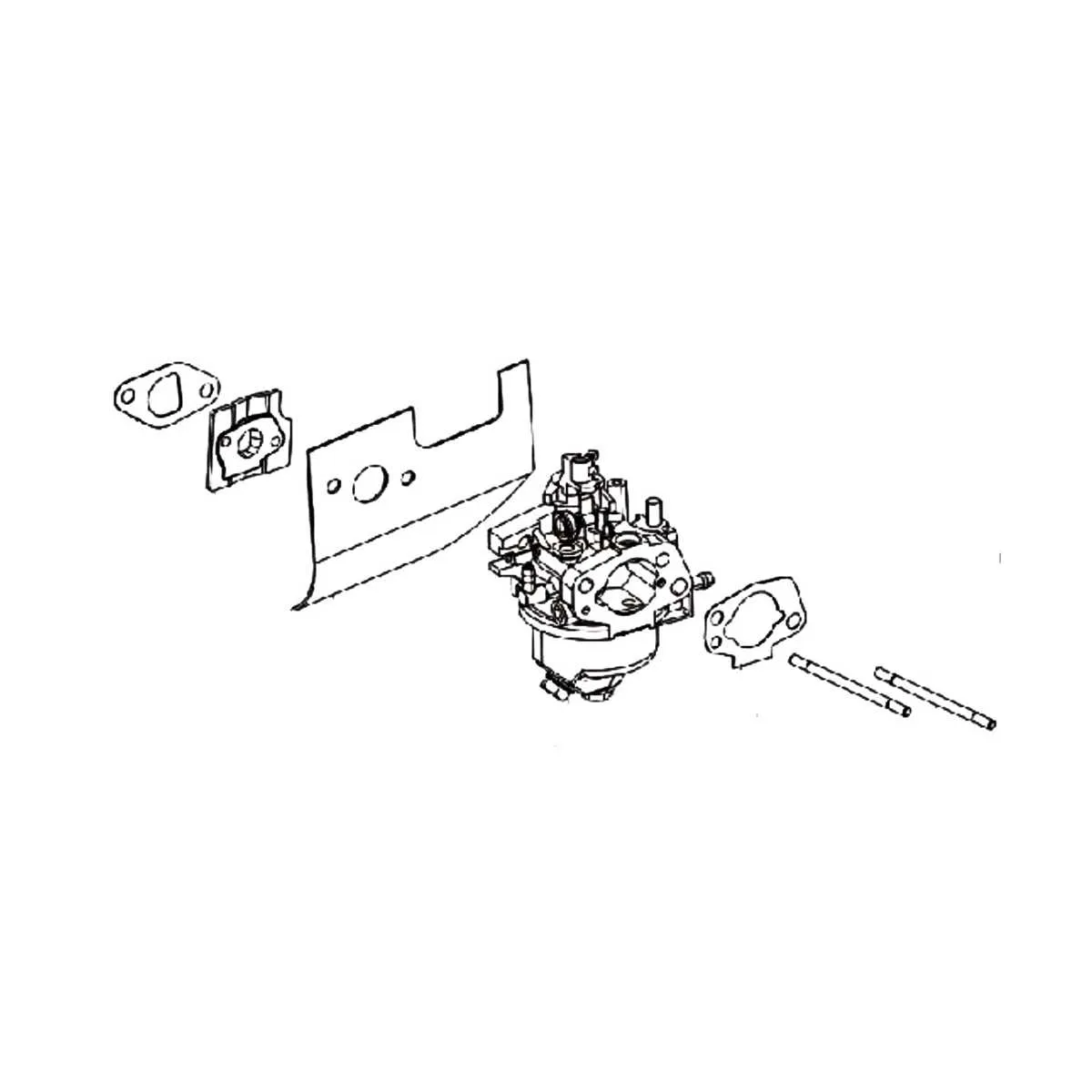
For anyone working on small engines, knowing the internal components of the fuel delivery system is crucial. If you’re experiencing issues with fuel flow or engine performance, inspecting the key parts of this system can often solve the problem. The component responsible for regulating the fuel-air mixture is located on the side of the engine and plays a critical role in starting and maintaining proper engine function.
Check the parts carefully: The main unit contains several small but essential pieces, such as the throttle valve, fuel inlet, and needle valve, all of which need to be in optimal condition. If the engine is not starting or running poorly, the first step is to examine the flow pathways for any signs of blockages or wear. A clear diagram can be an essential tool for disassembling and identifying the correct placement of each piece.
Additionally, it’s important to understand how the air intake interacts with the fuel mixture to achieve optimal combustion. Any misalignment or dirt build-up in these critical passages can cause significant performance degradation. A systematic cleaning and reassembly following a well-documented diagram will help ensure that each part functions as designed.
Understanding the Fuel System Layout
For proper maintenance of the small engine, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the internal fuel mechanism. The key to smooth engine operation lies in thoroughly understanding the components involved in the air-fuel mixing process. Start by identifying the choke plate, throttle valve, and fuel intake pathways. Ensure all gaskets are intact to avoid air leaks that disrupt the optimal air-fuel ratio.
When assembling or disassembling the fuel assembly, check the placement of the idle screw, which controls the minimum fuel flow. This setting is essential for consistent starting and idle performance. The venturi section is also critical; dirt or debris in this area can lead to poor engine response. Regular cleaning is necessary, especially around the main jet and needle valve.
The fuel bowl must be inspected for residue or contamination. Remove any deposits that could block fuel flow. Pay attention to the float level, as it directly impacts fuel delivery. Misalignment can lead to flooding or stalling. Be sure to verify the condition of the float needle and seat, as wear can lead to fuel leakage.
Proper installation of the fuel system parts requires accurate torque specifications, as overtightening can crack housing components. After reassembly, test the system to ensure there are no fuel leaks, and the engine runs smoothly at various throttle positions. Regular inspection and cleaning of these key components will prevent long-term performance issues.
How to Identify Key Components in the Engine’s Fuel System Layout

Focus on the following parts when analyzing the fuel delivery mechanism:
- Float Bowl: This is where the fuel accumulates before being mixed with air. It’s crucial for regulating fuel levels and preventing overflow.
- Throttle Valve: Controls the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine. It adjusts the speed of the engine when the accelerator is pressed.
- Needle Valve: Works with the float to control fuel flow into the bowl. A blocked needle valve can lead to irregular engine performance.
- Choke Mechanism: Regulates the airflow during engine startup. It ensures proper air-fuel ratio for easier ignition when cold.
- Jets: These are critical for fuel atomization. The main jet influences fuel delivery under load, while the idle jet affects engine performance at low speeds.
- Air-Fuel Mixture Screw: Allows fine-tuning of the air-fuel mixture to optimize engine efficiency and emission control.
- Venturi: The narrowing in the fuel intake path that increases airflow speed, which helps draw fuel from the bowl and mix it with the incoming air.
By understanding the role of each part, you can troubleshoot and optimize the engine’s fuel system for better performance. Pay attention to wear signs like clogging, corrosion, or unusual deposits, which can affect component efficiency and engine reliability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Parts in the Small Engine Fuel System
Start by disconnecting the spark plug wire to ensure safety. Drain the fuel tank completely before beginning disassembly to avoid spills.
Remove the intake assembly by unscrewing the fasteners and lifting the top cover. Access the main fuel system by detaching any securing bolts around the unit.
Carefully remove the fuel metering unit and set it aside. Inspect the rubber seals and gaskets for signs of wear, cracks, or corrosion. If damaged, replace them immediately to prevent air leaks.
Use a small wrench to loosen the screws securing the needle valve and float chamber. Gently pull them out and inspect for dirt or buildup. Clean with carburetor cleaner or replace if needed.
Next, remove the jet and clean it thoroughly with a small brush and air compressor. Blockages here can cause inefficient fuel flow and poor engine performance.
If the needle valve or float is worn out, replace these parts. They are critical in controlling the fuel flow and ensuring optimal engine operation.
Before reassembly, inspect all internal parts for cracks or other damage. Reinstall the cleaned or replaced components in reverse order, ensuring proper alignment and securing all bolts tightly.
Once reassembled, reconnect the spark plug wire and test the engine. If the system is functioning properly, the engine should start smoothly and run without hesitation.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep the engine in good condition. Follow this process periodically to ensure reliable operation and avoid costly repairs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Small Engine Fuel System Connections
First, inspect the fuel lines for cracks or leaks. A damaged line can prevent the engine from receiving adequate fuel, causing misfires or stalling. Replace any cracked or brittle hoses immediately.
Next, check the fuel filter for clogs. If the filter is blocked, fuel flow will be restricted, leading to poor performance. Clean or replace the filter as needed.
Examine the fuel inlet valve for any signs of blockage or wear. A malfunctioning valve can result in inconsistent fuel delivery, affecting engine stability. Clean or replace the valve if necessary.
If the engine is struggling to start, verify that the choke is functioning properly. An improperly set choke can cause an overly rich or lean fuel mixture, leading to hard starts. Adjust the choke to the correct position based on the engine’s operating conditions.
Inspect the air intake and ensure it’s free of dirt or debris. A blocked air filter can starve the engine of oxygen, causing rough idling or stalling. Clean or replace the air filter to restore normal airflow.
Finally, check the carburetor mounting bolts for tightness. Loose connections can lead to air and fuel leaks, disrupting the engine’s performance. Tighten any loose bolts to ensure a secure seal.