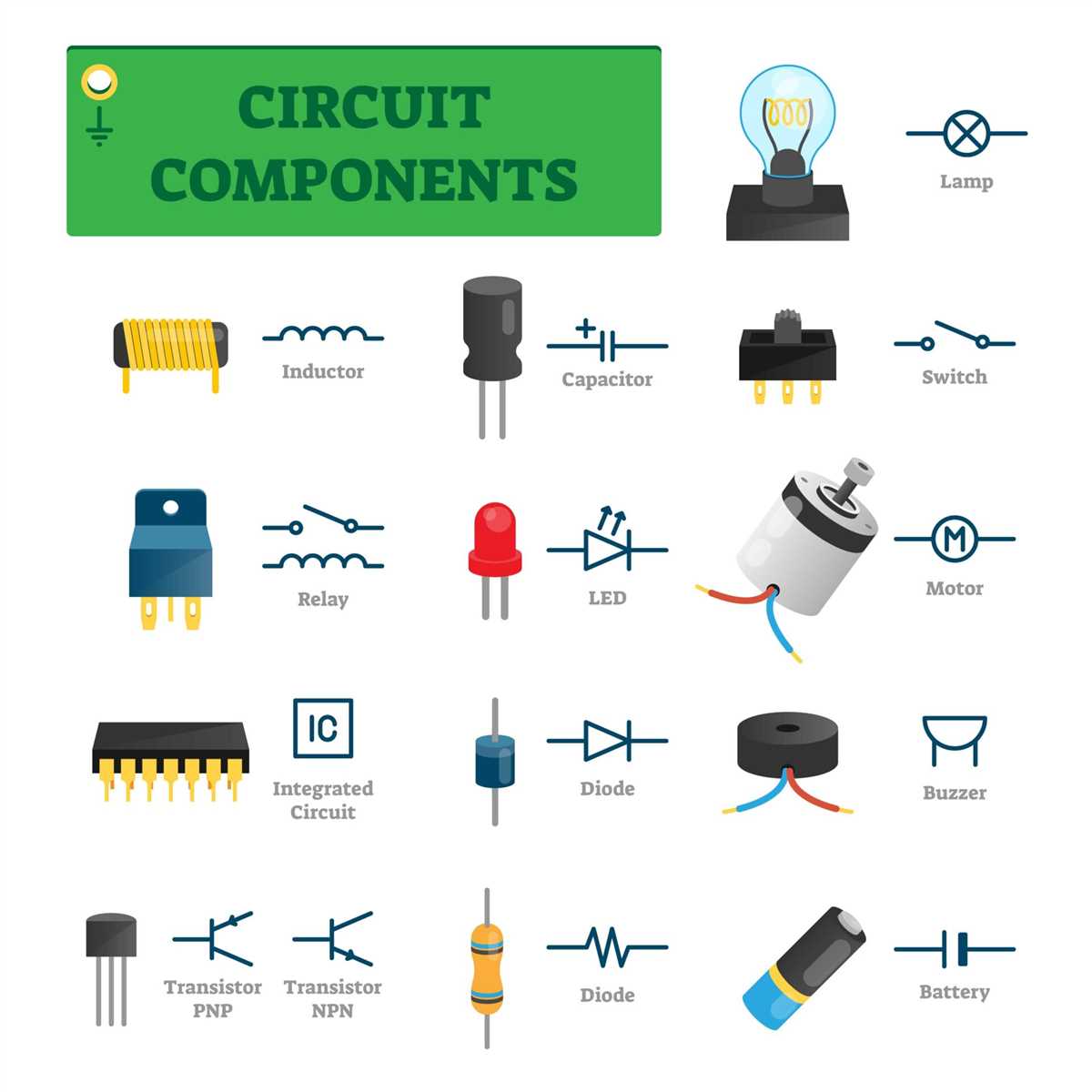
A circuit board, also known as a printed circuit board (PCB), is a crucial part of any electronic device. It serves as the base that connects and supports various components, allowing them to communicate and work together to perform specific functions. Understanding the different components on a circuit board is essential for anyone involved in the field of electronics.
One of the main components found on a circuit board is the resistors. These small, cylindrical components regulate the flow of electric current and are essential for controlling voltage and current levels within a circuit. They have specific resistance values that determine the amount of current that can pass through them.
Another important component is the capacitors. These are small, two-terminal devices that store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used to smooth power supply voltages, block DC current while allowing AC current to pass, and stabilize voltage levels in circuits. Capacitors come in different types, such as electrolytic capacitors and ceramic capacitors, each with its own specific properties and applications.
Circuit Board Components Diagram

When it comes to understanding the functionality and structure of a circuit board, a circuit board components diagram can be an invaluable tool. This diagram visually represents the various components that are present on a circuit board and how they are interconnected to form a functioning circuit. It aids in troubleshooting, repair, and designing of circuit boards.
1. Resistors: These components are used to limit or control the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are represented by a zigzag line in the diagram and are characterized by their resistance value, measured in ohms.
2. Capacitors: Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. Capacitors are represented in the diagram by two parallel lines with a curved line connecting them.
3. Diodes: Diodes allow the flow of electric current in one direction only. They are represented by an arrow pointing in the direction of the current flow and a line intersecting it.
4. Transistors: Transistors are semiconductor devices that amplify or switch electronic signals and power. They are represented by various symbols in the diagram, depending on the type of transistor (e.g., NPN or PNP).
5. Integrated Circuits (ICs): Integrated circuits are complex components that contain multiple electronic circuits and components on a single chip. They are represented by rectangular boxes in the diagram, with pins extending from the sides.
6. Inductors: Inductors store energy in the magnetic field created when current passes through them. They are represented by a series of coiled loops in the diagram.
7. Connectors: Connectors are used to join different parts of the circuit together. They may include USB ports, audio jacks, ribbon connectors, and more. Connectors are represented by specific symbols in the diagram.
8. Microcontrollers: Microcontrollers are small computer chips that contain a microprocessor, memory, and various peripheral devices. They are used to control and monitor the functioning of a circuit. Microcontrollers are represented by specific symbols in the diagram.
The circuit board components diagram provides a clear and organized representation of the various components present on a circuit board. It helps engineers, technicians, and hobbyists understand the circuit’s structure, identify faulty components, make necessary repairs, and design new circuits.
Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Integrated Circuits, also known as ICs or microchips, are vital components in modern circuit boards. They are small electronic devices that consist of numerous interconnected electronic components, such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, and diodes, all etched onto a tiny semiconductor material, usually silicon. ICs serve various functions in electronic devices, including amplifying signals, switching circuits on and off, storing and processing data, and controlling the overall operation of the device. They revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling complex circuits and reducing the size, cost, and power consumption of electronic devices.
ICs are classified into different types based on their applications and design, such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), microprocessors, memory chips, and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Each type of IC has a specific function and includes specialized circuitry tailored to meet the requirements of that function. For example, op-amps are widely used for amplifying and conditioning analog signals, microprocessors serve as the brain of computers and other advanced electronic devices, memory chips store digital data, and ADCs convert analog signals into digital form. ICs are available in various package forms, such as DIP (dual in-line package), SMD (surface-mount device), and BGA (ball grid array), which allow for easy integration onto circuit boards.
Major advancements in IC technology have led to the development of more powerful and efficient electronic devices. The constant miniaturization of ICs, also known as Moore’s Law, has allowed for the creation of increasingly complex and feature-rich devices that have become an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones and computers to automotive systems and medical devices, ICs play a crucial role in enabling the functionality and performance of modern electronics. Continued research and development in IC technology hold the promise of even more powerful and innovative devices in the future.
Resistors
Resistors are electrical components used in circuit boards that restrict the flow of electric current. They are passive components, meaning they do not produce or control electric current but instead regulate the amount of current flowing through a circuit.
Function: The main function of a resistor is to provide resistance to the flow of electric current. They are used to limit or control the amount of current passing through various parts of a circuit, protecting sensitive components from excessive current levels and ensuring proper operation.
Types: There are different types of resistors available, including carbon composition resistors, metal film resistors, and wirewound resistors. Each type has its own characteristics and is used for specific applications depending on factors such as power ratings, tolerance levels, and temperature coefficients.
Color coding: Resistors are typically color-coded to indicate their resistance value, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. The color bands on the resistor help identify the resistance value as per the standardized color code system.
Size and shape: Resistors come in various sizes and shapes, from small cylindrical components to larger rectangular ones. They may have two leads or multiple leads depending on their configuration and intended use. The size and shape of a resistor can affect its power handling capabilities and compatibility with different circuit board designs.
Applications: Resistors are used in a wide range of electronic devices and systems. They are commonly found in amplifiers, power supplies, sensors, and various other electronic circuits where precise control of current or voltage is required.
- Carbon composition resistors: These are made by mixing carbon powder with an insulating material and then forming it into a cylindrical shape.
- Metal film resistors: These resistors have a thin metal film layer on a ceramic substrate, providing good stability and high precision.
- Wirewound resistors: These resistors are made by winding a resistive wire around a non-conductive core. They are known for their higher power ratings and ability to handle high temperatures.
In summary, resistors play a crucial role in circuit boards by regulating the flow of electric current. They are available in different types, sizes, and shapes, and are essential for ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices and systems.
Capacitors
Capacitors are essential components of a circuit board, and they are widely used for storing and releasing electrical energy. They are passive electronic components that consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. Capacitors come in various shapes and sizes, but they all work on the same principle of storing charge.
Capacitors have several important applications in electrical circuits. One primary function is to filter out voltage fluctuations and stabilize power supply. They can smoothen out the ripples in the current or voltage, ensuring a steady and reliable power source for other components on the circuit board. Capacitors are also used in timing circuits, where they control the rate of charging and discharging, thus determining the frequency or period of a signal.
There are different types of capacitors, each suited for specific applications. Some common types include ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, tantalum capacitors, and film capacitors. The choice of capacitor depends on factors such as capacitance value, voltage rating, and frequency range. Capacitors are typically labeled with their capacitance value in farads (F) and voltage rating in volts (V).
Capacitors can be represented on a circuit board diagram using standardized symbols. The symbol consists of two parallel lines representing the conductive plates with a gap between them to indicate the dielectric material. The positive terminal of the capacitor is usually denoted by a plus sign (+), and the negative terminal by a minus sign (-). Understanding the role and properties of capacitors is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
Diodes
Diodes are electronic components that allow the flow of current in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They are widely used in circuit boards to control the flow of electrical signals and protect other components from potential damage.
One of the most common types of diodes is the rectifier diode, which is used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It allows current to flow in only one direction, allowing a smooth flow of power through the circuit. Rectifier diodes are essential in power supply circuits, helping to ensure steady and regulated power output.
Another type of diode is the light-emitting diode (LED). LEDs are used to produce light when an electric current is applied to them. They are widely used in electronic displays, indicators, and lighting applications. LEDs are efficient and long-lasting, making them a popular choice for various electronic devices.
Diodes can also be used for protection purposes, such as in reverse polarity protection circuits. These diodes are placed in a circuit to prevent damage caused by reverse polarity, ensuring that current flows in the correct direction. Additionally, diodes are used in voltage regulators and voltage clamping circuits to maintain a constant voltage level and protect sensitive components from voltage spikes.
In summary, diodes are vital components in circuit boards that control current flow and protect other components. Whether it’s converting AC to DC, producing light, or providing protection, diodes play a crucial role in the functionality and reliability of electronic devices.
Summary
Transistors are essential components in circuit boards, playing a crucial role in the amplification and switching of electrical signals. They are small semiconductor devices that can control the flow of electrons, making them a fundamental building block of modern electronics.
There are two primary types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs use two pn-junctions to amplify electrical signals, while FETs rely on an electric field to control the flow of electrons.
Key Takeaways:
- Transistors are semiconductor devices that control the flow of electrons in circuits.
- Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs) are the two main types of transistors.
- BJTs amplify electrical signals using two pn-junctions, while FETs rely on an electric field.
- Transistors are crucial for signal amplification, switching, and digital logic operations in electronic circuits.
- Understanding the operation and characteristics of transistors is essential for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
Overall, transistors are key components in circuit boards, enabling the functionality and performance of various electronic devices. Their ability to amplify signals and control the flow of electrons makes them essential for modern technology.
Q&A:
What is a transistor?
A transistor is a semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.
Who invented the transistor?
The transistor was invented by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at Bell Laboratories in 1947.
What are the three layers of a transistor?
The three layers of a transistor are the emitter, base, and collector.
What is the function of the emitter in a transistor?
The emitter in a transistor is responsible for emitting or releasing the majority charge carriers (electrons or holes) into the base region.
What are the two main types of transistors?
The two main types of transistors are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs).