
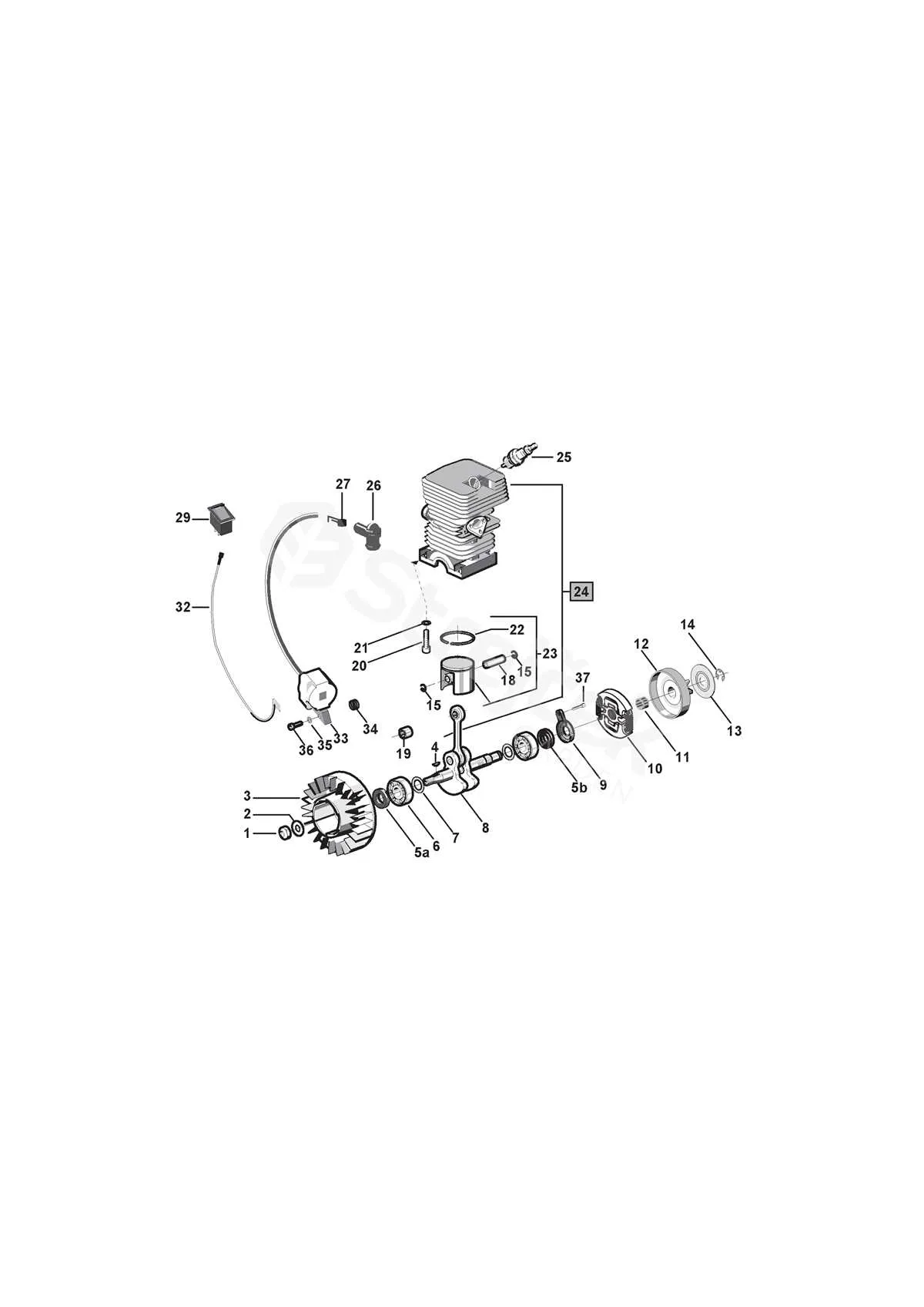
If you’re looking to repair or replace components of your blower, understanding the assembly layout is essential. The correct identification of each element helps streamline the process, ensuring you order the right replacement parts and avoid unnecessary confusion.
Inspecting the engine and fan housing is one of the first steps. These parts are crucial for the efficient functioning of the machine. Pay attention to the air intake and exhaust system. Check for any obstructions or wear that might reduce performance.
For the engine assembly, take note of the ignition system and fuel delivery components. The spark plug and carburetor should be checked for any signs of corrosion or damage. If you’re experiencing starting issues, these are common areas to inspect closely.
Additionally, examine the blower tube and nozzle for any cracks or blockages that could hinder airflow. A clogged nozzle can drastically reduce the blower’s efficiency, so be sure to clear out any debris regularly. Proper maintenance ensures your equipment runs smoothly over time.
Comprehensive Breakdown of the Tool’s Components
To effectively maintain or repair this model, focus on the key assemblies listed in the technical overview. Start with the air filter housing, which ensures clean airflow for optimal engine performance. Make sure to replace the filter regularly to avoid engine strain.
Next, inspect the fuel delivery system. The carburetor controls fuel mix; cleaning or adjusting it can solve many performance issues. A malfunctioning primer bulb might cause starting difficulties, so ensure it’s operating properly.
Pay attention to the ignition module. It’s responsible for the spark generation and starting the engine. If the engine has trouble firing, this part should be checked for wear or corrosion.
The fan housing is integral to cooling the engine. Overheating can lead to engine failure, so inspect the cooling fins for dirt and debris buildup regularly. Ensure the fan itself is securely attached and undamaged.
Throttle control and the trigger mechanism should function smoothly. If the throttle becomes stiff or unresponsive, it may be time to lubricate or replace components like the spring or trigger cable.
Don’t neglect the exhaust system. A clogged or damaged muffler not only reduces efficiency but can also lead to excessive noise and engine overheating. Inspect for cracks or blockages and replace the muffler if necessary.
Finally, check the handle assembly for cracks or loose screws. If the handles are worn or damaged, they can compromise user safety. Tighten all screws and replace broken or worn parts promptly to ensure a comfortable grip and stable control during use.
Understanding the Fuel System Components
Start by inspecting the fuel tank, as it holds the necessary liquid for combustion. Check for cracks or leaks, which can lead to fuel loss or engine malfunction.
- Fuel Filter: This component prevents impurities from entering the carburetor. Replace it regularly to avoid clogging.
- Carburetor: Responsible for mixing air and fuel in the right ratio for efficient combustion. A malfunctioning carburetor can cause hard starting or erratic engine behavior.
- Primer Bulb: Used to pump fuel into the carburetor before starting the engine. If damaged, it will fail to build pressure for ignition.
- Fuel Line: Carries fuel from the tank to the carburetor. Over time, lines can deteriorate or develop leaks, which should be replaced promptly.
- Fuel Cap: Ensures proper fuel flow and prevents leakage. Ensure the vent in the cap is clear to allow for pressure equalization.
- Choke: Regulates airflow to the carburetor to enrich the fuel mixture during cold starts. Improper use or failure can make starting difficult.
Maintain these elements by regularly cleaning the carburetor, checking for cracks, and replacing filters. Avoid using stale or contaminated fuel to prevent clogging or damage.
How to Identify and Replace the Air Filter Components
To begin, locate the air filter cover, typically secured with screws or clips, depending on the model. Once removed, inspect the filter for dirt or visible wear. If clogged with debris or damaged, replace it immediately to maintain optimal engine performance.
The replacement filter should match the dimensions and design of the original one. When installing, ensure a tight seal around the filter housing to prevent dirt from entering the engine. Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe any dust or particles from the housing before placing the new filter.
Check for any loose components during the replacement process. The air intake area should be free from obstructions to ensure proper airflow. If the filter cover’s seal is cracked or worn, replace it as well to avoid air leaks.
After installation, test the equipment by starting it and checking for smooth operation. A properly installed filter improves fuel efficiency and engine longevity.
Tip: Always refer to the specific model’s manual for exact instructions on replacing the air filter to avoid errors in installation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the Spark Plug

Start by disconnecting the spark plug wire to avoid any electrical accidents. Use a socket wrench with the appropriate size spark plug socket to loosen and remove the old plug from the engine. Inspect the spark plug for any signs of wear, such as excessive carbon buildup or corrosion. If the spark plug looks damaged, discard it.
Next, take the new spark plug and check its gap with a spark plug gap tool. Adjust it to the manufacturer’s recommended measurement, usually listed on the plug or in the engine manual. Ensure the new spark plug is compatible with your engine type and model.
Install the new spark plug by hand first, turning it gently to avoid cross-threading. Once the plug is hand-tight, use the socket wrench to tighten it securely, but do not overtighten as this can damage the engine threads. Reattach the spark plug wire and ensure it is seated firmly on the plug.
Finally, start the engine to verify that it runs smoothly. If the engine doesn’t start or runs unevenly, recheck the installation and ensure the plug is properly gapped and tightened. Test the machine’s performance before continuing regular use.