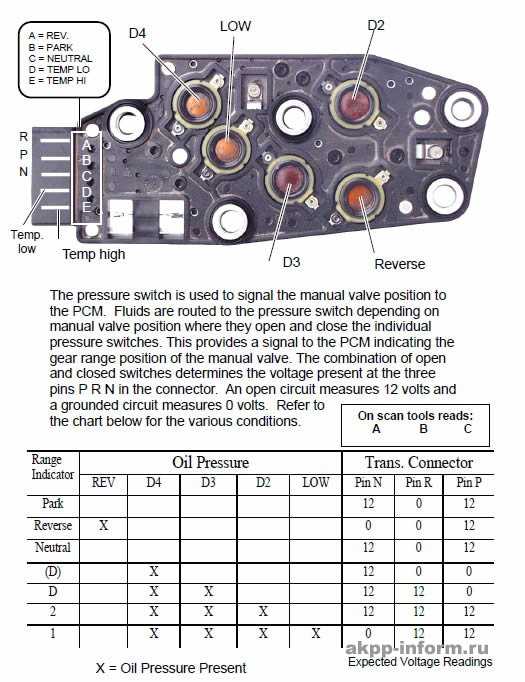
The GM 4L60E transmission is a popular automatic transmission found in a wide range of General Motors vehicles. It is known for its durability and smooth shifting, making it a popular choice for both everyday drivers and performance enthusiasts. Understanding the inner workings of this transmission can help car owners and mechanics diagnose and repair any issues that may arise.
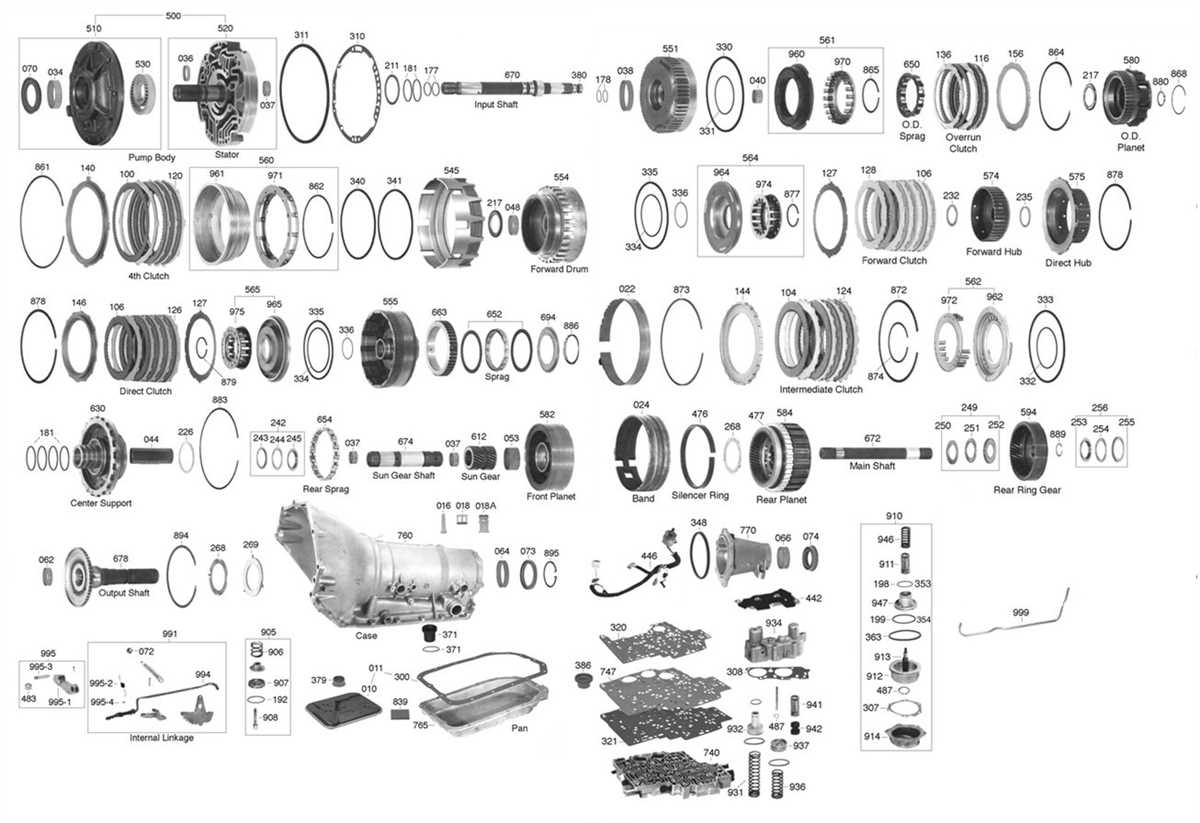
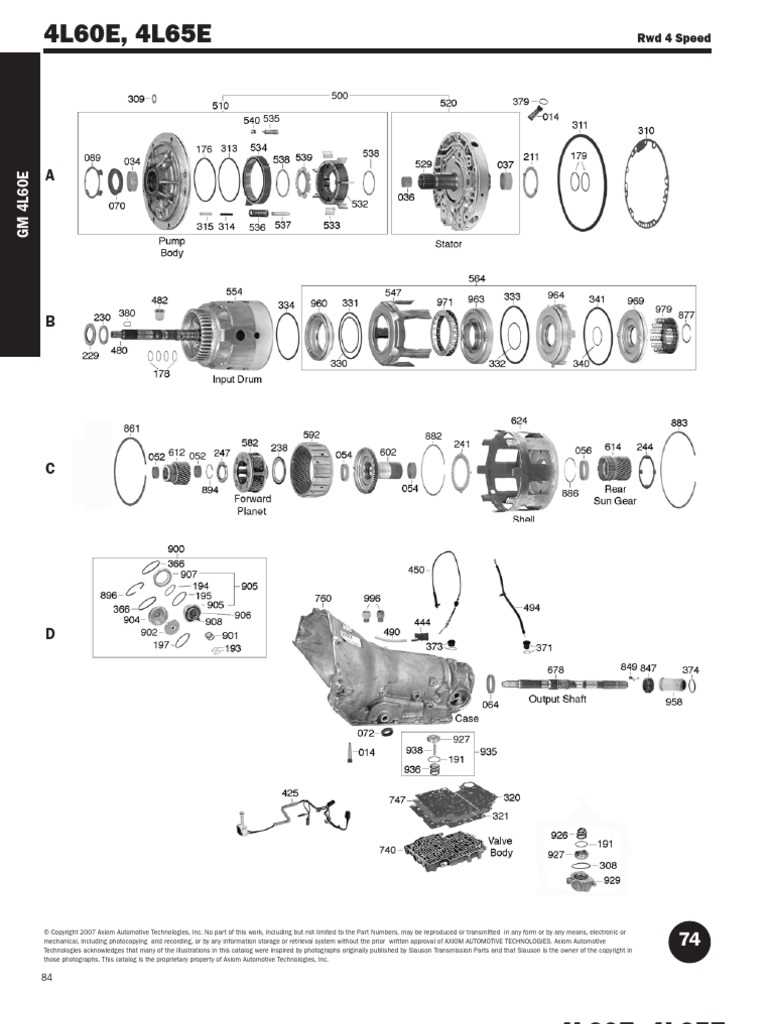
A GM 4L60E transmission diagram provides a visual representation of the various components and their positions within the transmission. This includes the torque converter, valve body, clutch packs, planetary gears, and other important parts. The diagram helps in understanding how these parts work together to transfer power from the engine to the wheels.
By studying a GM 4L60E transmission diagram, one can see how the hydraulic system controls the shifting of gears. The diagram shows the flow of transmission fluid through various channels and valves, allowing for the engagement or disengagement of different clutch packs and bands. This hydraulic system is crucial in ensuring smooth and precise gear shifts.
Overall, a GM 4L60E transmission diagram provides a valuable visual reference for understanding the workings of this popular transmission. Whether you’re a car owner looking to diagnose a transmission issue or a mechanic seeking to replace or repair components, the diagram can be a helpful tool in achieving a successful outcome.
GM 4l60e Transmission Diagram
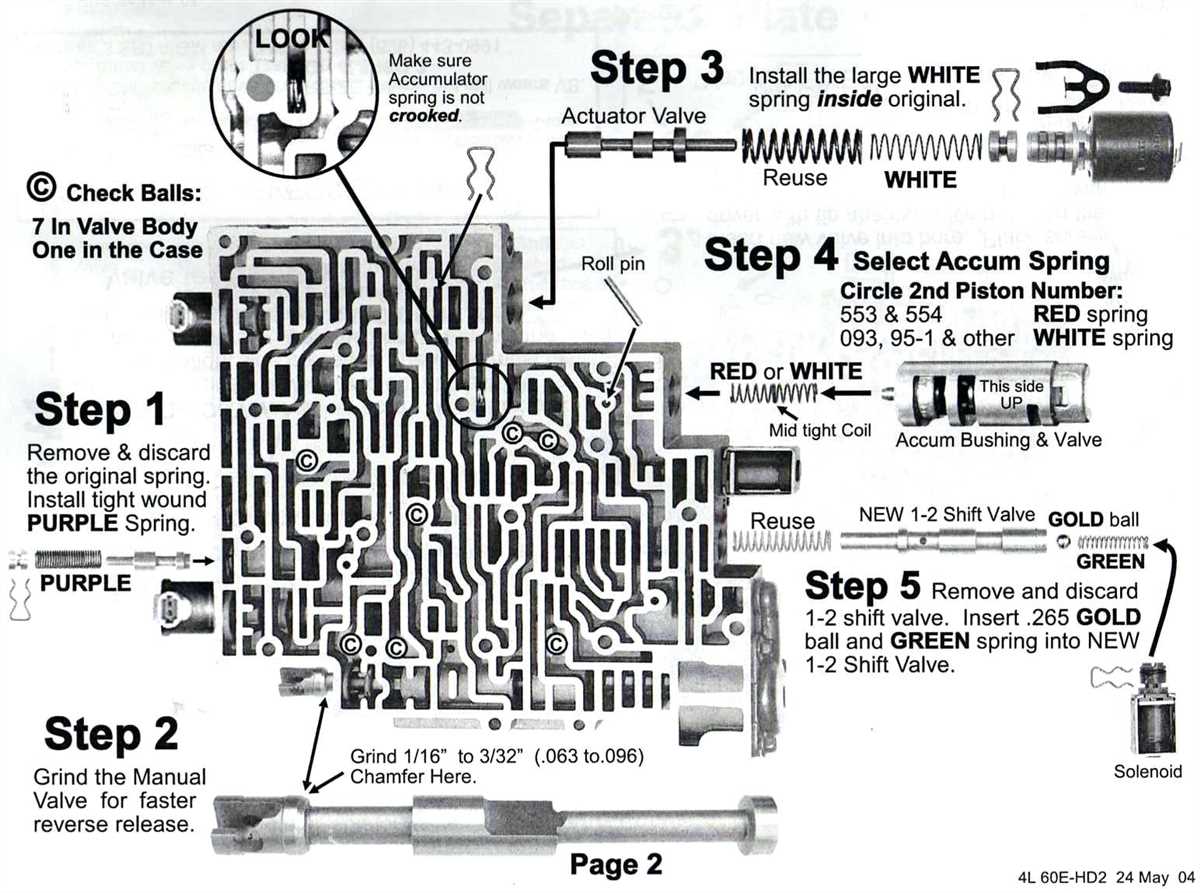
The GM 4l60e transmission diagram provides a visual representation of the internal components and design of this specific transmission model. It is a popular transmission used in many General Motors vehicles, including trucks, SUVs, and some cars. Understanding the layout and function of the various parts can be helpful for troubleshooting, repair, or transmission upgrades.
The diagram typically includes labels for key components, such as the torque converter, valve body, pump, clutches, bands, and sensors. It shows how these parts are interconnected and work together to facilitate the shifting of gears and transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. The diagram may also include arrows or lines indicating the flow of fluid throughout the transmission.
By studying the GM 4l60e transmission diagram, technicians and enthusiasts can gain a better understanding of how the transmission operates and identify any potential issues or areas of concern. It can also serve as a helpful reference when discussing transmission repairs or modifications with others in the automotive community.
Key Components in the GM 4l60e Transmission Diagram
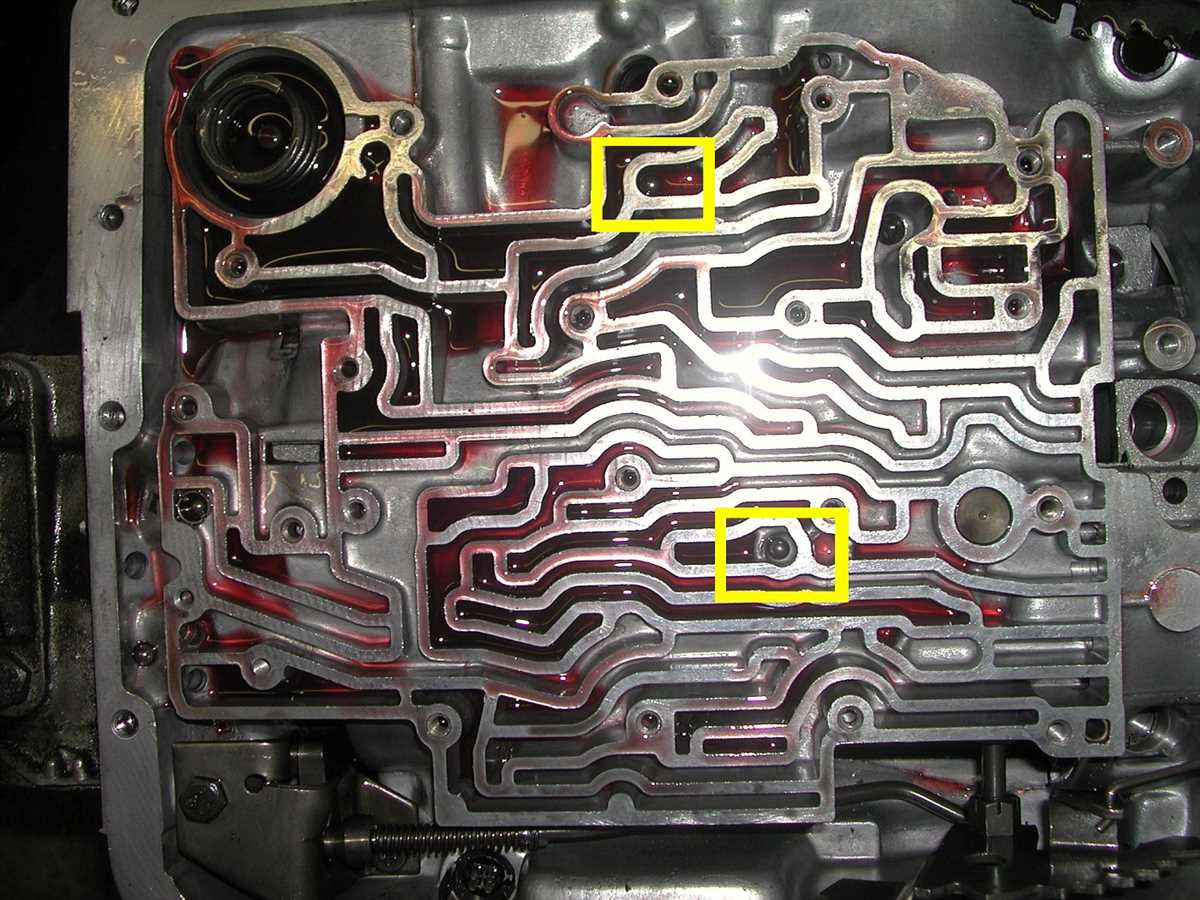
- Torque Converter: The torque converter is responsible for transmitting engine power to the transmission and allowing for smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine from the transmission.
- Valve Body: The valve body is a crucial component that controls the flow of fluid and directs it to the various circuits and clutches, enabling gear changes.
- Pump: The pump is responsible for pressurizing the transmission fluid and circulating it throughout the transmission.
- Clutches and Bands: These are the components that engage or disengage to facilitate the shifting of gears and transfer of power within the transmission.
- Sensors: Various sensors are located throughout the transmission to monitor its operation and provide input to the vehicle’s electronic control module (ECM).
When studying the GM 4l60e transmission diagram, it is important to refer to the specific model and year of the transmission to ensure accuracy. Diagrams may vary slightly depending on the specific vehicle application, but the overall design and function remain similar. Regular maintenance, proper fluid levels, and timely repairs can help keep the GM 4l60e transmission functioning properly and extend its lifespan.
Overview of the GM 4L60E Transmission
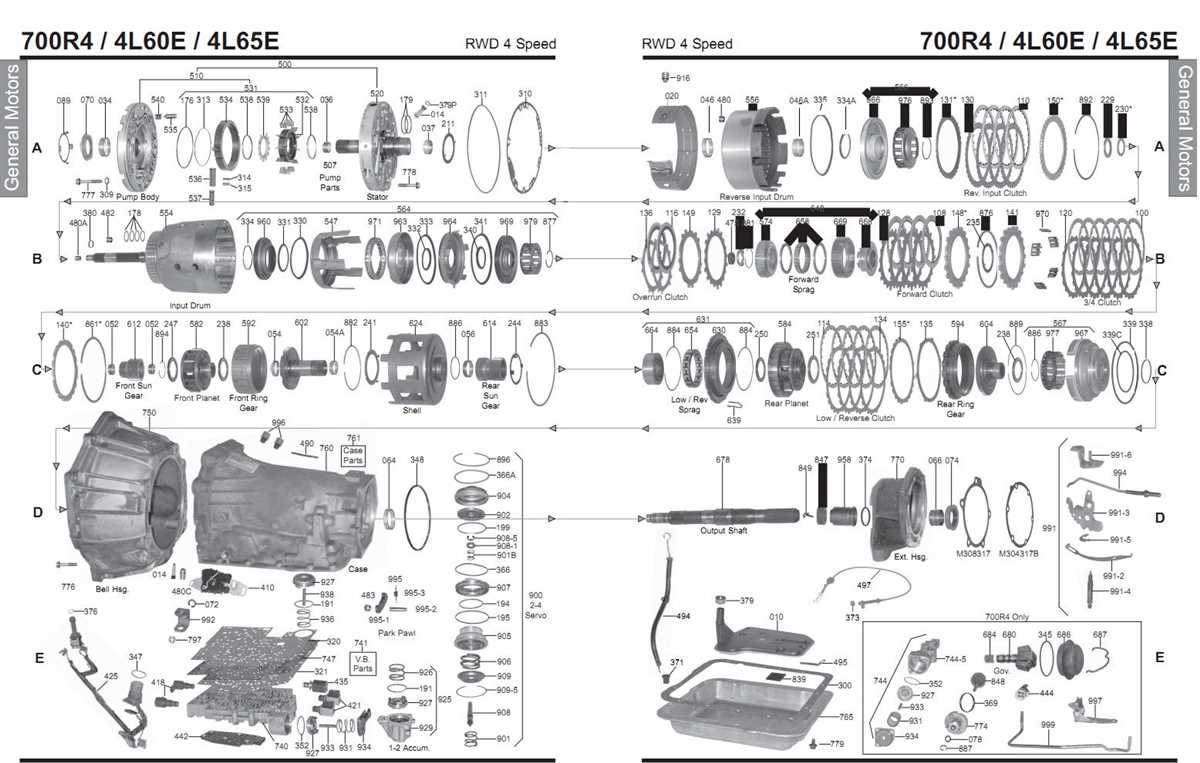
The GM 4L60E transmission is an automatic transmission that was produced by General Motors. It is commonly found in rear-wheel drive vehicles and has been used in a variety of GM vehicles, including trucks and SUVs. The 4L60E transmission is known for its reliability and smooth shifting, making it a popular choice for many drivers.
The 4L60E transmission is a four-speed transmission that has been in production since the early 1990s. It is an electronically controlled transmission, meaning that it uses a series of sensors and solenoids to monitor and control the shifting process. This allows for precise and accurate shifts, resulting in improved performance and fuel efficiency.
The internal components of the 4L60E transmission include a torque converter, a valve body, and a set of planetary gears. The torque converter is responsible for transferring the engine’s power to the transmission, while the valve body controls the flow of fluid and the shifting of gears. The planetary gears are responsible for changing the gear ratios, allowing the transmission to shift smoothly through different speeds.
Overall, the GM 4L60E transmission is a reliable and efficient transmission that has been used in a wide range of GM vehicles. Its electronic control system and smooth shifting make it a popular choice among drivers. Whether you are looking to repair or upgrade your 4L60E transmission, understanding its internal components and operation is essential.
Internal Components of the GM 4L60E Transmission
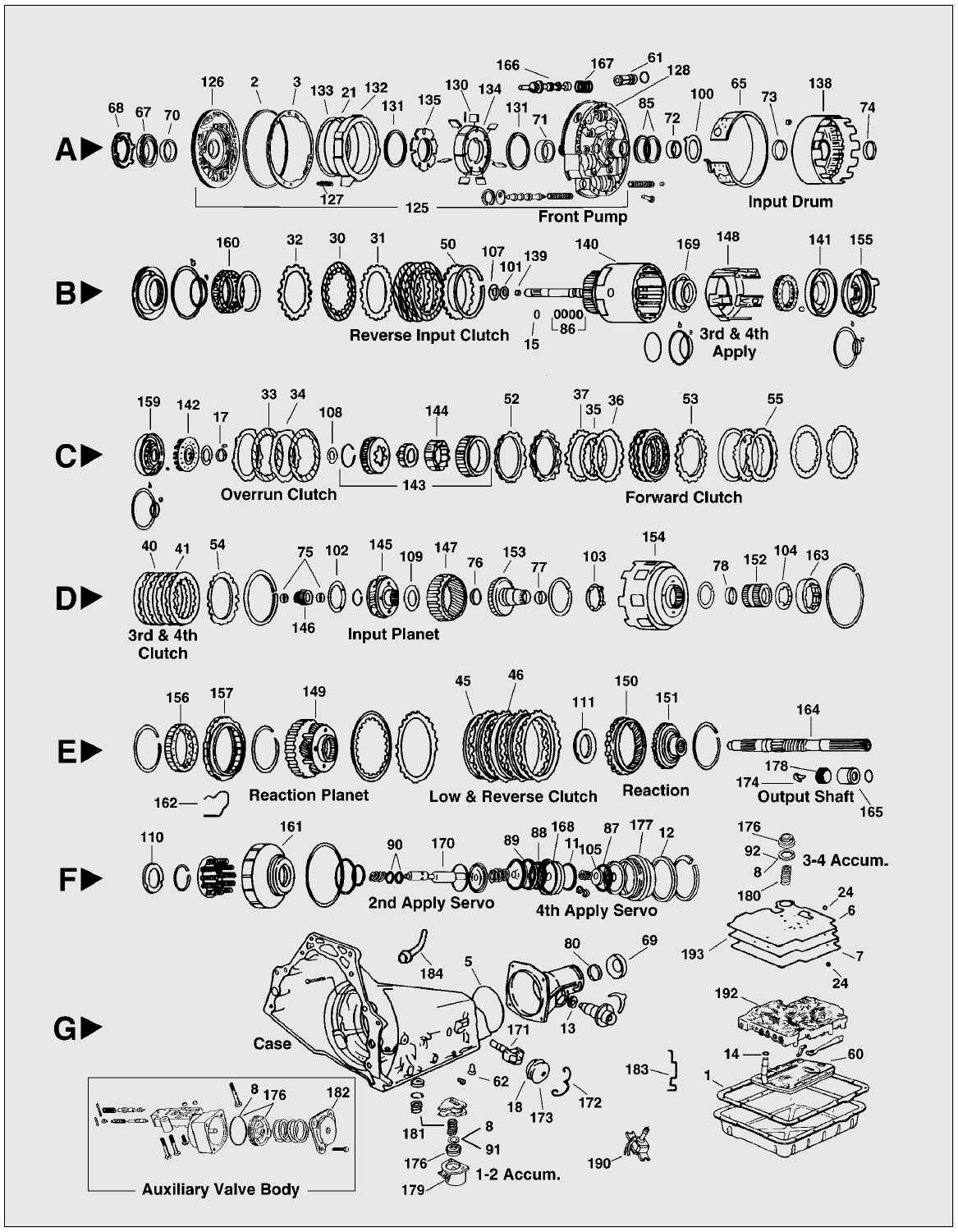
The GM 4L60E transmission, also known as the 4L60E or 4L60E transmission, is a four-speed automatic transmission that was manufactured by General Motors from the early 1990s until the mid-2000s. It is commonly used in many GM vehicles such as trucks, SUVs, and cars.
The 4L60E transmission consists of several internal components that work together to transmit power from the engine to the wheels. These components include the torque converter, pump, valve body, clutches, bands, planetary gears, and the transmission control module (TCM).
The torque converter is a fluid coupling that connects the engine to the transmission. It allows the engine to continue running even when the vehicle is stationary, and it provides smooth power delivery by converting the engine’s torque into hydraulic pressure.
The pump is responsible for circulating transmission fluid through the system, providing the necessary hydraulic pressure to engage and disengage the clutches and bands. It is driven by the engine through the torque converter and ensures that all the internal components receive the required amount of fluid for proper operation.
The valve body is the control center of the transmission and is responsible for directing the flow of transmission fluid to the appropriate clutches and gears. It contains various valves, solenoids, and check balls that control the shifting and engagement of the clutches and bands based on input from the TCM.
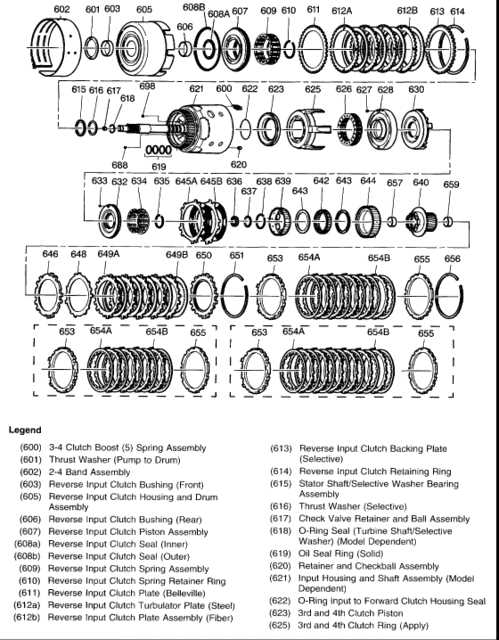
The clutches and bands are friction components that are engaged and disengaged to control the transfer of power within the transmission. They are located in the planetary gear sets and are responsible for switching gears and applying torque to the output shaft.
The planetary gear sets are a set of gears that allow the transmission to provide multiple gear ratios. By changing the connections between the different gears and bands, the transmission can effectively change gears and multiply torque as needed for optimal performance.
The TCM is the electronic control unit that monitors and controls the operation of the transmission. It receives input signals from various sensors such as the throttle position sensor and speed sensors, and it uses this information to determine when and how to shift gears and engage the clutches and bands.
In conclusion, the GM 4L60E transmission is a complex piece of machinery that utilizes a combination of hydraulic and electronic components to provide smooth and efficient power delivery. Understanding the internal components of this transmission can help in diagnosing and repairing any issues that may arise.
Valve Body and Control Solenoids
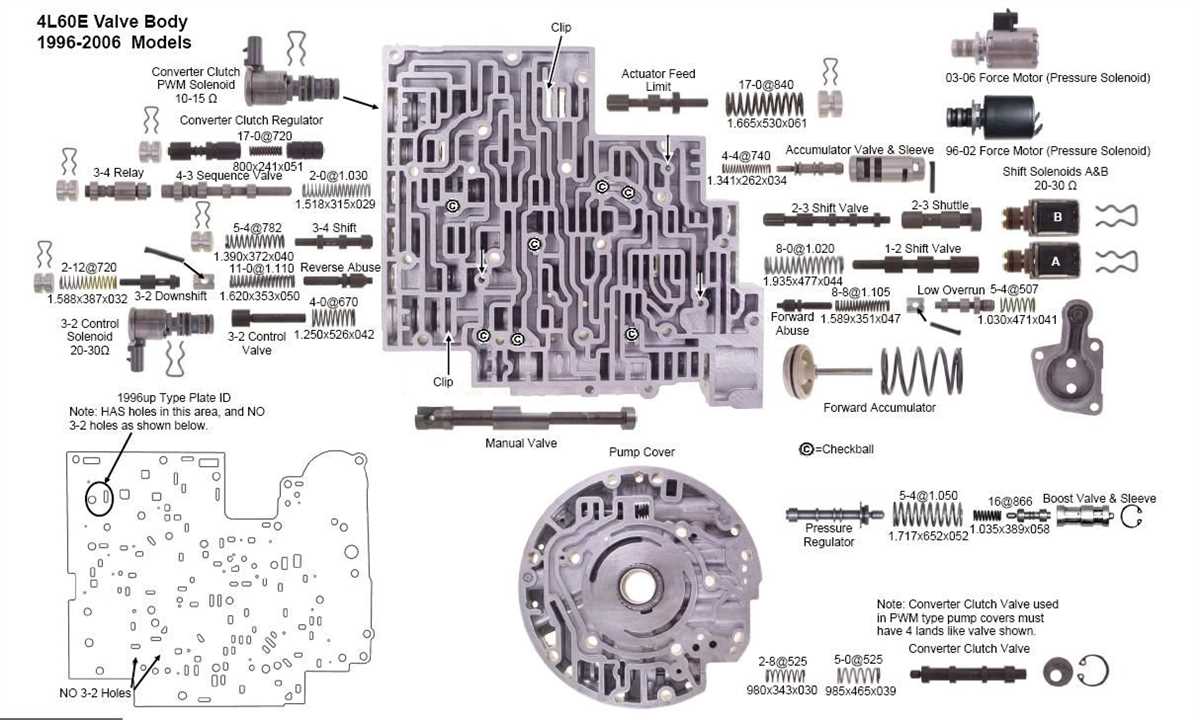
The valve body is an essential component of the GM 4L60E transmission, responsible for controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid to engage and disengage various gears. It is a complex assembly that houses multiple valves, passages, and solenoids. Understanding its structure and function is crucial for diagnosing and repairing transmission issues.
Within the valve body, there are various control solenoids that play a critical role in shifting gears smoothly and efficiently. These solenoids are electronically controlled and receive signals from the transmission control module (TCM) to open and close specific circuits. Each solenoid is responsible for controlling a specific hydraulic circuit, such as the 1-2, 2-3, or 3-4 shift.
The most common solenoids found in the GM 4L60E transmission are the shift solenoids A and B, the torque converter clutch solenoid, and the pressure control solenoid. Shift solenoid A controls the 1-2 and 3-4 shifts, while shift solenoid B controls the 2-3 shift. The torque converter clutch solenoid engages and disengages the torque converter lock-up clutch, improving fuel efficiency. The pressure control solenoid regulates line pressure to ensure proper transmission operation.
When any of these solenoids or the valve body itself malfunctions, it can lead to various transmission problems, such as harsh shifting, delayed engagement, or slipping gears. Diagnosing the issue requires careful inspection of the valve body and its solenoids, checking for physical damage, clogged passages, or electrical faults. In some cases, solenoids may need to be replaced, while in others, thorough cleaning and reassembly of the valve body can resolve the problem.
Torque Converter and Clutch Packs
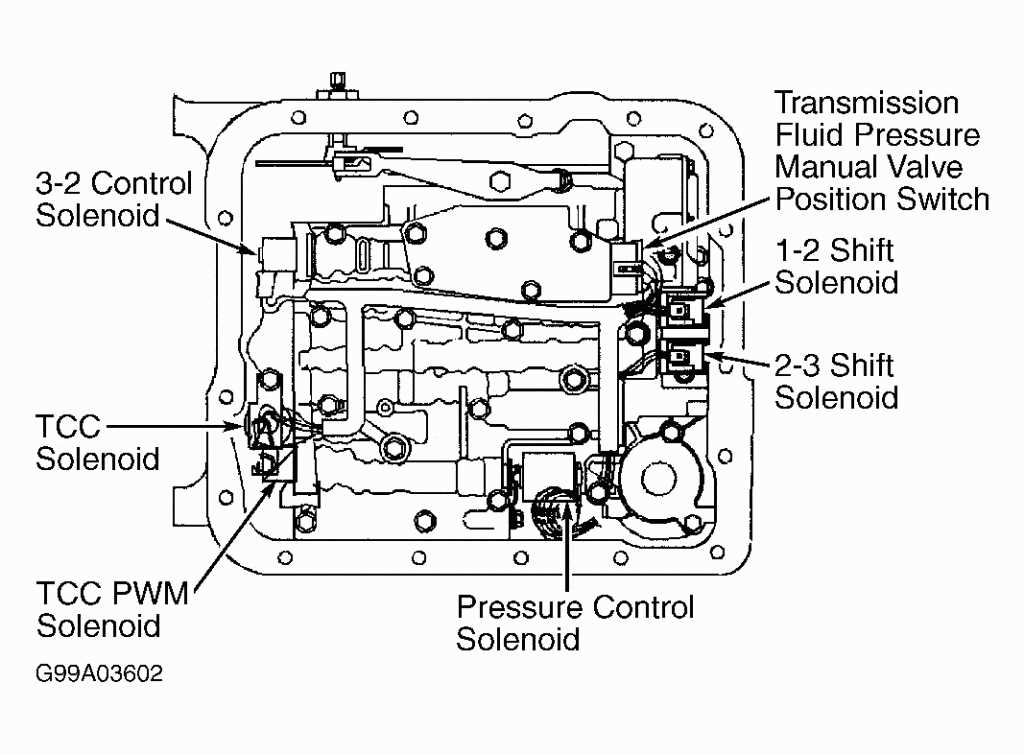
The torque converter and clutch packs are essential components of the GM 4L60E transmission, responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels. The torque converter is a fluid coupling device that connects the engine to the transmission. It uses hydraulic pressure to transfer power and allow for smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine from the drivetrain.
The torque converter consists of three main components: the impeller, turbine, and stator. The impeller is driven by the engine and creates fluid flow, which in turn drives the turbine. The stator redirects the fluid flow to increase torque output. This design allows for torque multiplication and helps the transmission to start the vehicle from a standstill or at low speeds. As the vehicle speeds up, the torque converter locks up, providing a direct mechanical connection between the engine and the transmission.
The clutch packs, on the other hand, are responsible for engaging and disengaging different gear ratios within the transmission. There are several clutch packs in the 4L60E transmission, including the forward clutch pack, reverse clutch pack, and the 3-4 clutch pack. Each clutch pack contains a series of friction plates and steel plates. When hydraulic pressure is applied, the friction plates clamp down on the steel plates, creating a mechanical connection and transmitting power.
The clutch packs are controlled by the transmission control module (TCM), which receives input from various sensors and determines the optimal gear ratio based on vehicle speed, throttle position, and other factors. The TCM modulates the hydraulic pressure to engage or disengage the appropriate clutch packs, allowing for smooth shifting and efficient power transfer.
In summary, the torque converter and clutch packs are integral components of the GM 4L60E transmission. The torque converter ensures smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine from the drivetrain, while the clutch packs allow for the selection of different gear ratios. Together, they provide reliable power transfer and efficient operation of the transmission.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the GM 4L60E Transmission
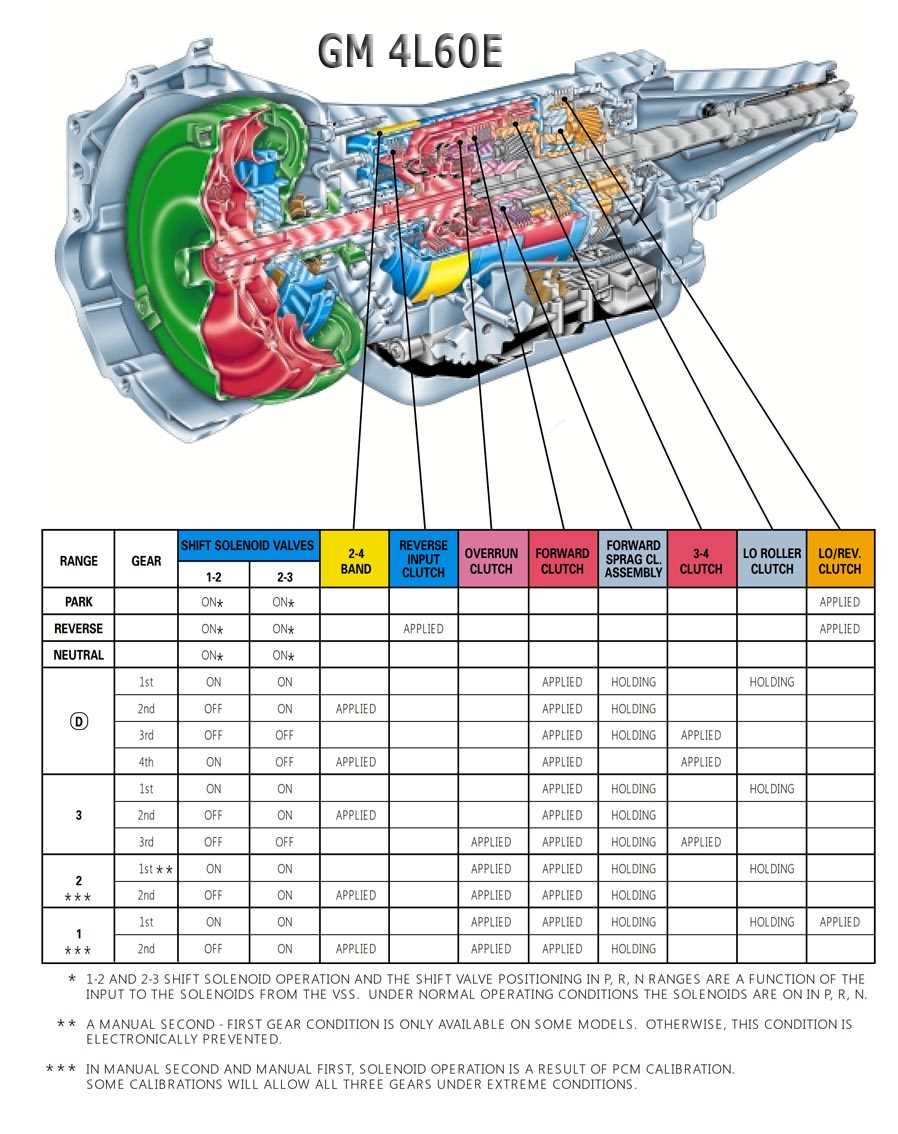
The GM 4L60E transmission is a popular automatic transmission used in many GM vehicles. While it is known for its durability and reliability, there are some common issues that can occur with this transmission. In this article, we will explore these issues and provide troubleshooting tips to help diagnose and fix them.
1. Slipping Gears
One common issue with the 4L60E transmission is slipping gears. This can occur when the transmission fails to engage properly, causing a loss of power and acceleration. Slipping gears can be caused by a variety of factors, including low transmission fluid level, worn out clutches or bands, or a faulty torque converter. Checking the transmission fluid level and condition, as well as inspecting the clutches and bands, can help identify the source of the problem.
2. Erratic Shifting
Erratic shifting is another common issue with the 4L60E transmission. This can manifest as sudden, harsh shifts or delayed shifts between gears. Erratic shifting can be caused by a faulty shift solenoid, a malfunctioning valve body, or a worn out transmission filter. Inspecting and cleaning the shift solenoids, replacing the transmission filter, or rebuilding the valve body can help resolve this issue.
3. Transmission Overheating
Transmission overheating is a serious problem that can lead to further damage if not addressed. Overheating can be caused by a lack of transmission fluid, a faulty transmission cooler, or excessive load on the transmission. To troubleshoot this issue, it is important to check the transmission fluid level and condition, ensure that the transmission cooler is functioning properly, and reduce any excessive load on the transmission, such as towing heavy loads.
4. Torque Converter Lockup Issues
Torque converter lockup issues can cause the transmission to stall or hesitate when shifting gears. This can be caused by a faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, a worn out torque converter, or a malfunctioning pressure regulator valve. Inspecting and replacing the torque converter clutch solenoid, rebuilding or replacing the torque converter, or repairing the pressure regulator valve can help resolve this issue.
In conclusion, while the 4L60E transmission is a reliable and durable transmission, it can experience common issues such as slipping gears, erratic shifting, transmission overheating, and torque converter lockup problems. By troubleshooting these issues and addressing them promptly, you can ensure the longevity and proper performance of your GM vehicle equipped with the 4L60E transmission.
Maintenance Tips for the GM 4L60E Transmission
The GM 4L60E transmission is a complex piece of machinery that is crucial for the proper functioning of your vehicle. To ensure its longevity and optimal performance, here are some important maintenance tips to keep in mind:
- Regular Fluid Checks: One of the most important aspects of maintaining the 4L60E transmission is to regularly check the fluid level and condition. Low fluid levels or dirty fluid can cause damage to the internal components, so it is essential to keep the fluid at the proper level and replace it as needed.
- Fluid and Filter Changes: Along with fluid checks, it is recommended to change the transmission fluid and filter at regular intervals. This helps to keep the transmission clean and prevent any debris or contaminants from causing damage.
- Proper Cooling: Overheating can significantly damage the 4L60E transmission, so it is important to ensure that the transmission is properly cooled. Regularly check the transmission cooler and radiator to ensure they are functioning efficiently, and consider using additional cooling solutions if necessary.
- Smooth Shifting: Avoid sudden and aggressive shifts, as this can put unnecessary strain on the transmission components. Instead, practice smooth and gradual shifting to minimize wear and tear.
- Avoid Towing Over Maximum Capacity: Exceeding the maximum towing capacity of your vehicle can cause the transmission to overwork, leading to potential damage. Always stay within the recommended towing limits to prevent any transmission-related issues.
- Address Any Issues Promptly: If you notice any signs of transmission problems such as slipping, harsh shifting, or unusual noises, it is crucial to address them promptly. Ignoring these issues can lead to further damage and costly repairs.
By following these maintenance tips, you can increase the lifespan of your GM 4L60E transmission and ensure its smooth and reliable performance. Remember to consult your vehicle’s manual for specific maintenance guidelines and always seek professional assistance if you are unsure about any maintenance procedures.