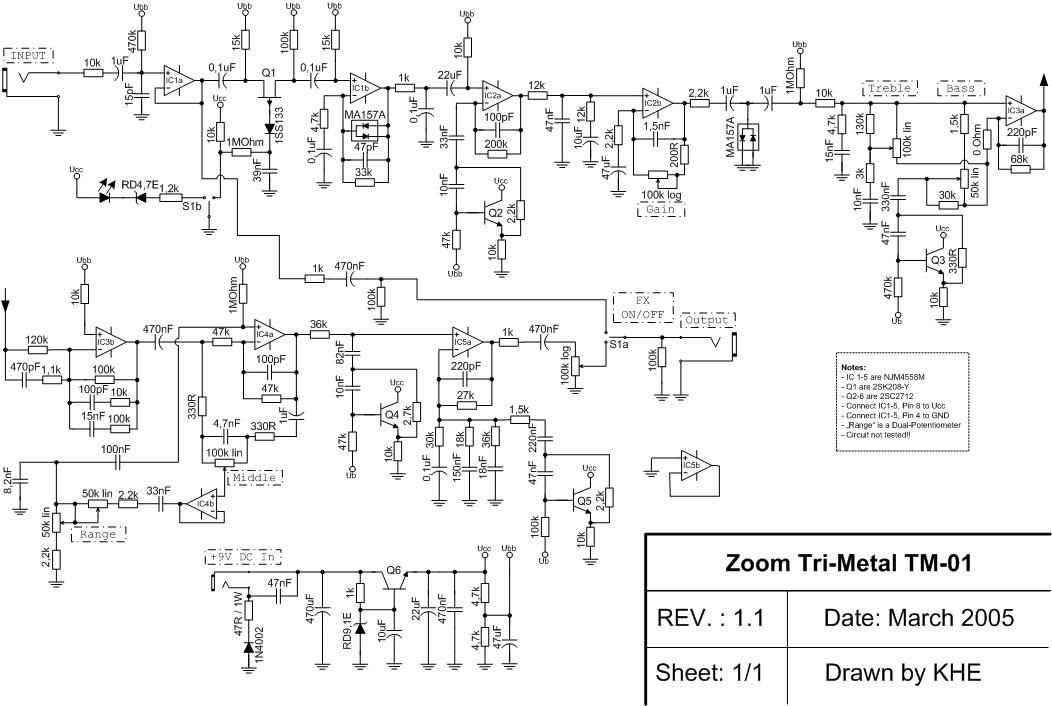
The MXR GT-OD is a popular overdrive pedal used by many musicians to add warmth and grit to their guitar tone. This pedal is known for its smooth and natural distortion, making it versatile for a wide range of genres. Many guitarists are interested in understanding the inner workings of the GT-OD pedal and how its circuitry produces its unique sound. In this article, we will explore the MXR GT-OD schematic, giving insight into the components and design choices responsible for its distinctive tone.
At the heart of the MXR GT-OD is a classic op-amp overdrive circuit. One of the key components in this circuit is the operational amplifier (op-amp), which is responsible for amplifying the guitar signal and creating the desired overdriven sound. The specific op-amp used in the GT-OD is the JRC4558, a popular choice known for its warm and smooth characteristics. This op-amp, along with carefully selected resistors and capacitors, forms the foundation of the GT-OD’s signature sound.
In addition to the op-amp circuitry, the GT-OD also features a tone control section that allows musicians to shape the pedal’s frequency response. This section consists of a potentiometer and a capacitor, which work together to adjust the high-end content of the signal. By turning the tone control knob, guitarists can tailor the pedal’s tone to their preference, whether they want a brighter and more articulate sound or a warmer and darker tone.
The MXR GT-OD schematic serves as a valuable resource for guitarists who are interested in modifying or building their own overdrive pedals. By studying the circuitry and understanding the role of each component, musicians can customize their pedals to suit their specific needs and achieve the desired tone. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or simply curious about the inner workings of the MXR GT-OD, a closer look at its schematic will provide insights into the design choices that contribute to its iconic sound.
Understanding the Schematic Diagram
The schematic diagram is a graphical representation of the electrical circuitry of a device or system. It shows the various components, their connections, and the flow of electricity through the circuit. By understanding the schematic diagram, one can analyze and troubleshoot the circuit more effectively.
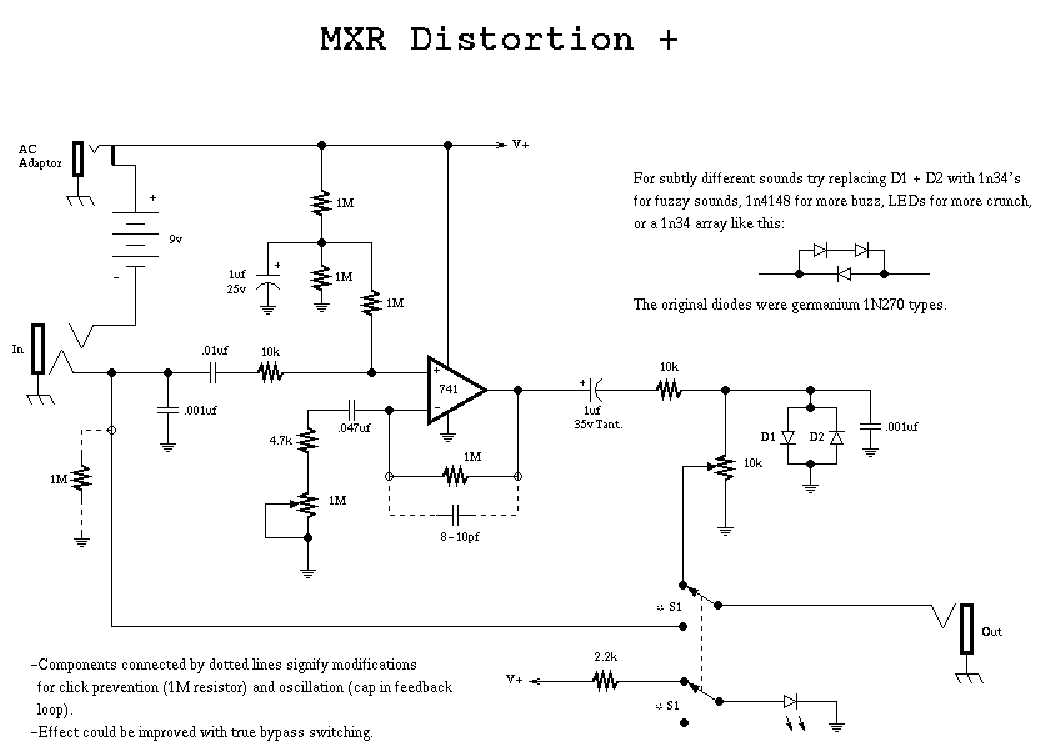
In the case of the MXR GT-OD pedal, the schematic diagram provides a detailed overview of how the various components, such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and diodes, are interconnected. It also shows the power supply connections, input and output jacks, and control knobs.
Resistors: The schematic diagram indicates the values of resistors used in the circuit. These values are represented by the resistance value in ohms or kilohms, indicated next to the resistor symbol. It is important to note that different resistors affect the gain and tone characteristics of the GT-OD pedal.
Capacitors: Capacitors store and release electrical energy. The schematic diagram specifies the capacitance value in microfarads (uF) or picofarads (pF), indicating the amount of energy the capacitor can hold. Capacitors are used in different parts of the circuit to filter, bypass, or delay the signal.
Transistors: Transistors act as amplifiers or switches in the circuit. The schematic diagram identifies the type of transistor (such as NPN or PNP) and provides information about the pin configuration and characteristics. Maintaining the correct transistor type and connections is crucial for proper functioning of the GT-OD pedal.
Diodes: Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. In the schematic diagram, diodes are represented by a triangle or arrow symbol, indicating the direction of current flow. Understanding the diode connections is important for ensuring proper signal routing and protection against reverse polarity.
- Power supply connections:
- Input and output jacks:
- Control knobs:
By studying and understanding the schematic diagram of the MXR GT-OD pedal, one can gain insights into how the different components interact, how the signal flow is controlled, and how adjustments to the control knobs can affect the overall sound. This understanding allows for modifications, repairs, or even the design of new circuits based on this knowledge.
Components of the Mxr gt-od Pedal
The Mxr gt-od pedal is a popular overdrive pedal used by guitarists to add gain and distortion to their tone. It is known for its versatility and ability to reproduce the sound of a cranked tube amplifier. The pedal is made up of several key components that work together to produce its unique sound.
1. Input and Output Jacks
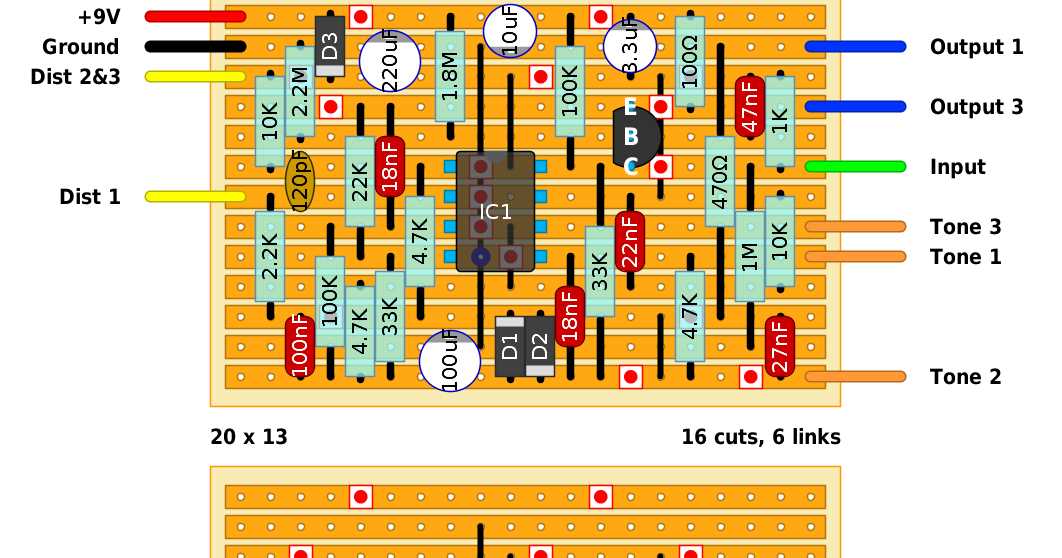
The Mxr gt-od pedal features a standard 1/4″ input jack and output jack. The input jack is where the guitar signal enters the pedal, while the output jack is where the processed signal exits the pedal and connects to the amplifier or other effects pedals. These jacks allow for easy integration into any guitar rig.
2. Gain and Tone Controls

- Gain control: The gain control adjusts the amount of overdrive and distortion in the signal. Turning it up increases the gain, resulting in a more saturated and distorted tone.
- Tone control: The tone control allows for fine-tuning of the pedal’s EQ. It can boost or cut specific frequencies, allowing guitarists to shape their tone to their preference.
3. Bypass Switch
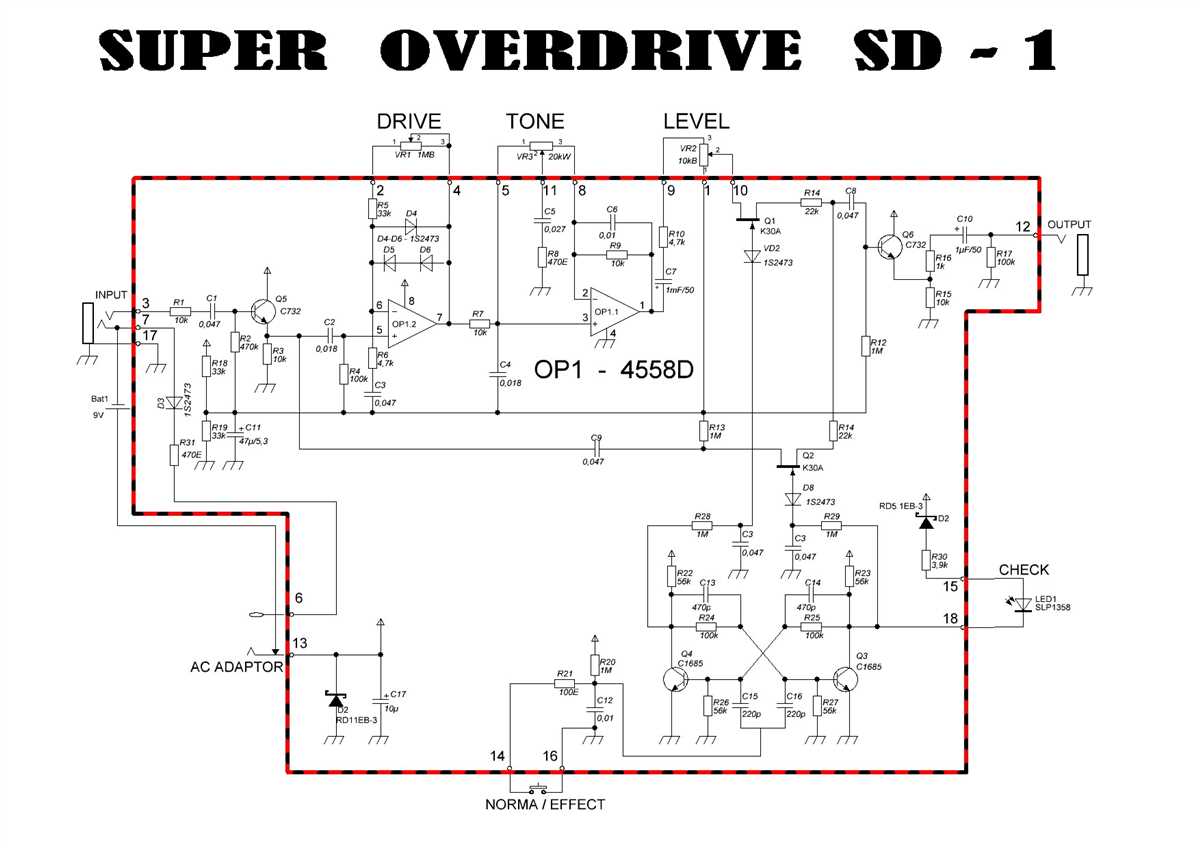
The Mxr gt-od pedal features a true bypass switch, which allows for bypassing the pedal’s circuitry when it is not in use. When the pedal is bypassed, the guitar signal is routed directly to the amplifier without going through the pedal, preserving the original tone of the guitar.
4. LED Indicator
The pedal is equipped with an LED indicator that lights up when the pedal is engaged. This provides visual feedback to the guitarist, indicating whether the pedal is on or off.
5. Power Input
The Mxr gt-od pedal is powered by a standard 9V DC power supply. It features a power input jack where the power supply is connected. Alternatively, it can also be powered by a 9V battery, making it convenient for gigging or playing on-the-go.
In conclusion, the Mxr gt-od pedal consists of various components such as input and output jacks, gain and tone controls, a bypass switch, LED indicator, and power input. These components work together to provide guitarists with a versatile and high-quality overdrive pedal that adds character and grit to their tone.
Analyzing the Circuitry
When analyzing the circuitry of the MXR GT-OD overdrive pedal, it’s important to understand the various components and their functions. One of the key elements in the circuit is the operational amplifier, which is responsible for amplifying the guitar signal. The operational amplifier used in the GT-OD is the JRC4558D, a popular choice for many overdrive pedals.
Another integral part of the circuit is the tone control, which allows the user to adjust the frequency response of the pedal. The GT-OD features a simple tone control circuit, consisting of a potentiometer and a capacitor. By turning the tone control knob, the user can either boost or cut the high frequencies, resulting in a darker or brighter sound.
- Op-Amp: JRC4558D
- Tone Control: Potentiometer and capacitor
The gain stage of the GT-OD is comprised of diodes that create clipping, which is the essence of an overdrive sound. These diodes act as switches that limit the voltage swing of the signal, creating distortion. One interesting feature of the GT-OD is the ability to switch between different diode configurations, allowing for different types of clipping and therefore different tonal characteristics.
Overall, the circuitry of the MXR GT-OD overdrive pedal is relatively simple but effective. The combination of the operational amplifier, tone control, and diode clipping stage produces a wide range of overdrive tones, making it a versatile choice for guitar players looking to add some grit to their sound.
DIY Modifications for the Mxr gt-od Pedal
The Mxr gt-od pedal is a popular choice among guitarists for its versatile overdrive tones. However, if you’re looking to take your sound to the next level, there are several DIY modifications you can make to the pedal to tailor it to your specific preferences and needs.
1. Tone Control Adjustment: One of the most common modifications for the Mxr gt-od pedal is adjusting the tone control. By replacing the original tone potentiometer with a higher quality one, you can achieve a more precise and responsive control over the pedal’s tone. This allows you to dial in the perfect amount of brightness or warmth to suit your playing style.
2. Gain Boost: Another popular modification is adding a gain boost switch to the pedal. This switch allows you to instantly engage a higher gain setting, giving you more saturation and sustain. It can be especially useful for solos or heavier genres where you need that extra kick and intensity in your sound.
3. True Bypass Conversion: Some guitarists prefer to have their pedals in true bypass mode to preserve the integrity of their signal when the pedal is not in use. By converting the Mxr gt-od pedal to true bypass, you can eliminate any potential tone loss or interference that may occur when the pedal is bypassed.
4. LED Indicator: Adding an LED indicator to the Mxr gt-od pedal can be a simple and useful modification. It allows you to easily see if the pedal is engaged or bypassed, even in low light situations. This can be especially helpful during live performances when you need to make quick adjustments to your pedalboard.
5. Clipping Diode Swapping: The Mxr gt-od pedal uses diodes to shape its overdrive tones. By swapping out the stock diodes with different ones, such as germanium or silicon diodes, you can alter the character and response of the overdrive. This can result in a smoother, more vintage-like overdrive or a more aggressive and modern tone.
These are just a few examples of the many DIY modifications you can make to the Mxr gt-od pedal. Depending on your skill level and knowledge of electronics, you can explore these modifications or even come up with your own ideas to further customize the pedal to your liking. Remember to always exercise caution and consult experts if necessary when working with electronics.
Troubleshooting and Repairing the Mxr gt-od Pedal
The MXR GT-OD pedal is a versatile overdrive pedal that is used by guitarists to add rich, warm tones to their sound. However, like any electronic device, it may encounter issues that require troubleshooting and repair.
In this guide, we have covered some common problems that you may encounter with the MXR GT-OD pedal, along with potential solutions for each issue. Here is a summary of the troubleshooting steps:
- No Power: If the pedal does not power on or does not light up, check the power source and cables. Ensure that the pedal is receiving the correct voltage and that the power cables are securely connected.
- No Sound: If the pedal is powered on but produces no sound, check the input and output cables. Make sure they are properly connected and not damaged. Also, check the pedal’s internal switch and controls to ensure they are set correctly.
- Distorted Sound: If the pedal produces distorted or muddy sound, check the settings and controls. Adjust the gain, tone, and volume knobs to achieve the desired sound. If the issue persists, it may be due to a faulty pedal component that requires repair or replacement.
- Intermittent Sound: If the sound cuts in and out or is intermittent, check the input and output jacks for loose connections. Also, inspect the pedal’s internal wiring for any loose or broken connections. Repair or replace any faulty components as necessary.
- Scratchy or Noisy Potentiometers: If the pedal’s potentiometers (knobs) produce scratchy or noisy sounds when turned, apply contact cleaner to the potentiometers to remove any dirt or debris. If the issue persists, the potentiometers may need replacement.
Remember, it is always recommended to refer to the official MXR GT-OD pedal manual or consult a qualified technician if you are unsure about performing any repairs or modifications on the pedal. Proper knowledge and understanding of electronics are essential to avoid damage and ensure the pedal’s optimal performance.
By troubleshooting and addressing common issues, you can keep your MXR GT-OD pedal in excellent condition and continue to enjoy its overdrive capabilities for years to come. Happy playing!