It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction .
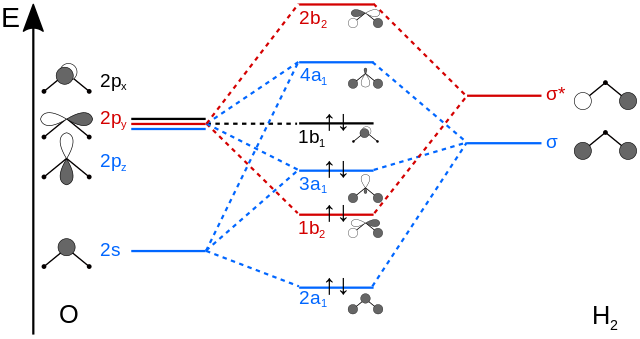
As can be seen from the energy diagram – four of the molecular orbitals. General procedure for simple molecules that contain a central atom: build group orbitals using the outer atoms, then interact the group orbitals.

function is shaded. Figure 4 Symmetry elements for. H2O.
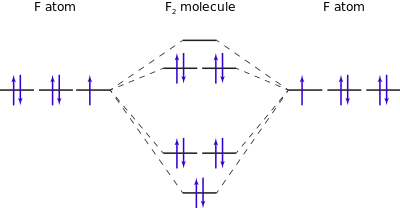
↓ ψ1s. ↓.
R1sY1s. ↓ Form the molecular orbitals for the basic or first stage MO diagram.
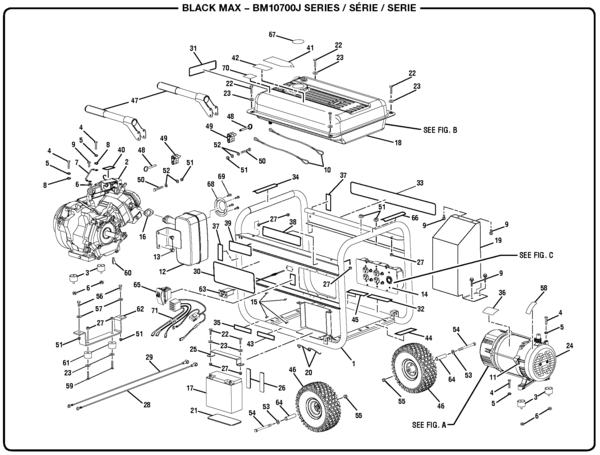
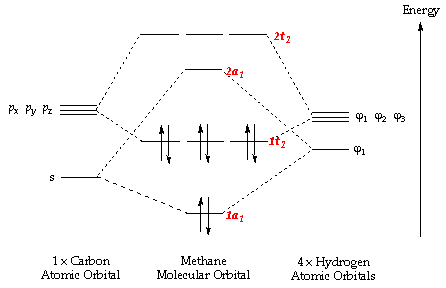
• first work. General procedure for simple molecules that contain a central atom: build group orbitals using the outer atoms, then interact the group orbitals.
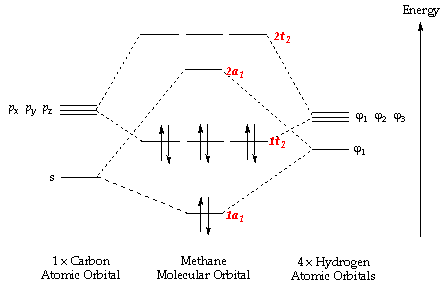
Molecular Orbitals for Water (H2O). H2O molecular orbitals.
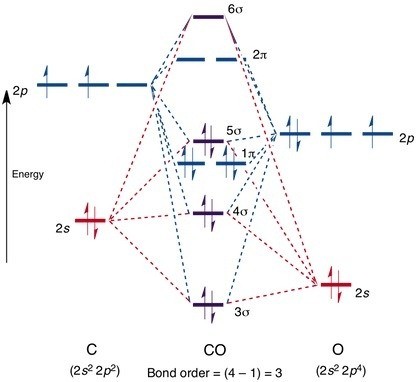
The five occupied and the lowest three unoccupied molecular orbitals of the.Jul 31, · Oxygen is sp3 hybridised in H2O molecule. Two hybrid orbitals are occupied by lone pairs and two are used in bonding with Hydrogen atoms.
Since lone pairs does not contribute to the geometry of a molecule, therefore H2O has an angular geometry. Molecular Orbitals for Water (H 2 O) The five occupied and the lowest three unoccupied molecular orbitals of the isolated molecule (1 a 1) 2 (2 a 1) 2 (1 b 2) 2 (3 a 1) 2 (1 b 1) 2 were calculated using the Restricted Hartree-Fock wave function (RHF) using the G** basis set.
b (experimental data is given in [ ]). orbitals are largely responsible for the donation of hydrogen bonding with the 3a 1 orbital shown experimentally to contribute the most [].
Also, the 4a 1 and 2b 2 antibonding orbitals are reported to be partially occupied in hydrogen bond formation, receiving . Orbitals of same symmetry and similar energy levels can then be mixed to form a new set of molecular orbitals with bonding, nonbonding, and antibonding characteristics. In the simple MO diagram of H 2 O, the 2s orbital of oxygen is mixed with the premixed hydrogen orbitals, forming a new bonding (2a1) and antibonding orbital (4a1).
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Chemical bonding of H2O – WikipediaChemical bonding of H2O – Wikipedia