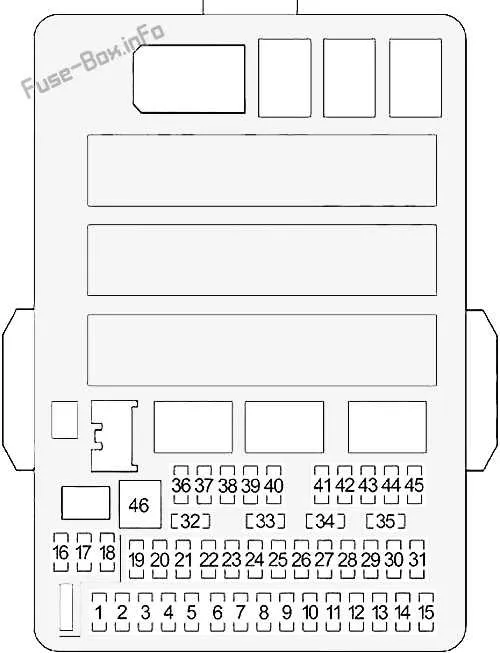
If you’re troubleshooting electrical issues in your 2000 sedan model, understanding the wiring setup is crucial. Start by locating the main panel, where critical components such as the ignition system, lighting, and climate control are connected. This area is essential for diagnosing problems like blown connections or non-functional accessories.
The layout includes multiple sections with different amperage ratings, designed to protect circuits from overload. Pay particular attention to the primary relay, which handles the most sensitive systems in the car. Each section should be checked against a detailed reference to ensure that the correct fuses are intact and that no connections are compromised.
It’s recommended to first inspect the main terminal block, as it often contains issues with power supply. In case of any malfunction, ensure the connections are clean and free from corrosion. A visual check of each individual terminal will reveal if any wires are loose or if the connection has been worn out due to age.
Finally, ensure that all circuit paths are clearly identified. If you experience electrical failures, cross-reference the details in the detailed schematic for proper routing and component placement. Understanding the electrical map will save you time and effort in pinpointing the exact source of malfunction.
Electrical System Overview and Component Layout
For optimal vehicle functionality, refer to the layout for the main power distribution and relay components. This layout is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues, as it clearly maps out the location of various critical circuits and connections.
Ensure proper identification of the locations for fuses and relays that protect systems such as ignition, lighting, and HVAC. A specific guide is available that shows the connections for each individual component, which helps in isolating faults like blown fuses or malfunctioning relays.
Pay attention to the different sections in the system, including the interior and engine bay panels. These sections may have different fuse ratings based on the power demands of the respective components. Always use the recommended fuse size to avoid damage to the wiring or connectors.
If the system malfunctions, start by inspecting the critical relays associated with major vehicle functions. A quick visual inspection of the connection points can often reveal corrosion or looseness that could impair electrical continuity.
For troubleshooting, use a multimeter to check for continuity between the relevant terminals, ensuring that each system is receiving proper current. For components that require frequent fuse replacement, consider evaluating the related circuits to check for underlying electrical faults.
By regularly reviewing and maintaining this layout, you can prevent issues that arise from electrical failures and ensure all components remain in good working condition.
Locating the Electrical Panel in the Vehicle
To access the electrical control panel in the vehicle, follow these steps:
- Check beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. The panel is positioned near the footwell area, close to the side of the dashboard.
- Look for a small cover, usually made of plastic, which can be easily removed by pulling it off or releasing clips.
- In some cases, you may need to adjust the seat to get a better view or access to the lower part of the dashboard.
Additionally, there’s another panel located in the engine compartment:
- Open the hood and locate the panel near the battery or along the side of the engine bay, typically secured with clips or bolts.
- Check the area near the windshield for a secondary cover that may require a simple twist or pull to open.
Once you locate the access panels, you can proceed with replacing or inspecting the components inside.
Understanding the Layout for Different Models
Identify the exact placement of components within the electrical distribution system by referring to model-specific schematics. Each version of the vehicle may have a distinct configuration for relays, breakers, and circuits. For accurate troubleshooting or maintenance, always cross-check the specific year and model before proceeding with repairs.
Look for clear markings on the cover that indicate the exact function of each section. Some models may have additional compartments, while others might consolidate everything in one area. Understanding the power allocation for various systems–like lighting, ignition, or entertainment–helps in diagnosing issues faster and more efficiently.
If a particular component is malfunctioning, test individual circuits by using a multimeter. Understanding the layout ensures that you can pinpoint issues without having to inspect each component separately. Always verify the amperage ratings and ensure that replacement parts match the original specifications to prevent system failures.
Common Electrical Issues and How to Fix Them
If your car experiences power loss or non-functioning accessories, it’s likely due to blown or faulty electrical connections. The first step is to locate the problem by checking the relevant relays or circuits linked to the malfunctioning component. Most vehicles have several circuits that control interior and exterior elements such as lights, windows, or air conditioning.
Start by identifying any components that stop working, and then trace the wires that power them. Most common failures are due to poor connections, corrosion, or overload. Inspect for any obvious signs of wear, such as burnt or broken connectors. Replacing or cleaning these will often restore normal function. If the issue persists, consider testing with a multimeter to ensure proper voltage flow.
In case of repeated electrical failures, you may need to replace the entire connector or rewire the affected sections. Ensure that all terminals are properly tightened and protected from moisture. If you notice consistent power failures even after replacing parts, it could indicate an underlying short or grounding issue. A deeper inspection may be required, and in some cases, professional help might be necessary.
Another common issue is when components suddenly stop responding but work intermittently. This often signals a loose or faulty connection. You can address this by removing the faulty part, cleaning the area thoroughly, and reattaching it securely. If the component continues to malfunction, replacing the entire unit is the safest approach.
Lastly, always check for signs of overloads. Overloaded circuits may cause permanent damage to connected components. If you’re experiencing multiple malfunctions simultaneously, a system-wide inspection should be performed to ensure there are no issues in the primary electrical routing of the vehicle.