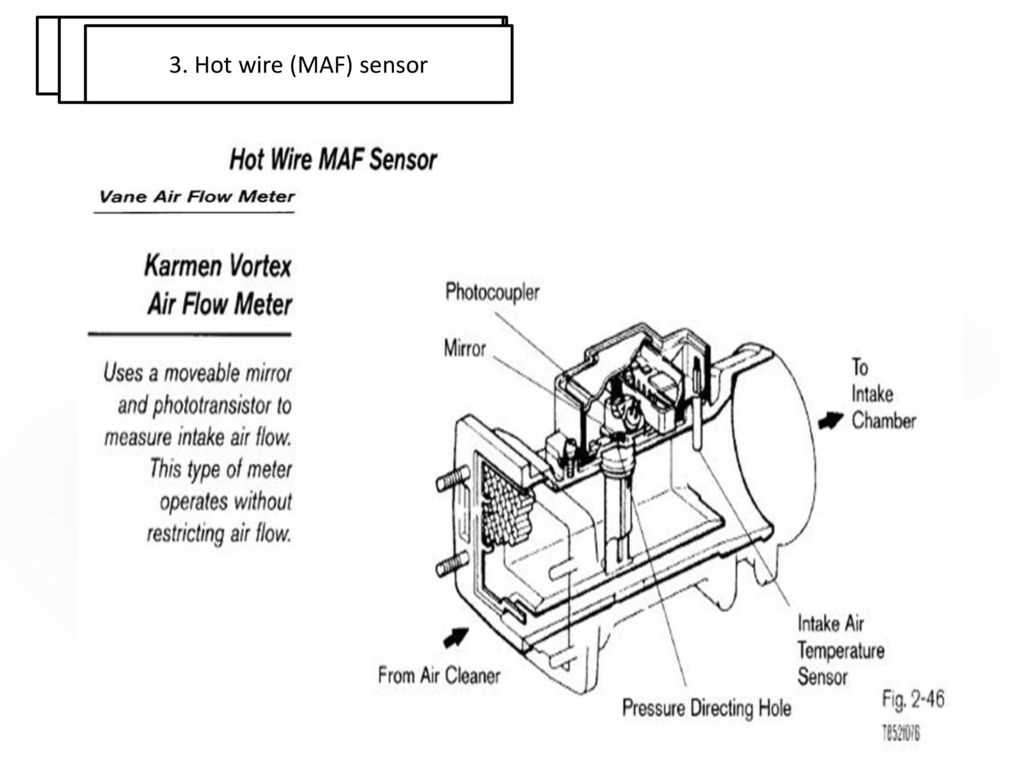
A hot wire mass air flow sensor is a crucial component of a vehicle’s electronic fuel injection system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine to ensure the appropriate fuel-to-air mixture for combustion. By accurately measuring the mass of the air, the sensor helps optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
The hot wire mass air flow sensor operates on the principle of using a thin and heated wire that is cooled by the incoming air. As more air flows past the wire, it cools down and the sensor detects this change in temperature. The sensor then sends this information to the engine control unit, which adjusts the fuel injection accordingly to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio.
This type of sensor provides precise and real-time data on the amount of air entering the engine, allowing the fuel injection system to make continuous adjustments for optimal performance. It is capable of accurately measuring both high and low air flows, ensuring reliable engine operation across a wide range of driving conditions. However, it is important to note that hot wire mass air flow sensors can be sensitive to contaminants like dirt and oil, which can affect their accuracy.
What Is a Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor?
A hot wire mass air flow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component of a vehicle’s engine management system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to determine the optimum air and fuel mixture for combustion, ensuring efficient engine performance.
The hot wire MAF sensor consists of a heated wire and a temperature sensor. As the air flows over the wire, it cools it down, and the ECU measures the current required to maintain the wire’s temperature. By measuring the current, the ECU can calculate the mass of air passing over the wire, enabling it to fine-tune the fuel injection and ignition timing.
The hot wire MAF sensor is more commonly found in modern vehicles as compared to its predecessor, the hot film MAF sensor. It offers several advantages, including improved accuracy, faster response time, and better reliability. The hot wire MAF sensor is also less prone to contamination, making it less likely to be affected by dirt or oil particles in the intake air.
- Advantages of a Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor:
- Faster response time: The hot wire MAF sensor quickly reacts to changes in airflow, allowing the ECU to adjust fuel injection and ignition timing accordingly.
- Accurate measurements: The hot wire MAF sensor provides precise readings of the mass of air entering the engine, enabling the ECU to optimize the air-fuel mixture for improved performance and fuel efficiency.
- Reliability: Hot wire MAF sensors are less prone to failure due to their simpler design and lack of moving parts.
- Less prone to contamination: The design of the hot wire MAF sensor makes it less susceptible to debris or dust buildup, ensuring consistent and reliable measurements over time.
How Does a Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor Work?
A hot wire mass air flow (MAF) sensor is a key component in the engine’s air-fuel mixture control system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine, allowing the computer to adjust the fuel delivery accordingly. Understanding how this sensor operates can help in diagnosing and troubleshooting engine performance issues.
The hot wire MAF sensor operates on the principle of heat transfer. Inside the sensor, there is a thin wire (usually platinum) that is heated to a specific temperature. As air flows over the wire, it cools it down, causing a change in its electrical resistance. The amount of cooling that occurs is directly proportional to the airflow, allowing the sensor to measure the incoming air mass accurately.
The MAF sensor is typically located between the air filter and the intake manifold. When the engine is running, the incoming air passes through the sensor, causing the wire to cool down. The sensor measures the change in resistance and converts it into a voltage signal, which is then sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
The ECU uses the voltage signal from the MAF sensor to determine the mass airflow rate and adjusts the fuel injection accordingly. This ensures the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal combustion. If the MAF sensor malfunctions or becomes dirty, it can result in incorrect airflow readings, leading to poor engine performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased emissions.
To maintain accurate readings, it is important to keep the MAF sensor clean and check for any signs of damage or contamination. If necessary, the sensor can be cleaned using a specialized MAF cleaner. If cleaning does not resolve the issue, the sensor may need to be replaced.
In conclusion, the hot wire mass air flow sensor plays a critical role in the engine’s air-fuel mixture control system. By measuring the incoming air mass accurately, it ensures the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal combustion and performance. Regular maintenance and inspection of the MAF sensor are essential for proper engine operation.
Advantages of Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor
The hot wire mass air flow sensor is a commonly used type of sensor in modern vehicles. It offers several advantages over other types of air flow sensors, making it a popular choice for manufacturers and mechanics.
Precise and Accurate Measurement
One of the main advantages of a hot wire mass air flow sensor is its ability to provide precise and accurate measurements of the air flow entering the engine. This is important for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the appropriate air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion. By accurately measuring the air flow, the ECU can ensure the engine is running at its most efficient and avoid any performance issues.
Highly Responsive
The hot wire mass air flow sensor is known for its high responsiveness. It can quickly detect changes in the air flow and provide real-time data to the ECU. This allows the ECU to make instant adjustments to the fuel injection and ignition timing, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the engine under different driving conditions.
Compact and Lightweight
Another advantage of the hot wire mass air flow sensor is its compact and lightweight design. This makes it easier to integrate into the vehicle’s engine compartment without taking up much space or adding unnecessary weight. The smaller size also allows for greater flexibility in installation, making it suitable for a wide range of vehicle models.
Durable and Long-lasting
The hot wire mass air flow sensor is designed to be durable and long-lasting, capable of withstanding the harsh conditions of the engine compartment. It is made from high-quality materials that can resist heat, vibrations, and contaminants. This ensures the sensor remains accurate and reliable throughout the vehicle’s lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs.
Compatibility and Availability
Hot wire mass air flow sensors are widely used in the automotive industry and are compatible with most modern vehicles. They are also readily available, making it easier for mechanics and car owners to find replacements or upgrades when needed. This widespread compatibility and availability make the hot wire mass air flow sensor a reliable choice for maintaining and repairing vehicles.
Disadvantages of Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor
The hot wire mass air flow sensor is a popular choice for measuring the amount of air entering an engine, but it does have its limitations and disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is its sensitivity to dirt and contaminants. The hot wire element can easily become contaminated, leading to inaccurate readings and potential damage to the sensor.
Another disadvantage of the hot wire mass air flow sensor is its susceptibility to damage from excessive moisture or condensation. Moisture can disrupt the flow of current through the hot wire, resulting in inaccurate readings and potentially causing the sensor to fail altogether.
- Limitations:
- The hot wire mass air flow sensor may struggle to accurately measure air flow at low speeds, such as when idling or driving at low RPMs. This can lead to a loss of engine performance and increased fuel consumption.
- The hot wire sensor is also affected by temperature changes, which can cause variations in the readings and affect the engine’s fuel mixture. This can result in poor engine performance and reduced efficiency.
In addition, the hot wire mass air flow sensor is often more expensive to replace compared to other types of air flow sensors. This can be a disadvantage for vehicle owners who need to replace a faulty sensor and are looking for a more cost-effective solution.
Overall, while the hot wire mass air flow sensor is commonly used in automotive applications, it does have its drawbacks. The sensor’s sensitivity to contaminants, susceptibility to moisture damage, limitations at low speeds, and vulnerability to temperature changes make it important for vehicle owners and technicians to be aware of these potential issues.
Common Issues with Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor
The hot wire mass air flow sensor is a critical component of a vehicle’s engine management system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine and provides this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). However, like any other sensor, the hot wire mass air flow sensor can experience issues that affect its performance and accuracy.
One common issue with the hot wire mass air flow sensor is contamination. Over time, dirt, dust, and oil particles can accumulate on the sensor’s hot wire, affecting its ability to accurately measure the airflow. This can result in incorrect fuel-air ratios and poor engine performance. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the sensor can help prevent this issue and ensure accurate measurements.
Another issue that can arise with the hot wire mass air flow sensor is a faulty or damaged sensor element. The delicate hot wire can be easily damaged if the sensor is mishandled or if excessive force is applied during cleaning. A damaged sensor element can lead to inaccurate readings or a complete failure of the sensor. In such cases, replacing the sensor is necessary to restore proper engine performance.
Additionally, the hot wire mass air flow sensor can be affected by electrical problems. Wiring issues, such as loose connections or damaged wires, can disrupt the sensor’s signal transmission to the ECU. This can lead to erratic or inconsistent readings, causing the engine to run improperly. Thorough inspection of the sensor’s wiring and proper repairs or replacements should be done to address these electrical problems.
In conclusion, while the hot wire mass air flow sensor is a crucial component for engine performance, it can experience common issues such as contamination, faulty sensor elements, and electrical problems. Regular maintenance, proper handling, and timely repairs can help prevent and resolve these issues, ensuring accurate measurements and optimal engine performance.
Troubleshooting Hot Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor Problems
Hot wire mass air flow sensors are an essential component of a vehicle’s engine management system. They measure the amount of air entering the engine and provide data to the engine control unit for proper fuel delivery. However, like any other sensor, they can develop problems over time. Here are some troubleshooting steps to help diagnose and resolve issues with hot wire mass air flow sensors.
1. Check for contamination
Contamination is a common problem with hot wire mass air flow sensors. Dirt, dust, and oil particles can accumulate on the sensor element, causing inaccurate readings. Inspect the sensor for any visible signs of contamination and clean it using a specialized sensor cleaner. Be careful not to damage the delicate sensor element.
2. Test the sensor’s voltage
Using a multimeter, test the voltage output of the hot wire mass air flow sensor. It should provide a steady voltage signal within the specified range. If the voltage reading is erratic or outside the normal range, the sensor may be faulty and need to be replaced.
3. Inspect the wiring and connections
Check the wiring and connections of the hot wire mass air flow sensor for any signs of damage or loose connections. A poor connection or damaged wire can result in inaccurate readings or a complete failure of the sensor. Repair or replace any damaged wires or connectors.
4. Perform a scan with a diagnostic tool
Using a diagnostic tool, conduct a scan of the vehicle’s engine control unit to check for any error codes related to the hot wire mass air flow sensor. These codes can provide valuable information about the specific problem and help in the troubleshooting process.
5. Consult a professional technician
If the above steps do not resolve the issue, it is recommended to consult a professional technician. They have the expertise and specialized equipment to diagnose and repair complex sensor problems. They can also perform additional tests, such as a smoke test or airflow verification, to further identify the root cause of the issue.
In conclusion, troubleshooting hot wire mass air flow sensor problems involves checking for contamination, testing the sensor’s voltage, inspecting the wiring and connections, performing a scan with a diagnostic tool, and consulting a professional technician if needed. By following these steps, you can diagnose and resolve issues with hot wire mass air flow sensors, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.