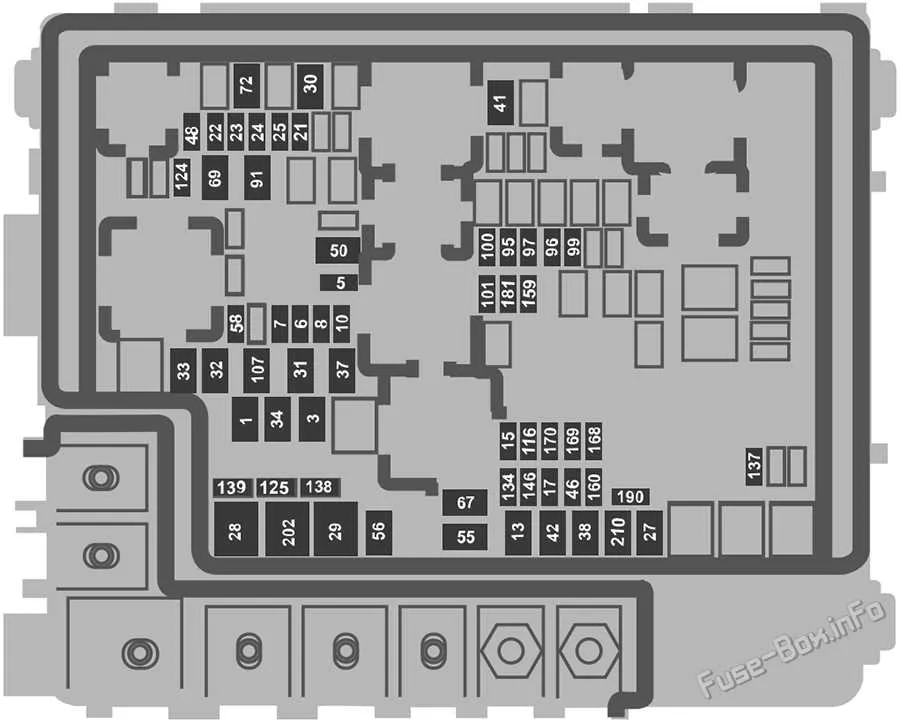
If you’re experiencing electrical issues in your truck, start by consulting the component chart under the hood. Knowing the exact position of each relay and breaker can help you quickly identify and solve problems related to power loss or malfunctions in key systems. Check your owner’s manual for an overview of this setup, or refer to the detailed schematic for precise information about the locations and specifications of each part.
Start with the main distribution block, typically located near the driver’s side. Here, you’ll find critical relays for essential systems like the engine management and fuel pumps. If one of these relays fails, it may cause a sudden drop in performance or complete shutdown of the vehicle. Look for a labeled section that divides the high-amperage components from the low-current circuits for ease of maintenance.
For smaller circuits, such as those controlling the air conditioning, lighting, or sound system, check the secondary distribution area, usually found inside the cabin or behind a removable cover. This section houses smaller switches and connectors that control non-essential features but can still have a significant impact on the vehicle’s overall functionality.
Remember to confirm the amperage ratings before replacing any part, as using the wrong size can lead to overheating or, worse, fire hazards. Keep a copy of the detailed chart handy for reference, and make sure you follow proper safety protocols when handling live components.
Electrical System Layout
To ensure proper functioning of your vehicle’s electrical components, you need to understand the layout of the central power distribution unit. Here’s how you can identify and manage each fuse for smooth operation.
- Locate the main block inside the cabin on the driver’s side, near the footwell or dashboard.
- There will be several relays and connections marked for critical systems, such as lights, ignition, and radio.
- For specific component protection, refer to the legend detailing each fuse’s amperage and designated part.
- Always replace blown units with the exact amperage to avoid damaging wiring or electrical parts.
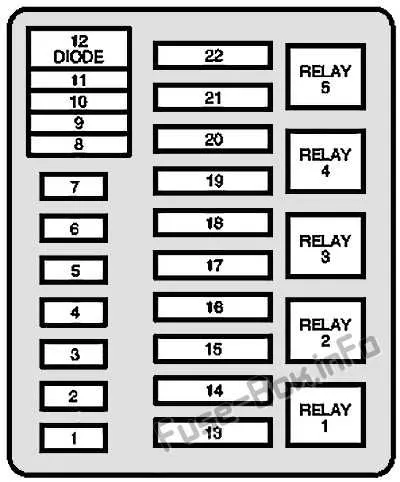
For the engine bay, the external relay box controls high-power systems like the cooling fans, alternator, and ABS. Make sure you regularly inspect the integrity of the cover to prevent moisture or dirt from interfering with power distribution.
- Check the legend for each system under the hood, including power steering, battery charging, and air conditioning.
- Take extra care with high-current components that demand a specific fuse for safe operation.
Regular inspection and maintenance will keep the electrical network running efficiently and prevent unexpected failures. Use the provided key for troubleshooting and restoring power to the vehicle’s critical functions quickly.
How to Locate and Access the Fuse Panel in Your F150
To locate the electrical component distribution box, check the driver’s side footwell, near the lower part of the dashboard. You’ll find a cover that can be removed by pulling it gently or releasing latches, depending on the model year. This compartment houses multiple circuit connections, which are critical for the vehicle’s electrical system.
Alternatively, the second location to check is under the hood. Open the engine bay and look near the battery or near the front side of the engine compartment. The lid should be easily removable with clips or screws that can be undone by hand or with a simple tool.
Before attempting any work, ensure the vehicle is powered off, and use gloves to prevent accidental contact with live components. If you’re unsure about the exact location, refer to the owner’s manual for precise instructions on where the specific boxes are located in your vehicle model.
Tip: If the cover is difficult to remove, apply gentle pressure at the edges. Do not force it, as this may damage the fasteners. In case of tight fit, using a plastic tool to pry open is recommended.
Once you’ve located and opened the box, identify the specific section based on the labels on the inside of the lid or the manual. The layout will help you quickly find and troubleshoot any issues with your electrical system.
Identifying Fuses for Common Electrical Issues in the F150

For electrical issues like non-functioning lights, radio, or malfunctioning accessories, start by checking the relevant circuit protection. Key components such as the headlight circuit or power window switches are often connected to specific protective elements. Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or component reference for precise locations and amperage values.
Headlights and Taillights: If either of these is unresponsive, check the circuit responsible for lighting. This is typically located in the central section of the vehicle’s electrical system. Inspect the associated relay and confirm its integrity.
Power Windows: Unresponsive power windows could point to a broken connection or overloaded circuit. The corresponding protection often resides in the compartment near the driver’s side, easily identifiable by its amperage ratings, which should align with the power window motor specs.
Radio and Infotainment: In case of a non-working stereo, the electrical element governing the entertainment unit is often near the dashboard. It may be placed near the cabin’s central fuse block, marked clearly with a dedicated section for interior electronics.
Blower Motor: When climate control stops working, the issue might involve a protective mechanism for the blower motor. Look for this within the section linked to the HVAC system, typically located near the vehicle’s dashboard area.
Each circuit’s protection is usually listed with a number and amperage, so it’s important to replace any damaged protection with the correct specifications. Double-check all relays and fuses for signs of damage or corrosion.
Replacing Fuses and Troubleshooting Electrical Issues in Your Truck
Start by identifying the malfunctioning circuit using the vehicle’s electrical system chart. If an issue arises, locate the corresponding protection component. Before removing the faulty item, ensure the vehicle is turned off and the key is out of the ignition. For safety, disconnect the battery to avoid electrical shock or short circuits.
When replacing, use the same amperage rating as the original part. Installing an incorrect one can cause serious electrical malfunctions or even fire hazards. Gently pull out the damaged component using appropriate pliers or a fuse puller to avoid damaging the slot. Insert the new one securely, ensuring it fits tightly in place.
If multiple circuits are malfunctioning, check for potential issues with the power supply or a faulty relay. Inspect connectors for corrosion, and ensure no exposed wires are touching each other. Tighten any loose terminals and replace damaged wiring to prevent future electrical failures.
If the issue persists after replacing the protection component, examine the system for underlying problems. A continuous power drop may indicate an issue with the alternator or a deeper electrical fault. Seek professional inspection if the problem isn’t resolved with basic troubleshooting steps.