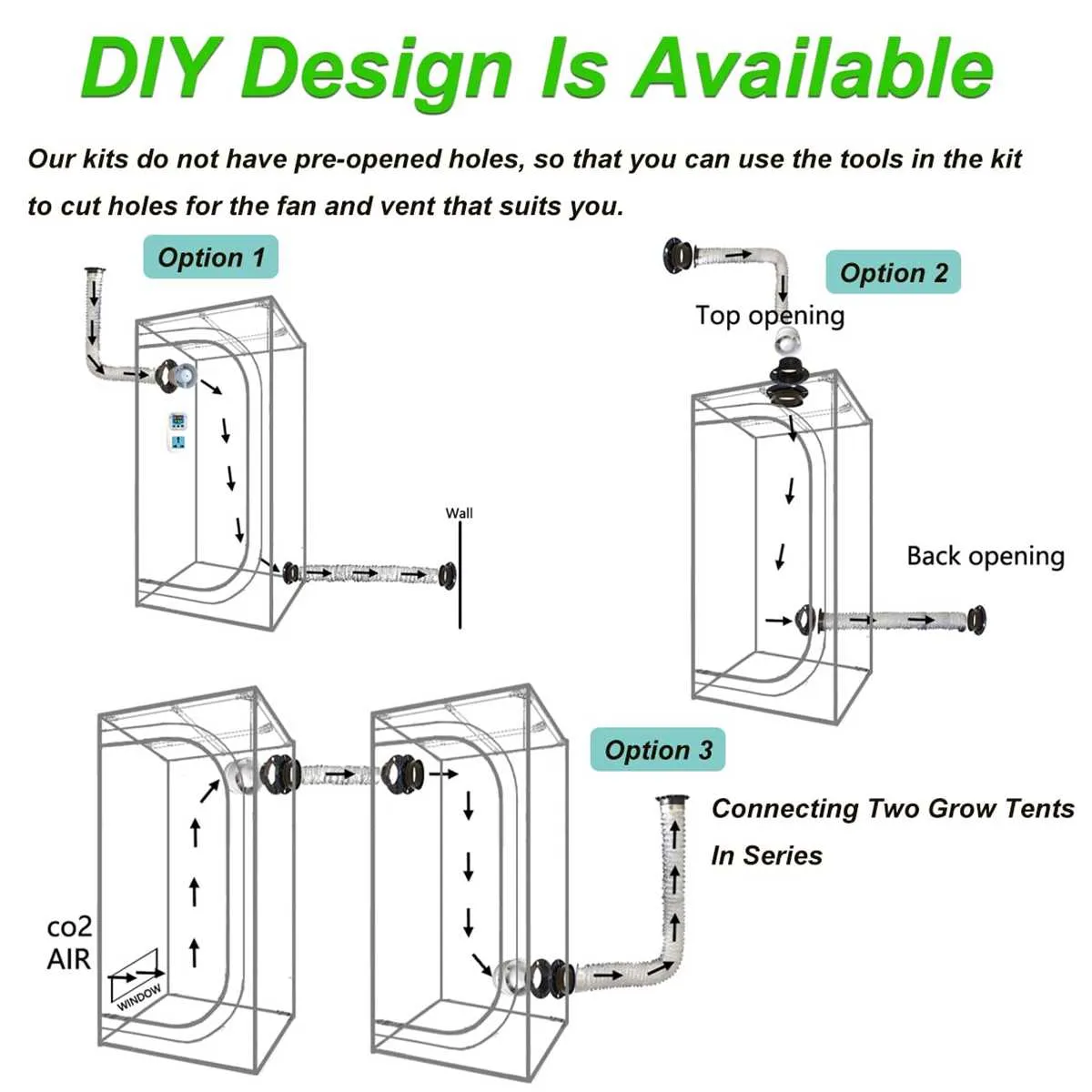
To ensure optimal growth conditions for your indoor plants, the placement of air circulation elements is crucial. Start by positioning an exhaust fan at the highest point of the space, ensuring hot air is removed efficiently. This helps maintain a balanced atmosphere by preventing heat buildup and providing fresh airflow. The intake fan should be placed at the opposite end, ideally near the bottom, to allow cooler, fresh air to enter the environment.
Proper placement of these components is key to maintaining consistent air exchange. The exhaust system should have a direct path to the outside, avoiding unnecessary bends or restrictions that can reduce airflow efficiency. The intake should allow a constant flow of fresh air, without creating turbulence or drafts that could disturb plant growth.
Consider using ducting with the appropriate diameter to match the power of your fans. This ensures air moves freely without excessive resistance, which can slow down the exchange process. Also, it’s important to have a passive intake or additional vents to compensate for the exhaust fan’s airflow, balancing the pressure within the space.
Remember that proper airflow isn’t just about removing heat; it also helps regulate humidity levels. Without adequate air movement, moisture can accumulate, leading to potential mold or mildew issues. Regularly check the humidity levels and adjust the air circulation if needed to keep conditions in the ideal range.
Optimal Airflow Configuration for Indoor Gardens
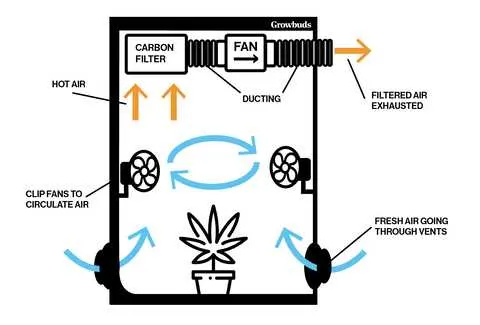
To achieve balanced airflow in a controlled growing environment, place the intake fan at the lower section of the enclosure, ensuring fresh air is directed towards the plant roots. Position the exhaust system at the top, allowing hot air to escape naturally, as warm air rises. Use a high-quality carbon filter connected to the exhaust fan to prevent odor leakage.
Ensure the intake and exhaust are properly balanced, preventing excessive pressure fluctuations inside the space. The intake fan should be slightly larger than the exhaust to facilitate optimal airflow without strain. This ensures a consistent supply of fresh air, enhancing plant growth.
For effective air circulation, consider using oscillating fans within the structure to ensure uniform distribution of air, preventing hotspots and maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels. Additionally, incorporate a passive vent system to allow for unrestricted air movement when the fan system is off or in lower-power mode.
The placement of the fans should also take into account the proximity to the plants to avoid direct drafts that could damage delicate foliage. Mounting the intake fan slightly above the ground ensures dust and debris are avoided, while placing the exhaust fan higher up allows for effective removal of heat and humidity.
Use ducting that is appropriately sized for both intake and exhaust systems. The longer the ducting, the more resistance the airflow encounters, potentially reducing efficiency. Keep the ducting runs as short and direct as possible to maximize airflow capacity.
Choosing the Right Fan Size for Your Indoor Space
To ensure optimal airflow in your cultivation area, select a fan based on the volume of air you need to circulate. The required airflow is measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). To determine the correct CFM for your space, follow this simple formula:
- Measure the length, width, and height of the room in feet.
- Multiply the length, width, and height to find the total cubic footage of the area.
- Multiply the total cubic footage by 3 to account for proper air exchange (3 air exchanges per minute is standard for most setups).
For example, if your room is 10 feet long, 10 feet wide, and 8 feet high, the calculation would be:
10 x 10 x 8 = 800 cubic feet.
800 x 3 = 2400 CFM needed for efficient air circulation.
Keep in mind the following factors when selecting the right fan:
- Room Size: Larger spaces require more powerful fans to achieve the same airflow.
- Fan Efficiency: Not all fans are equally efficient. Check the specifications for airflow ratings at specific static pressures.
- Obstructions: If ducts or filters are used, they add resistance, which may reduce airflow. Choose a fan with a higher CFM rating to compensate for this loss.
- Fan Type: Inline fans are generally more effective in larger rooms, while smaller, quieter fans may work for compact spaces.
For high humidity environments or areas with intense heat, consider increasing the airflow capacity by 20-30% to ensure adequate air exchange.
Optimal Airflow Direction and Placement of Ducting
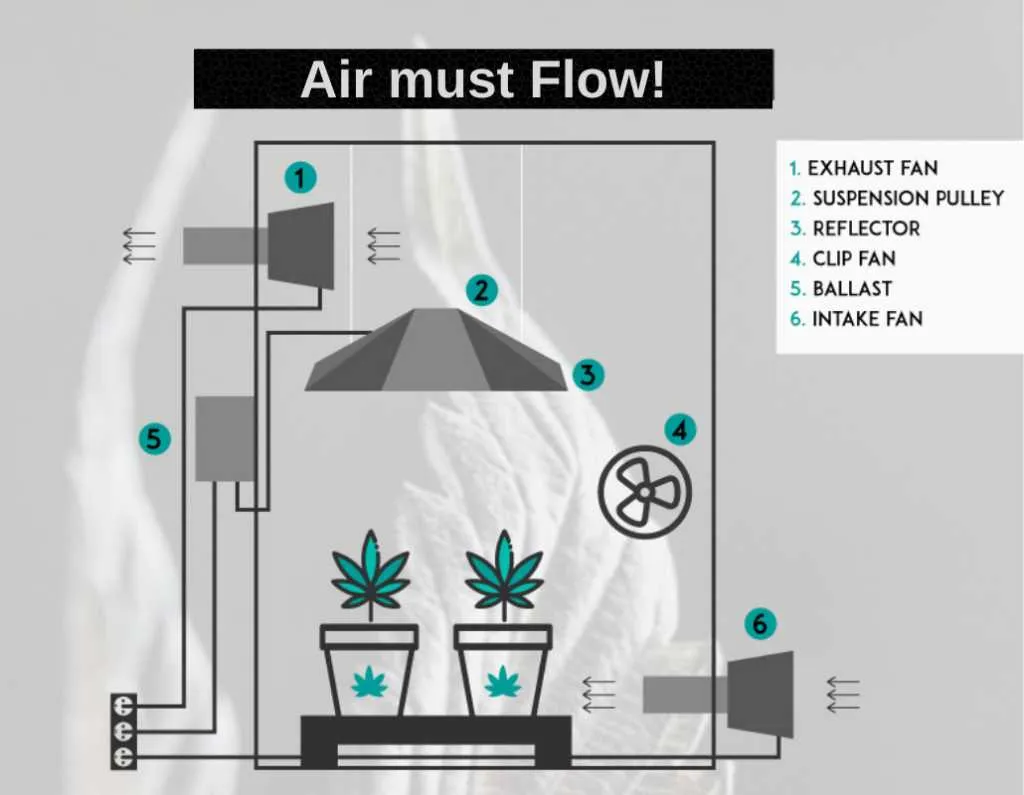
Ensure air intake is positioned at the lower part of the space, close to the plants. This promotes the flow of fresh air directly to the root zone, helping to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels. Exhaust ducts should be placed higher up to remove warm, stale air. This positioning utilizes the natural tendency of hot air to rise, optimizing the system’s efficiency.
Position the intake duct away from direct light sources to prevent the air from absorbing heat before reaching the plants. Use a carbon filter attached to the exhaust duct for odor control, ensuring it’s placed at the highest point of the system for maximum efficiency.
The ducting should be as short as possible with minimal bends to reduce resistance and airflow loss. When possible, use insulated ducts to prevent temperature fluctuations that can affect the air quality within the growing environment.
Managing Temperature and Humidity with Airflow Systems
To maintain optimal conditions for plant growth, it’s essential to balance temperature and humidity. First, use an exhaust fan with adjustable speed settings to regulate airflow. This allows you to control heat buildup, especially when lights are on. A fan should be positioned near the ceiling to expel warm air, while an intake system at ground level brings in fresh, cooler air. Ensure that the air intake has a filter to prevent contaminants from entering.
Humidity is controlled through the airflow’s interaction with the environment. When humidity levels rise, the airflow must be increased to prevent excessive moisture buildup. Conversely, reducing airflow during dry periods can help maintain higher humidity levels. Use a hygrometer to measure and adjust the relative humidity (RH) to keep it within the ideal range of 40-60% for most plants.
Temperature regulation is best achieved with the combination of exhaust fans and passive intakes. During the day, when temperatures are higher, increase the exhaust fan speed to remove the excess heat. At night, when temperatures drop, slow down the airflow to prevent heat loss. For larger areas, an automated system with temperature and humidity sensors can further optimize control, adjusting the fans based on real-time data.
In addition to fans, consider using a humidifier or dehumidifier for precise control. A dehumidifier is effective in high-humidity situations, such as after watering or during rainy weather, while a humidifier helps in dry climates or when heating systems increase air dryness. Keep these devices placed away from direct airflow paths to ensure even distribution.