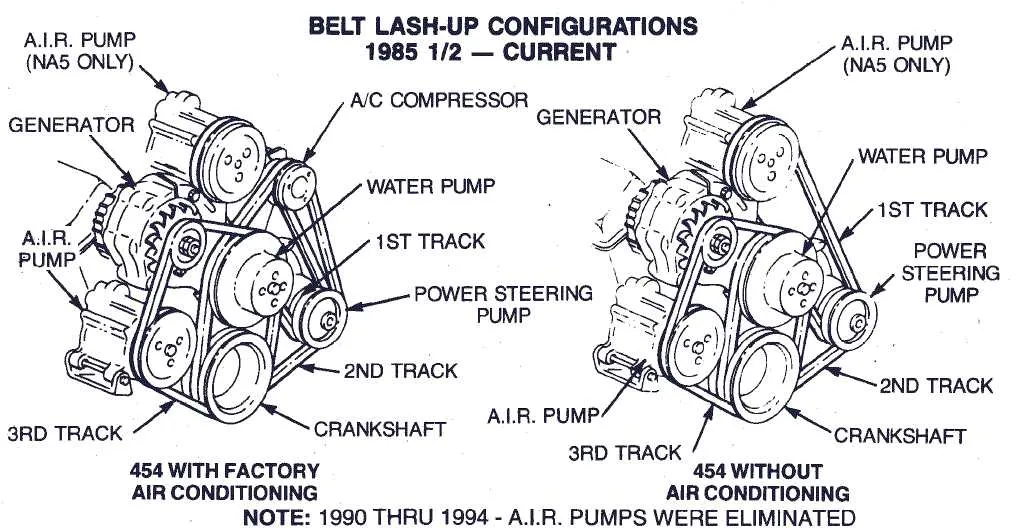
For efficient engine performance, the correct routing of the serpentine system is crucial. Ensure that the drive components such as the alternator, water pump, and air conditioning unit are properly linked by the right tensioned components. A common issue in older V8 engines is misalignment or excessive wear in the tensioners and pulleys, which can cause improper operation of these systems.
The correct routing starts from the main crankshaft pulley, passing through the power steering pump, alternator, and air conditioning compressor. This setup ensures that each component receives the required torque to operate smoothly. Make sure to verify that the drive system follows the right sequence of pulleys to avoid undue strain on any individual component.
Step-by-step inspection: First, check the orientation of the crankshaft, ensuring it provides adequate grip for the drive system. Next, inspect the alternator and power steering connections to confirm they rotate in the proper direction. Ensure the belt’s condition is free from cracks or abrasions, and the tensioners are functioning correctly. A worn-out component can lead to malfunctioning, resulting in performance loss.
For optimal function, ensure the tension is even across all components, and the alignment stays true to prevent slippage or excessive wear.
Correct Routing of Accessory Drive Components
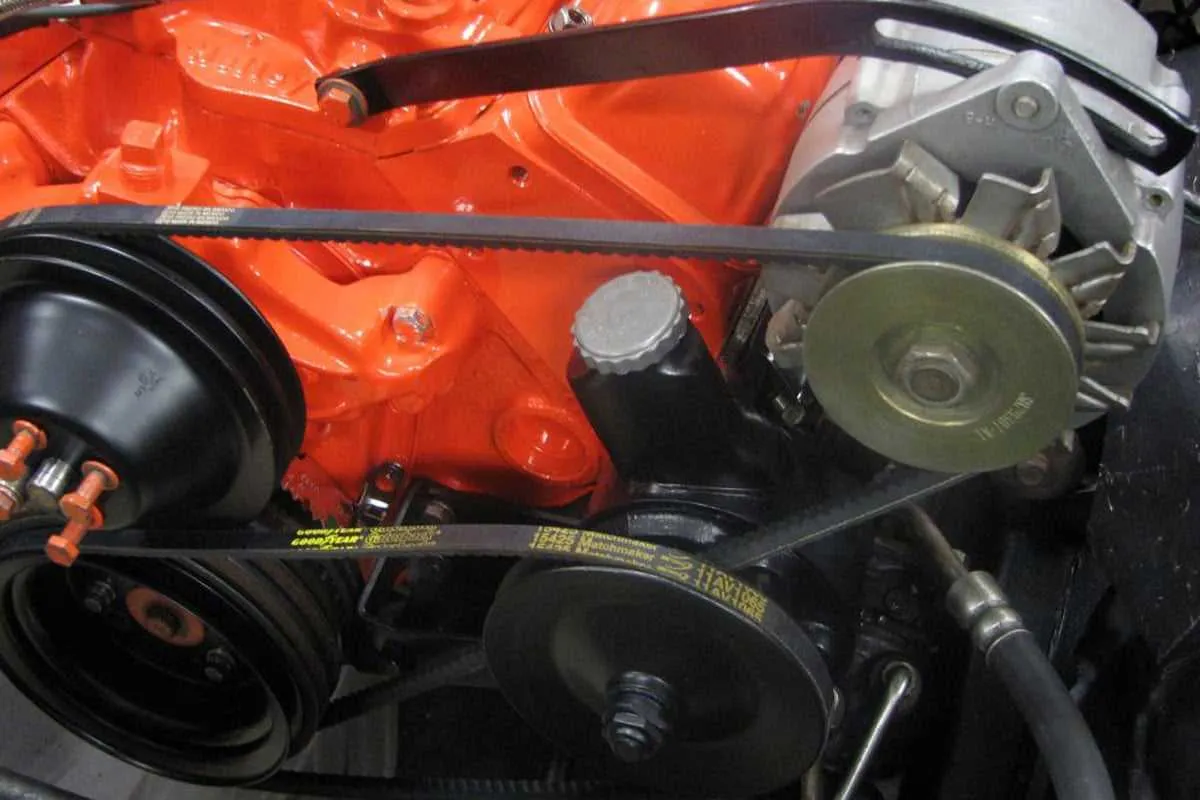

To ensure proper operation of your engine’s auxiliary systems, follow this pulley system configuration. Accurate routing is crucial for optimal performance, preventing excessive wear and ensuring reliability.
| Component | Location | Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Alternator | Front left | From the crankshaft pulley to the alternator pulley |
| Power Steering Pump | Front right | From the crankshaft pulley to the power steering pump pulley |
| Water Pump | Front center | From the crankshaft pulley to the water pump pulley |
| Air Conditioning Compressor | Front left | From the crankshaft pulley to the compressor pulley |
| Crankshaft Pulley | Bottom front | Drives the system |
Ensure the tension is adjusted to prevent slippage or excessive tightness. Use a proper tool for tensioning and verify that all components align correctly. Periodic inspection is recommended to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding the Layout of the Chevy 350 Fan Belt System
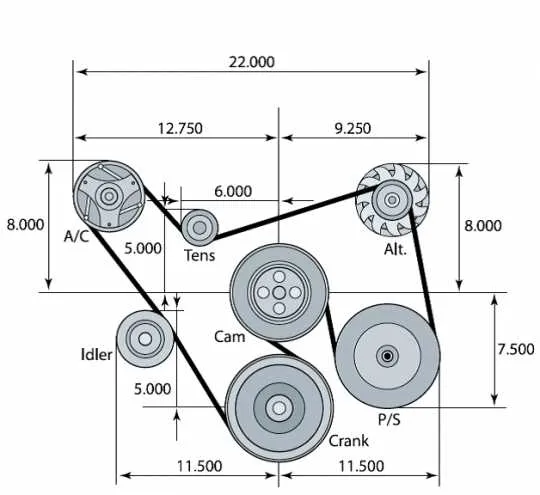
Start by identifying the pulleys: the crankshaft, water pump, alternator, and power steering. These components must be correctly aligned to ensure proper tension and smooth operation. Incorrect routing can lead to premature wear or failure.
Key Steps: First, check the routing of the primary drive component, which is typically the crankshaft pulley. It should loop around other components, including the water pump and alternator, while maintaining the necessary tension. Make sure each pulley is in proper condition–damaged or loose pulleys can misalign the entire setup.
After routing the drive component, adjust the tension using the tensioner, typically located near the alternator or power steering pump. A loose setup can cause slipping, while excessive tightness may strain components. A properly tensioned system ensures maximum efficiency and longevity.
Finally, always inspect for wear. Cracking or fraying on the belt suggests it’s time for replacement. Keep an eye on the alignment of all components and the tension to avoid breakdowns, especially in high-load situations like towing or off-road driving.
Steps to Correctly Install the Chevy 350 Fan Belt
1. Position the Pulley System: Ensure all pulleys are properly aligned before installation. Misalignment can lead to premature wear and inefficient operation. Double-check the positioning of the alternator, water pump, and other components involved in the drive system.
2. Loosen Tensioner: If applicable, loosen the tensioner pulley to reduce pressure on the component. This makes it easier to install the new unit and avoids unnecessary stress on the system.
3. Route the New Component: Begin at the crankshaft pulley and thread the component through the routing sequence. Make sure the path follows the manufacturer’s recommended configuration. Pay attention to any grooves and ensure the unit is seated properly in each pulley.
4. Adjust Tension: Once the unit is in place, tighten the tensioner pulley to restore correct tension. The component should have a slight flex but not be overly tight. Too much tension can lead to wear and premature failure.
5. Inspect the Setup: Double-check that the component is correctly aligned on all pulleys. Ensure it’s properly seated and not rubbing against other parts of the system.
6. Test the System: Start the engine and observe the operation. Listen for any unusual noises or vibrations. The component should run smoothly without any signs of slipping or misalignment.
Troubleshooting Common Engine Drive System Issues
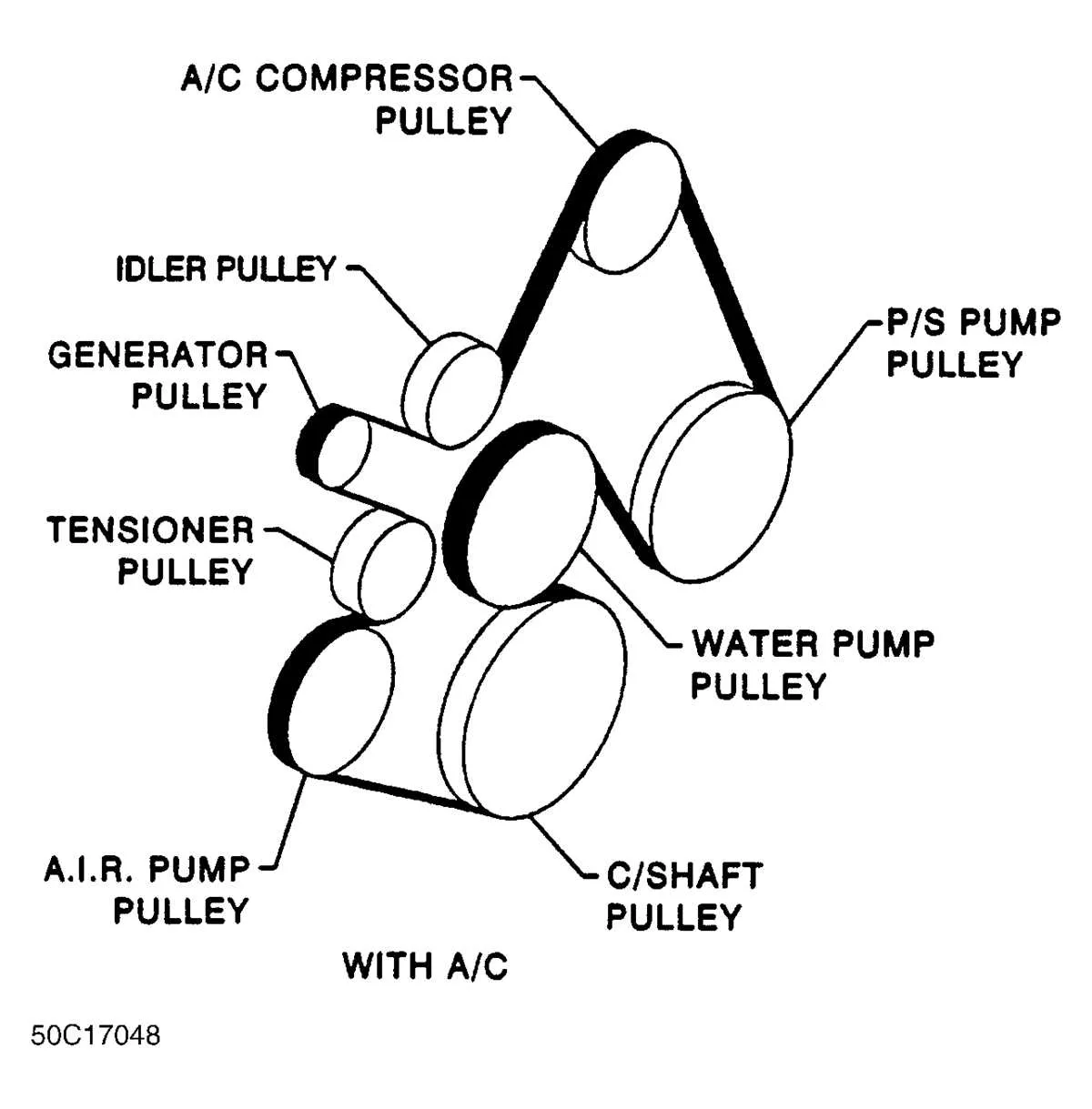
If you hear squeaking, slipping, or notice poor performance in your engine’s auxiliary systems, the problem may lie in the tension or alignment of the drive components. Here are the most common issues and solutions:
- Excessive Tension: If the drive is too tight, it can cause premature wear on both the component and the tensioner. Inspect the tensioner spring and adjust accordingly to avoid unnecessary stress.
- Loose System: A loose connection can lead to slippage, causing a decrease in efficiency. Regularly check for proper tightness and ensure that no part is worn or stretched.
- Misalignment: Misaligned pulleys or tensioners can cause uneven wear and slipping. Ensure the pulleys are aligned correctly and replace any worn bearings or pulleys.
- Cracking or Wear: If the system shows visible signs of cracking or surface wear, replace the part immediately. Continuing to use damaged components could cause further damage to the engine.
- Incorrect Routing: Always refer to the correct routing for your specific setup. Incorrect routing can cause misalignment and premature wear, as well as hinder engine performance.
Regular inspection and timely adjustments will help ensure that the engine drive system remains efficient and functional, preventing unnecessary breakdowns.