, the ATV fuel line system is a vital part of the vehicle’s overall performance. Maintaining and inspecting the fuel line system regularly can help prevent issues such as fuel leaks, clogs, or improper fuel delivery, which can negatively affect the ATV’s performance and potentially cause damage to the engine. Therefore, it is essential to understand the components of the fuel line system and ensure proper maintenance to keep the ATV running smoothly.
Components of an ATV Fuel Line System
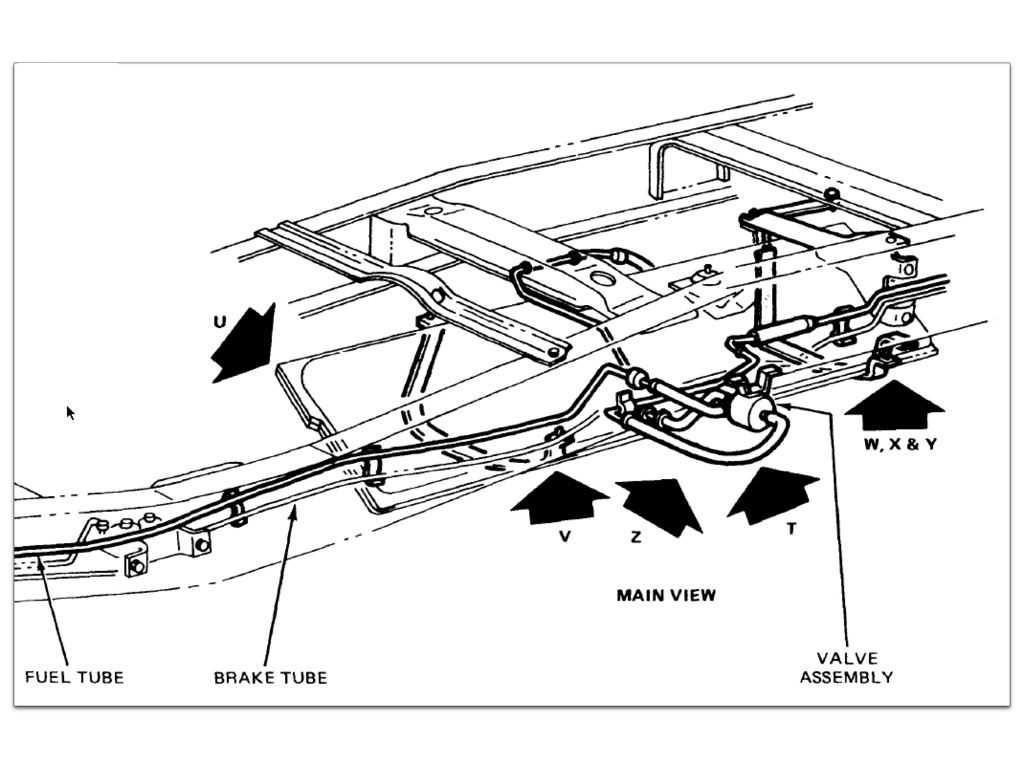
The fuel line system is a crucial component of an ATV’s fuel delivery system. It is responsible for transporting fuel from the fuel tank to the engine, ensuring a steady flow of fuel for combustion. Understanding the different components of an ATV fuel line system is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining the ATV’s fuel system.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank is the reservoir where the ATV’s fuel is stored. It is usually made of plastic or metal and is designed to hold a specific amount of fuel. The fuel tank has an opening that allows fuel to be pumped in and a fuel outlet that connects to the fuel line.
Fuel Pump: The fuel pump is an electric or mechanical device that is responsible for pumping fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. The type of fuel pump used in an ATV fuel line system may vary depending on the ATV’s make and model. Electric fuel pumps are commonly found in newer ATVs, while mechanical fuel pumps are often used in older models.
Fuel Filter: The fuel filter is a component that is installed in the fuel line system to remove dirt, debris, and other contaminants from the fuel. It prevents these particles from reaching the engine and causing damage. Regularly replacing the fuel filter is important to maintain the performance and longevity of the ATV’s engine.
Fuel Line: The fuel line is a hose or tube that connects the fuel tank to the fuel pump and the fuel pump to the engine. It is designed to withstand the pressure and temperature changes that occur in an ATV’s fuel system. The fuel line should be inspected for any signs of wear or leakage and replaced if necessary.
Fuel Injector/Carburetor: The fuel injector or carburetor is the component that mixes the fuel with air and delivers it to the engine for combustion. In fuel-injected ATVs, the fuel injector directly injects fuel into the engine’s intake manifold. In carbureted ATVs, the carburetor regulates the fuel-air mixture before it is delivered to the engine.
Fuel Pressure Regulator: Some ATVs may have a fuel pressure regulator in their fuel line system. The fuel pressure regulator regulates the fuel pressure to ensure it is within the specified range for the ATV’s engine. This helps maintain proper fuel flow and prevent damage to the engine.
Understanding the different components of an ATV fuel line system is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining the fuel system. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can help ensure a reliable and efficient fuel delivery system, which is essential for the optimal performance of the ATV.
Fuel Tank: The Heart of the System
In the world of ATVs, the fuel tank is often referred to as the heart of the system. It is the essential component that stores and supplies fuel to the engine, ensuring proper performance and functionality. Without a well-maintained fuel tank, an ATV cannot function optimally, and the overall riding experience may be compromised.
The fuel tank is typically made of durable materials, such as plastic or metal, designed to withstand rugged off-road conditions. It is strategically positioned on the ATV chassis to provide easy access for refueling while also being protected from potential damage. The tank is usually secured firmly and may have additional features like baffles or fuel filters to ensure fuel cleanliness and stability.
The fuel tank’s primary function is to store an adequate amount of fuel to support the ATV’s operation during rides. It holds enough fuel to maintain a consistent supply to the engine, even during demanding off-road adventures. The tank is equipped with a fuel cap and vent system to prevent fuel leakage and maintain pressure levels within safe limits.
Within the fuel tank, there is often a fuel level sensor or float mechanism that provides information to the ATV’s fuel gauge, allowing riders to monitor their fuel levels. This feature helps to prevent running out of fuel unexpectedly and gives riders the opportunity to plan accordingly during long rides.
It is essential to regularly inspect and maintain the fuel tank, including checking for any cracks or leaks and ensuring proper sealing of the fuel cap. A clean fuel tank is also crucial to prevent debris and contaminants from reaching the engine, as this can clog fuel lines and filters, leading to decreased performance and potential damage.
Connecting the Fuel Tank to the Engine
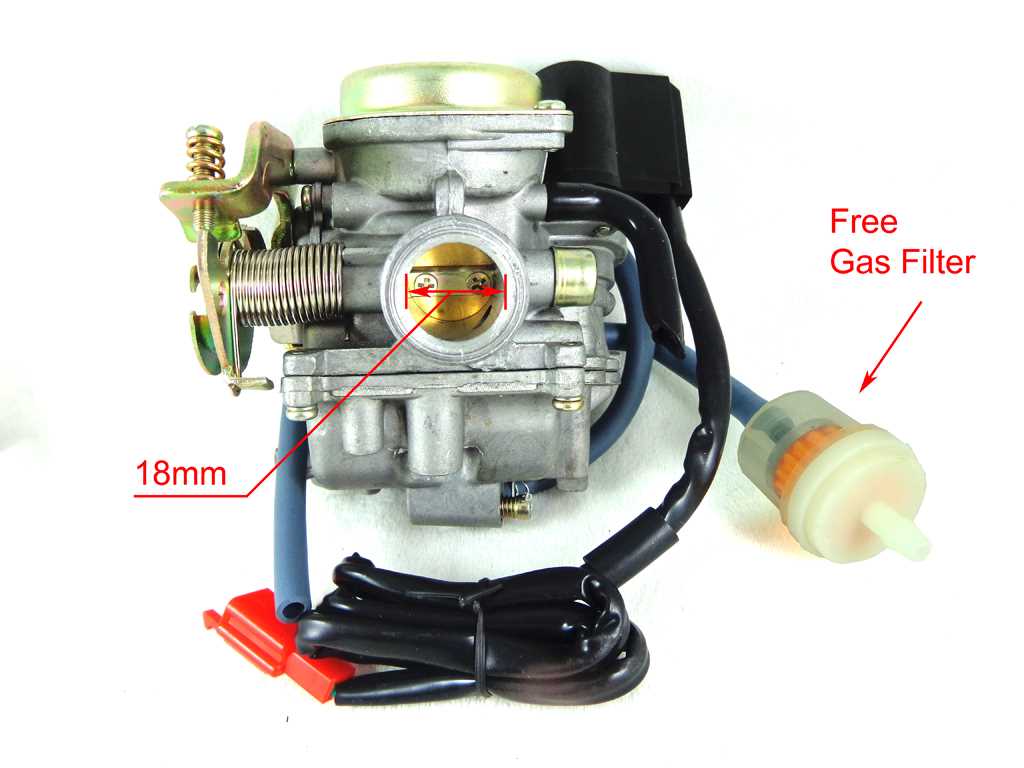

When it comes to fueling up an ATV, one crucial component is the fuel line that connects the fuel tank to the engine. This essential part ensures a steady flow of fuel from the tank to the engine, allowing the ATV to run smoothly and efficiently. A properly connected fuel line is essential for the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle.
The fuel line diagram for an ATV typically includes several key components:
- The fuel tank: This is where the fuel is stored. It is usually located near the rear of the ATV and is made of durable materials to withstand the outdoor elements.
- The fuel line: This hose connects the fuel tank to the engine. It is typically made of a flexible material, such as rubber or nylon, to allow for movement and vibration without leaking.
- The fuel filter: This small device is often located between the fuel tank and the engine. Its purpose is to remove impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine, protecting it from potential damage.
- The fuel pump: Some ATVs have a fuel pump that helps to move the fuel from the tank to the engine. It may be mechanical or electric, depending on the specific ATV model.
When connecting the fuel tank to the engine, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and ensure a proper fit and tight connection. The fuel line should be securely attached to both the tank and the engine, with no leaks or loose fittings. Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel line is crucial to avoid any issues or malfunctions while operating the ATV.
Understanding the Fuel Line Routing
The fuel line routing of an ATV is a crucial aspect to understand for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. The fuel line is responsible for delivering the necessary fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring efficient combustion and performance. Without proper fuel line routing, the ATV may experience fuel delivery issues, leading to poor performance or even engine damage.
When studying the fuel line routing diagram of an ATV, it is essential to pay attention to the specific arrangement and connection points. Typically, the fuel line starts at the fuel tank and travels towards the carburetor or fuel injector. Along the way, there may be various connectors, filters, and valves that regulate the fuel flow and ensure its cleanliness.
Fuel Line Components
- Fuel Tank: The fuel tank is where the fuel is stored and acts as the starting point for the fuel line.
- Fuel Line: The fuel line is a hose or tube that transports the fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Carburetor/Fuel Injector: The carburetor or fuel injector is the component responsible for mixing the fuel with air and delivering it to the combustion chamber.
- Connectors: Connectors are used to join different sections of the fuel line together.
- Filters: Fuel filters are placed along the fuel line to remove impurities and ensure clean fuel reaches the engine.
- Valves: Valves, such as shut-off valves or check valves, may be present to control the fuel flow and prevent backflow.
By familiarizing yourself with the specific fuel line routing diagram for your ATV model, you will be able to identify any potential issues or malfunctions that may arise. If you encounter any problems with the fuel system, such as fuel leaks or poor fuel delivery, referring to the fuel line diagram can help you locate the source of the problem and take the appropriate steps to resolve it.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for the ATV Fuel Line System
Proper maintenance of the ATV fuel line system is essential for the overall performance and longevity of your ATV. By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can ensure that your ATV’s fuel line system remains in top shape.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly inspect the fuel lines for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Replace any damaged or worn-out fuel lines immediately.
- Keep the fuel lines clean and free from debris. Use compressed air or a gentle flush with water to remove any dirt or particles that may clog the fuel lines.
- Ensure that the fuel lines are properly connected and tightened. Loose connections can cause fuel leakage and compromise the performance of the ATV.
- Inspect the fuel filter regularly and replace it if it is dirty or clogged. A clogged fuel filter can restrict the flow of fuel and cause engine performance issues.
- Periodically check the fuel pump for any signs of malfunction. If you notice any unusual noises or a decrease in fuel pressure, it may be necessary to replace the fuel pump.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- If your ATV is experiencing fuel delivery issues, check for any kinks or blockages in the fuel lines. A kinked or blocked fuel line can restrict the flow of fuel and cause engine stalling or hesitation.
- If you suspect a fuel leak in the fuel line system, inspect all the connections and fittings for any signs of fuel leakage. Tighten any loose connections and replace any damaged fittings to resolve the issue.
- If your ATV is consuming an excessive amount of fuel or experiencing poor fuel economy, consider checking the fuel pressure regulator or the fuel injectors. These components may need cleaning or replacement if they are not functioning correctly.
- If the engine is running rough or misfiring, it could be a result of a clogged fuel injector or a faulty fuel pressure regulator. Cleaning or replacing these components may help resolve the issue.
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting of the ATV fuel line system are crucial for the optimal performance and reliability of your ATV. By following these tips, you can prevent potential issues and ensure that your ATV runs smoothly for years to come.