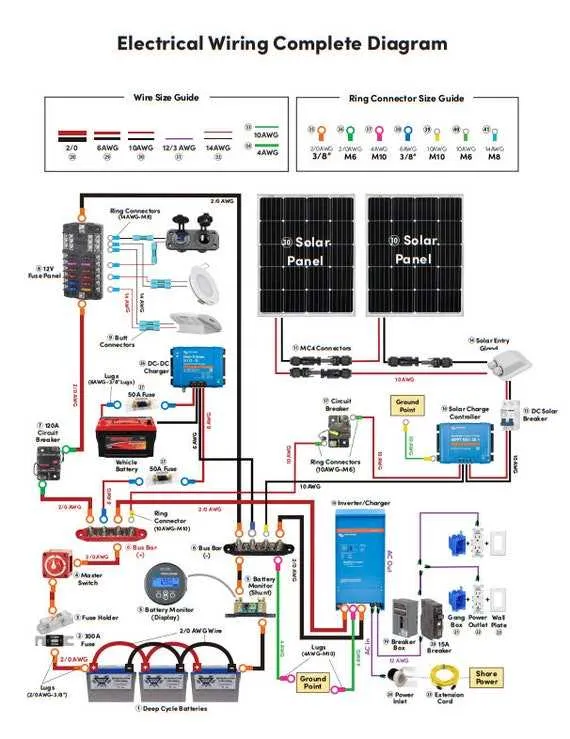
Start by planning the electrical system of your mobile living space with the right components. Use high-quality wires and circuit breakers designed for vehicle installations to ensure safety and reliability. Begin with a solid power source, such as a deep cycle battery or solar panel setup, to provide consistent energy while on the move. Make sure to include a DC-AC inverter to convert the stored energy into usable power for appliances.
Position each component carefully, with an emphasis on accessibility and ease of maintenance. Place your battery close to the power source but away from excessive heat or moisture. Properly size the cables to handle the load without risk of overheating. Use fuses or circuit breakers in key locations to protect the system from overloads and short circuits.
It is also crucial to establish a proper grounding system, which reduces the risk of electric shock and ensures equipment operates as intended. Secure all connections tightly, use waterproof connectors, and consider adding fuse panels for an organized setup. The final step is testing the entire system under different conditions to verify everything is functioning smoothly.
Electrical Setup in a Mobile Home
To ensure reliable power supply and safety in your mobile home, it’s crucial to understand how to connect electrical components properly. Here’s a concise guide to assist in building a stable and efficient system.
- Battery Selection: Choose a deep-cycle lead-acid or lithium battery with a capacity that suits your energy needs. For most mobile setups, a 12V system is standard.
- Fuse Protection: Install fuses near power sources (e.g., battery) to protect circuits from overloads. Fuse ratings should match the wire gauge and device requirements.
- Grounding: Grounding is essential for safety. Use a copper ground wire to connect the battery negative terminal to the metal frame of your mobile unit. Ensure connections are corrosion-resistant.
- Voltage Converter: If using AC appliances, invest in a DC to AC inverter. For smoother performance, select a pure sine wave inverter, especially if sensitive electronics are involved.
- Wiring Connections: Use high-quality marine-grade wire with proper insulation to prevent shorts. Always match the wire size to the load it will carry to avoid overheating.
- Solar Panel Integration: Solar panels can be a reliable power source. Connect the panel to a charge controller, then to your battery system. Ensure your panel is mounted in an optimal location to maximize sunlight exposure.
Regularly inspect connections, clean terminals, and test components to avoid electrical malfunctions. Keep backup components like fuses and cables on hand for emergencies.
Understanding the Electrical System Layout of a Mobile Living Space
Ensure proper grounding throughout the entire system. This prevents electrical surges and ensures a safe connection to the power source, reducing the risk of shocks or fires.
Plan power sources effectively: Integrate both shore power and solar systems to provide a reliable energy supply. Use a transfer switch to easily switch between shore power and battery when necessary.
Battery configuration: Lead-acid or lithium batteries should be connected in a way that supports both 12V and 24V systems, depending on your usage. Always incorporate a battery management system (BMS) to monitor voltage levels, state of charge, and prevent overcharging.
Fuses and circuit breakers: Protect circuits from overloads by installing fuse boxes or circuit breakers at key points in the setup. Ensure all connections are rated for the intended current to avoid overheating.
Lighting setup: Use low-voltage LED lights to minimize power consumption. Ensure your lighting circuit is separated from high-power circuits to maintain optimal energy use.
DC-AC inverter: Choose an inverter with sufficient wattage to support your devices. A pure sine wave inverter is recommended for sensitive electronics like laptops and TVs.
Proper wiring gauge: Use the correct wire gauge for each application. For longer runs, select thicker wires to minimize voltage drop, which can affect performance.
Monitor system performance: Install a battery monitor and a power meter to keep track of usage, remaining capacity, and overall system health. This will help you avoid power shortages during extended trips.
How to Set Up a 12V System for Lighting and Appliances
Start by choosing the right gauge wire based on the total current draw. Use 12 AWG wire for up to 20 amps, 10 AWG for up to 30 amps. For safety, always calculate the power consumption of each appliance and light fixture to avoid overloading circuits.
1. Power Source: Select a deep-cycle battery to supply consistent voltage. Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the main fuse block using a 30-amp fuse to prevent damage from short circuits.
2. Fuse Protection: Install fuses on each individual circuit to protect against overcurrent. Choose fuse ratings according to the appliance’s wattage, with a little margin (e.g., for a 100W light, use a 10A fuse).
3. Distribution Block: Set up a power distribution block to branch off the main circuit to various components. This keeps the system organized and easy to troubleshoot.
4. Lighting: For LED fixtures, use a 12V DC power supply and ensure connections are solid and insulated. Use toggle or push-button switches to control each light.
5. Appliances: For larger devices like a mini-fridge or fan, make sure the circuit is rated for higher amperage, and install separate breakers to prevent system overload.
6. Grounding: Secure a solid grounding system by attaching a thick wire from the negative terminal of the battery to a common metal point in your setup. This reduces the risk of electric shock and enhances system stability.
7. Testing: Before connecting the power source, verify each connection with a multimeter to ensure no short circuits or faulty wiring. After powering up, check all devices to confirm they are operating correctly.
Important: Never connect multiple high-current appliances to the same circuit without a fuse or breaker, as this could lead to overheating and possible fire hazards.
Connecting Solar Panels and Battery Banks to Your Mobile Setup

To ensure reliable power for your off-grid needs, start by linking your solar panels to a charge controller. The controller regulates the voltage, preventing overcharging of your storage units. Choose a PWM or MPPT controller, with MPPT being more efficient for larger systems.
Use cables with adequate thickness (12-10 AWG) to minimize voltage loss, ensuring they are rated for outdoor use. Connect the positive and negative terminals from the panel to the input of the charge controller, and then from the controller’s output to your battery bank.
Your storage bank should consist of deep cycle batteries (AGM or lithium are preferred). Keep the battery bank’s voltage in sync with the charge controller’s capacity. Typically, a 12V system works for small setups, but larger setups may require 24V or 48V configurations to support higher energy loads.
Use fuses or circuit breakers for safety. Place them on the positive wire between the controller and battery bank, and between the panels and the controller. The fuse should be rated according to the wire gauge and the system’s total capacity.
When connecting the batteries, ensure that the positive terminal of one unit connects to the negative of another if you’re linking multiple batteries in series. For parallel connections, keep all positives and negatives on the same bus bar, maintaining balanced loads across all batteries.
Finally, verify the system’s output regularly to avoid issues with power fluctuation. A battery monitor can help you track usage and battery health, ensuring long-term performance.