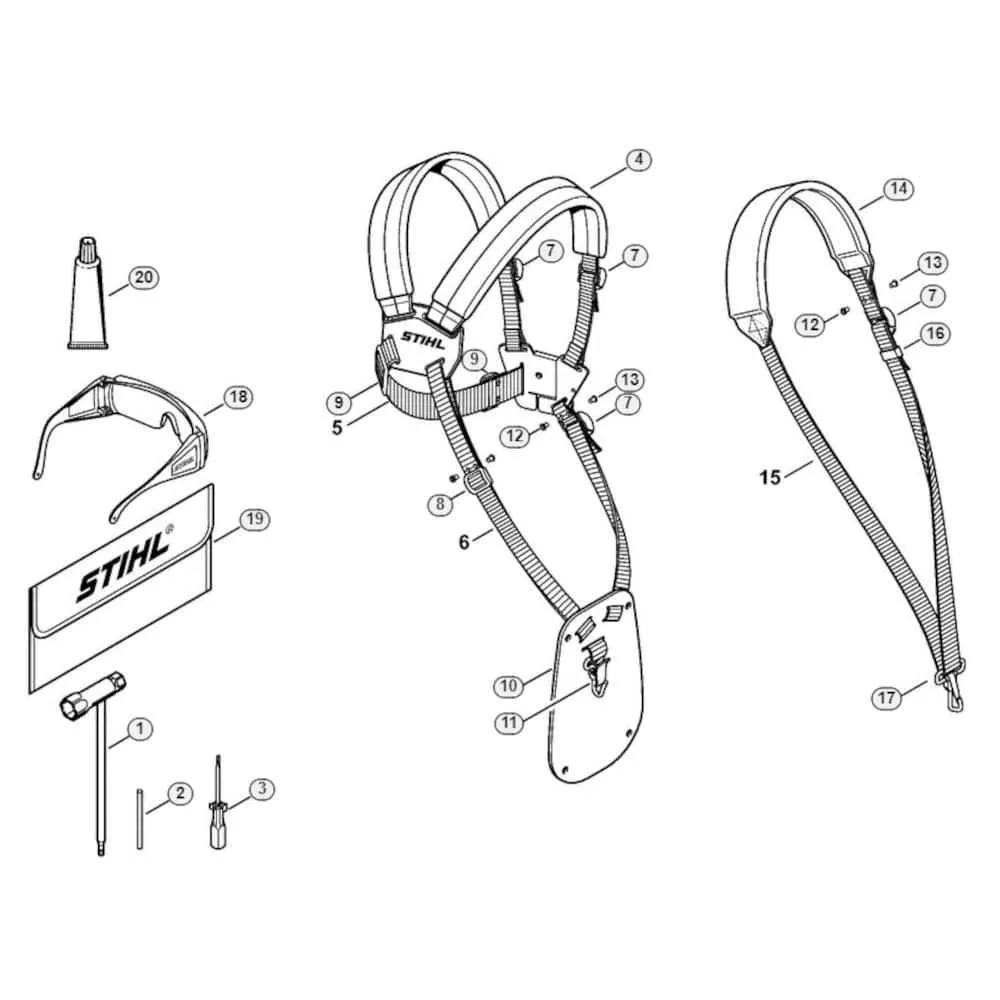
When repairing or maintaining your garden equipment, understanding its key components is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Knowing where each part fits and how they interact can save you time and prevent unnecessary damage. Start by identifying the engine housing and drive system, which form the heart of the machine’s functionality. Pay close attention to the clutch assembly and spool mechanism, as these are often the source of wear and tear.
For proper assembly, make sure the fuel tank is securely placed, ensuring no leaks. The cutting head and its related components, like the hub and gearbox, require regular checks for tightness and functionality. Always verify the positioning of the starter recoil, as misalignment can hinder the starting process. Make sure all fasteners are tightened according to manufacturer specifications to avoid future issues.
Refer to a detailed exploded view for precise placement, ensuring you don’t miss any small but important parts. For smoother operation, inspect the air filter and clean it regularly, as this can drastically affect engine performance. An oil filter replacement should also be done periodically to avoid contamination of the engine’s internals.
Detailed Breakdown of Trimmer Components

For efficient maintenance and repair, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the specific components of your equipment. When disassembling or assembling, refer to a labeled visual map that identifies each piece and its function. Start by checking the drive shaft, ensuring it’s securely connected to the engine. Follow by inspecting the gearbox for any wear and tear, ensuring proper lubrication. The cutting head should be properly mounted, with the correct attachment to prevent excessive vibration during operation. Replace worn-out components immediately to avoid compromising performance.
Ensure all fasteners are tightly secured and that no parts are loose or missing. Pay attention to the fuel tank assembly, as any cracks or leaks can lead to operational issues. Verify that the spark plug and ignition system are working smoothly, as they directly influence engine start-up and power delivery. Lastly, don’t overlook the air filter, which should be clean to avoid engine choking, particularly if you’re working in dusty conditions.
For reference, always cross-check part numbers from your tool’s manual to ensure you’re using the right components for repairs or upgrades. A clear and organized schematic is an invaluable tool for identifying compatible parts when replacements are needed. By staying on top of these maintenance tasks, you can extend the longevity and efficiency of your trimmer.
How to Identify Key Components in the Parts Breakdown
To efficiently identify and understand the main components in a machine’s schematic, follow these steps:
- Start with the Powerhead: Locate the engine assembly, often labeled at the top of the breakdown. This is typically the largest part and includes the ignition system, fuel system, and the crankcase.
- Examine the Drive Shaft: This part connects the engine to the cutting tool. Look for a long cylindrical component that runs through the middle of the schematic.
- Check the Cutting Head Assembly: This includes the trimmer head and the components that connect it to the drive shaft. The diagram should show a collection of smaller, intricately designed parts.
- Fuel System: Identify the fuel tank, fuel lines, and carburetor. These parts are often grouped together, typically near the powerhead.
- Handle and Guard: The handlebar or frame assembly and any protective guards will be in the lower section of the drawing, often in a more abstract shape for easier identification.
By following the flow of assembly, you can isolate individual systems within the tool, making troubleshooting and part replacement easier.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Worn-Out Components Using the Manual
Start by securing the necessary tools and a replacement kit that matches your equipment model. Make sure the engine is turned off and completely cooled down before proceeding.
Consult the breakdown chart to identify the specific components that need replacement. Pay attention to the condition of the drive shaft, trimmer head, and fuel lines, as these are common parts that wear out quickly.
Begin by removing the protective cover. Loosen the screws holding it in place, using a screwdriver suited for the fasteners. Once removed, check for any debris or damage in the housing area.
Next, inspect the cutting head assembly. Detach it carefully, noting the sequence of parts. For example, the trimmer line or spool might be worn out. Replace them with new ones, ensuring the correct fitting according to the schematic.
If the fuel lines are cracked or brittle, disconnect them and install new tubing. Ensure a tight, secure fit to avoid leaks. Refer to the schematic for proper placement and alignment of each section.
When replacing the drive shaft, make sure to detach it from the engine housing and replace any worn-out bearings or couplers. Ensure smooth rotation by checking for any obstructions or misalignment before reassembly.
Finally, reattach all removed components in reverse order, confirming each part is securely fastened. Recheck the alignment of the motor and handle to ensure everything is properly aligned for optimal performance.
Test the unit in a safe area before resuming normal use to ensure all replacements were completed correctly and everything is functioning as intended.
Troubleshooting Common Issues Using the Assembly Blueprint
If the engine stalls frequently, inspect the fuel system. Check the fuel filter for any blockages or contamination. A clogged filter restricts fuel flow, causing irregular engine performance. If necessary, replace the filter with a new one. Refer to the exploded view for precise placement and identification of parts.
For a machine that won’t start, verify the ignition system. Ensure the spark plug is not fouled or damaged. A worn spark plug can prevent proper ignition, leading to starting problems. Clean or replace the spark plug as needed. The ignition coil should also be checked for wear or moisture, which can affect performance.
Unusual vibrations are often caused by a misaligned drive shaft or loose components. Tighten all fasteners and inspect for any bent or damaged parts. If the vibration persists, inspect the flexible coupling for wear or cracks that could lead to instability during operation.
Reduced power or poor cutting performance may be linked to a dull or damaged cutting head. Ensure the cutting blades or trimmer line are in good condition. If the line is worn, replace it according to the recommended specifications. Also, check for debris buildup that could be obstructing the cutting area.
If fuel is leaking, examine the fuel tank cap and fuel lines for cracks or loose connections. Leaks typically occur due to wear or improper sealing. Replace any damaged components to prevent fuel wastage and potential safety hazards.
Finally, poor throttle response can often be traced back to a malfunctioning carburetor. If the engine runs erratically at different speeds, disassemble and clean the carburetor, checking for any blocked jets or internal damage that might prevent proper fuel-air mixture regulation.