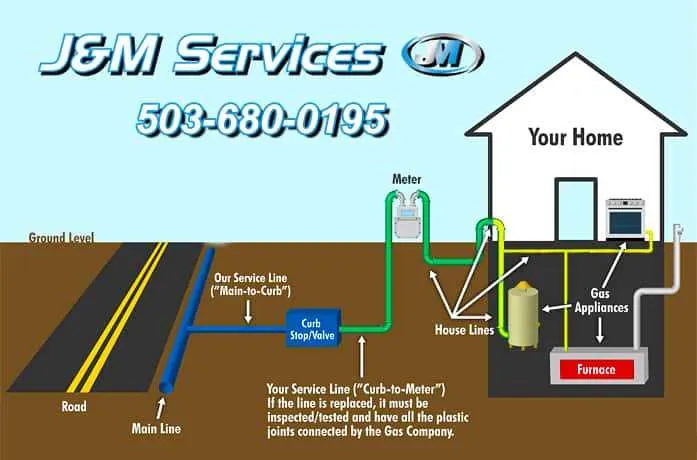
Ensure proper placement of all fuel supply lines by following the recommended layout for home installations. Start with the main supply line, which should be positioned to minimize bends and avoid sharp turns. This reduces pressure drops and enhances the efficiency of the entire system.
Prioritize safety by correctly sizing each pipe according to local regulations and industry standards. Over-sized or under-sized pipes can lead to dangerous situations, including inefficient fuel flow or excessive pressure buildup. Pay particular attention to materials–use only approved, durable substances to prevent corrosion and leaks.
Installation should focus on easy accessibility for future maintenance. Place shutoff valves at key locations, ensuring they are reachable and clearly labeled. This will allow for quick response in case of emergencies. Also, use flexible connectors where movement or vibration is expected, as these can prevent undue stress on the lines.
Make sure all connections are secured with appropriate fittings. Check for leaks during and after installation using a soapy water solution, which will help identify weak spots. Finally, confirm compliance with local building codes to ensure long-term safety and efficiency.
Essential Guidelines for Home Fuel Distribution Layout
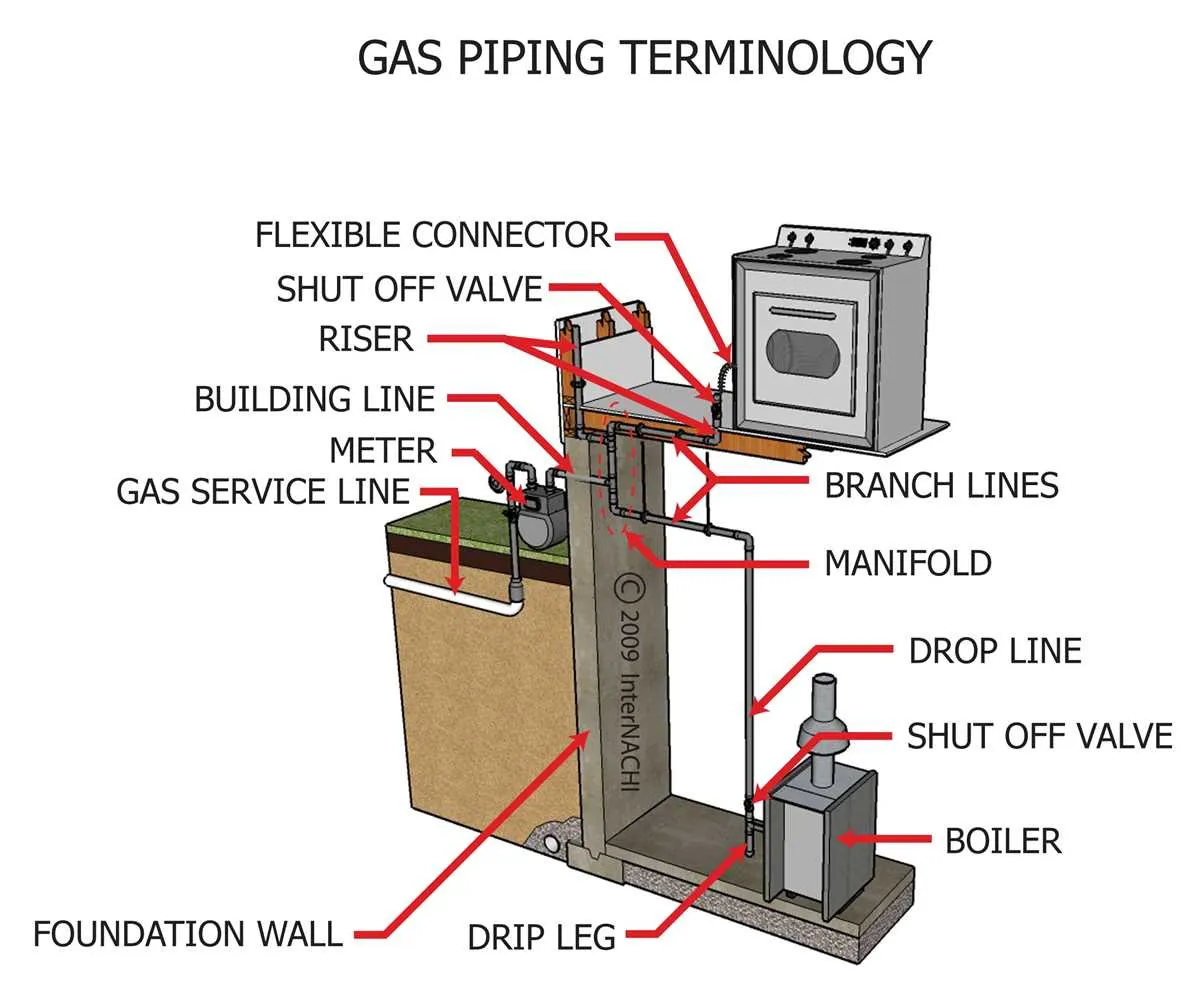
Ensure the system is designed to comply with local codes and regulations. Plan the path for the fuel from the meter to various appliances with the shortest and safest route in mind. Avoid sharp bends, as they can increase the risk of pressure drops or leaks.
Use materials approved for internal installation, such as copper or steel, and ensure proper sizing of each segment based on appliance requirements. Each appliance should have an individual shut-off valve, and these should be easily accessible for maintenance and emergencies.
Account for ventilation needs around all fixtures and connections. Properly seal all joints using appropriate sealants to prevent leaks. Perform pressure tests after installation to confirm the system is airtight and functioning correctly.
Consider future expansions when planning the layout. Always overestimate the required capacity to allow for upgrades without significant modifications to the structure. Keep the lines clear of obstructions to avoid accidental damage during home renovations or repairs.
In high-risk areas, such as near water sources or extreme weather conditions, opt for corrosion-resistant materials and conduct regular inspections to identify potential issues before they become hazards.
Choosing the Right Materials for Fuel Supply Lines
Selecting the correct materials for fuel supply lines is critical for ensuring both safety and efficiency. Here are the top recommendations:
- Steel: Commonly used due to its durability and resistance to pressure. Ideal for underground or external installations. Requires protection against corrosion when exposed to moisture.
- Flexible Copper: Often used for internal connections due to its ease of installation and resistance to corrosion. Avoid in areas subject to high temperature fluctuations.
- Polyethylene (PE): A plastic material used mainly for outdoor and underground installations. Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, but not suitable for high-pressure systems or locations with high temperatures.
- Corrugated Stainless Steel Tubing (CSST): Flexible and easy to install, CSST is used for both indoor and outdoor applications. It requires proper grounding and protection to avoid potential damage from lightning strikes.
When choosing, consider the following factors:
- Pressure Resistance: Ensure the material can withstand the pressure required for the system. Steel and CSST are often better for high-pressure needs.
- Corrosion Resistance: Select materials like PE or copper for areas with high moisture exposure, as they prevent rust and deterioration over time.
- Installation Flexibility: For complex or hard-to-reach areas, flexible options like copper or CSST make the process easier.
- Local Codes: Always check local regulations and requirements to ensure the chosen material meets safety and installation standards.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Gas Piping in a Home
1. Begin by determining the location for each appliance or fixture. Ensure each area complies with local regulations for distance from walls and other objects.
2. Measure and plan the route for the lines, taking into account obstacles such as studs and joists. Choose the most direct path to minimize the number of fittings.
3. Use high-quality, durable materials approved for the installation. Copper or steel tubes are commonly used for their strength and resistance to corrosion.
4. Cut the tubing to the necessary lengths using a tube cutter or hacksaw, ensuring all cuts are clean and smooth for proper connections.
5. Install the first section of pipe, ensuring it’s securely fastened with brackets or straps. Leave room for expansion and contraction due to temperature changes.
6. Fit the sections together using appropriate connectors and ensure all joints are tightly sealed with Teflon tape or pipe joint compound to prevent leaks.
7. Test for leaks after every connection. Use a soap solution on joints to check for bubbles. If any leaks are detected, tighten the joints or replace faulty fittings.
8. Once all sections are connected, run a final pressure test to ensure the entire system is secure and functioning properly. Consult with a professional inspector if required.
9. After passing the pressure test, cover the exposed lines with protective materials, ensuring no part is left vulnerable to physical damage.
10. Finally, connect the appliances to the system, verifying each connection and making sure everything is properly secured before turning the supply back on.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Improper Sizing of Pipes can lead to low pressure and inefficient flow. Always calculate the correct diameter based on the number of appliances and the distance from the source. Use standardized pressure loss tables to ensure proper selection.
Incorrect Joint Connections are a major source of leaks. Use only the appropriate materials and tools when making connections. Ensure all fittings are tightened according to manufacturer specifications to avoid air gaps or weak seals.
Neglecting Proper Ventilation may result in dangerous buildups of hazardous substances. Make sure that the venting system is installed according to local regulations and that all exhaust outlets are clear and unobstructed.
Unapproved Materials can compromise safety and efficiency. Always use certified materials that meet industry standards. Avoid using flexible hoses or cheap, non-rated components, as they may not provide long-term reliability.
Incorrect Pressure Settings should be checked regularly. Installing pressure regulators incorrectly or failing to adjust them as needed can cause dangerous over- or under-pressurization, leading to potential damage to appliances or system failure.
Lack of Proper Sealing at junction points is a frequent cause of inefficiencies and hazards. Ensure all seals are properly installed, and regularly check for leaks using a soap solution or gas detector to ensure safety.
Improper Placement of Appliances is a common oversight. Maintain required clearances between your system and surrounding structures to ensure proper air circulation and easy maintenance access.
Ignoring Local Codes can lead to unsafe installations and potential fines. Always adhere to local safety codes and consult professionals for compliance with national standards.