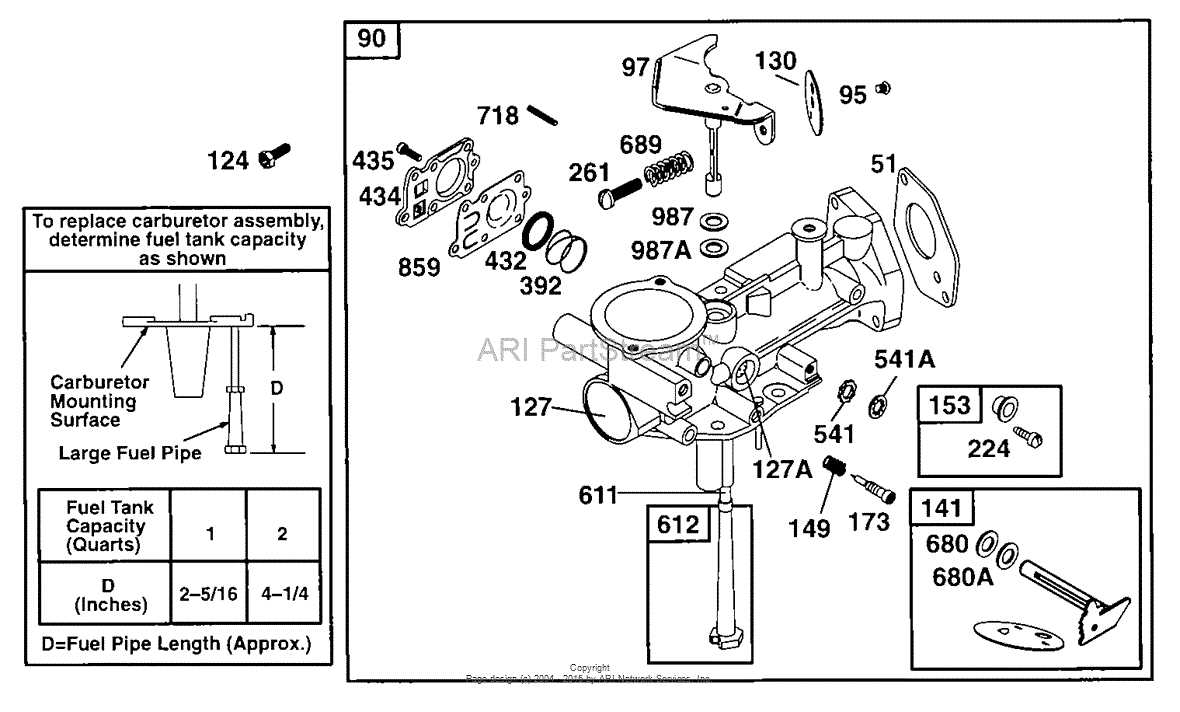
When it comes to the intricacies of internal combustion engines, one component that often confuses people is the carburetor. This crucial part of an engine’s fuel system is responsible for blending the right amount of air and fuel to ensure efficient and smooth combustion. And one key element of a carburetor is the spring.
Carburetor springs play a crucial role in regulating the flow of fuel by controlling the opening and closing of various valves inside the carburetor. These springs are designed to provide the right amount of tension to ensure proper functioning of the valves at different engine speeds and conditions.
Understanding the carburetor spring diagram is essential for anyone who wants to troubleshoot issues with their engine’s fuel system or modify their carburetor for better performance. The diagram provides a visual representation of the different springs and their locations within the carburetor, helping individuals identify and replace worn-out or broken springs.
By studying the carburetor spring diagram, enthusiasts can also gain a deeper understanding of how the fuel system works and make adjustments to optimize their engine’s performance. Whether it’s adjusting the idle speed, fine-tuning the air-fuel mixture, or upgrading to high-performance springs, knowing the ins and outs of the carburetor and its springs can have a significant impact on an engine’s power output and fuel efficiency.
Understanding the Basics of Carburetor Springs
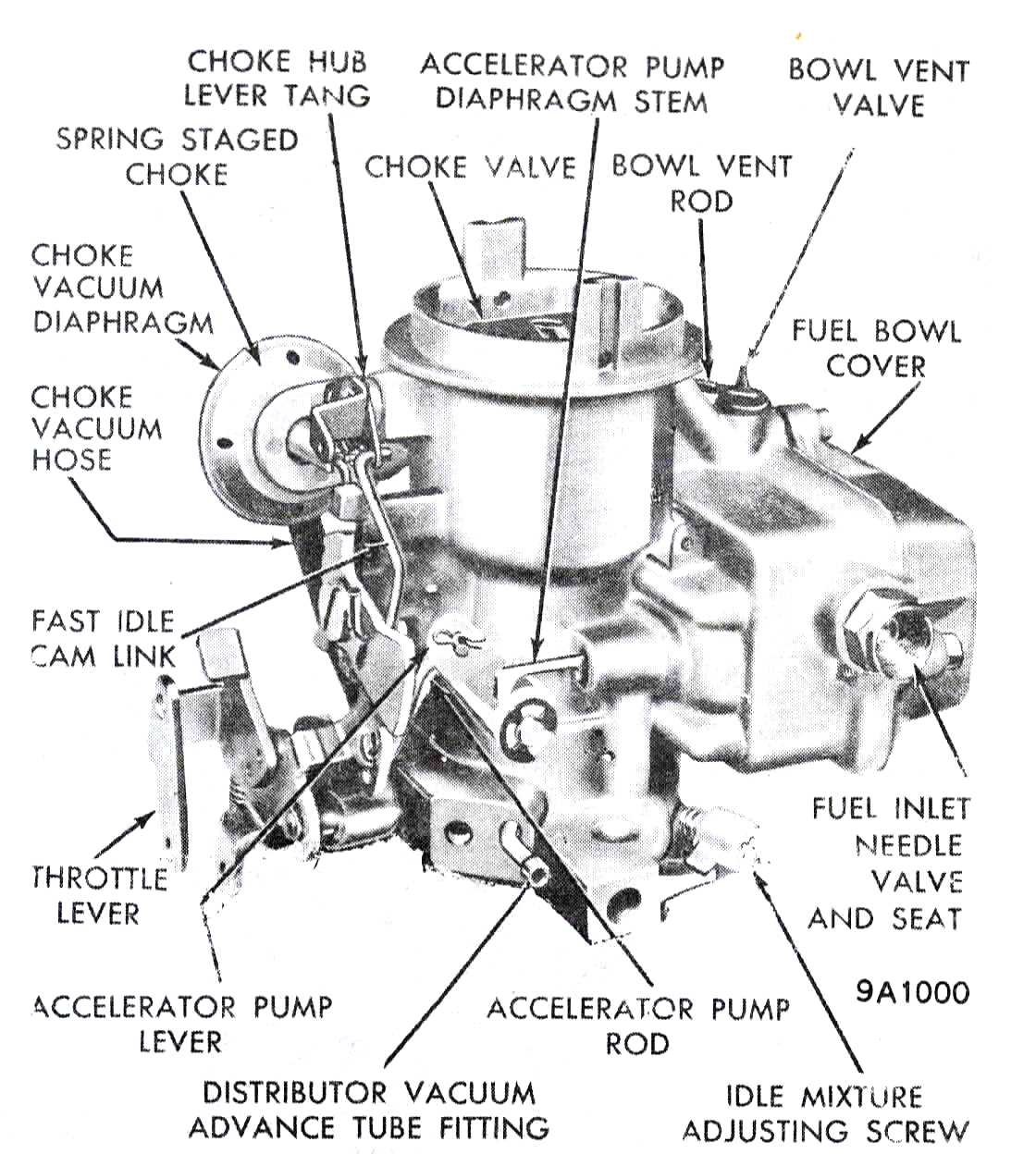
Carburetor springs play a crucial role in the operation of an engine. They are responsible for controlling the fuel and air mixture that enters the combustion chamber. Understanding the basics of carburetor springs is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency of an engine.
Carburetor springs come in different types and sizes, and each serves a specific purpose in the functioning of the carburetor. The primary purpose of these springs is to regulate the throttle valve, which controls the amount of air that enters the combustion chamber. This, in turn, affects the fuel delivery, resulting in the combustion process.
Main Types of Carburetor Springs:
- Throttle Return Spring: This spring ensures that the throttle valve returns to its idle position after the accelerator pedal is released. It helps to prevent engine stalling and provides smooth operation during low-speed driving.
- Main Metering Spring: The main metering spring controls the opening and closing of the main metering jet in the carburetor. It determines the amount of fuel that is delivered to the engine during various driving conditions, such as acceleration, cruising, and deceleration.
- Mixture Control Spring: The mixture control spring is responsible for controlling the mixture of fuel and air in the carburetor. It adjusts the position of the mixture control valve, allowing for rich or lean mixtures depending on the engine’s requirements.
Proper maintenance and adjustment of carburetor springs are essential for the overall performance of an engine. If the springs are worn out or incorrectly set, it can lead to issues such as poor fuel economy, rough idling, and decreased power output. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional assistance when dealing with carburetor springs to ensure optimal engine performance.
The Role of Carburetor Springs in Engine Performance
Carburetor springs play a crucial role in the overall performance of an engine. These small, but important components are responsible for maintaining the correct tension and position of various parts within the carburetor, ensuring optimal fuel delivery and air-fuel mixture. Without properly functioning carburetor springs, an engine may experience issues such as poor acceleration, reduced power, and decreased fuel efficiency.
One of the key functions of carburetor springs is to control the opening and closing of the throttle valve. The throttle valve regulates the amount of air entering the carburetor, which in turn affects the fuel flow and combustion process. By adjusting the tension of the throttle return spring, the engine’s idle speed and responsiveness can be optimized. If the spring is too weak, it may cause the throttle valve to close too slowly, resulting in sluggish acceleration. Conversely, if the spring is too stiff, it may cause the throttle valve to close too quickly, leading to stalling or hesitation.
Another important role of carburetor springs is to control the operation of the fuel enrichment circuit, commonly known as the accelerator pump. This circuit delivers an extra burst of fuel when the throttle is rapidly opened, compensating for the momentary lean condition that can occur during sudden acceleration. The spring used in the accelerator pump mechanism determines the timing and intensity of the fuel squirt, ensuring a smooth transition from idle to full throttle. An incorrectly adjusted or worn-out spring can cause the accelerator pump to deliver too much or too little fuel, resulting in engine hesitation or bogging.
In addition to the throttle and accelerator pump springs, carburetor systems may also incorporate other types of springs to control various valves, diaphragms, and linkages. These springs help maintain proper tension, prevent component binding, and ensure reliable operation. Regular inspection and maintenance of these springs are essential to keep the carburetor functioning optimally and the engine running smoothly.
Exploring the Types of Carburetor Springs
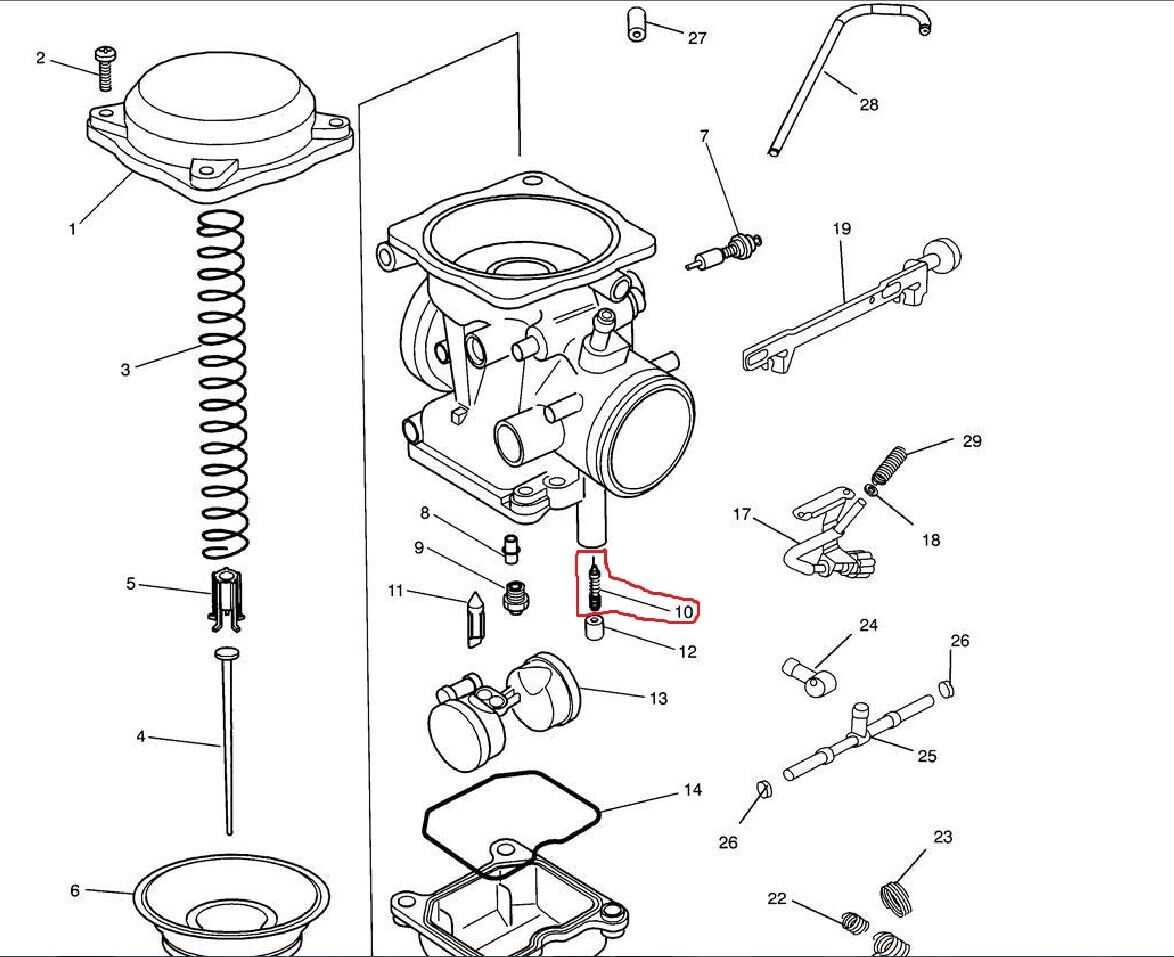
Carburetors are an essential component of the internal combustion engine, responsible for mixing air and fuel in the correct proportions for combustion. Carburetor springs play a crucial role in regulating the flow of fuel and air within the carburetor. As there are different types of carburetors, there are also various types of carburetor springs, each designed to serve a specific purpose.
1. Idle Speed Adjustment Spring: This type of spring is responsible for controlling the throttle valve’s idle speed. It ensures that the engine runs smoothly at idle by maintaining the correct amount of air and fuel mixture. The idle speed adjustment spring can be found near the throttle linkage and can be adjusted to fine-tune the engine’s idle speed.
2. Float Bowl Spring: The float bowl spring is located inside the carburetor’s float bowl. Its main function is to provide tension for the float valve, which regulates the fuel level within the float bowl. The proper tension of the float bowl spring ensures that the fuel level remains consistent, preventing flooding or starvation of fuel in the carburetor.
3. Throttle Return Spring: As the name suggests, the throttle return spring is responsible for returning the throttle valve to its closed position after acceleration. It assists in maintaining smooth and consistent throttle response by ensuring that the throttle valve does not stick open. This spring is usually located near the throttle linkage or throttle plate.
4. Accelerator Pump Spring: The accelerator pump spring is an essential component for carburetors equipped with an accelerator pump. It provides the necessary pressure to activate the accelerator pump, which sprays additional fuel into the engine during acceleration. The proper tension of this spring ensures a smooth transition from idle to full throttle, preventing hesitation or bogging down of the engine.
5. Choke Spring: The choke spring is responsible for controlling the choke valve’s movement. The choke valve restricts the air supply to the carburetor, enriching the air-fuel mixture during cold starts. The choke spring provides the necessary tension to open or close the choke valve based on engine temperature, allowing for optimal cold starting and warm-up performance.
In conclusion, carburetor springs are crucial components in maintaining the proper functioning of a carburetor. Each type of spring serves a specific purpose in regulating various aspects of the fuel and air mixture. Understanding the different types of carburetor springs can help in troubleshooting and fine-tuning the carburetor for optimal engine performance.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Read a Carburetor Spring Diagram
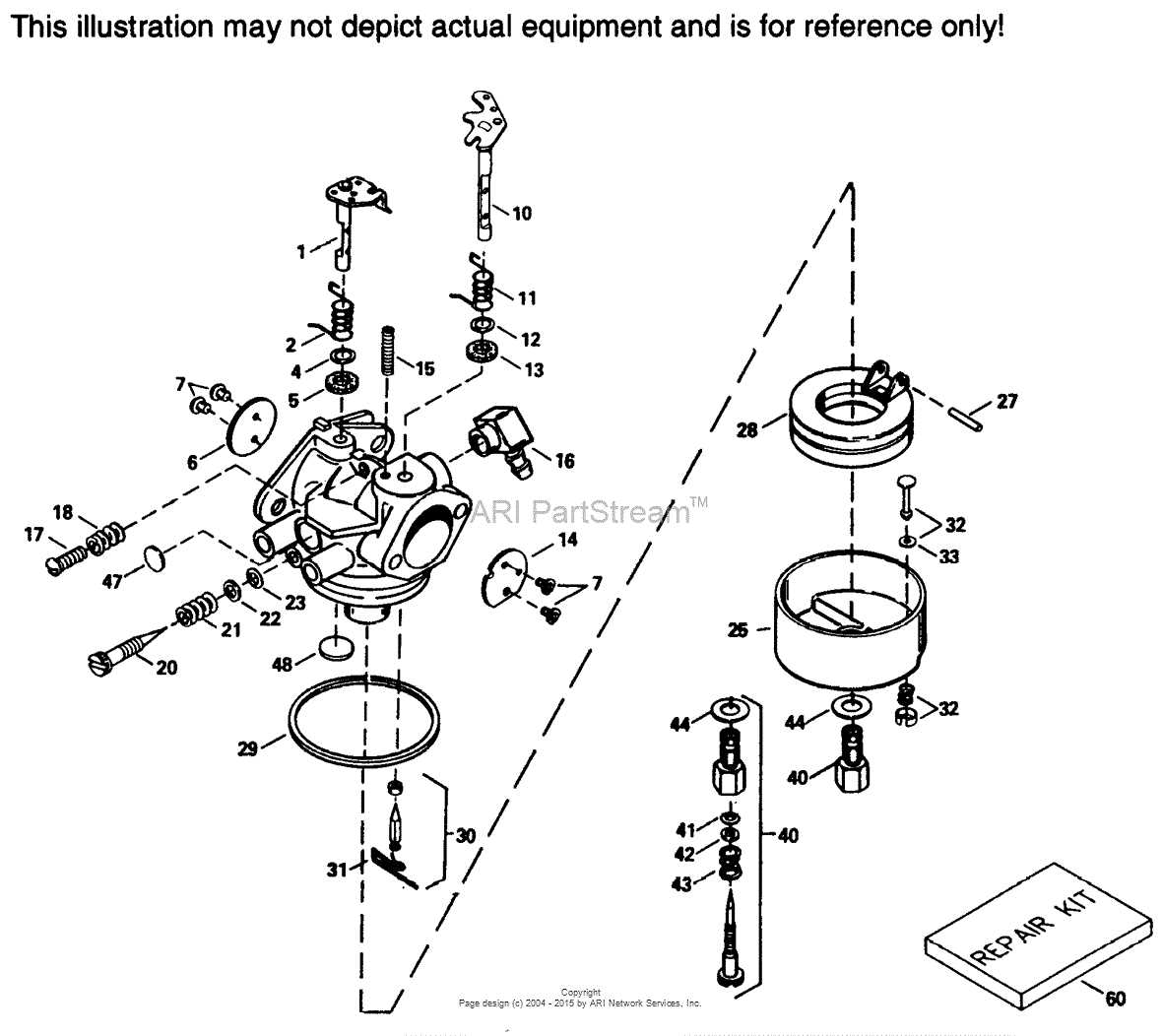
In order to properly understand and work with a carburetor spring diagram, it is essential to know how to read it correctly. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of deciphering a carburetor spring diagram and help you gain a better understanding of how it functions.
Step 1: Familiarize yourself with the parts
Start by identifying and familiarizing yourself with the various parts of the carburetor. This includes the throttle valve, idle mixture screw, choke plate, and of course, the carburetor spring. Understanding the function and location of each part will make it easier to interpret the diagram.
Step 2: Determine the layout and orientation
Examine the carburetor spring diagram and determine the layout and orientation of the parts. Look for arrows or symbols that indicate the direction of airflow or movement. This will give you a visual representation of how each component connects and interacts with one another.
Step 3: Analyze the connections and interactions
Next, analyze the connections and interactions between the parts in the diagram. Pay close attention to how the carburetor spring is positioned and connected to other components. This will help you understand how the spring affects the movement or adjustment of other parts within the carburetor.
Step 4: Identify tension and compression
Look for indications of tension or compression in the carburetor spring diagram. This can be represented by squiggly lines or different patterns on the diagram. Understanding the tension and compression points will give you insights into how the spring is intended to function and support the overall operation of the carburetor.
Step 5: Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions
If you are still unsure about any aspect of the carburetor spring diagram, it is always best to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions. These will provide detailed information and explanations specific to your carburetor model, ensuring that you interpret the diagram accurately and make any necessary adjustments correctly.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you can effectively read and interpret a carburetor spring diagram. This knowledge will enable you to troubleshoot and make adjustments to your carburetor with confidence, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in your vehicle’s engine.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Carburetor Springs: Summary
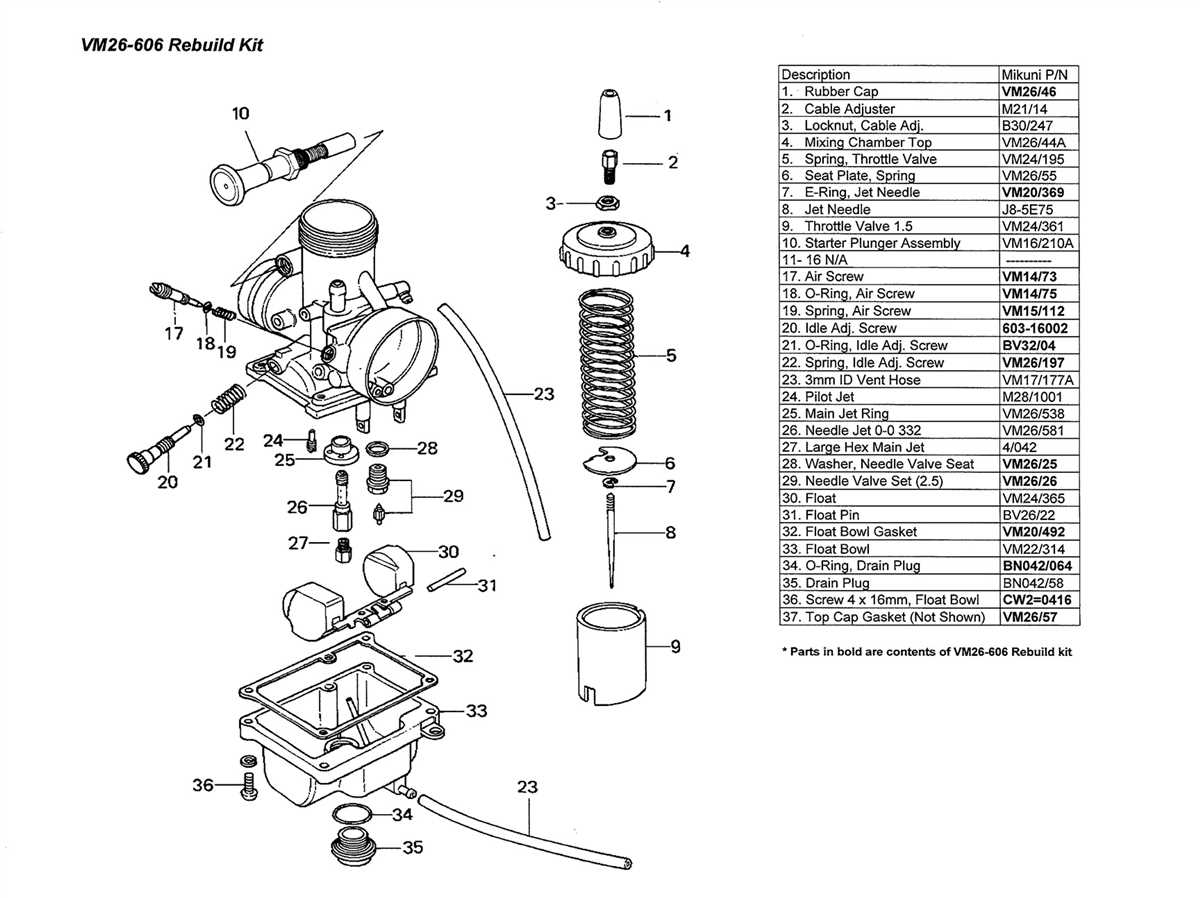
Carburetor springs play a crucial role in controlling the fuel and air mixture within a carburetor. However, they can sometimes experience issues that affect the performance of the engine. By understanding the common problems associated with carburetor springs and knowing how to troubleshoot them, you can ensure optimal engine performance and improve efficiency.
Summary of Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for spring damage, such as stretching, corrosion, or breakage. Replace any damaged springs.
- Ensure that the spring is properly installed in the correct orientation and position according to the carburetor diagram.
- Inspect the spring tension and adjust if necessary. Refer to the carburetor specifications for the correct tension range.
- Clean and lubricate the spring with carburetor cleaner and appropriate lubricant to prevent sticking or binding.
- Verify that the spring is correctly connected to the throttle linkage and other components. Make any necessary adjustments.
- Check for any vacuum or air leaks in the carburetor system. Repair or replace any faulty gaskets or seals.
- Ensure that the carburetor is properly adjusted and calibrated for the specific engine requirements.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can address common issues with carburetor springs and ensure that your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance and inspection of carburetor springs are essential to prevent problems and prolong the life of your carburetor and engine.