
To ensure proper functionality and prevent premature wear on your engine’s accessories, it’s essential to follow the correct routing of the drive components. The path for each component plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s performance, from power steering to the alternator. A clear understanding of how to properly position each part is necessary for efficient operation.
Consulting the right guide is crucial for accurate alignment of the drive components. The configuration shown in the appropriate schematic provides clear, step-by-step instructions on how to position each element around the engine. This precise layout ensures that the system operates smoothly, preventing slippage or misalignment.
Be sure to verify the components’ tension and positioning before completing the installation. Proper tension is vital to maintain optimal power transfer between parts. Regular checks and replacements should be done to avoid any damage that could result from misalignment or failure of any of the connected elements.
Engine Accessory Drive Routing
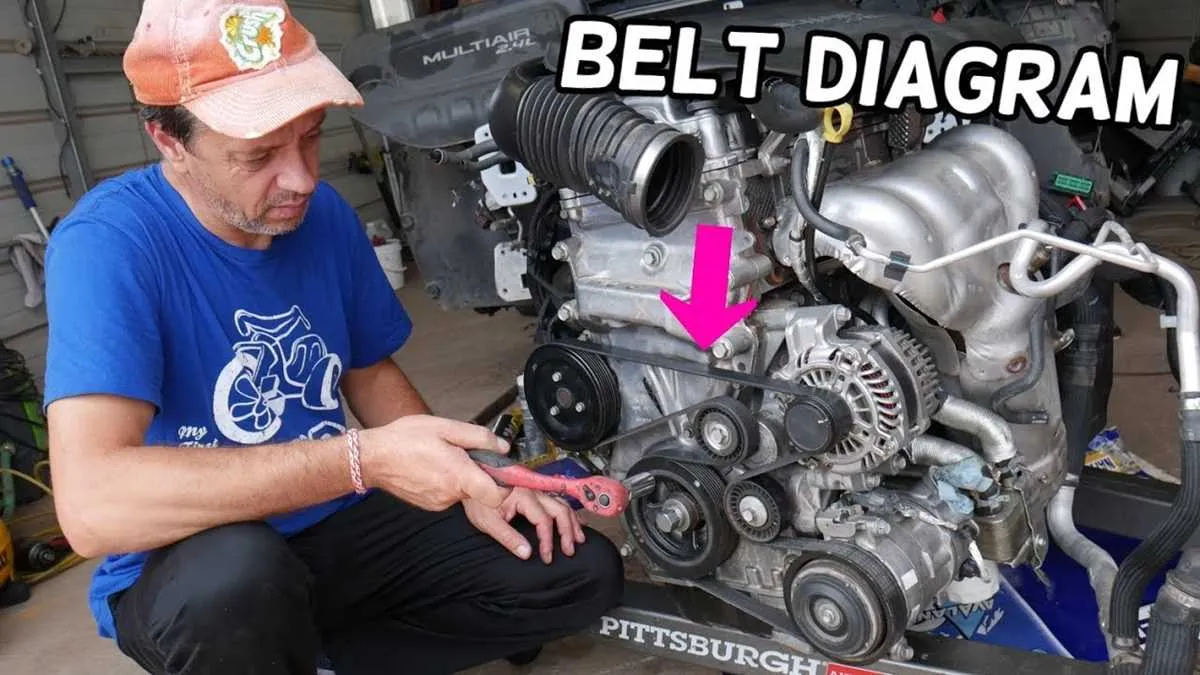

For proper installation, ensure the drive components are aligned according to the following sequence: the alternator should be driven by the main pulley, with the tensioner positioned to maintain correct belt tension. The power steering pump should be routed next, followed by the air conditioning compressor. Lastly, ensure the water pump is engaged in the circuit, following the correct routing path.
Start by placing the drive loop over the largest pulley, ensuring that the belt runs through each of the components in the designated order. Pay special attention to the tensioner; it must be engaged lightly under spring pressure to maintain consistent tension. Incorrect routing or tension may lead to premature wear or component malfunction, so verify all paths are clear and the drive is snug without excessive slack.
Understanding the Drive System Layout
Ensure the proper alignment of the accessory components by following the correct routing sequence. The system operates through a continuous loop that powers essential parts such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. A misalignment or incorrect routing can lead to malfunction or even component damage.
Check the tension of the components regularly, as improper tension can cause premature wear or slip. Utilize a tensioner pulley to maintain consistent pressure throughout the system. It’s essential to inspect for any cracks or wear on the components after every major maintenance session to avoid unexpected failures.
Be mindful of the recommended routing path for the system, which ensures efficient operation of the engine’s auxiliary functions. This system usually requires a specific sequence for the optimal performance of all attached components. Following the routing instructions exactly is crucial to avoid operational issues and keep all systems running smoothly.
When replacing or adjusting parts, always verify the routing path against the vehicle’s technical manual to ensure the loop is configured correctly. Incorrect routing not only hampers functionality but can also lead to excess strain on components, leading to costly repairs.
Identifying Components in the Belt System
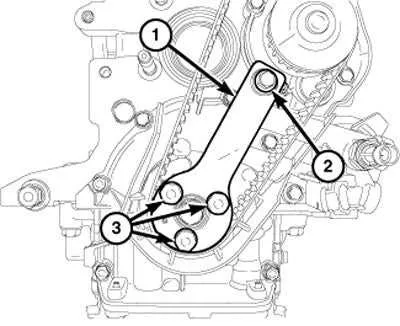
To effectively identify components in the engine’s drive system, focus on the following key parts: the tensioner, alternator, power steering pump, idler pulleys, and air conditioning compressor. Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring the proper functioning of the system.
The tensioner, typically located near the top of the system, helps maintain the correct tension on the loop, preventing slippage. The alternator is often situated towards the front of the engine and is responsible for generating electrical power. Nearby, the power steering pump ensures the vehicle’s steering remains smooth and responsive. Idler pulleys, which guide the loop around various components, are placed at strategic points, while the air conditioning compressor controls the flow of refrigerant in the cooling system, often located towards the engine’s front side.
Make sure to check for signs of wear such as cracking, fraying, or uneven wear across the pulleys, which may indicate the need for replacement or adjustment. Properly identifying these components will streamline maintenance and ensure the system operates at its optimal capacity.
Steps to Replace the Drive Belt
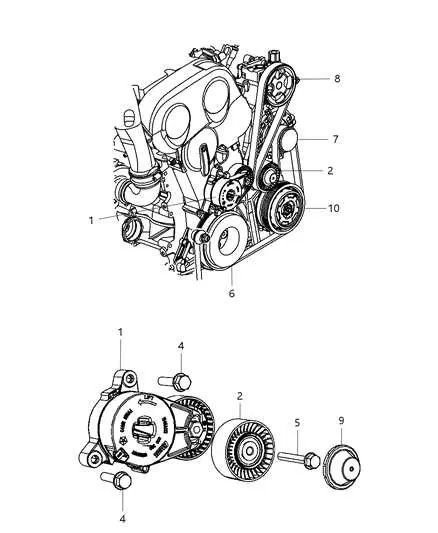
Follow these steps to replace the drive belt on your vehicle:
- Locate the Belt Tensioner: Find the tensioner pulley that holds the belt in place. It’s usually near the front of the engine and is spring-loaded. You may need to use a wrench or ratchet to move the tensioner.
- Release Tension: Use a ratchet or breaker bar to rotate the tensioner pulley, which will loosen the tension on the belt. This will allow you to remove the old belt.
- Remove the Old Belt: Once the tension is released, carefully slide the belt off the pulleys. Pay attention to the routing of the belt, as you’ll need to replicate it when installing the new one.
- Inspect Components: Before installing the new belt, check all pulleys, the tensioner, and the idler pulley for wear. Replace any faulty parts to prevent future damage.
- Install the New Belt: Route the new belt around the pulleys, following the correct path. Ensure it sits properly in the grooves of each pulley, making sure it’s aligned correctly with the tensioner.
- Apply Tension: Move the tensioner again to allow the belt to slip into place. Release the tensioner slowly to apply the necessary tension on the new belt.
- Double-Check Alignment: Spin the pulleys by hand to ensure the belt is correctly installed and rotates freely without slipping or coming off.
- Test Drive: Start the engine and observe the belt in operation. Listen for any unusual noises and check that the belt is running smoothly on all pulleys.