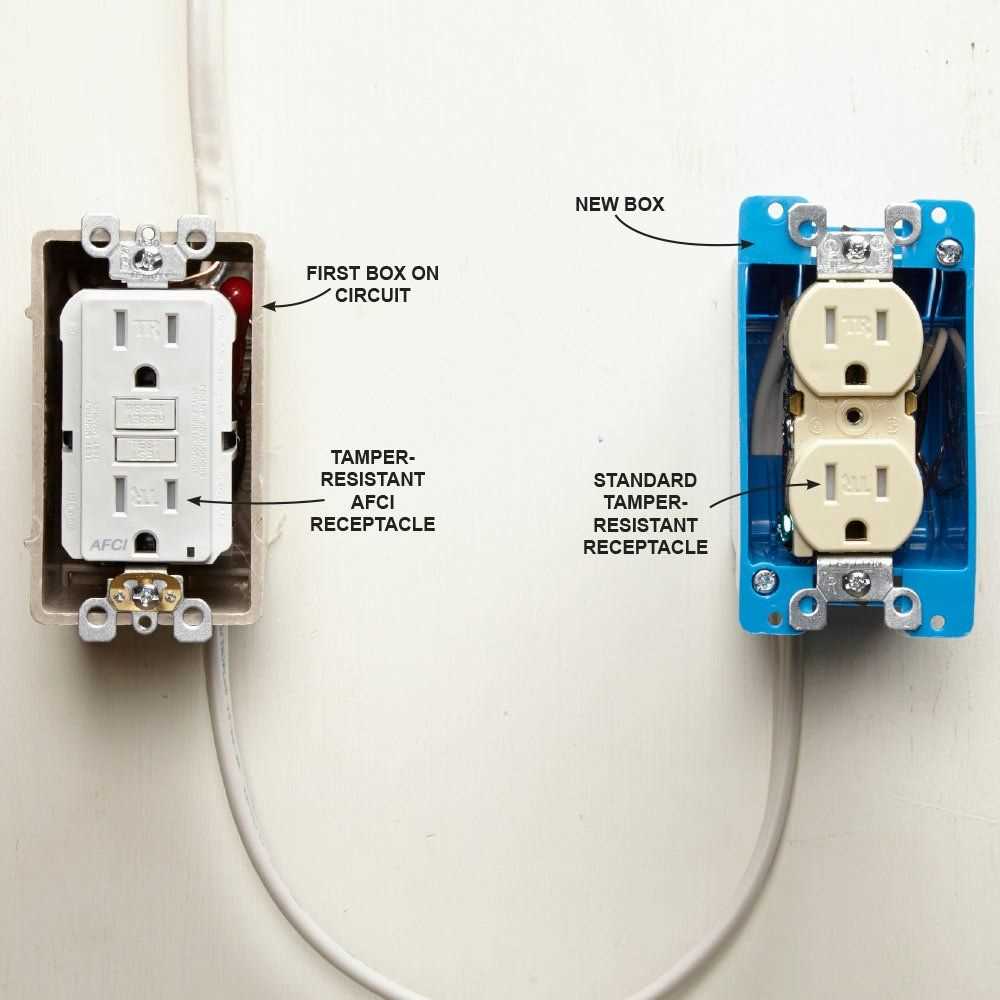
Electrical outlets are a fundamental component of our daily lives, providing us with the power we need to run our various electronic devices. While most of us are familiar with how to use an electrical outlet, few of us understand the inner workings that make it all possible. In this article, we will explore the electrical outlet schematic, breaking down the various components and their functions.
At the heart of every electrical outlet is the receptacle, which is where we plug in our devices. The receptacle consists of two or three slots, each with a specific purpose. The smaller slot, often on the left side, is known as the hot slot and carries the electricity to power our devices. The larger slot on the right is the neutral slot and completes the electrical circuit. For outlets that have a ground slot, it serves as a safety measure by providing an alternate path for the electrical current in the event of a fault.
Beyond the receptacle, the electrical outlet schematic includes additional components to ensure a safe and efficient flow of electricity. One of these components is the breaker or fuse, which is designed to protect the electrical circuit from overloading. When too much electricity flows through the circuit, the breaker or fuse will trip, cutting off the power and preventing damage to the outlet and connected devices. Additionally, outlets may also include switches that allow us to control the flow of electricity to a specific device or set of devices.
Understanding the electrical outlet schematic is crucial for anyone working with electricity, whether it be for household repairs or professional installations. By having a clear understanding of how an electrical outlet works, individuals can ensure they are using the appropriate safety measures and avoiding the risk of electrical shock or fire hazards. So the next time you plug in your phone or laptop, take a moment to appreciate the intricate design of the electrical outlet schematic that makes it all possible.
Understanding Electrical Outlet Schematic: A Comprehensive Guide
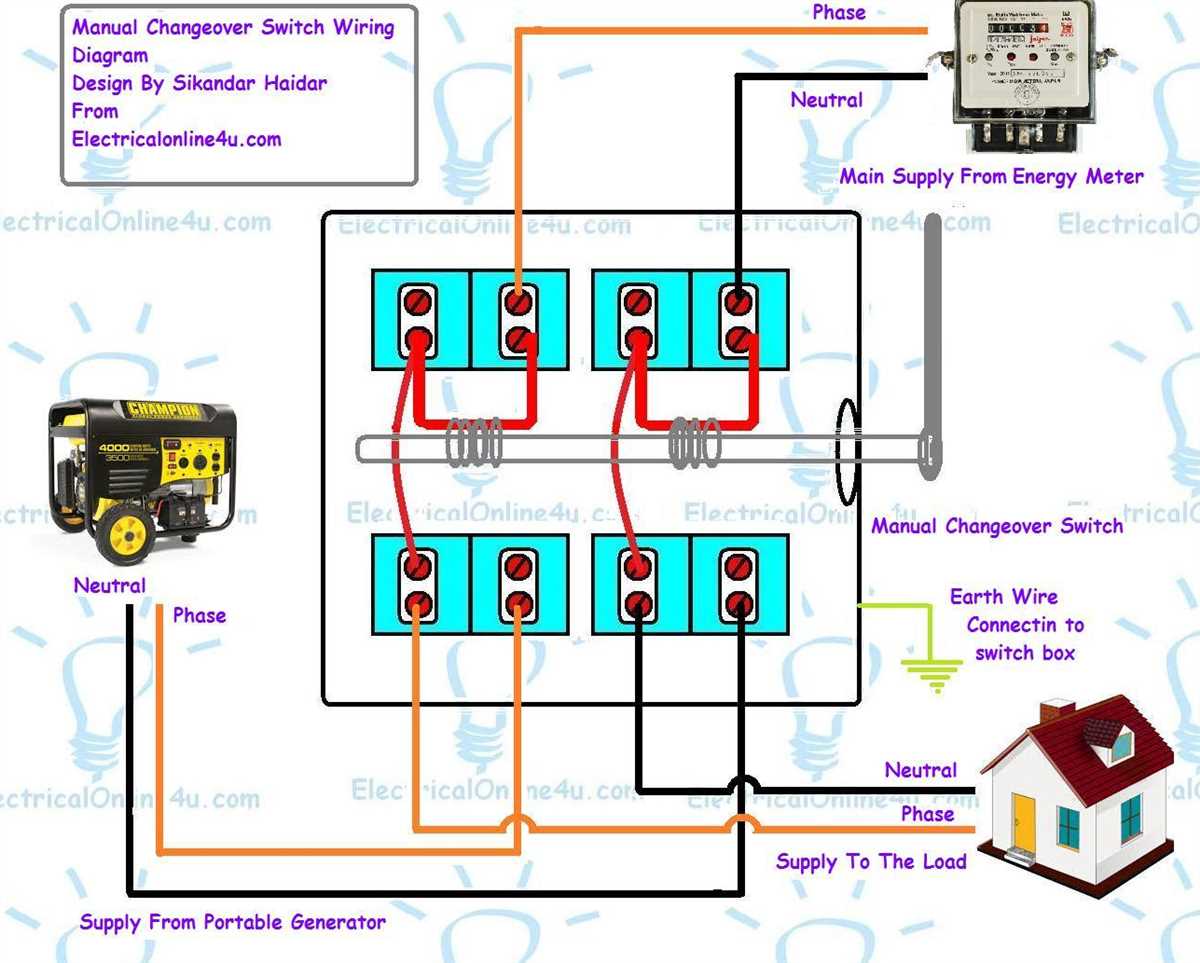
Electrical outlets are a crucial component of any building’s electrical system. They provide a convenient way to access electricity for various devices and appliances. To better understand how electrical outlets work and how they are connected in a circuit, it is important to have a good grasp of electrical outlet schematics.
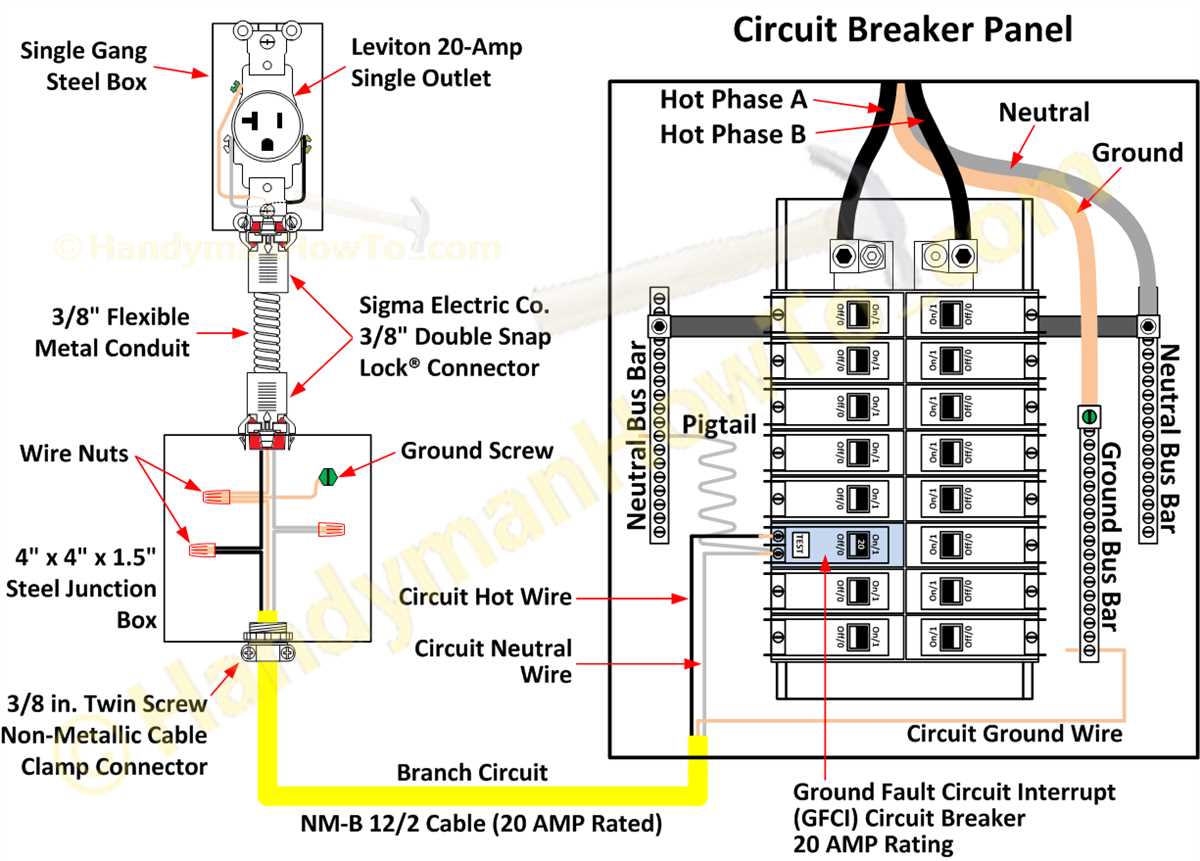
A schematic diagram is a visual representation of an electrical circuit, showing how the various components are interconnected. In the case of an electrical outlet, the schematic diagram provides a detailed illustration of the wiring connections inside the outlet, including the hot wire, neutral wire, and ground wire.
Hot wire: The hot wire carries the electrical current from the power source to the outlet. It is typically colored black or red and is responsible for delivering the electrical energy to the connected device or appliance.
Neutral wire: The neutral wire completes the circuit and provides a safe path for the electrical current to return to the power source. It is usually colored white and is crucial for maintaining a balanced flow of electricity.
Ground wire: The ground wire is a safety feature that provides a path for electrical current in the event of a short circuit or electrical fault. It is typically colored green or copper and is connected directly to the building’s grounding system to prevent electrical shock.
When looking at an electrical outlet schematic, you will see three terminals or screws labeled “H,” “N,” and “G.” These correspond to the hot, neutral, and ground wires, respectively. The hot wire is connected to the “H” terminal, the neutral wire to the “N” terminal, and the ground wire to the “G” terminal.
Understanding the electrical outlet schematic is essential for anyone working with electrical systems, whether it be for installation, repair, or maintenance. It ensures proper wiring connections and helps prevent electrical hazards and accidents. Remember, always consult a professional electrician if you are unsure or unfamiliar with electrical work.
What is an Electrical Outlet?
An electrical outlet is a device that allows electrical equipment to be connected to a source of electricity by plugging in a power cord. It is an essential component of any electrical system, providing a convenient and safe way to connect devices such as lamps, appliances, and electronics to the power supply.
The basic design of an electrical outlet consists of multiple metal contacts, usually in the form of slots or holes, which are connected to the electrical wiring in a building. These contacts are often referred to as “prongs” or “pins” and are designed to match the shape and size of the plugs on power cords. The contacts are connected to the electrical circuit, allowing electricity to flow from the power source to the connected device.
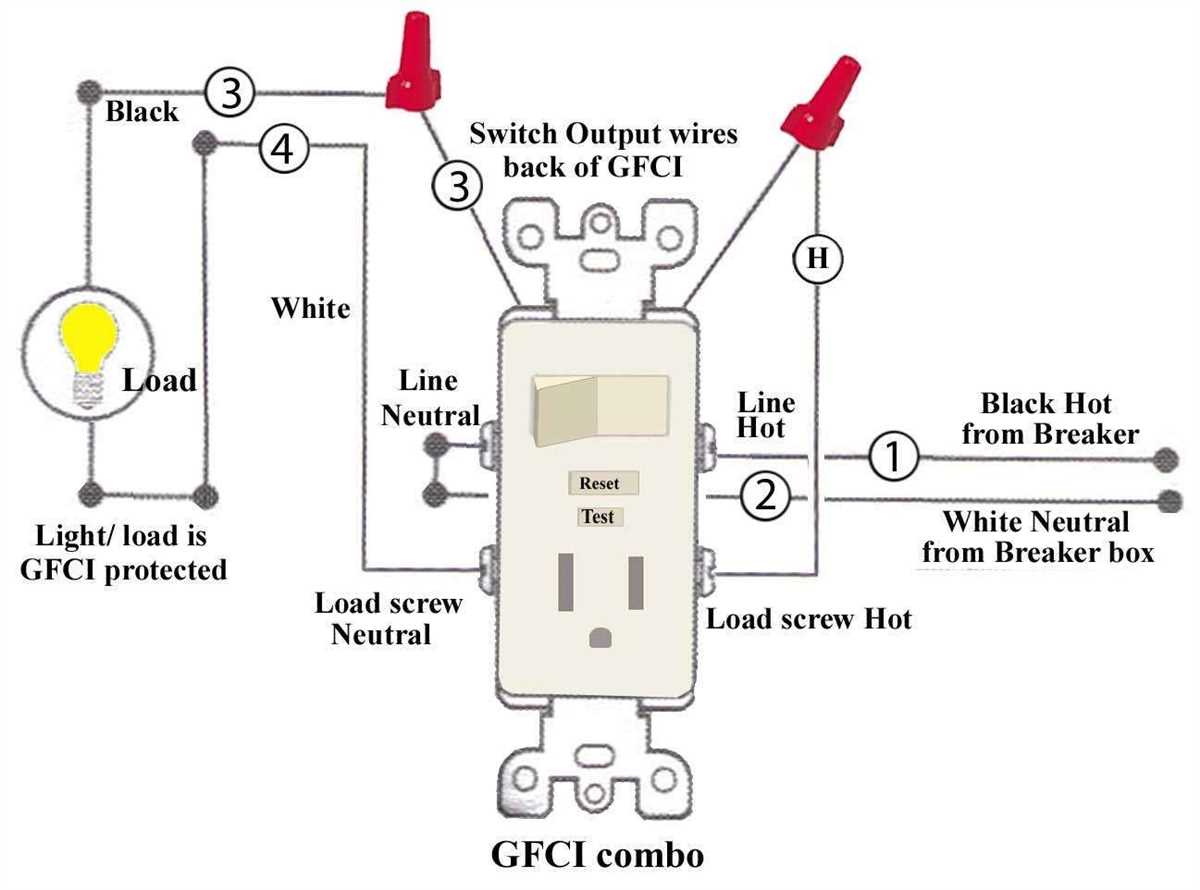
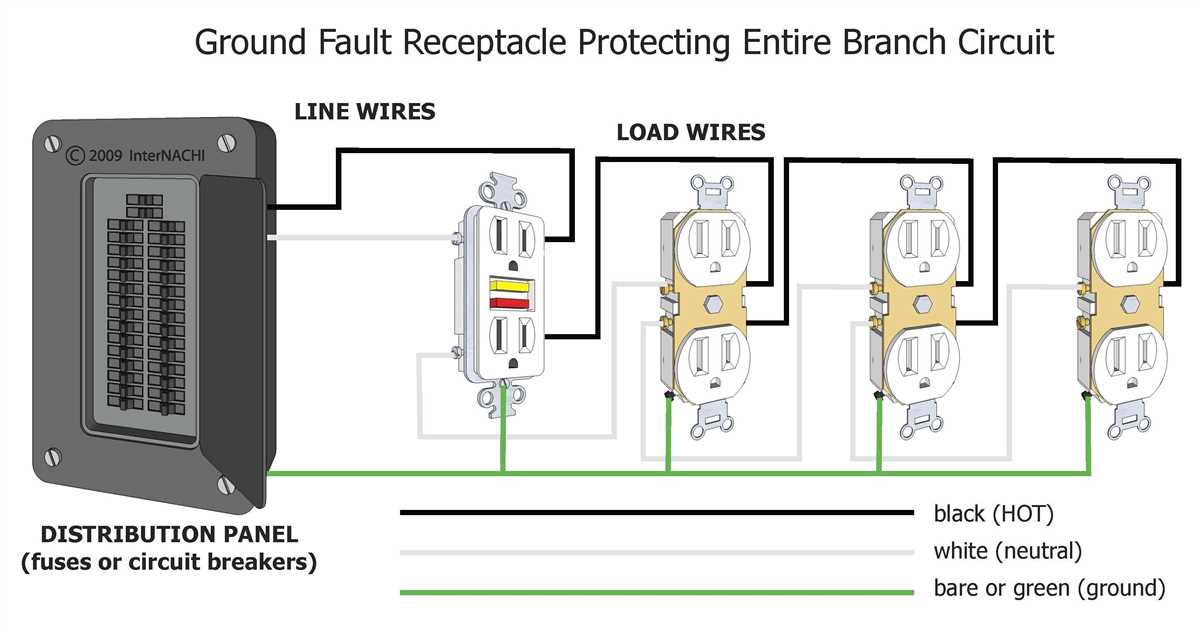
There are various types of electrical outlets available, each designed for specific purposes and power requirements. Common types include two-prong outlets, three-prong outlets with grounded contacts, and specialized outlets for appliances such as stoves or dryers. Additionally, some outlets may have built-in safety features such as GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter) protection, which helps prevent electrical shocks in case of faults or short circuits.
Electrical outlets are typically installed at convenient locations throughout a building, often in walls or floors, allowing for easy access to power in different areas. It is important to use outlets that are properly installed and meet electrical safety standards to ensure the safe operation of electrical equipment and prevent electrical hazards.
Overall, electrical outlets are a crucial part of our everyday lives, providing the power required to operate various devices and appliances. They play a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient use of electricity in homes, offices, and other buildings.
The Importance of Electrical Outlet Schematic
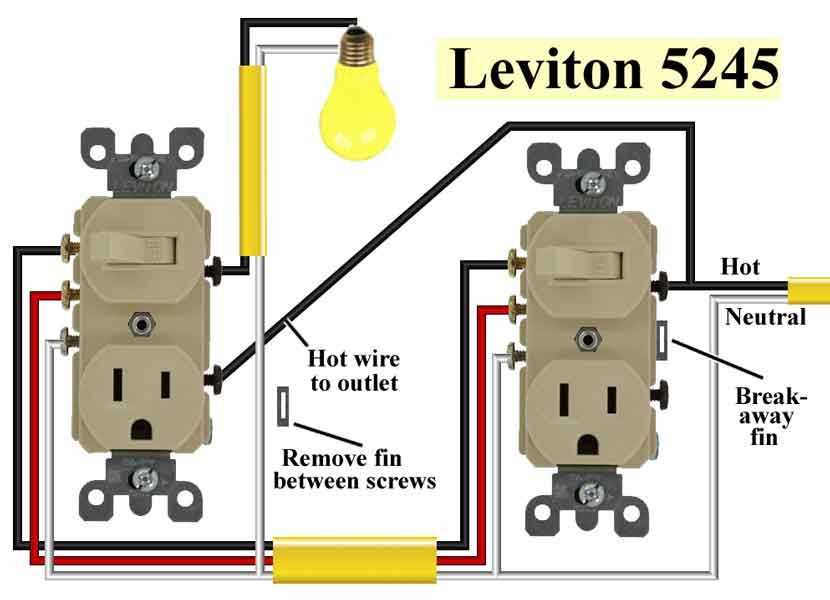
Electrical outlet schematic refers to a diagram or drawing that shows the wiring and connections of an electrical outlet. This schematic is crucial in ensuring the safe and efficient functioning of the outlet, as it provides a detailed representation of how the electrical components are connected and how the power is distributed.
One of the key reasons why electrical outlet schematic is important is because it allows electricians and technicians to understand and troubleshoot any issues that may arise with the outlet. By referring to the schematic, they can identify the specific wires and connections involved, making it easier to pinpoint the source of the problem and carry out the necessary repairs or replacements. This not only saves time and effort but also reduces the risk of potential accidents or electrical hazards.
Furthermore, electrical outlet schematic is vital for proper installation and maintenance of outlets. By following the schematic, electricians can ensure that the connections are made correctly and that all safety standards and regulations are met. This is especially important when dealing with complex or multiple outlets, as the schematic provides a clear guide on how to properly wire and connect them. It also helps in labeling and organizing the connections, making it easier to trace and manage the electrical system.
In addition, electrical outlet schematic plays a crucial role in designing and planning the electrical layout of a building or space. Architects and engineers can refer to the schematic to determine the placement and distribution of outlets, taking into account factors such as load requirements, proximity to appliances, and overall aesthetics. This ensures that the electrical system is well-designed and meets the specific needs and specifications of the building.
Overall, electrical outlet schematic is an essential tool in the field of electrical wiring and installation. It allows for efficient troubleshooting, proper installation, and accurate planning, ultimately ensuring the safety and functionality of electrical outlets.
Key Components of an Electrical Outlet
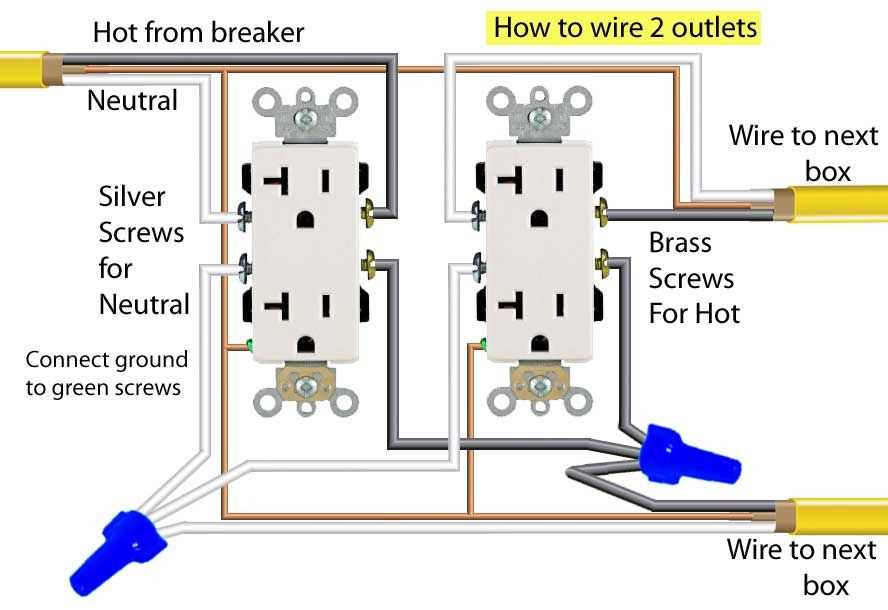
An electrical outlet is an essential component in our modern homes and buildings, allowing us to easily access electrical power for various devices. While it may seem like a simple everyday object, an electrical outlet consists of several key components that ensure its functionality and safety.
1. Receptacle: The main component of an electrical outlet is the receptacle, which provides the electrical connection for a device to be plugged in. The receptacle consists of slots or holes where the prongs of a plug can be inserted. The design of the receptacle can vary depending on the country or region, but it generally follows a standard format.
2. Terminal connections: Inside the electrical outlet, there are terminal connections that securely hold the wiring in place. These connections are typically made of metal and are responsible for transferring electricity from the power source to the device being plugged in. The quality and reliability of these connections are crucial for the proper functioning of the outlet.
3. Grounding mechanism: In order to ensure safety, many electrical outlets are equipped with a grounding mechanism. This mechanism provides a path for electrical current to flow into the ground if there is a fault or surge in the electrical system. It helps protect both the device being used and the user from potential electric shocks.
4. Faceplate: The faceplate is the visible part of the electrical outlet that covers the receptacle and the terminal connections. It serves to protect the internal components from dust, moisture, and accidental contact. The faceplate can be easily removed for maintenance or repairs, but it should always be reinstalled securely to maintain the safety and functionality of the outlet.
5. Mounting box: The mounting box, also known as a junction box, is the enclosure that holds the electrical outlet in place. It provides support and protection for the wiring connections and prevents them from being exposed. The mounting box is usually made of metal or plastic and can be embedded in the wall or surface-mounted, depending on the installation requirements.
6. Circuit breaker or fuse: While not technically a component of the electrical outlet itself, the circuit breaker or fuse is an integral part of the electrical system. It is responsible for controlling the flow of electricity and protecting the circuit from overloading or short circuits. The circuit breaker or fuse is typically located in the electrical panel and should be regularly inspected and maintained.
In conclusion, an electrical outlet may seem like a simple device, but it consists of several important components that work together to provide a safe and reliable source of electrical power. Understanding these key components can help us better appreciate the importance of proper installation and maintenance of electrical outlets in our homes and buildings.
Types of Electrical Outlets
In the world of electrical installations, there are several types of electrical outlets available for various applications. Each type of electrical outlet has its unique design and function. Understanding the different types of electrical outlets is crucial for ensuring proper electrical connections and safety.
1. Type A Outlet
The Type A outlet is commonly used in North America, Central America, and Japan. It has two flat parallel pins and is designed to handle 15-20 Amps of current. This type of outlet is typically used for low-power devices such as lamps, TVs, and small appliances.
2. Type B Outlet
The Type B outlet is also prevalent in North America and Japan but with an additional grounding pin. It has two flat parallel pins and one grounding pin in the shape of a semi-circle. This grounding pin provides protection against electrical shocks and is used for higher power consuming devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, and computers.
3. Type C Outlet
The Type C outlet, also known as the Europlug, is widely used in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It has two round pins and does not include a grounding pin. These outlets are suitable for low-power devices such as smartphones, tablets, and chargers.
4. Type D Outlet
The Type D outlet is found in India and has three round pins in a triangular pattern. It is primarily used for heavy appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines. The Type D outlet can handle high power levels and is designed to prevent accidental electrical shocks.
5. Type G Outlet
The Type G outlet is the standard outlet in the United Kingdom, Ireland, and other countries. It has three rectangular pins in a triangular formation. This outlet type is known for its robust design and ability to handle high power loads. It is used for various appliances, tools, and equipment.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of electrical outlets is essential for safe and proper electrical connections. Always ensure that you use the correct outlet type for your specific electrical needs and consult a qualified electrician if you have any doubts or questions.
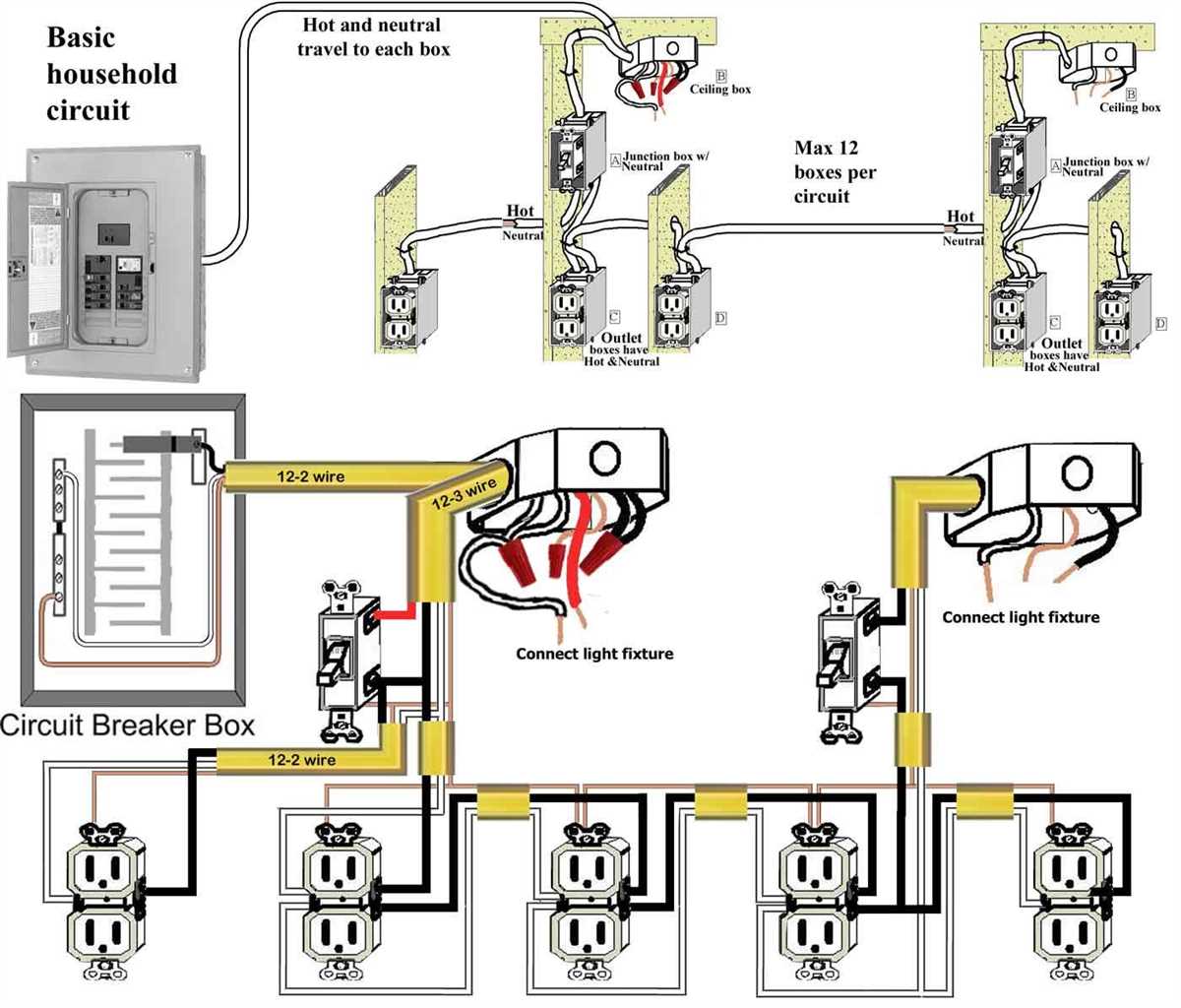
How to Read an Electrical Outlet Schematic
Electrical outlet schematics are diagrams that show the electrical connections and circuitry of an outlet. These schematics are useful for understanding how an outlet is wired and can be helpful when troubleshooting electrical problems or when installing new outlets.
When reading an electrical outlet schematic, it is important to understand the symbols and markings used in the diagram. The symbols represent different electrical components and the lines connecting them indicate the flow of electricity. Some common symbols include a circle with a cross inside to represent an outlet, a straight line to represent a wire, and a zigzag line to represent a resistor or load.
The schematic will also include labels and numbers to indicate specific components or connections. These labels can help identify which wires or terminals need to be connected or disconnected. Additionally, the numbers on the schematic can correspond to a wiring diagram or legend that provides more detailed information about the electrical connections.
When analyzing an electrical outlet schematic, it is important to follow the flow of electricity from the power source to the outlet and any connected devices. This can help identify any potential issues or areas where the circuit may be overloaded. It is also important to understand the voltage and current requirements of the outlet and ensure that the circuit is properly grounded.
In conclusion, reading an electrical outlet schematic requires an understanding of the symbols, labels, and connections used in the diagram. By following the flow of electricity and understanding the voltage and current requirements, one can effectively analyze and troubleshoot electrical outlet circuits.
Common Issues with Electrical Outlets and Their Solutions
Electrical outlets are an essential part of our daily lives, providing power to appliances, electronics, and other devices. However, like any other electrical component, outlets can experience problems from time to time. In this section, we will discuss some common issues with electrical outlets and their possible solutions.
1. Outlet Not Working
One of the most common issues homeowners face is an electrical outlet that is not working. This can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as a tripped circuit breaker, a blown fuse, a loose wire connection, or a faulty outlet. To resolve this issue, you can try the following solutions:
- Check the circuit breaker or fuse box and reset or replace if necessary.
- Inspect the outlet for loose or damaged wires. If any are found, tighten or replace them as needed.
- If the outlet still doesn’t work, replace it with a new one.
2. Outlet Overheating
If you notice that an outlet feels hot to the touch or emits a burning smell, it is a sign of potential overheating. This can be caused by excessive current flow or a loose connection. To address this issue:
- Turn off the power to the outlet at the circuit breaker or fuse box.
- Inspect the outlet for any loose or charred wires. If found, tighten or replace them.
- If the outlet continues to overheat, consult a licensed electrician, as it may require professional attention to prevent electrical fires.
3. Outlet Not Grounded
A grounded outlet, indicated by three prongs, provides an extra level of safety. If you have an outlet without a ground connection or notice any grounding issues, you can take the following steps:
- Ensure the outlet is properly grounded by hiring a licensed electrician to inspect and install a proper grounding system.
- Consider upgrading your outlets to ones that are grounded, if feasible.
4. Insufficient Outlets
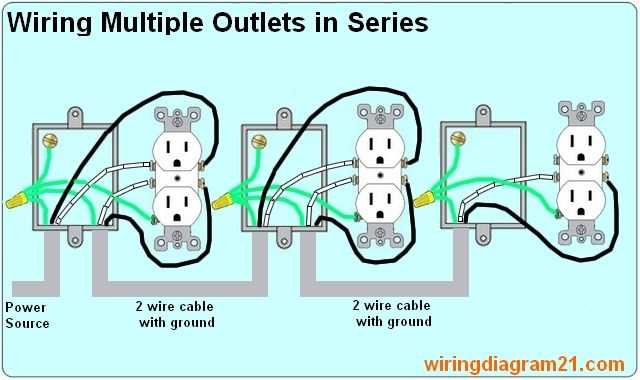
In homes with a limited number of outlets, it can be inconvenient and unsafe to rely on power strips and extension cords. To address this issue:
- Add more outlets in areas where they are needed, either by hiring a licensed electrician or using surface-mounted raceway systems.
- Avoid overloading outlets by spreading the load across multiple outlets or installing dedicated circuits for high-power devices.
Remember, electrical work can be dangerous, so it’s always best to consult a licensed electrician if you’re unsure how to handle any electrical issues or need assistance with repairs or installations. By addressing these common issues promptly, you can ensure the safety and functionality of your electrical outlets.
Q&A:
What are common issues with electrical outlets?
Common issues with electrical outlets include loose connections, socket burnout, tripping circuits, and faulty wiring.
How can I fix a loose connection in an electrical outlet?
To fix a loose connection, you can turn off the power to the outlet, remove the cover plate, and tighten any loose screws or wires. If necessary, you may need to replace the outlet.
What causes socket burnout in electrical outlets?
Socket burnout can be caused by overloading the outlet with too many appliances, loose connections, or faulty wiring. It can also occur due to poor quality outlets or improper use.
Why does my circuit keep tripping when I use certain appliances?
If your circuit keeps tripping when you use certain appliances, it could be due to an overload on the circuit. Large appliances like air conditioners or refrigerators can draw a lot of power, causing the circuit to trip. You may need to redistribute the load on different circuits or have an electrician install additional circuits.
How can I fix faulty wiring in an electrical outlet?
Fixing faulty wiring in an electrical outlet should only be done by a qualified electrician. They will be able to identify and repair any wiring issues safely and efficiently.