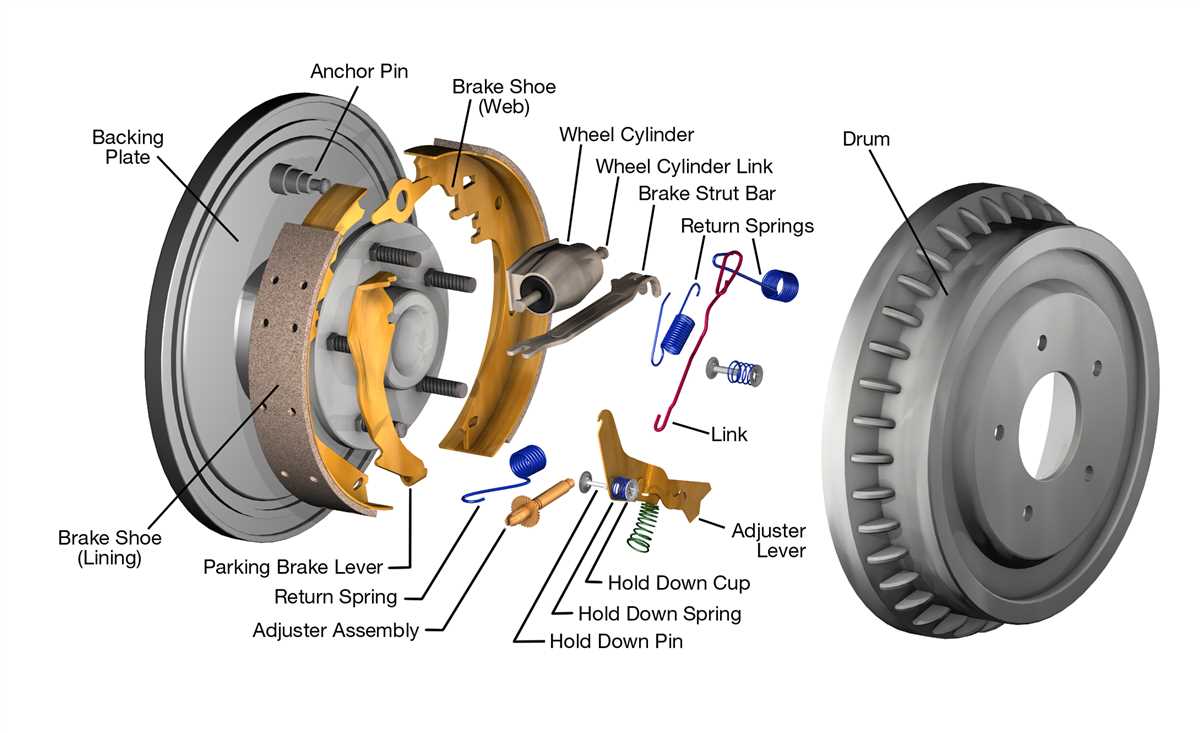
Understanding how a car brake system works is crucial for every driver. The brake system is a vital component of a vehicle’s safety, allowing the driver to slow down or stop the car when necessary. A diagram of the car brake system can help visualize the different parts and their functions, providing a clearer understanding of how the system operates.
The car brake system consists of several key components, including the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, brake calipers, brake pads, and rotors. When the driver presses the brake pedal, it activates the master cylinder, which in turn applies hydraulic pressure to the brake lines. The pressurized fluid then travels through the brake lines to the brake calipers.
The brake calipers house the brake pads, which are pressed against the rotors to create friction. This friction is what ultimately slows down or stops the car. The rotors, also known as brake discs, are attached to the car’s wheels and rotate alongside them. When the brake pads make contact with the rotors, the friction generated helps transform the kinetic energy of the rotating wheels into heat energy, gradually bringing the car to a halt.
Understanding the diagram of a car brake system can help drivers pinpoint potential issues or diagnose problems when their brakes are not working properly. Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake system are essential for ensuring the safety of both the driver and passengers. By familiarizing themselves with the diagram and understanding how each component interacts, drivers can make informed decisions about the maintenance and repair of their vehicle’s brake system.
What is a Car Brake System?
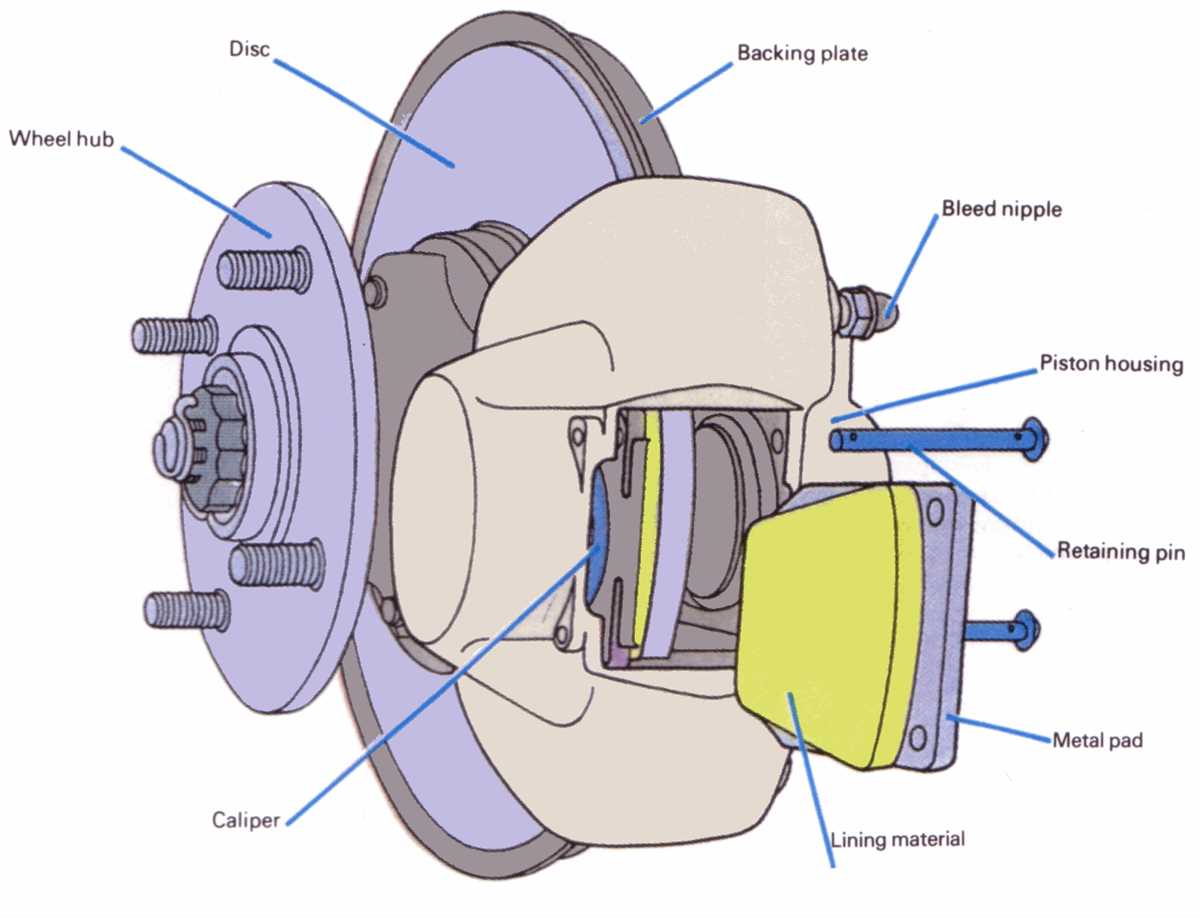
A car brake system is a critical component of a vehicle that ensures safe and efficient stopping power. It is responsible for converting the kinetic energy of a moving car into heat energy, allowing the car to come to a controlled stop or slow down when necessary.
The brake system is comprised of several key components, including the brake pedal, brake lines, brake fluid, brake calipers, and brake pads. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is generated, which is transmitted through the brake lines to the brake calipers. The calipers, which contain pistons, then apply pressure to the brake pads, causing them to clamp down on the brake rotors or drums, depending on the type of brake system used.
The brake pads are crucial elements of the brake system, as they are the components that make direct contact with the brake rotors or drums. They are typically made of a high-friction material, such as ceramic or semi-metallic, which allows them to create the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle.
In addition to the mechanical components, the brake system also relies on brake fluid to transfer the hydraulic pressure from the brake pedal to the brake calipers. Brake fluid is a specialized hydraulic fluid that has a high boiling point and is resistant to moisture. It needs to be regularly checked and replaced to ensure the proper operation of the brake system.
Overall, a car brake system plays a critical role in ensuring the safety of the vehicle and its occupants. Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake system are essential to detect any potential issues and ensure optimal performance.
Components of a Car Brake System
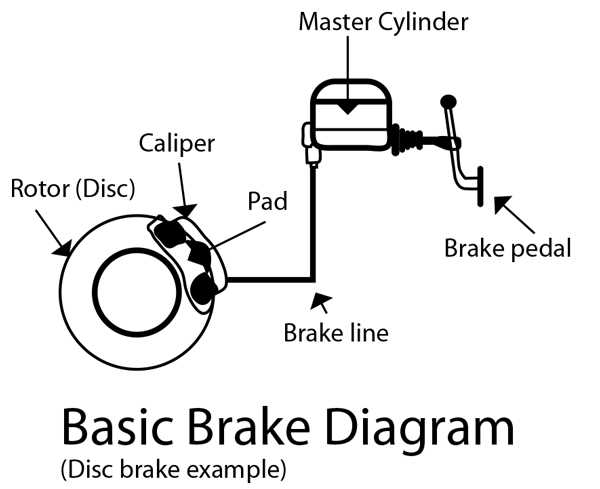
The brake system in a car is a complex and vital component that ensures the safety of the vehicle and its passengers. It consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functioning of the system.
Brake Pads: One of the key components of the brake system is the brake pads. These are metal plates with a high-friction material attached to them. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the brake pads come into contact with the brake rotor or disc, creating the necessary friction to slow down or stop the car.
Brake Calipers: The brake calipers are responsible for squeezing the brake pads against the rotor. They contain pistons that are actuated by hydraulic pressure, resulting in the movement of the brake pads. The calipers need to be in good condition to ensure effective braking performance.
Brake Rotors: The brake rotors, also known as brake discs, are circular metal discs that are attached to the wheel hubs. When the brake pads press against the rotors, the resulting friction creates the necessary stopping force. It is essential for the brake rotors to be properly maintained, as worn or damaged rotors can affect braking performance.
Brake Lines and Hoses: The brake lines and hoses are responsible for transmitting hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers. They need to be in good condition and free from leaks to ensure that the braking force is effectively transmitted to the wheels.
Master Cylinder: The master cylinder is a key component of the brake system that converts the pressure applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. It contains a reservoir for holding brake fluid and is connected to the brake lines. A faulty master cylinder can result in a loss of braking power and should be promptly replaced.
Brake Fluid: Brake fluid is a specialized hydraulic fluid that is used in the brake system. It transfers pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers, facilitating the movement of the brake pads. It is important to regularly check the brake fluid level and replace it as needed to ensure optimal brake performance.
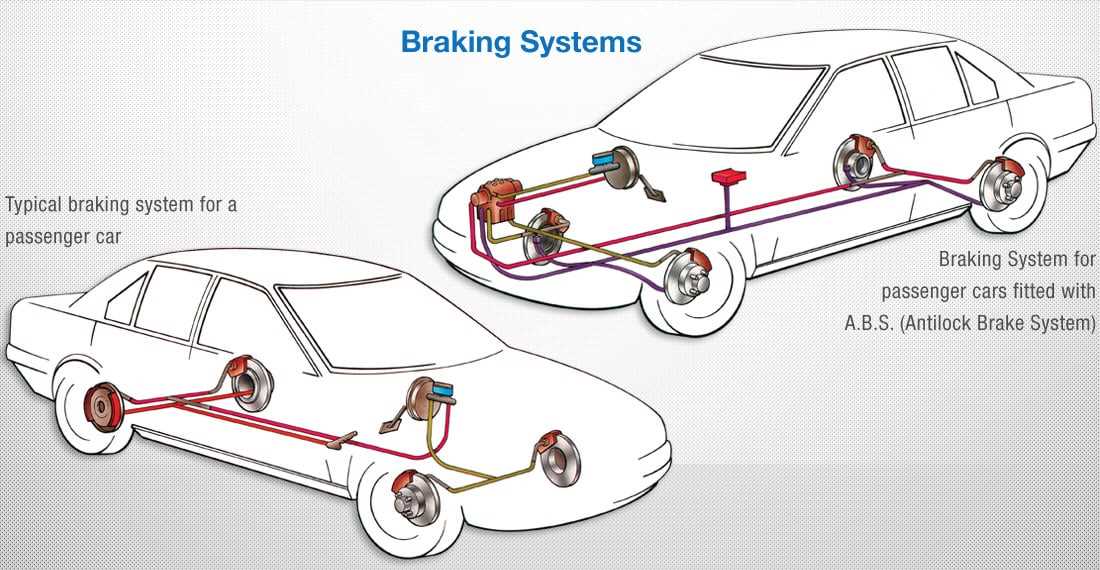
Antilock Braking System (ABS): Many modern vehicles are equipped with an antilock braking system, which helps prevent the wheels from locking up during emergency braking. The ABS uses sensors to detect when a wheel is about to lock up and modulates the braking pressure accordingly, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
In conclusion, the brake system in a car consists of various components that work together to ensure safe and efficient braking. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to ensure optimal brake performance and the safety of the vehicle and its occupants.
Types of Car Brake Systems
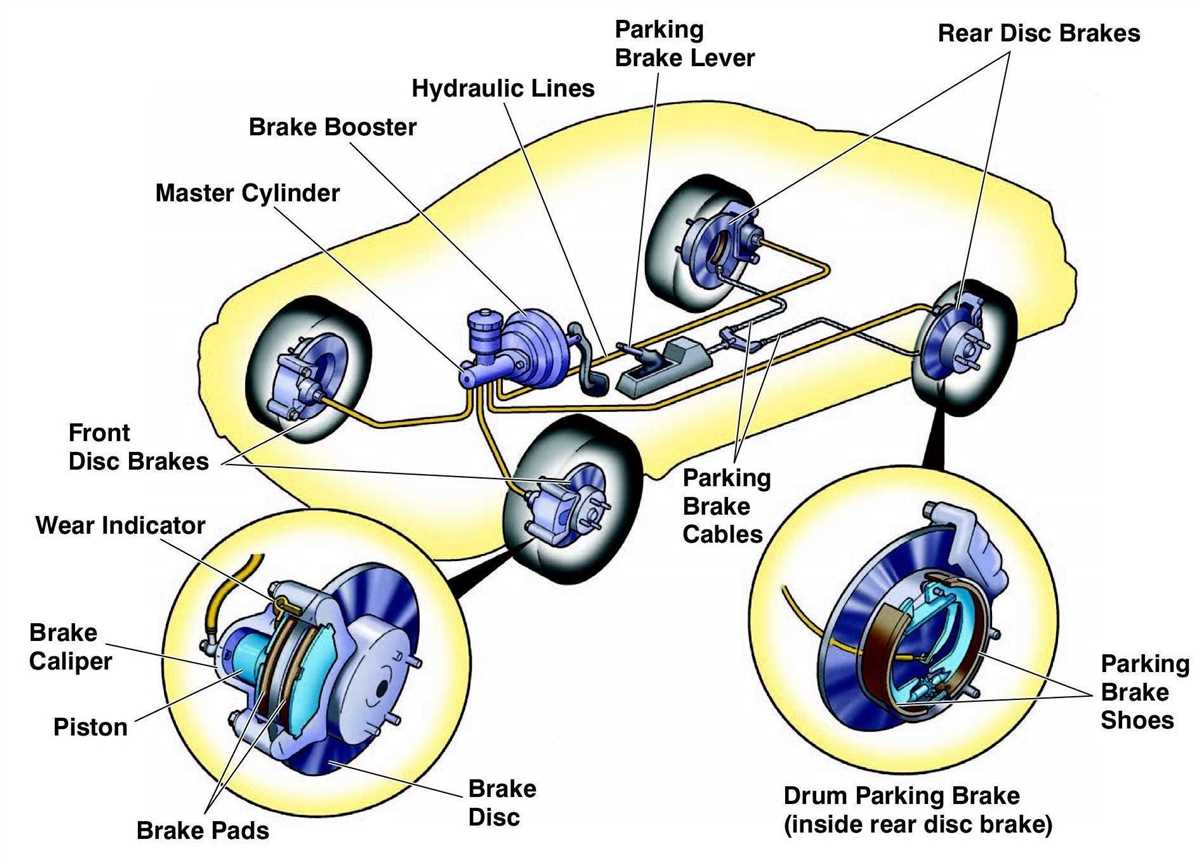
When it comes to car brake systems, there are several different types that are commonly used in today’s vehicles. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important for car owners to understand the differences in order to make informed decisions about their brakes.
1. Disc Brakes: Disc brakes are the most common type of brake system used in modern cars. They consist of a rotor, caliper, and brake pads. When the brake pedal is pressed, the caliper squeezes the brake pads against the rotor, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle. Disc brakes are known for their excellent stopping power and resistance to fade, making them a popular choice for high-performance cars.
2. Drum Brakes: While less common in modern vehicles, drum brakes are still found in some cars, particularly in the rear. Drum brakes consist of a drum, brake shoes, and wheel cylinder. When the brake pedal is pressed, the wheel cylinder forces the brake shoes against the drum, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle. Drum brakes are generally less expensive to manufacture, but they tend to have less stopping power and are more prone to overheating than disc brakes.
3. Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS is a safety feature that is included in many modern car brake systems. It works by preventing the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. ABS uses sensors to monitor the rotational speed of each wheel and modulates the brake pressure to prevent skidding. This system can greatly improve braking performance and stability, particularly in emergency situations.
4. Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD): EBD is another advanced feature that is often found in modern car brake systems. It works by automatically adjusting the amount of brake force applied to each wheel, based on factors such as vehicle load and road conditions. EBD helps to optimize braking performance and ensure that each wheel is able to stop the vehicle effectively, improving overall safety.
- Conclusion: In summary, there are several types of car brake systems that car owners should be familiar with. Disc brakes are the most common and offer excellent stopping power, while drum brakes are still used in some cars but generally have less stopping power. ABS and EBD are advanced features that can greatly enhance braking performance and safety. When it comes to choosing the right brake system for a car, it is important to consider factors such as the vehicle’s performance, driving conditions, and personal preferences.
How Does a Car Brake System Work?
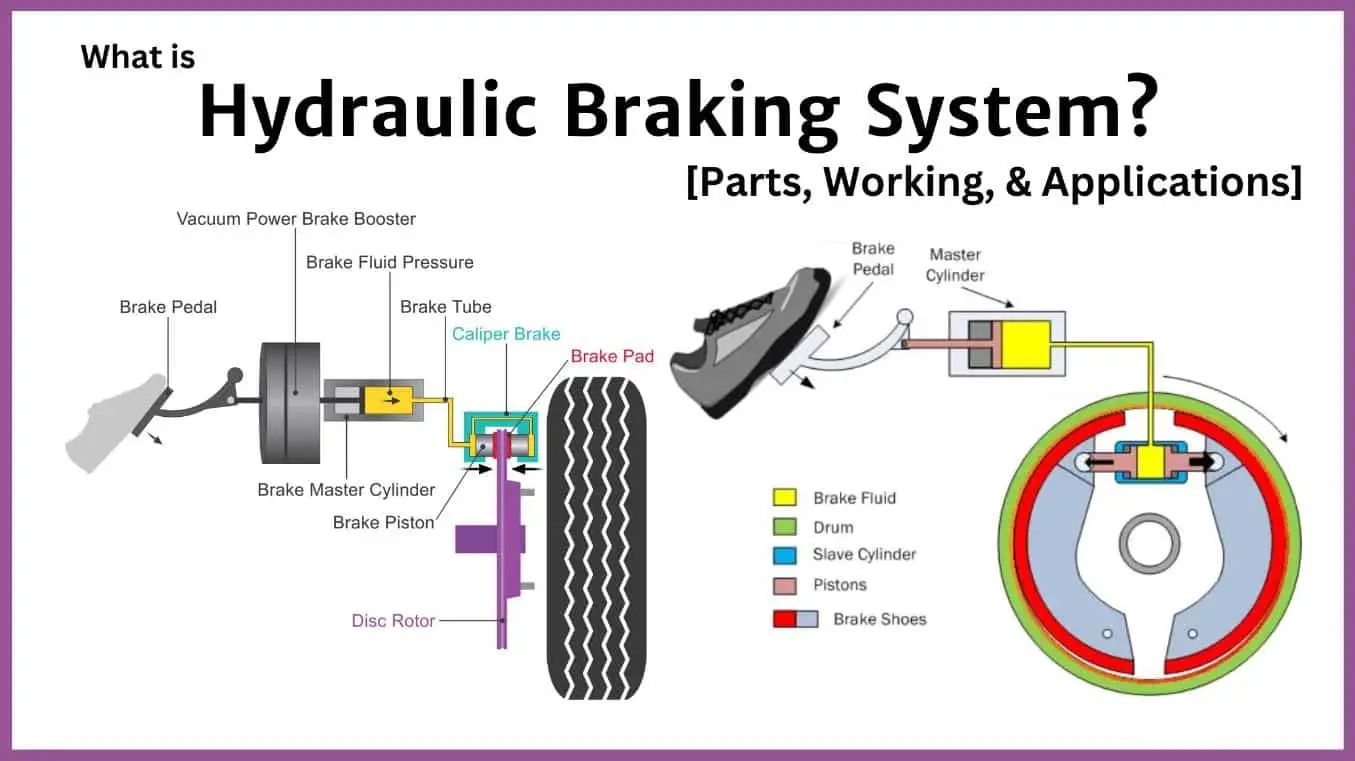
When it comes to stopping a vehicle, the car brake system plays a crucial role in ensuring safety on the road. Understanding how the brake system works can help drivers maintain and diagnose any potential issues.
The car brake system consists of several components, including the brake pedal, brake lines, brake pads, brake calipers, and brake rotors. When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, it pushes a piston in the master cylinder, which in turn pushes brake fluid through the brake lines.
As the brake fluid flows through the brake lines, it reaches the brake calipers. The calipers contain pistons that press the brake pads against the spinning brake rotors. The friction between the brake pads and the rotors slows down or stops the rotation of the wheels, eventually bringing the vehicle to a halt.
Regular maintenance of the brake system is crucial to ensure its proper function. Over time, the brake pads wear down and need to be replaced. Additionally, brake fluid should be periodically checked and replaced to prevent brake fade and maintain optimal braking performance.
In summary, the car brake system works by converting the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which then activates the brake calipers and pads to generate friction and slow down or stop the vehicle. Understanding how the brake system works enables drivers to detect any potential issues and keeps them safe on the road.
Common Brake System Issues
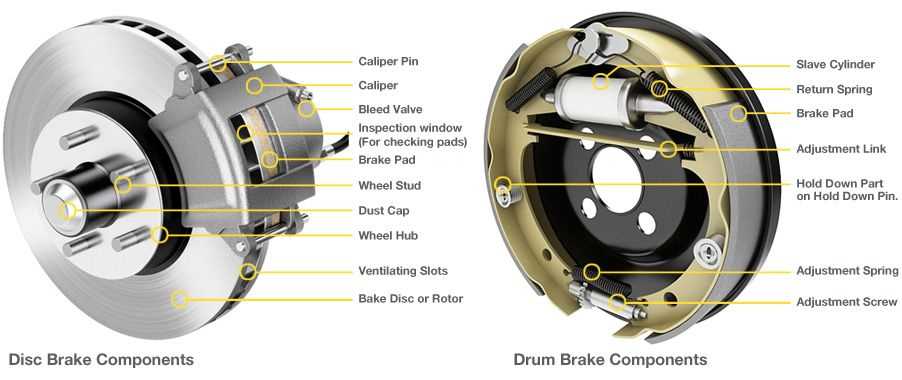
Brake system issues are a common problem in cars and can lead to dangerous situations if not addressed promptly. It is important to be aware of common brake system issues in order to identify them early and prevent potential accidents on the road.
One of the most common brake system issues is brake fluid leakage. Brake fluid is responsible for transferring force from the brake pedal to the brake calipers, initiating the braking process. If there is a leakage in the brake system, it can reduce the amount of brake fluid available, leading to reduced braking power or complete brake failure. Signs of brake fluid leakage include a soft or spongy brake pedal, an illuminated brake warning light, or visible fluid under the vehicle.
Another common issue is brake pad wear. Brake pads are responsible for creating friction against the brake rotors, which slows down or stops the vehicle. Over time, brake pads can wear out due to the constant friction. When brake pads become too thin, they can cause a screeching or squealing noise when applying the brakes. If left unaddressed, worn brake pads can damage the brake rotors, leading to more expensive repairs.
Furthermore, brake rotor damage is another common issue. Brake rotors are the discs that the brake pads clamp down on to create the necessary friction. Over time, brake rotors can become warped or worn due to excessive heat and friction. This can result in brake pulsation or vibration when braking, which can affect the overall braking performance of the vehicle.
In conclusion, being aware of common brake system issues and knowing the signs to look out for can help prevent potential accidents on the road. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensure the safety and reliability of the brake system. If any signs of brake system issues are detected, it is important to take immediate action and seek professional assistance to address the problem.
The Importance of Regular Brake System Maintenance
Regular brake system maintenance is crucial for the safety and optimal performance of a car. Ignoring or neglecting the maintenance of the brake system can lead to serious consequences, including accidents and damage to the vehicle.
Here are some key reasons why regular brake system maintenance is important:
- Safe Driving: A well-maintained brake system ensures that the vehicle stops quickly and effectively when necessary. Regular maintenance helps identify any potential issues with the brakes and allows for timely repairs, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Extending Brake Life: Regular maintenance, such as replacing brake pads and inspecting brake lines, helps prolong the lifespan of the braking system. By catching and resolving problems early on, you can avoid more costly repairs or premature replacement of brake components.
- Cost Savings: Regular brake system maintenance can save you money in the long run. By addressing minor issues before they become major problems, you can avoid expensive repairs or even a complete brake system overhaul.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your brake system is regularly maintained gives you confidence and peace of mind while driving. You can trust that your vehicle will respond properly when you need to stop or slow down, enhancing your overall driving experience.
In conclusion, regular brake system maintenance is vital for your safety, the longevity of your vehicle’s braking system, and your overall driving experience. Investing time and effort in maintaining your brakes will pay off in the form of improved safety, reduced repair costs, and increased peace of mind.